Editorial |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Similarity regression predicts evolution of transcription factor sequence specificity
Similarity regression predicts evolution of transcription factor sequence specificity
Similarity regression is an improved method for predicting transcription factor motifs, enabling analysis of DNA-binding motifs across eukaryotes and an expansion of the Cis-BP database of measured and predicted transcription factor motifs.
- Samuel A. Lambert
- , Ally W. H. Yang
- & Timothy R. Hughes
-
Letter |
 Evolution of buffering in a genetic circuit controlling plant stem cell proliferation
Evolution of buffering in a genetic circuit controlling plant stem cell proliferation
A study of a stem cell receptor–ligand signaling module across tomato, maize and Arabidopsis identifies different genetic mechanisms of compensation that contribute to homeostasis.
- Daniel Rodriguez-Leal
- , Cao Xu
- & Zachary B. Lippman
-
Technical Report |
 Linked-read analysis identifies mutations in single-cell DNA-sequencing data
Linked-read analysis identifies mutations in single-cell DNA-sequencing data
Linked-read analysis is a method for analyzing single-cell DNA-sequencing data that accurately identifies somatic single-nucleotide variants by using read-level phasing with nearby germline variants, enabling the characterization of mutational signatures and estimation of somatic mutation rates in single cells.
- Craig L. Bohrson
- , Alison R. Barton
- & Peter J. Park
-
Editorial |
Brave new dialogue
The development of CRISPR–Cas technology and its applications in biomedical research have generated much excitement. If fully realized, this technology has the potential to help treat or prevent severe diseases. However, these tools also carry considerable risk if improperly used. The scientific community must promote constructive dialogue among its members and within society at large to ensure that research on genome editing is conducted responsibly.
-
Article |
 Genome-wide stability of the DNA replication program in single mammalian cells
Genome-wide stability of the DNA replication program in single mammalian cells
scRepli-seq measures DNA replication timing in single cells on the basis of copy number. Applying haplotype-resolved scRepli-seq to mESCs establishes basic principles of replication-timing conservation and heterogeneity among populations of cells.
- Saori Takahashi
- , Hisashi Miura
- & Ichiro Hiratani
-
Article |
 Integrated analysis of population genomics, transcriptomics and virulence provides novel insights into Streptococcus pyogenes pathogenesis
Integrated analysis of population genomics, transcriptomics and virulence provides novel insights into Streptococcus pyogenes pathogenesis
This study presents the genomes of 2,101 emm28 Streptococcus pyogenes invasive strains, of which 492 were transcriptionally profiled, and 50 were assessed for virulence. GWAS, eQTL analysis, and study of isogenic mutant strains identified an intergenic region that alters global transcript profiles and bacterial virulence.
- Priyanka Kachroo
- , Jesus M. Eraso
- & James M. Musser
-
Article |
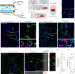 Lung regeneration by multipotent stem cells residing at the bronchioalveolar-duct junction
Lung regeneration by multipotent stem cells residing at the bronchioalveolar-duct junction
Fate-mapping and clonal analysis show that bronchioalveolar stem cells (BASCs) become activated and respond distinctly to different lung injuries and differentiate into multiple cell types. Single-cell RNA-seq analysis identifies new BASC markers.
- Qiaozhen Liu
- , Kuo Liu
- & Bin Zhou
-
Article |
 The landscape of selection in 551 esophageal adenocarcinomas defines genomic biomarkers for the clinic
The landscape of selection in 551 esophageal adenocarcinomas defines genomic biomarkers for the clinic
Genomic analysis of 551 esophageal adenocarcinomas identifies new driver mutations and biomarkers associated with poor prognosis. More than 50% of esophageal adenocarcinomas contain sensitizing events for CDK4/CDK6 inhibitors, thus providing an evidence base for targeted therapeutics.
- Alexander M. Frankell
- , SriGanesh Jammula
- & Rebecca C. Fitzgerald
-
Editorial |
Genomics and our future food security
Ensuring that agricultural production meets the goal of feeding a world experiencing continued human population growth and increasingly severe effects from climate change is an urgent challenge. Genomics has a role to play in maximizing the utility, diversity and yield of resources, as well as in contributing to sustained food security in the future.
-
News & Views |
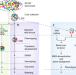 Harnessing the potential of germplasm collections
Harnessing the potential of germplasm collections
Contemporary genomics and informatics technologies were used to provide a meaningful and insightful overview of more than 20,000 wild and domesticated barley genotypes from one of the largest crop germplasm collections. The data provide a framework for the rational exploitation of genetic resources in crop improvement, which will be central to addressing global food security.
- Peter Langridge
- & Robbie Waugh
-
Perspective |
 Single-cell and single-molecule epigenomics to uncover genome regulation at unprecedented resolution
Single-cell and single-molecule epigenomics to uncover genome regulation at unprecedented resolution
Single-cell and single-molecule epigenomics to uncover genome regulation at unprecedented resolution.
- Efrat Shema
- , Bradley E. Bernstein
- & Jason D. Buenrostro
-
Article |
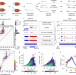 Single-molecule nascent RNA sequencing identifies regulatory domain architecture at promoters and enhancers
Single-molecule nascent RNA sequencing identifies regulatory domain architecture at promoters and enhancers
Sequencing nascent RNAs at single-molecule resolution with CoPRO unravels the interplay between Pol II initiation, capping and pausing. Transcription start site clusters provide a framework for understanding genome regulatory architecture.
- Jacob M. Tome
- , Nathaniel D. Tippens
- & John T. Lis
-
Article |
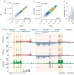 Chromatin run-on and sequencing maps the transcriptional regulatory landscape of glioblastoma multiforme
Chromatin run-on and sequencing maps the transcriptional regulatory landscape of glioblastoma multiforme
Chromatin run-on and sequencing (ChRO-seq) is a new method that maps the location of RNA polymerase using virtually any input sample. Here, ChRO-seq is used to study nascent transcription in human glioblastoma, and to identify regulators of tumor subtype.
- Tinyi Chu
- , Edward J. Rice
- & Charles G. Danko
-
Letter |
 Mutational processes shape the landscape of TP53 mutations in human cancer
Mutational processes shape the landscape of TP53 mutations in human cancer
Large-scale loss-of-function screens and TP53 saturation mutagenesis screens in human cancer cell lines suggest that mutational processes combine with phenotypic selection to shape the landscape of somatic mutations at the TP53 locus.
- Andrew O. Giacomelli
- , Xiaoping Yang
- & William C. Hahn
-
Article |
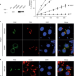 Type 2 diabetes risk alleles in PAM impact insulin release from human pancreatic β-cells
Type 2 diabetes risk alleles in PAM impact insulin release from human pancreatic β-cells
Coding variants in peptidylglycine α-amidating monooxygenase (PAM) associated with type 2 diabetes risk negatively impact overall PAM activity via defects in expression and catalytic function, resulting in reduced insulin content and altered dynamics of insulin secretion.
- Soren K. Thomsen
- , Anne Raimondo
- & Anna L. Gloyn
-
Article |
 CRISPR–Cas9 genome editing in human cells occurs via the Fanconi anemia pathway
CRISPR–Cas9 genome editing in human cells occurs via the Fanconi anemia pathway
A coupled knockdown-editing screen shows that CRISPR–Cas9 editing in human cells requires the Fanconi anemia pathway, which acts by diverting double-strand break repair away from non-homologous end joining toward single-strand template repair.
- Chris D. Richardson
- , Katelynn R. Kazane
- & Jacob E. Corn
-
Article |
 High-throughput identification of noncoding functional SNPs via type IIS enzyme restriction
High-throughput identification of noncoding functional SNPs via type IIS enzyme restriction
A high-throughput method for functional SNP identification uses enzymatic restriction to detect altered regulatory protein binding and identifies 148 candidate fSNPs associated with juvenile idiopathic arthritis, including two that regulate STAT4 via the regulatory proteins SATB2 and H1.2.
- Gang Li
- , Marta Martínez-Bonet
- & Peter A. Nigrovic
-
Article |
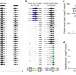 The transcription factor Grainy head primes epithelial enhancers for spatiotemporal activation by displacing nucleosomes
The transcription factor Grainy head primes epithelial enhancers for spatiotemporal activation by displacing nucleosomes
The authors show that the transcription factor Grainy head (Grh) is necessary and sufficient for opening of epithelial enhancers, but not for their activation. Grh is shown to function as a pioneer factor, displacing nucleosomes and paving the way for other transcription factors to activate enhancers.
- Jelle Jacobs
- , Mardelle Atkins
- & Stein Aerts
-
Article |
 Resequencing a core collection of upland cotton identifies genomic variation and loci influencing fiber quality and yield
Resequencing a core collection of upland cotton identifies genomic variation and loci influencing fiber quality and yield
The authors resequence a core collection of upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) comprising 419 accessions. They analyze genomic variation and conduct a genome-wide association study for 13 fiber quality and yield traits in 12 different environments.
- Zhiying Ma
- , Shoupu He
- & Xiongming Du
-
News & Views |
 Expanding the toolbox for 3D genomics
Expanding the toolbox for 3D genomics
The ability to visualize and study the 3D folding of chromosomes in cells has been propelled forward by several major technological advances in the past two decades. Two new studies now further expand the scientific toolbox for studying chromosome conformation by providing novel methodologies for accurate mapping of genome topology and predicting the topological effects of genomic structural variation.
- Ralph Stadhouders
-
Technical Report |
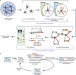 Digestion-ligation-only Hi-C is an efficient and cost-effective method for chromosome conformation capture
Digestion-ligation-only Hi-C is an efficient and cost-effective method for chromosome conformation capture
DLO Hi-C is a new method to investigate the 3D genome. It requires only two rounds of digestion and ligation and removes non-ligated DNA in a cost-effective step by purifying specific linker-ligated DNA fragments.
- Da Lin
- , Ping Hong
- & Gang Cao
-
News & Views |
 Correcting CRISPR for copy number
Correcting CRISPR for copy number
The CRISPR–Cas9 system enables global screens of gene function with high sensitivity and specificity, but off-target effects have been reported for CRISPR guide RNAs targeting genes that are amplified at high copy number. A new study describes a computational approach to correct for this copy number effect, increasing the specificity of CRIPSR screens to identify essential genes.
- John Paul Shen
- & Trey Ideker
-
Article |
 High-throughput annotation of full-length long noncoding RNAs with capture long-read sequencing
High-throughput annotation of full-length long noncoding RNAs with capture long-read sequencing
RNA Capture Long Seq (CLS) is a new method for transcript annotation that combines targeted RNA capture with long-read sequencing. CLS reannotates GENCODE lncRNAs and increases the number of validated splice junctions and transcript models for targeted loci.
- Julien Lagarde
- , Barbara Uszczynska-Ratajczak
- & Rory Johnson
-
News & Views |
 Enhancers looping to target genes
Enhancers looping to target genes
High-resolution maps of enhancer–promoter interactions in rare primary human T cell subsets and coronary artery smooth muscle cells link variants associated with autoimmune and cardiovascular diseases to target genes. This represents an important step forward for mapping genes involved in complex diseases.
- Gosia Trynka
-
Editorial |
The multidimensional nucleus
This issue highlights a range of genetic techniques and cell biological models required to begin to understand the levels of long-range regulation of gene expression as it occurs during cell differentiation. Explanations based on the specificity of covalent modifications and binding interactions intersect with evidence for conjectured mechanisms of topological loop creation and maintenance by transcription and motile protein activities.
-
Editorial |
Ancestry-inspired genomic health
A solution to screening for recessive heritable disorders and identifying genetic influences on common diseases is to be found in the history of one of the world's most populous regions. Large South Asian populations are a mosaic of smaller populations, many of which have founder effects as extreme as those in the European isolates that first inspired genetic medicine.
-
Letter |
 Condensin-mediated remodeling of the mitotic chromatin landscape in fission yeast
Condensin-mediated remodeling of the mitotic chromatin landscape in fission yeast
Frank Uhlmann and colleagues use chromosome conformation capture (Hi-C) to study mitotic chromosome condensation in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe, reporting that small chromatin domains in interphase are replaced by fewer and larger domains in mitosis. They show that condensin sets up longer-range DNA interactions that compact and individualize chromosomes while also restraining local chromatin contacts.
- Yasutaka Kakui
- , Adam Rabinowitz
- & Frank Uhlmann
-
News & Views |
 Adenine N6-methylation in diverse fungi
Adenine N6-methylation in diverse fungi
A DNA modification—methylation of cytosines and adenines—has important roles in diverse processes such as regulation of gene expression and genome stability, yet until recently adenine methylation had been considered to be only a hallmark of prokaryotes. A new study identifies abundant adenine methylation of transcriptionally active genes in early-diverging fungi that, together with recent other work, emphasizes the importance of adenine methylation in eukaryotes.
- Michael F Seidl
-
Article |
 Paused RNA polymerase II inhibits new transcriptional initiation
Paused RNA polymerase II inhibits new transcriptional initiation
Julia Zeitlinger and Wanqing Shao use ChIP-nexus to study RNA polymerase II (Pol II) promoter pausing and its relation to the formation of new initiation complexes in Drosophila cells. They find that pausing affects the initiation of new transcripts and propose that paused RNA Pol II helps to prevent new initiation between transcription bursts.
- Wanqing Shao
- & Julia Zeitlinger
-
Editorial |
The future of human genome editing
With the advent of precision genome editing, the ability to modify living organisms has proceeded with remarkable speed and breadth. Any application of this technology to the human germ line must be tightly coupled to deliberate consideration of the consequences, both scientific and social, of introducing heritable alterations to the human population. We recommend constant oversight and evaluation of human germline genome editing to balance prudence with discovery, and risk with progress.
-
Article |
 A single-copy Sleeping Beauty transposon mutagenesis screen identifies new PTEN-cooperating tumor suppressor genes
A single-copy Sleeping Beauty transposon mutagenesis screen identifies new PTEN-cooperating tumor suppressor genes
Juan Cadiñanos and colleagues perform an insertional mutagenesis screen with a single-copy inactivating Sleeping Beauty transposon to look for Pten-cooperating tumor suppressor genes in mice. They find novel candidate cancer genes, verify their clinical relevance in patient cohorts and functionally demonstrate their synergistic relationship to Pten in tumor suppression.
- Jorge de la Rosa
- , Julia Weber
- & Juan Cadiñanos
-
Article |
 Avian W and mammalian Y chromosomes convergently retained dosage-sensitive regulators
Avian W and mammalian Y chromosomes convergently retained dosage-sensitive regulators
David Page and colleagues report the sequence of the chicken W sex chromosome and compare ancestral W-linked genes across bird species. They find that the W chromosome did not acquire genes expressed exclusively in reproductive tissue, but retained genes through selection to maintain appropriate dosage levels of broadly expressed genes.
- Daniel W Bellott
- , Helen Skaletsky
- & David C Page
-
News & Views |
 The gut microbiome—an emerging complex trait
The gut microbiome—an emerging complex trait
As the first series of genetic analyses of gut microbiome composition in humans is now emerging, the results should be met with enthusiasm, but also with caution. Findings from the initial offerings demonstrate how population-scale approaches can provide deeper insights into host–microbiome interactions while at the same time illustrating that our understanding of the architecture of highly complex microbiome 'traits' is still rudimentary.
- Andrew K Benson
-
Letter |
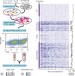 Prospective functional classification of all possible missense variants in PPARG
Prospective functional classification of all possible missense variants in PPARG
Amit Majithia and colleagues employ a pooled assay in human macrophages to assess the functional effects of all possible missense variants in PPARG. Their study shows the value of saturation mutagenesis and prospective experimental characterization to support diagnostic interpretation of newly discovered missense variants in disease-related genes.
- Amit R Majithia
- , Ben Tsuda
- & David Altshuler
-
Article |
 Meta-analysis identifies common and rare variants influencing blood pressure and overlapping with metabolic trait loci
Meta-analysis identifies common and rare variants influencing blood pressure and overlapping with metabolic trait loci
Daniel Chasman, Daniel Levy, Christopher Newton-Cheh, Georg Ehret and colleagues perform an association meta-analysis for blood pressure in ∼330,000 individuals and identify 31 new risk loci, implicating biological pathways related to vascular function and cardiometabolic traits. Their findings highlight potential therapeutic strategies for hypertension, emphasizing a link with cardiometabolic risk.
- Chunyu Liu
- , Aldi T Kraja
- & Daniel I Chasman
-
Letter |
 Inferring expressed genes by whole-genome sequencing of plasma DNA
Inferring expressed genes by whole-genome sequencing of plasma DNA
Michael Speicher and colleagues analyze plasma DNA whole-genome sequencing data from healthy donors and patients with cancer to infer nucleosome positioning on the basis of read depth coverage patterns. They use this approach to accurately predict expression of cancer driver genes from circulating tumor DNA in regions with somatic copy number gains.
- Peter Ulz
- , Gerhard G Thallinger
- & Michael R Speicher
-
Article |
 DNMT3A and TET2 compete and cooperate to repress lineage-specific transcription factors in hematopoietic stem cells
DNMT3A and TET2 compete and cooperate to repress lineage-specific transcription factors in hematopoietic stem cells
Margaret Goodell, Wei Li and colleagues use double-knockout mice for Dnmt3a and Tet2 to model leukemia development. Through epigenetic and transcriptional analyses, they show that loss of DNMT3A and TET2 upregulates lineage-specific transcription factors such as KLF1 in hematopoietic stem cells and accelerates malignancy.
- Xiaotian Zhang
- , Jianzhong Su
- & Margaret A Goodell
-
News & Views |
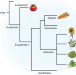 The carrot genome sequence brings colors out of the dark
The carrot genome sequence brings colors out of the dark
The genome sequence of carrot (Daucus carota L.) is the first completed for an Apiaceae species, furthering knowledge of the evolution of the important euasterid II clade. Analyzing the whole-genome sequence allowed for the identification of a gene that may regulate the accumulation of carotenoids in the root.
- Jordi Garcia-Mas
- & Manuel Rodriguez-Concepcion
-
News & Views |
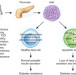 Intolerable secretion and diabetes in tolerant transgenic mice, revisited
Intolerable secretion and diabetes in tolerant transgenic mice, revisited
A new mouse model linking diabetes, insulin secretion and autoimmunity with a high-fat diet supports a shared mechanism for type 1 (T1D) and type 2 (T2D) diabetes. In this model, the protein secretion system of insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells is stressed, leading to increased beta cell apoptosis and diabetes via reduced levels of the transcription factor GLIS3, a pathogenic pathway that can be mimicked by a high-fat diet.
- John A Todd
-
Article |
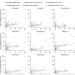 Genomic and functional analyses of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains implicate ald in D-cycloserine resistance
Genomic and functional analyses of Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains implicate ald in D-cycloserine resistance
Alexander Pym, Ashlee Earl and colleagues use the whole-genome sequences from 498 strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to identify new genotypes conferring resistance to antitubercular drugs. They find that loss-of-function mutations in ald (Rv2780), encoding L-alanine dehydrogenase, are associated with unexplained drug resistance and demonstrate that these mutations confer resistance to D-cycloserine.
- Christopher A Desjardins
- , Keira A Cohen
- & Alexander S Pym
-
Letter |
 A role for the bacterial GATC methylome in antibiotic stress survival
A role for the bacterial GATC methylome in antibiotic stress survival
James Collins and colleagues explore the role of the bacterial epigenome in antibiotic stress survival. They find that Escherichia coli survival under antibiotic pressure is strongly compromised in the absence of adenine methylation at GATC sites, suggesting that targeting adenine methylation might be a viable approach to enhance antibiotic activity.
- Nadia R Cohen
- , Christian A Ross
- & James J Collins
-
Article |
 An oncogenic MYB feedback loop drives alternate cell fates in adenoid cystic carcinoma
An oncogenic MYB feedback loop drives alternate cell fates in adenoid cystic carcinoma
Bradley Bernstein, Birgit Knoechel and colleagues identify super-enhancer translocations that drive overexpression of MYB in adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC). They find that MYB binds to the translocated enhancers and to other active enhancers that drive different regulatory programs in alternate cell lineages in ACC.
- Yotam Drier
- , Matthew J Cotton
- & Bradley E Bernstein
-
Editorial |
Where genome editing is needed
The journal endorses the principle of transparency in the production of genome-edited crops and livestock as a precondition for the registration of a breed or cultivar, with no further need for regulation or distinction of these goods from the products of traditional breeding.
-
News & Views |
 Hybridization speeds up the emergence and evolution of a new pathogen species
Hybridization speeds up the emergence and evolution of a new pathogen species
Plant pathogens can evolve new host specificities and overcome host resistances over surprisingly few generations, a process that is greatly accelerated by agricultural practices. A new study provides a striking example in which the rapid emergence of a new pathogen via introgressive hybridization mirrors the evolution of a hybrid cereal crop.
- Eva H Stukenbrock
-
Letter
| Open Access Hybridization of powdery mildew strains gives rise to pathogens on novel agricultural crop species
Hybridization of powdery mildew strains gives rise to pathogens on novel agricultural crop species
Beat Keller, Thomas Wicker and colleagues compare the genomes of 46 isolates of powdery mildew, Blumeria graminis. They find that B. graminis f. sp. triticale, a pathogen growing on triticale (a wheat × rye hybrid plant), is a hybrid of B. graminis f. sp. tritici and B. graminis f. sp. secalis, which grow on wheat and rye, respectively.
- Fabrizio Menardo
- , Coraline R Praz
- & Beat Keller
-
Editorial |
A diamond in the ruff
-
Analysis |
 Abundant contribution of short tandem repeats to gene expression variation in humans
Abundant contribution of short tandem repeats to gene expression variation in humans
Yaniv Erlich and colleagues report a genome-wide survey of the contribution of short tandem repeats (STRs) to gene expression in humans and identify 2,060 significant expression STRs (eSTRs). They find that eSTRs contribute 10–15% of the cis heritability mediated by all common variants and are associated with various clinically relevant phenotypes.
- Melissa Gymrek
- , Thomas Willems
- & Yaniv Erlich
-
Editorial |
Key mendelian variants
-
News & Views |
 Standardized phenotyping enhances Mendelian disease gene identification
Standardized phenotyping enhances Mendelian disease gene identification
Whole-exome sequencing has revolutionized the identification of genes with dominant disease-associated variants for rare clinically and genetically heterogeneous disorders, but the identification of genes with recessive disease-associated variants has been less successful. A new study now provides a framework integrating Mendelian variant filtering with statistical assessments of patients' genotypes and phenotypes, thereby catalyzing the discovery of novel mutations associated with recessive disease.
- Lisenka E L M Vissers
- & Joris A Veltman
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Analytical biochemistry
- Behavioural methods
- Bioinformatics
- Biological models
- Biophysical methods
- Cytological techniques
- Electrophysiology
- Epigenetics analysis
- Experimental organisms
- Gene delivery
- Gene expression analysis
- Genetic engineering
- Genetic techniques
- Genomic analysis
- High-throughput screening
- Imaging
- Immunological techniques
- Isolation, separation and purification
- Lab-on-a-chip
- Mass spectrometry
- Metabolomics
- Microbiology techniques
- Microscopy
- Molecular engineering
- Nanobiotechnology
- Optogenetics
- Proteomic analysis
- Sensors and probes
- Sequencing
- Software
- Optical spectroscopy
- Structure determination
