Featured
-
-
Letter |
 Nuclear envelope assembly defects link mitotic errors to chromothripsis
Nuclear envelope assembly defects link mitotic errors to chromothripsis
The mitotic spindle prevents normal nuclear envelope assembly on missegregated chromosomes, leading to spontaneous envelope disruption of micronuclei and subsequent genome instability.
- Shiwei Liu
- , Mijung Kwon
- & David Pellman
-
Letter |
 Experimental and computational framework for a dynamic protein atlas of human cell division
Experimental and computational framework for a dynamic protein atlas of human cell division
Quantitative live-cell imaging provides a dynamic protein atlas of mitosis.
- Yin Cai
- , M. Julius Hossain
- & Jan Ellenberg
-
Article |
 Extensive sex differences at the initiation of genetic recombination
Extensive sex differences at the initiation of genetic recombination
Differential DNA methylation and the long-range effects of chromatin organization lead to pronounced differences in recombination landscape between males and females.
- Kevin Brick
- , Sarah Thibault-Sennett
- & Galina V. Petukhova
-
Article |
 Kinase-controlled phase transition of membraneless organelles in mitosis
Kinase-controlled phase transition of membraneless organelles in mitosis
The dual-specificity kinase DYRK3 acts as a central ‘dissolvase’, mediating the phase transitions of several types of membraneless organelles during mitosis.
- Arpan Kumar Rai
- , Jia-Xuan Chen
- & Lucas Pelkmans
-
Letter |
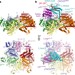 Mechanism for remodelling of the cell cycle checkpoint protein MAD2 by the ATPase TRIP13
Mechanism for remodelling of the cell cycle checkpoint protein MAD2 by the ATPase TRIP13
Structural analysis demonstrates how TRIP13 and p31comet disassemble the mitotic checkpoint complex.
- Claudio Alfieri
- , Leifu Chang
- & David Barford
-
Letter |
 EMI1 switches from being a substrate to an inhibitor of APC/CCDH1 to start the cell cycle
EMI1 switches from being a substrate to an inhibitor of APC/CCDH1 to start the cell cycle
The transition between early mitotic inhibitor 1 acting as a substrate of the APC/C and as an inhibitor of the same complex results in an irreversible switch that mediates human cell-cycle commitment.
- Steven D. Cappell
- , Kevin G. Mark
- & Tobias Meyer
-
Article |
 SAMHD1 acts at stalled replication forks to prevent interferon induction
SAMHD1 acts at stalled replication forks to prevent interferon induction
SAMHD1 has an essential role in the replication stress response and prevents inflammation by activating the MRE11 nuclease to degrade nascent DNA strands at stalled replication forks, thus enabling replication.
- Flavie Coquel
- , Maria-Joao Silva
- & Philippe Pasero
-
Article
| Open Access The genome of Schmidtea mediterranea and the evolution of core cellular mechanisms
The genome of Schmidtea mediterranea and the evolution of core cellular mechanisms
An improved genome assembly for Schmidtea mediterranea shows that the genome is highly polymorphic and repetitive, and lacks multiple genes encoding core components of cell biological mechanisms.
- Markus Alexander Grohme
- , Siegfried Schloissnig
- & Jochen Christian Rink
-
Letter |
 A reversible haploid mouse embryonic stem cell biobank resource for functional genomics
A reversible haploid mouse embryonic stem cell biobank resource for functional genomics
The Haplobank contains over 100,000 individually reversibly mutagenized, barcoded, mouse embryonic cell lines; proof-of-principle experiments were used to search for genes that are required for rhinovirus infection and angiogenesis using forward and reverse genetic screens, respectively.
- Ulrich Elling
- , Reiner A. Wimmer
- & Josef M. Penninger
-
Letter |
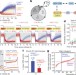 Competing memories of mitogen and p53 signalling control cell-cycle entry
Competing memories of mitogen and p53 signalling control cell-cycle entry
Mother cells transmit mitogen-induced CCND1 mRNA and DNA damage-induced p53 protein to newly born daughter cells, where synthesized cyclin D1 and the p53-regulated CDK inhibitor p21 directly compete to decide between proliferation and quiescence.
- Hee Won Yang
- , Mingyu Chung
- & Tobias Meyer
-
Letter |
 CDK4/6 inhibition triggers anti-tumour immunity
CDK4/6 inhibition triggers anti-tumour immunity
Mouse models of breast carcinoma and other solid tumours show that selective cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) inhibitors not only induce tumour cell cycle arrest but also promote anti-tumour immunity.
- Shom Goel
- , Molly J. DeCristo
- & Jean J. Zhao
-
Letter |
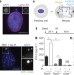 cGAS surveillance of micronuclei links genome instability to innate immunity
cGAS surveillance of micronuclei links genome instability to innate immunity
The cytoplasmic DNA sensor cGAS detects DNA in ruptured micronuclei and activates an innate immune response.
- Karen J. Mackenzie
- , Paula Carroll
- & Andrew P. Jackson
-
Letter |
 The metabolic function of cyclin D3–CDK6 kinase in cancer cell survival
The metabolic function of cyclin D3–CDK6 kinase in cancer cell survival
The cyclin D3–CDK6 kinase complex, which is overactive in some cancers, inhibits two key glycolysis enzymes and thereby enhances the levels of antioxidants in cells, promoting tumour cell survival.
- Haizhen Wang
- , Brandon N. Nicolay
- & Piotr Sicinski
-
Letter |
 DHX9 suppresses RNA processing defects originating from the Alu invasion of the human genome
DHX9 suppresses RNA processing defects originating from the Alu invasion of the human genome
In the absence of DHX9, circular RNAs accumulate and transcription and translation are dysregulated—effects that are exacerbated by concomitant depletion of the RNA-editing enzyme ADAR.
- Tuğçe Aktaş
- , İbrahim Avşar Ilık
- & Asifa Akhtar
-
Letter |
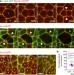 Transmission of cytokinesis forces via E-cadherin dilution and actomyosin flows
Transmission of cytokinesis forces via E-cadherin dilution and actomyosin flows
Under physiological forces, resulting from cytokinesis, the mechanosensitivity of adherens junction arises from a local decrease in E-cadherin concentration and results in actomyosin flows.
- Diana Pinheiro
- , Edouard Hannezo
- & Yohanns Bellaïche
-
Letter |
 Mechanical stretch triggers rapid epithelial cell division through Piezo1
Mechanical stretch triggers rapid epithelial cell division through Piezo1
The stretch-activated channel Piezo1 controls homeostatic epithelial cell numbers by activating cells to divide rapidly when under stretch strain from low density, and by activating cells to extrude and die when cells are under crowding strain.
- S. A. Gudipaty
- , J. Lindblom
- & J. Rosenblatt
-
Letter |
 Molecular mechanism for the regulation of yeast separase by securin
Molecular mechanism for the regulation of yeast separase by securin
The crystal structure of yeast separase in complex with its inhibitor securin sheds light on the mechanism of inhibition, in which securin inhibits separase by inserting a short segment into the active site.
- Shukun Luo
- & Liang Tong
-
Letter |
 Basis of catalytic assembly of the mitotic checkpoint complex
Basis of catalytic assembly of the mitotic checkpoint complex
The near-complete in vitro reconstitution of the mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint reveals how the assembly of its effector, the mitotic checkpoint complex, is catalysed.
- Alex C. Faesen
- , Maria Thanasoula
- & Andrea Musacchio
-
Letter |
 Insights from biochemical reconstitution into the architecture of human kinetochores
Insights from biochemical reconstitution into the architecture of human kinetochores
Biochemical reconstitution of a synthetic human kinetochore with 21 protein subunits and centromeric nucleosomal DNA unveils fundamental principles of kinetochore organization and function.
- John R. Weir
- , Alex C. Faesen
- & Andrea Musacchio
-
Article |
 Molecular basis of APC/C regulation by the spindle assembly checkpoint
Molecular basis of APC/C regulation by the spindle assembly checkpoint
A high-resolution structure of a complex between the anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C) and the mitotic checkpoint complex (MCC) reveals how MCC interacts with and represses APC/C by obstructing substrate recognition and suppressing E3 ligase activity.
- Claudio Alfieri
- , Leifu Chang
- & David Barford
-
Letter |
 Ki-67 acts as a biological surfactant to disperse mitotic chromosomes
Ki-67 acts as a biological surfactant to disperse mitotic chromosomes
During cell division, chromosomes are maintained as individual units; this process is shown to be mediated by the cell proliferation marker Ki-67, which has biophysical properties similar to those of surfactants.
- Sara Cuylen
- , Claudia Blaukopf
- & Daniel W. Gerlich
-
Letter |
 Pitx2 promotes heart repair by activating the antioxidant response after cardiac injury
Pitx2 promotes heart repair by activating the antioxidant response after cardiac injury
The transcription factor Pitx2 is upregulated in injured neonatal and Hippo-deficient mouse hearts, where it interacts with the Hippo effector protein Yap to activate reactive oxygen species scavengers, thus preventing the heart from oxidative damage.
- Ge Tao
- , Peter C. Kahr
- & James F. Martin
-
Letter |
 Metabolic maintenance of cell asymmetry following division in activated T lymphocytes
Metabolic maintenance of cell asymmetry following division in activated T lymphocytes
The asymmetric distribution of mTORC1 and c-Myc in the first division of daughter cells of activated CD8 T cells affects the proliferation, metabolism and differentiation potential of their progeny.
- Katherine C. Verbist
- , Cliff S. Guy
- & Douglas R. Green
-
Letter |
 Structural basis of cohesin cleavage by separase
Structural basis of cohesin cleavage by separase
The crystal structures of the protease domain of separase are reported, showing how separase recognizes cohesin, and how phosphorylation of the cleavage site enhances separase activity.
- Zhonghui Lin
- , Xuelian Luo
- & Hongtao Yu
-
Letter |
 Epithelial tricellular junctions act as interphase cell shape sensors to orient mitosis
Epithelial tricellular junctions act as interphase cell shape sensors to orient mitosis
As fruitfly epithelial cells round up during mitosis, tricellular junctions serve as spatial landmarks, encoding information about interphase cell shape directionality to orient mitosis, and promoting geometric and mechanical sensing in epithelial tissues.
- Floris Bosveld
- , Olga Markova
- & Yohanns Bellaïche
-
Letter |
 Replication stress activates DNA repair synthesis in mitosis
Replication stress activates DNA repair synthesis in mitosis
Common fragile sites (CFSs) are difficult-to-replicate regions of eukaryotic genomes that are sensitive to replication stress and that require resolution by the MUS81–EME1 endonuclease to re-initiate POLD3-dependent DNA synthesis in early mitosis; this study defines the specific pathway of events causing the CFS fragility phenotype.
- Sheroy Minocherhomji
- , Songmin Ying
- & Ian D. Hickson
-
Letter |
 Dilution of the cell cycle inhibitor Whi5 controls budding-yeast cell size
Dilution of the cell cycle inhibitor Whi5 controls budding-yeast cell size
Saccharomyces cerevisiae controls its cell size through the differential size-dependency of the synthesis of the cell cycle activator Cln3 relative to the cell cycle inhibitor Whi5.
- Kurt M. Schmoller
- , J. J. Turner
- & Jan M. Skotheim
-
Letter |
 Kinetochore-localized PP1–Sds22 couples chromosome segregation to polar relaxation
Kinetochore-localized PP1–Sds22 couples chromosome segregation to polar relaxation
A study of division in proliferating animal cells points to the existence of a kinetochore-based signalling pathway, independent of furrow formation, centrosomes and microtubules, that couples chromosome segregation to cell division.
- Nelio T. L. Rodrigues
- , Sergey Lekomtsev
- & Buzz Baum
-
Letter |
 Live imaging RNAi screen reveals genes essential for meiosis in mammalian oocytes
Live imaging RNAi screen reveals genes essential for meiosis in mammalian oocytes
A high-content phenotypic screening method has been developed allowing the first systematic RNA interference screen for nearly 800 genes mediating mammalian meiosis.
- Sybille Pfender
- , Vitaliy Kuznetsov
- & Melina Schuh
-
Letter |
 Cell death during crisis is mediated by mitotic telomere deprotection
Cell death during crisis is mediated by mitotic telomere deprotection
Cells that bypass senescence in the absence of the p53 tumour suppressor protein have shortened telomeres that undergo fusion, and these fusions trigger mitotic arrest and cell death in crisis.
- Makoto T. Hayashi
- , Anthony J. Cesare
- & Jan Karlseder
-
Letter |
 Hypoxia fate mapping identifies cycling cardiomyocytes in the adult heart
Hypoxia fate mapping identifies cycling cardiomyocytes in the adult heart
Fate-mapping hypoxic cells in the mouse heart identifies a rare population of cycling cardiomyocytes, which show characteristics of neonatal cardiomyocytes, including smaller size and mononucleation, and contribute to new cardiomyocyte formation in the adult heart.
- Wataru Kimura
- , Feng Xiao
- & Hesham A. Sadek
-
Article |
 Atomic structure of the APC/C and its mechanism of protein ubiquitination
Atomic structure of the APC/C and its mechanism of protein ubiquitination
A cryo-electron microscopy determination of the atomic structures of anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C)–coactivator complexes with either Emi1 or a UbcH10–ubiquitin conjugate.
- Leifu Chang
- , Ziguo Zhang
- & David Barford
-
Letter |
 Spastin and ESCRT-III coordinate mitotic spindle disassembly and nuclear envelope sealing
Spastin and ESCRT-III coordinate mitotic spindle disassembly and nuclear envelope sealing
ESCRT-III, a protein complex best known for membrane constriction and sealing during various cellular processes, mediates reassembly of the nuclear envelope during late anaphase.
- Marina Vietri
- , Kay O. Schink
- & Harald Stenmark
-
Letter |
 ESCRT-III controls nuclear envelope reformation
ESCRT-III controls nuclear envelope reformation
The ESCRT-III complex is implicated in the reformation of the nuclear envelope; the CHMP2A component of ESCRT-III is directed to the forming nuclear envelope through classical ESCRT-assembly mechanisms, with the help of the p97 complex component UFD1, and provides an activity essential for nuclear envelope reformation.
- Yolanda Olmos
- , Lorna Hodgson
- & Jeremy G. Carlton
-
Article |
 Chromothripsis from DNA damage in micronuclei
Chromothripsis from DNA damage in micronuclei
The mechanism for chromothripsis, “shattered” chromosomes that can be observed in cancer cells, is unknown; here, using live-cell imaging and single-cell sequencing, chromothripsis is shown to occur after a chromosome is isolated into a micronucleus, an abnormal nuclear structure.
- Cheng-Zhong Zhang
- , Alexander Spektor
- & David Pellman
-
Article |
 Fatty acid carbon is essential for dNTP synthesis in endothelial cells
Fatty acid carbon is essential for dNTP synthesis in endothelial cells
This study identifies a crucial role for fatty acid oxidation (FAO) in endothelial cells during angiogenesis, and reveals that fatty-acid-derived carbons are used for the de novo synthesis of nucleotides, and hence FAO stimulates vessel sprouting by increasing endothelial cell proliferation.
- Sandra Schoors
- , Ulrike Bruning
- & Peter Carmeliet
-
Letter |
 Tel1ATM-mediated interference suppresses clustered meiotic double-strand-break formation
Tel1ATM-mediated interference suppresses clustered meiotic double-strand-break formation
Meiotic recombination is initiated by a fairly uniform distribution of hundreds of DNA double-strand breaks catalysed by the Spo11 protein; here, Tel1 (orthologue of human ATM) is shown to be required for the localized inhibition that prevents double-strand breaks from forming close to one another.
- Valerie Garcia
- , Stephen Gray
- & Matthew J. Neale
-
Article |
 Meikin is a conserved regulator of meiosis-I-specific kinetochore function
Meikin is a conserved regulator of meiosis-I-specific kinetochore function
The long elusive mammalian meiosis-specific kinetochore factor has been identified in mice; MEIKIN—which plays an equivalent role to the yeast proteins Spo13 and Moa1—ensures mono-orientation, protects sister chromatid cohesion and recruits the kinase PLK1 to the kinetochores.
- Jihye Kim
- , Kei-ichiro Ishiguro
- & Yoshinori Watanabe
-
Letter |
 A PP1–PP2A phosphatase relay controls mitotic progression
A PP1–PP2A phosphatase relay controls mitotic progression
The activation and coordination of phosphatase activity is important during mitotic exit; here, a mitotic phosphatase relay is described in fission yeast between the two major phosphatases, PP1 and PP2A, a mode of regulation that may be a feature of signalling networks across eukaryotes.
- Agnes Grallert
- , Elvan Boke
- & Iain M. Hagan
-
Letter |
 MapZ marks the division sites and positions FtsZ rings in Streptococcus pneumoniae
MapZ marks the division sites and positions FtsZ rings in Streptococcus pneumoniae
A new mechanism is identified for correct placement of the division machinery in Streptococcus pneumoniae that relies on the novel factor MapZ to form ring structures at the cell equator; these structures move apart as the cell elongates, acting as permanent markers of division sites.
- Aurore Fleurie
- , Christian Lesterlin
- & Christophe Grangeasse
-
Letter |
 The mitotic checkpoint complex binds a second CDC20 to inhibit active APC/C
The mitotic checkpoint complex binds a second CDC20 to inhibit active APC/C
By binding and inhibiting a second CDC20 molecule, the mitotic checkpoint complex can convert a local ‘wait’ signal from unattached kinetochores to inhibit the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome throughout the cell and avoid premature cell division.
- Daisuke Izawa
- & Jonathon Pines
-
Letter |
 Synergistic blockade of mitotic exit by two chemical inhibitors of the APC/C
Synergistic blockade of mitotic exit by two chemical inhibitors of the APC/C
Simultaneous disruption of two different protein–protein interactions within the (APC/C–Cdc20)–substrate complex can synergistically inhibit APC/C-dependent proteolysis and mitotic exit.
- Katharine L. Sackton
- , Nevena Dimova
- & Randall W. King
-
Article |
 Molecular architecture and mechanism of the anaphase-promoting complex
Molecular architecture and mechanism of the anaphase-promoting complex
The anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) is a large E3 ligase that mediates ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis of cell cycle regulatory proteins; here the complete secondary structure architecture of human APC/C complexed with its coactivator CDH1 and substrate HSL1 is determined at 7.4 Å resolution, revealing allosteric changes induced by the coactivator that enhance affinity for UBCH10–ubiqutin.
- Leifu Chang
- , Ziguo Zhang
- & David Barford
-
Letter |
 mTORC1 controls the adaptive transition of quiescent stem cells from G0 to GAlert
mTORC1 controls the adaptive transition of quiescent stem cells from G0 to GAlert
A mouse study reveals that the stem cell quiescent state is composed of two distinct phases, G0 and GAlert; stem cells reversibly transition between these two phases in response to systemic environmental stimuli acting through the mTORC1 pathway.
- Joseph T. Rodgers
- , Katherine Y. King
- & Thomas A. Rando
-
Article |
 Homologue engagement controls meiotic DNA break number and distribution
Homologue engagement controls meiotic DNA break number and distribution
DNA double-stranded breaks (DSBs) are shown to form in greater numbers in yeast cells lacking ZMM proteins, which are traditionally regarded as acting strictly downstream of DSB formation; these findings shed light on how cells balance the beneficial and deleterious outcomes of DSB formation.
- Drew Thacker
- , Neeman Mohibullah
- & Scott Keeney
-
Letter |
 Cyclin A regulates kinetochore microtubules to promote faithful chromosome segregation
Cyclin A regulates kinetochore microtubules to promote faithful chromosome segregation
Cyclin A is shown to maintain unstable kinetochore–microtubule (k–MT) attachments in prometaphase in order to allow for error correction; at the prometaphase–metaphase switch, k-MT attachments are stabilized when cyclin A drops below threshold levels.
- Lilian Kabeche
- & Duane A. Compton
-
Letter |
 Epithelial junctions maintain tissue architecture by directing planar spindle orientation
Epithelial junctions maintain tissue architecture by directing planar spindle orientation
The Drosophila tumour suppressors Scribbled and Discs large 1 are found to be essential regulators of planar spindle alignment during epithelial cell division; aberrant effects of spindle alignment are shown to be corrected through apoptosis, and the suppression of this mechanism can result in epithelial dysplasia and tumorigenesis.
- Yu-ichiro Nakajima
- , Emily J. Meyer
- & Matthew C. Gibson
-
Letter |
 Structural basis for molecular recognition of folic acid by folate receptors
Structural basis for molecular recognition of folic acid by folate receptors
Folate receptor-α (FRα) is overexpressed in many cancer cells and is therefore an important therapeutic target: here the X-ray crystal structure of folate-bound FRα is presented, revealing details of the ligand-binding pocket that may be useful in the development of small-molecule inhibitors for anticancer therapy.
- Chen Chen
- , Jiyuan Ke
- & Karsten Melcher
-
Letter |
 BAF complexes facilitate decatenation of DNA by topoisomerase IIα
BAF complexes facilitate decatenation of DNA by topoisomerase IIα
Mutations in the subunits of BAF chromatin-remodelling complexes are frequently found in human cancer; here deletion of BAF subunits or expression of mutants of the ATPase subunit BRG1 attenuates genome-wide binding of topoisomerase IIα, resulting in tangled chromosomes, anaphase bridges and G2/M arrest.
- Emily C. Dykhuizen
- , Diana C. Hargreaves
- & Gerald R. Crabtree

 Mechanosensing by β1 integrin induces angiocrine signals for liver growth and survival
Mechanosensing by β1 integrin induces angiocrine signals for liver growth and survival