Featured
-
-
Article |
 Thermodynamic behaviour of supercritical matter
Thermodynamic behaviour of supercritical matter
A physical description of supercritical fluids remains challenging because common approximations for solids and gases do not apply to liquids. Bolmatov et al. identify a liquid/gas dynamic crossover of specific heat above the critical point, and formulate a theory to shed light on its nature.
- Dima Bolmatov
- , V. V. Brazhkin
- & K. Trachenko
-
Article |
 Selective anion exchange with nanogated isoreticular positive metal-organic frameworks
Selective anion exchange with nanogated isoreticular positive metal-organic frameworks
Crystalline porous materials are commonly based around negatively charged frameworks, so ion-exchange is limited to cations. Here, the authors report a series of positive metal-organic frameworks, capable of ion exchange of large organic anions, with potential in separation and purification applications.
- Xiang Zhao
- , Xianhui Bu
- & Pingyun Feng
-
Article |
 Polymeric pseudo-crown ether for cation recognition via cation template-assisted cyclopolymerization
Polymeric pseudo-crown ether for cation recognition via cation template-assisted cyclopolymerization
Cyclopolymers have potentially interesting molecular recognition properties due to their in-chain multiple rings. Here, the authors report cation-templated, controlled radical cyclopolymerization of poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylates, yielding polymeric pseudo-crown ethers with large in-chain cavities.
- Takaya Terashima
- , Minami Kawabe
- & Mitsuo Sawamoto
-
Article |
 Disk-cylinder and disk-sphere nanoparticles via a block copolymer blend solution construction
Disk-cylinder and disk-sphere nanoparticles via a block copolymer blend solution construction
Compositionally and geometrically complex nano-objects are an important goal in medicinal, photonic and electronic materials research. Here, the authors fabricate disk-sphere and disk-cylinder nanoparticles with defined multicompartments from binary mixtures of block copolymers.
- Jiahua Zhu
- , Shiyi Zhang
- & Darrin J. Pochan
-
Article |
 Structured cone arrays for continuous and effective collection of micron-sized oil droplets from water
Structured cone arrays for continuous and effective collection of micron-sized oil droplets from water
Effective methods for the removal of micro-droplets of oil from water are sought-after to combat oil spills. Here, the authors report cactus-inspired oleophilic conical needle arrays capable of capturing micron-sized oil droplets with both high continuity and high throughput.
- Kan Li
- , Jie Ju
- & Lei Jiang
-
Article |
 Reversible patterning and actuation of hydrogels by electrically assisted ionoprinting
Reversible patterning and actuation of hydrogels by electrically assisted ionoprinting
Techniques for shape-controlling of hydrogels, that is, crosslinked networks of polymers, could make possible various biomimetic applications. Palleau et al.propose a strategy to pattern three-dimensional hydrogels using electric potential, which allows directed bending and fast controllable actuation.
- Etienne Palleau
- , Daniel Morales
- & Orlin D. Velev
-
Article
| Open Access Stable platinum nanoclusters on genomic DNA–graphene oxide with a high oxygen reduction reaction activity
Stable platinum nanoclusters on genomic DNA–graphene oxide with a high oxygen reduction reaction activity
Platinum nanoclusters are well-known catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction, although the performance of clusters smaller than 2 nm is poorly studied. Here, the authors report 1.4 nm platinum clusters supported on DNA–graphene oxide composites and demonstrate promising electrochemical activity and stability.
- Jitendra N. Tiwari
- , Krishna Nath
- & Kwang S. Kim
-
Article |
 Nitrate formation from atmospheric nitrogen and oxygen photocatalysed by nano-sized titanium dioxide
Nitrate formation from atmospheric nitrogen and oxygen photocatalysed by nano-sized titanium dioxide
Nitrate pollutants are known to contribute to a variety of environmental problems. Here, the authors suggest that nano-sized titanium dioxide, as used in numerous surface coatings, may catalyse the formation of nitrate via the photochemical reaction of atmospheric nitrogen and oxygen.
- Shi-Jie Yuan
- , Jie-Jie Chen
- & Han-Qing Yu
-
Article |
 Interfacial assembly of protein–polymer nano-conjugates into stimulus-responsive biomimetic protocells
Interfacial assembly of protein–polymer nano-conjugates into stimulus-responsive biomimetic protocells
Proteins are ideal building blocks for self-assembly of artificial cell-like architectures, but their realization is rare. Huang et al.report an interfacial assembly of protein–polymer conjugates, which exhibit cellular properties such as encapsulating guest molecules and switching enzyme activity.
- Xin Huang
- , Mei Li
- & Stephen Mann
-
Article
| Open Access Role of point defects on the reactivity of reconstructed anatase titanium dioxide (001) surface
Role of point defects on the reactivity of reconstructed anatase titanium dioxide (001) surface
Theory suggests that the anatase (001) surface is the most catalytically reactive of all the crystal facets of titanium dioxide. Wang et al.show that the active sites are four-coordinated titanium states and in their absence this surface is even inert for water adsorption at room temperature.
- Yang Wang
- , Huijuan Sun
- & J. G. Hou
-
Article
| Open Access Hypervalent surface interactions for colloidal stability and doping of silicon nanocrystals
Hypervalent surface interactions for colloidal stability and doping of silicon nanocrystals
Electrically insulating ligands and doping of colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals continue to be significant challenges for practical nanocrystal-based optoelectronics. Wheeler et al.demonstrate a new surface chemistry technique that confronts both of these challenges simultaneously.
- Lance M. Wheeler
- , Nathan R. Neale
- & Uwe R. Kortshagen
-
Article |
 Probing the nature of gold–carbon bonding in gold–alkynyl complexes
Probing the nature of gold–carbon bonding in gold–alkynyl complexes
Fundamental understanding of gold–carbon bonding in homogeneous catalysts is vital for improved catalyst design, although spectroscopic information is limited. Here, the authors probe the bonding in gold–alkyne complexes using a combination of photoelectron spectroscopy and ab initiocalculations.
- Hong-Tao Liu
- , Xiao-Gen Xiong
- & Lai-Sheng Wang
-
Article |
 A green lead hydrometallurgical process based on a hydrogen-lead oxide fuel cell
A green lead hydrometallurgical process based on a hydrogen-lead oxide fuel cell
Lead-acid batteries are used worldwide, but their recycling remains challenging because of lead pollution and high energy consumption. Pan et al. solve these problems in a high-yield, hydrometallurgical process based on hydrogen-lead oxide fuel cell reactions, which produce water as the by-product.
- Junqing Pan
- , Yanzhi Sun
- & Arumugam Manthiram
-
Article |
 Understanding the role of phase in chemical bond breaking with coincidence angular streaking
Understanding the role of phase in chemical bond breaking with coincidence angular streaking
Ultrafast laser pulses are useful to study electron dynamics in chemical bonds, but their influence on bond breaking is not fully understood. Wu et al. study H2 bond breaking with coincidence techniques, and find a phase-dependent anisotropy of the H+fragmentation even for isotropic multicycle laser pulses.
- J. Wu
- , M. Magrakvelidze
- & R. Dörner
-
Article
| Open Access Semiclassical Monte-Carlo approach for modelling non-adiabatic dynamics in extended molecules
Semiclassical Monte-Carlo approach for modelling non-adiabatic dynamics in extended molecules
Many interesting chemical problems like photosynthesis and photovoltaics involve non-adiabatic dynamical phenomena, which are difficult to predict theoretically. Here, the authors develop a new numerical method capable of recovering quantum interferences that are neglected by conventional methods.
- Vyacheslav N. Gorshkov
- , Sergei Tretiak
- & Dmitry Mozyrsky
-
Article |
 Interfacial liquid-state surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Interfacial liquid-state surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Assembly of functional colloidal nanoparticles has many technological applications, but its three-dimensional realization remains challenging. Kim et al.report a spontaneous self-orientation of gold nanorods at an oil/water interface and use it to amplify signal in surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy.
- Kihoon Kim
- , Hye Soo Han
- & Taewook Kang
-
Article
| Open Access Femtolitre chemistry assisted by microfluidic pen lithography
Femtolitre chemistry assisted by microfluidic pen lithography
Chemical reactions on femtolitre scales are necessary to study confined biological processes. Here, the authors use a microfluidic pen lithography technique to perform a series of discrete femtoscale acid-base and synthetic reactions, and crystallizations on a surface with high registration accuracy.
- Carlos Carbonell
- , Kyriakos C. Stylianou
- & Daniel Maspoch
-
Article
| Open Access NMR spectroscopic detection of chirality and enantiopurity in referenced systems without formation of diastereomers
NMR spectroscopic detection of chirality and enantiopurity in referenced systems without formation of diastereomers
The enantiopurity of chiral compounds is key in determining their activity or therapeutic action. Here, the authors present a versatile NMR method of enantiomeric excess determination using a symmetrical achiral molecule as resolving agent, based on complexation with analyte, without formation of diastereomers.
- Jan Labuta
- , Shinsuke Ishihara
- & Jonathan P. Hill
-
Article |
 Gold peroxide complexes and the conversion of hydroperoxides into gold hydrides by successive oxygen-transfer reactions
Gold peroxide complexes and the conversion of hydroperoxides into gold hydrides by successive oxygen-transfer reactions
Gold peroxide-derived complexes are important in oxidation catalysis, although structural information on these species is sparse. Here, the authors have synthesized a range of gold complexes and have shown a reaction pathway from peroxides to hydrides, via oxygen-transfer events.
- Dragoş-Adrian Roşca
- , Joseph A. Wright
- & Manfred Bochmann
-
Article
| Open Access Conducting linear chains of sulphur inside carbon nanotubes
Conducting linear chains of sulphur inside carbon nanotubes
Elemental sulphur is an insulator in the bulk phase, although it may become conducting under ultrahigh-pressure conditions. Here, the authors report a one-dimensional conducting form of sulphur formed by encapsulation inside single-walled and double-walled carbon nanotubes.
- Toshihiko Fujimori
- , Aarón Morelos-Gómez
- & Katsumi Kaneko
-
Article |
 Chemical synthesis of lactic acid from cellulose catalysed by lead(II) ions in water
Chemical synthesis of lactic acid from cellulose catalysed by lead(II) ions in water
The direct transformation of cellulose into high-value chemicals is a key process in the establishment of biomass-derived chemical production. Here, the authors present the lead(II)-catalysed conversion of cellulose into lactic acid via a cascade reaction, which proceeds in water under mild conditions.
- Yanliang Wang
- , Weiping Deng
- & Huilin Wan
-
Article
| Open Access Tetrasaccharide iteration synthesis of a heparin-like dodecasaccharide and radiolabelling for in vivo tissue distribution studies
Tetrasaccharide iteration synthesis of a heparin-like dodecasaccharide and radiolabelling for in vivo tissue distribution studies
Heparin-like oligosaccharides are implicated in various diseases. Hansen et al. report an efficient two-cycle [4+4+4] tetrasaccharide-iteration-based approach to synthesize a structurally defined heparin dodecasaccharide with a latent aldehyde tag for labelling and conjugation.
- Steen U. Hansen
- , Gavin J. Miller
- & John M. Gardiner
-
Article |
 Direct measurement and modulation of single-molecule coordinative bonding forces in a transition metal complex
Direct measurement and modulation of single-molecule coordinative bonding forces in a transition metal complex
The nature of metal–ligand interactions remains unclear in coordination chemistry. Hao et al. address this question using in situelectrochemically controlled atomic force microscopy, which can monitor and modulate the coordinative bonding in a transition metal complex at a molecular level.
- Xian Hao
- , Nan Zhu
- & Qijin Chi
-
Article |
 Promotion of oxygen reduction by a bio-inspired tethered iron phthalocyanine carbon nanotube-based catalyst
Promotion of oxygen reduction by a bio-inspired tethered iron phthalocyanine carbon nanotube-based catalyst
The rational design of inexpensive and durable oxygen reduction catalysts may lead to enhanced fuel cell performance. Here, the authors report a bio-inspired catalyst in which hybridization of iron 3delectrons with a carbon nanotube alters its electronic structure and improves catalytic performance.
- Ruiguo Cao
- , Ranjit Thapa
- & Jaephil Cho
-
Article |
 Photolatently modulable hydrogels using unilamellar titania nanosheets as photocatalytic crosslinkers
Photolatently modulable hydrogels using unilamellar titania nanosheets as photocatalytic crosslinkers
Postsynthetic modulation of the structural properties of hydrogels is desirable for a range of biomaterials applications. Here, the authors fabricate photolatently modulable polymer hydrogels crosslinked by titania nanosheets, which may be micropatterned with high spatial and temporal resolution.
- Mingjie Liu
- , Yasuhiro Ishida
- & Takuzo Aida
-
Article
| Open Access A solid with a hierarchical tetramodal micro-meso-macro pore size distribution
A solid with a hierarchical tetramodal micro-meso-macro pore size distribution
Porous solids have potential applications in energy storage, gas separation and catalysis technologies. Here, the authors report a hierarchical solid with porosity spanning the micro, meso and macro ranges, which is synthesized using templating silica, and potassium ions as both templates and reactive species.
- Yu Ren
- , Zhen Ma
- & Peter G. Bruce
-
Article |
 A ladder polysilane as a template for folding palladium nanosheets
A ladder polysilane as a template for folding palladium nanosheets
Since the isolation of graphene, there has been extensive interest in other two-dimensional structures including metallic nanosheets. Here, the authors report the use of ladder polysilane ligands for the synthesis of palladium clusters containing eleven metal ions, made up of two heptametallic nanosheets.
- Yusuke Sunada
- , Ryohei Haige
- & Hideo Nagashima
-
Article |
 Giant cationic polyelectrolytes generated via electrochemical oxidation of single-walled carbon nanotubes
Giant cationic polyelectrolytes generated via electrochemical oxidation of single-walled carbon nanotubes
Reduced carbon nanotube anions can be effectively processed and functionalized. Here, the authors prepare discrete nanotube cations by electrochemical oxidation, and the confirmation of their reactivity towards nucleophiles suggests a new library of covalent nanotube modifications.
- Stephen A. Hodge
- , Mustafa K. Bayazit
- & Milo S. P. Shaffer
-
Article |
 Mechanical stimulation and solid seeding trigger single-crystal-to-single-crystal molecular domino transformations
Mechanical stimulation and solid seeding trigger single-crystal-to-single-crystal molecular domino transformations
Despite extensive research on mechanical control of phase change in crystals, a molecular-level understanding of the forces involved is lacking. Here, the authors observe a phase change process optically, and show that it is induced by mechanical stimulation and proceeds through domino-like self-replication.
- Hajime Ito
- , Mai Muromoto
- & Tomohiro Seki
-
Article |
 Synthetic regimes due to packing constraints in dendritic molecules confirmed by labelling experiments
Synthetic regimes due to packing constraints in dendritic molecules confirmed by labelling experiments
Classical theory predicts that branching defects are unavoidable in large dendritic molecules when steric congestion becomes important. Zhang et al. present the first direct evidence of this effect by means of defect labelling of a homologous series of dendronized polymers.
- Baozhong Zhang
- , Hao Yu
- & Martin Kröger
-
Article |
 Multistep kinetic self-assembly of DNA-coated colloids
Multistep kinetic self-assembly of DNA-coated colloids
The final state of self-assembled systems is determined by both their thermodynamic and kinetic pathways. Di Michele et al.develop a strategy to realize predesigned amorphous structures of complex DNA colloidal mixtures by selectively activating local inter- or intra-species interactions upon freezing.
- Lorenzo Di Michele
- , Francesco Varrato
- & Erika Eiser
-
Article |
 Solution-based circuits enable rapid and multiplexed pathogen detection
Solution-based circuits enable rapid and multiplexed pathogen detection
Rapid, highly multiplexed molecular detection platforms may enable more specific and effective disease diagnosis. Here, a solution-based circuit is reported that enables the analysis of samples for panels of pathogens and antibiotic-resistance profiles at clinically relevant levels in less than 2 min.
- Brian Lam
- , Jagotamoy Das
- & Shana O. Kelley
-
Article
| Open Access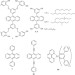 Nonvolatile liquid anthracenes for facile full-colour luminescence tuning at single blue-light excitation
Nonvolatile liquid anthracenes for facile full-colour luminescence tuning at single blue-light excitation
Nonvolatile luminescent liquids are solvent-free fluids with a range of flexible electronic applications. Here, the authors show that anthracenes enveloped in branched aliphatic compounds are stable emissive liquids, with emissive and thermoresponsive properties that may be tuned by addition of dopants.
- Sukumaran Santhosh Babu
- , Martin J. Hollamby
- & Takashi Nakanishi
-
Article |
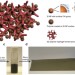 Stable Li-ion battery anodes by in-situ polymerization of conducting hydrogel to conformally coat silicon nanoparticles
Stable Li-ion battery anodes by in-situ polymerization of conducting hydrogel to conformally coat silicon nanoparticles
Nanostructured silicon is a promising anode material for lithium ion batteries but needs to tolerate large volume increase upon lithiation. Wu et al. solve this problem by binding silicon nanoparticles to a conducting polymer hydrogel via in-situpolymerization, which also improves cycling stability.
- Hui Wu
- , Guihua Yu
- & Yi Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Capture and conversion of CO2 at ambient conditions by a conjugated microporous polymer
Capture and conversion of CO2 at ambient conditions by a conjugated microporous polymer
Conjugated microporous polymers are highly flexible materials that may be used for gas storage and catalysis applications. Here, the authors report metal-functionalized conjugated microporous polymers capable of both capturing CO2and functioning as a heterogeneous catalyst in its conversion to propylene carbonate.
- Yong Xie
- , Ting-Ting Wang
- & Wei-Qiao Deng
-
Article |
 Photo-oxidative enhancement of polymeric molecular sieve membranes
Photo-oxidative enhancement of polymeric molecular sieve membranes
Membranes for molecular-level sieving based on processable, permeable polymers are desirable for industrial processes. Here, the authors report the photo-oxidative surface modification of these membranes, which results in asymmetric materials with high selectivity and permeability for gas separations.
- Qilei Song
- , Shuai Cao
- & Easan Sivaniah
-
Article |
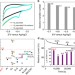 Catalytically active single-atom niobium in graphitic layers
Catalytically active single-atom niobium in graphitic layers
Noble metallic subnanometre clusters exhibit superior catalytic activities, but their stability remains a problem. Zhang et al. report that single niobium atoms can be stabilized in graphitic layers and the resulting carbide complex exhibits higher activity compared with commercial platinum nanoclusters.
- Xuefeng Zhang
- , Junjie Guo
- & Matthew F. Chisholm
-
Article |
 An influenza virus-inspired polymer system for the timed release of siRNA
An influenza virus-inspired polymer system for the timed release of siRNA
Small interfering RNA is degraded by plasma and can’t cross the cell membrane due to its negative charge. Here, the authors present an influenza inspired polymer carrier, capable of local RNA delivery, which degrades to a non-toxic by-product, and is thus suitable for multiple doses.
- Nghia P Truong
- , Wenyi Gu
- & Michael J Monteiro
-
Article
| Open Access Amorphous nickel hydroxide nanospheres with ultrahigh capacitance and energy density as electrochemical pseudocapacitor materials
Amorphous nickel hydroxide nanospheres with ultrahigh capacitance and energy density as electrochemical pseudocapacitor materials
Nickel hydroxide is a promising material for capacitor electrodes and most research has focussed on the crystalline form. Here, the authors report that amorphous nickel hydroxide nanospheres, which may be synthesized relatively easily, also exhibit excellent integrated electrochemical performance.
- H. B. Li
- , M. H. Yu
- & G. W. Yang
-
Article |
 High-performance rechargeable lithium-iodine batteries using triiodide/iodide redox couples in an aqueous cathode
High-performance rechargeable lithium-iodine batteries using triiodide/iodide redox couples in an aqueous cathode
Aqueous lithium batteries can store more energy because of their high ionic conductivity compared with the all-solid-state or non-aqueous electrolyte based counterparts. Zhao et al. report a large energy storage density by using safe and low-cost triiodide/iodide redox reaction in an aqueous cathode.
- Yu Zhao
- , Lina Wang
- & Hye Ryung Byon
-
Article |
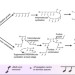 Controlled multi-vinyl monomer homopolymerization through vinyl oligomer combination as a universal approach to hyperbranched architectures
Controlled multi-vinyl monomer homopolymerization through vinyl oligomer combination as a universal approach to hyperbranched architectures
Hyperbranched polymers have desirable properties as novel materials, and may be synthesized from homopolymerization of multi-vinyl momomers, although this can form insoluble products at low conversions. Here, the authors produce hyperbranched polymers in high yield owing to a kinetic control mechanism.
- Tianyu Zhao
- , Yu Zheng
- & Wenxin Wang
-
Article |
 Stimuli-responsive selection of target DNA sequences by synthetic bZIP peptides
Stimuli-responsive selection of target DNA sequences by synthetic bZIP peptides
The expression of specific genes can be controlled by the combination of DNA-binding proteins, which determines their binding site selectivity. Here, simplified synthetic basic region leucine zipper-based peptides are induced to dimerize either through their C- or N-terminus, and thus are targeted to different DNA sequences.
- Jesús Mosquera
- , Adrián Jiménez-Balsa
- & José L Mascareñas
-
Article
| Open Access Assembly of a π–π stack of ligands in the binding site of an acetylcholine-binding protein
Assembly of a π–π stack of ligands in the binding site of an acetylcholine-binding protein
AChBP is used as a structurally accessible prototype for studying ligand binding to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Stornaiuolo et al. report that a small molecule binds AChBP in an ordered p–p stack of three molecules per binding site, which may lead to new approaches in drug design.
- Mariano Stornaiuolo
- , Gerdien E. De Kloe
- & Titia K. Sixma
-
Article |
 Direct atomic-scale confirmation of three-phase storage mechanism in Li4Ti5O12 anodes for room-temperature sodium-ion batteries
Direct atomic-scale confirmation of three-phase storage mechanism in Li4Ti5O12 anodes for room-temperature sodium-ion batteries
The development of suitable anode materials for room-temperature sodium-ion batteries remains a challenging issue. Sun et al. show that the well-known zero-strain Li4Ti5O12anode for lithium storage is capable of reversibly hosting sodium ions via a three-phase storage mechanism.
- Yang Sun
- , Liang Zhao
- & Xuejie Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Selective isolation of gold facilitated by second-sphere coordination with α-cyclodextrin
Selective isolation of gold facilitated by second-sphere coordination with α-cyclodextrin
Currently, gold recovery from waste materials requires inorganic cyanides and more environmentally benign methods are required. Here, the authors report that host–guest interactions between α-cyclodextrin and gold lead to the precipitation of one-dimensional superstructures, offering a selective and green alternative.
- Zhichang Liu
- , Marco Frasconi
- & J. Fraser Stoddart
-
Article |
 Advanced zinc-air batteries based on high-performance hybrid electrocatalysts
Advanced zinc-air batteries based on high-performance hybrid electrocatalysts
Metal-air batteries are promising for energy storage because of their high theoretical energy density, but their realization is hampered by the lack of efficient and robust air catalysts. Li et al. construct stable zinc-air batteries using novel catalysts for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions.
- Yanguang Li
- , Ming Gong
- & Hongjie Dai
-
Article |
 A reversible long-life lithium–air battery in ambient air
A reversible long-life lithium–air battery in ambient air
Lithium air batteries have among the highest energy storage capacities, but their effective lifetime is short when using liquid electrolytes. Zhang et al. realize a lithium air battery with much improved cycling stability in ambient air by combining a solid electrolyte and a gel cathode.
- Tao Zhang
- & Haoshen Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Linkage control between molecular and supramolecular chirality in 21-helical hydrogen-bonded networks using achiral components
Linkage control between molecular and supramolecular chirality in 21-helical hydrogen-bonded networks using achiral components
Chiral molecules form one-handed supramolecular assemblies but may be induced to switch to the other handed assembly, although the mechanisms driving these processes are unclear. Here, the authors demonstrate control of the supramolecular assembly handedness via the introduction of achiral counter ions.
- Toshiyuki Sasaki
- , Ichiro Hisaki
- & Mikiji Miyata
-
Article |
 Porous boron nitride nanosheets for effective water cleaning
Porous boron nitride nanosheets for effective water cleaning
The development of materials for the effective removal of oils and solvents from water is of global importance. Here, the authors show that porous, hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets are capable of absorbing many times their own weight in oil while repelling water, and may be cleaned for reuse by heating or burning in air.
- Weiwei Lei
- , David Portehault
- & Ying Chen
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Analytical chemistry
- Biochemistry
- Biosynthesis
- Catalysis
- Chemical biology
- Chemical education
- Chemical engineering
- Chemical safety
- Cheminformatics
- Chemistry publishing
- Communicating chemistry
- Coordination chemistry
- Electrochemistry
- Energy
- Environmental chemistry
- Green chemistry
- History of chemistry
- Inorganic chemistry
- Materials chemistry
- Medicinal chemistry
- Nuclear chemistry
- Organic chemistry
- Chemical origin of life
- Photochemistry
- Physical chemistry
- Polymer chemistry
- Process chemistry
- Supramolecular chemistry
- Surface chemistry
- Chemical synthesis
- Theoretical chemistry

 Membrane-less hydrogen bromine flow battery
Membrane-less hydrogen bromine flow battery