Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Semiconductor SERS enhancement enabled by oxygen incorporation
Semiconductor SERS enhancement enabled by oxygen incorporation
The application of non-metal-oxide semiconductor materials as surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) substrates is impeded by their low SERS enhancement and detection sensitivity. Here, the authors develop a general oxygen incorporation strategy to magnify these parameters.
- Zuhui Zheng
- , Shan Cong
- & Zhigang Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access A bioreducible N-oxide-based probe for photoacoustic imaging of hypoxia
A bioreducible N-oxide-based probe for photoacoustic imaging of hypoxia
Hypoxia is a hallmark of many diseases including cancer and ischemia, and detection can be invasive and of low resolution and specificity. Here the authors show a hypoxia probe that converts non-ionizing light to ultrasound, which enables the acquisition of high-resolution 3D images in deep tissue.
- Hailey J. Knox
- , Jamila Hedhli
- & Jefferson Chan
-
Article
| Open Access A rapidly-reversible absorptive and emissive vapochromic Pt(II) pincer-based chemical sensor
A rapidly-reversible absorptive and emissive vapochromic Pt(II) pincer-based chemical sensor
Solid state Pt(II)-pincer complexes exhibiting vapochromic responses show promise for chemical sensing applications, but their slow responses typically limit their utility. Here, Raithby and colleagues design a Pt(II)-pincer complex with a subsecond, highly-selective vapochromic response to water and methanol.
- M. J. Bryant
- , J. M. Skelton
- & P. R. Raithby
-
Article
| Open Access Deconvoluting interrelationships between concentrations and chemical shifts in urine provides a powerful analysis tool
Deconvoluting interrelationships between concentrations and chemical shifts in urine provides a powerful analysis tool
The NMR chemical shifts of a substance in urine strongly depend on the composition of the mixture itself, and this makes automatic assignment for quantification very difficult. Here the authors show the chemical shifts of signals and the concentration of NMR-invisible inorganic ions in urine, are predictable.
- Panteleimon G. Takis
- , Hartmut Schäfer
- & Claudio Luchinat
-
Article
| Open Access In situ detection of the protein corona in complex environments
In situ detection of the protein corona in complex environments
In situ detection of protein coronas is usually performed via optical methods, but light scattering may hamper these measurements. Here, the authors use diffusion NMR techniques to characterize protein corona formation on 19F-labeled nanoparticles in blood and other complex media.
- Monica Carril
- , Daniel Padro
- & Wolfgang J. Parak
-
Article
| Open Access Significance estimation for large scale metabolomics annotations by spectral matching
Significance estimation for large scale metabolomics annotations by spectral matching
Matching fragment spectra to reference library spectra is an important procedure for annotating small molecules in untargeted mass spectrometry based metabolomics studies. Here, the authors develop strategies to estimate false discovery rates (FDR) by empirical Bayes and target-decoy based methods which enable a user to define the scoring criteria for spectral matching.
- Kerstin Scheubert
- , Franziska Hufsky
- & Sebastian Böcker
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrathin two-dimensional porous organic nanosheets with molecular rotors for chemical sensing
Ultrathin two-dimensional porous organic nanosheets with molecular rotors for chemical sensing
Molecular rotors that fluoresce upon restriction are useful components in functional materials. Here, the authors incorporate molecular rotors into 2D porous organic nanosheets, creating sensitive and selective fluorescent sensors for volatile organic compounds and metal ions.
- Jinqiao Dong
- , Kang Zhang
- & Dan Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Mass spectrometry sequencing of long digital polymers facilitated by programmed inter-byte fragmentation
Mass spectrometry sequencing of long digital polymers facilitated by programmed inter-byte fragmentation
Digital information can be stored in monomer sequences of non-natural macromolecules, but only short chains can be read. Here the authors show long multi-byte digital polymers sequenced in a moderate resolution mass spectrometer. Full sequence coverage can be attained without pre-analysis digestion or the help from sequence databases.
- Abdelaziz Al Ouahabi
- , Jean-Arthur Amalian
- & Jean-François Lutz
-
Article
| Open Access Exact mass analysis of sulfur clusters upon encapsulation by a polyaromatic capsular matrix
Exact mass analysis of sulfur clusters upon encapsulation by a polyaromatic capsular matrix
The structures of inorganic clusters are commonly characterized by mass spectrometry (MS), but neutral sulfur clusters heavily fragment under MS conditions, preventing their exact mass determination. Here, the authors successfully perform MS on labile cyclic sulfur clusters by stabilizing them within ionic supramolecular capsules.
- Sho Matsuno
- , Masahiro Yamashina
- & Michito Yoshizawa
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmonic silver nanoshells for drug and metabolite detection
Plasmonic silver nanoshells for drug and metabolite detection
Preparation of samples for diagnosis can affect the detection of biomarkers and metabolites. Here, the authors use a silver nanoparticle plasmonics approach for the detection of biomarkers in patients as well as investigate the distribution of drugs in serum and cerebral spinal fluid.
- Lin Huang
- , Jingjing Wan
- & Kun Qian
-
Article
| Open Access Singlet oxygen-based electrosensing by molecular photosensitizers
Singlet oxygen-based electrosensing by molecular photosensitizers
Application of enzyme-based sensors is usually affected by costs, enzyme stability and immobilization and use of additional chemicals. Here, the authors show a cost-effective and robust photoelectrochemical detection system that can mimic enzymatic sensors using only air and light.
- Stanislav Trashin
- , Vanoushe Rahemi
- & Karolien De Wael
-
Article
| Open Access Thermal annihilation of photo-induced radicals following dynamic nuclear polarization to produce transportable frozen hyperpolarized 13C-substrates
Thermal annihilation of photo-induced radicals following dynamic nuclear polarization to produce transportable frozen hyperpolarized 13C-substrates
Hyperpolarized molecules provide unique contrast for MRI but due to their short relaxation time need to be prepared shortly before injection. Here the authors report a method for eliminating the main source of relaxation and producing frozen polarized substances that can be stored and transported.
- Andrea Capozzi
- , Tian Cheng
- & Arnaud Comment
-
Article
| Open Access Beat frequency quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy for fast and calibration-free continuous trace-gas monitoring
Beat frequency quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy for fast and calibration-free continuous trace-gas monitoring
Quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy is a sensitive gas detection method whereby radiation-induced sound waves from gas absorption are detected. Here, Wuet al. use the beat frequency between a modulated laser and a tuning fork resonance to increase sensitivity and avoid frequent calibrations.
- Hongpeng Wu
- , Lei Dong
- & Frank K. Tittel
-
Article
| Open Access Antibody-powered nucleic acid release using a DNA-based nanomachine
Antibody-powered nucleic acid release using a DNA-based nanomachine
Responsive molecular machines can perform specific tasks triggered by environmental or chemical stimuli. Here, the authors show that antibodies can be used as inputs to modulate the binding of a molecular cargo to a designed DNA-based nanomachine, with potential applications in diagnostics and drug delivery.
- Simona Ranallo
- , Carl Prévost-Tremblay
- & Francesco Ricci
-
Article
| Open Access Facile access to potent antiviral quinazoline heterocycles with fluorescence properties via merging metal-free domino reactions
Facile access to potent antiviral quinazoline heterocycles with fluorescence properties via merging metal-free domino reactions
Heterocycles are ubiquitous in bioactive compounds and routes to different substitution patterns are important to access the full substrate space. Here the authors report a route to 4,5,7,8-substituted antiviral fluorescent quinazolines, to allow cellular uptake visualization without external marker.
- Felix E. Held
- , Anton A. Guryev
- & Svetlana B. Tsogoeva
-
Article
| Open Access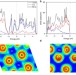 A metallic molybdenum dioxide with high stability for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy
A metallic molybdenum dioxide with high stability for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Semiconducting materials are potential SERS substrates as alternatives to noble metals, but often suffer from poor stabilities and sensitivities. Here, the authors use molybdenum dioxide as a SERS material, showing high enhancement factors and stability to oxidation even at high temperatures.
- Qiqi Zhang
- , Xinshi Li
- & Guangcheng Xi
-
Article
| Open Access Naked d-orbital in a centrochiral Ni(II) complex as a catalyst for asymmetric [3+2] cycloaddition
Naked d-orbital in a centrochiral Ni(II) complex as a catalyst for asymmetric [3+2] cycloaddition
Understanding the interplay between electronic structure and performance and how it relates to mechanism is important for catalysis. Here the authors report an asymmetric [3+2] cycloaddition and show the Ni(II) catalyst possesses a weakly bound acetate ligand, leaving thedz2orbital partially vacant.
- Yoshihiro Sohtome
- , Genta Nakamura
- & Mikiko Sodeoka
-
Article
| Open Access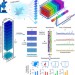 Quantitative volumetric Raman imaging of three dimensional cell cultures
Quantitative volumetric Raman imaging of three dimensional cell cultures
Advances in chemical imaging capability can add to our understanding of complex cellular systems. Here the authors develop a framework for label-free quantitative volumetric Raman spectroscopic imaging and use it to visualize and quantify biomolecules in various 3D cellular systems.
- Charalambos Kallepitis
- , Mads S. Bergholt
- & Molly M. Stevens
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time reliable determination of binding kinetics of DNA hybridization using a multi-channel graphene biosensor
Real-time reliable determination of binding kinetics of DNA hybridization using a multi-channel graphene biosensor
Monitoring DNA binding and single-base mismatches accurately in real time is difficult, especially for miniaturized devices. Here the authors report a graphene field-effect transistor array capable of reliably measuring DNA hybridization kinetics and affinity at the picomolar level.
- Shicai Xu
- , Jian Zhan
- & Yaoqi Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Proposal for dark exciton based chemical sensors
Proposal for dark exciton based chemical sensors
Two-dimensional materials have shown great promise as efficient chemical sensors. Here, the authors present a sensing mechanism to allow the detection of molecules based on dark excitons in atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides.
- Maja Feierabend
- , Gunnar Berghäuser
- & Ermin Malic
-
Article
| Open Access A microRNA-initiated DNAzyme motor operating in living cells
A microRNA-initiated DNAzyme motor operating in living cells
Synthetic DNA nanomachines have been designed to perform a variety of tasksin vitro. Here, the authors build a nanomotor system that integrates a DNAzyme and DNA track on a gold nanoparticle, to facilitate cellular uptake, and apply it as a real-time miRNA imaging tool in living cells.
- Hanyong Peng
- , Xing-Fang Li
- & X. Chris Le
-
Article
| Open Access Mass spectrometric monitoring of interfacial photoelectron transfer and imaging of active crystalline facets of semiconductors
Mass spectrometric monitoring of interfacial photoelectron transfer and imaging of active crystalline facets of semiconductors
Monitoring interfacial electron transfer in photocatalytic systems is fundamentally important but experimentally challenging. Here the authors use mass spectrometry to detect and monitor intermediates formed through photoelectron transfer and to image active crystalline facets of semiconductor photocatalysts.
- Hongying Zhong
- , Juan Zhang
- & Zhiwei Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access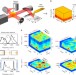 Hyperspectral infrared nanoimaging of organic samples based on Fourier transform infrared nanospectroscopy
Hyperspectral infrared nanoimaging of organic samples based on Fourier transform infrared nanospectroscopy
In hyperspectral imaging a broadband spectrum is recorded at each pixel, which creates information-rich images. Here, the authors combine this concept with Fourier transform infrared nanospectroscopy to achieve 5,000-pixel, nanoscale-resolution images at wavelengths between 5 and 10 micrometres.
- Iban Amenabar
- , Simon Poly
- & Rainer Hillenbrand
-
Article
| Open Access Phase transformation mechanism in lithium manganese nickel oxide revealed by single-crystal hard X-ray microscopy
Phase transformation mechanism in lithium manganese nickel oxide revealed by single-crystal hard X-ray microscopy
As an intercalation electrode material for lithium ion batteries, spinel LixMn1.5Ni0.5O4possesses a metastable nature during the electrochemical operation. Here the authors reveal the phase transformation mechanism by using single-crystal hard X-ray microscopy to detect the local phase distribution.
- Saravanan Kuppan
- , Yahong Xu
- & Guoying Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Transportable hyperpolarized metabolites
Transportable hyperpolarized metabolites
MRI imaging can be significantly enhanced by injecting highly magnetized chemical agents, but the short magnetization lifetime requires processing at the point of use. Here, the authors demonstrate a method that could extend the lifetime from seconds to hours, enabling remote preparation.
- Xiao Ji
- , Aurélien Bornet
- & Sami Jannin
-
Article
| Open Access Nonlinear detection of secondary isotopic chemical shifts in NMR through spin noise
Nonlinear detection of secondary isotopic chemical shifts in NMR through spin noise
Nuclear spin noise allows passive monitoring of magnetization using the sole NMR detection circuit. Here, the authors report spectroscopic signatures of low abundance molecules and of weak magnetic field gradients which are nonlinearly amplified by cooled-coil probes and large overlapping signals.
- Maria Theresia Pöschko
- , Victor V. Rodin
- & Hervé Desvaux
-
Article
| Open Access Electronic single-molecule identification of carbohydrate isomers by recognition tunnelling
Electronic single-molecule identification of carbohydrate isomers by recognition tunnelling
Carbohydrates are common biological molecules, but display huge stereochemical complexity that often cannot be elucidated by mass spectrometry. Here the authors show that recognition tunnelling can distinguish individual stereoisomers, utilizing picomole quantities of analytes.
- JongOne Im
- , Sovan Biswas
- & Peiming Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Brønsted acid sites based on penta-coordinated aluminum species
Brønsted acid sites based on penta-coordinated aluminum species
Until now, it has been believed that Brønsted acid sites in amorphous silica-alumina are formed from only tetra-coordinated (AlIV) sites. Here, the authors use 27Al-{1H} correlation NMR experiments to identify a new AlV-based Brønsted acid site, with implications for increasing the acidity of solid acid catalysts.
- Zichun Wang
- , Yijiao Jiang
- & Jun Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Carbene footprinting accurately maps binding sites in protein–ligand and protein–protein interactions
Carbene footprinting accurately maps binding sites in protein–ligand and protein–protein interactions
Mapping protein-ligand interactions is fundamental to advance the understanding of cellular processes and to develop drug discovery strategies. Here, the authors present a photo-activated probe that allows highly efficient labelling and identification of protein binding sites using mass spectrometry.
- Lucio Manzi
- , Andrew S. Barrow
- & Neil J. Oldham
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical zwitterionic modification of a SERS substrate enables real-time drug monitoring in blood plasma
Hierarchical zwitterionic modification of a SERS substrate enables real-time drug monitoring in blood plasma
Despite the high sensitivity of SERS analysis, non-specific binding of proteins can impact the effectiveness in biologically important media such as blood. Here the authors report a SERS substrate modified to prevent protein fouling and demonstrate drug detection in undiluted plasma.
- Fang Sun
- , Hsiang-Chieh Hung
- & Qiuming Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Mass and stiffness spectrometry of nanoparticles and whole intact bacteria by multimode nanomechanical resonators
Mass and stiffness spectrometry of nanoparticles and whole intact bacteria by multimode nanomechanical resonators
Mass spectrometry can accurately identify species by molecular mass, but measuring large species can be difficult. Here the authors show that nanomechanical resonators can identify both the mass and stiffness of larger analytes, demonstrating it for gold nanoparticles and E. Colibacteria.
- O. Malvar
- , J. J. Ruz
- & J. Tamayo
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-mechanism-based engineering of chemical regulators targeting distinct pathological factors in Alzheimer’s disease
Structure-mechanism-based engineering of chemical regulators targeting distinct pathological factors in Alzheimer’s disease
To advance our understanding of pathological features associated with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), chemical tools with distinct specificity towards AD targets would be valuable. Here the authors used a structure-mechanism-based design strategy to obtain small molecules as chemical regulators for distinct pathological factors linked to AD pathology.
- Michael W. Beck
- , Jeffrey S. Derrick
- & Mi Hee Lim
-
Article
| Open Access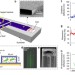 Microfluidic cantilever detects bacteria and measures their susceptibility to antibiotics in small confined volumes
Microfluidic cantilever detects bacteria and measures their susceptibility to antibiotics in small confined volumes
Analysis of bacteria and their response to antibiotics in real time is challenging. Here the authors report a microcantilever based system that can detect and discriminate between bacteria species and, due to the ability to discriminate between alive and dead samples, measure response to antibiotics.
- Hashem Etayash
- , M. F. Khan
- & Thomas Thundat
-
Article
| Open Access Chemoselective synthesis and analysis of naturally occurring phosphorylated cysteine peptides
Chemoselective synthesis and analysis of naturally occurring phosphorylated cysteine peptides
Protein phosphorylation mediates signalling and other important cellular processes, but the specific effect of cysteine phosphorylation is unclear. Here, the authors present a chemical strategy to selectively phosphorylate cysteine residues and a mass spectrometry approach to detect and characterize endogenous pCys sites.
- Jordi Bertran-Vicente
- , Martin Penkert
- & Christian P. R. Hackenberger
-
Article
| Open Access Simple direct formation of self-assembled N-heterocyclic carbene monolayers on gold and their application in biosensing
Simple direct formation of self-assembled N-heterocyclic carbene monolayers on gold and their application in biosensing
Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) have shown tremendous number of applications but can suffer from low stability. Here, the authors report air and bench stable carbene precursors allowing facile SAM formation, and furthermore demonstrate an application in biosensing
- Cathleen M. Crudden
- , J. Hugh Horton
- & Akiko Yagi
-
Article
| Open Access Chirality imprinting and direct asymmetric reaction screening using a stereodynamic Brønsted/Lewis acid receptor
Chirality imprinting and direct asymmetric reaction screening using a stereodynamic Brønsted/Lewis acid receptor
Determining results of asymmetric reactions can take long periods of time and consume large amounts of organic solvents during work-up and analysis. Here, the authors report a bifunctional organic probe that can bind to chiral hydroxyacids, and provide yield, enantiomeric excess and absolute configuration even with crude mixtures.
- Keith W. Bentley
- , Daysi Proano
- & Christian Wolf
-
Article
| Open Access Mass spectrometry locates local and allosteric conformational changes that occur on cofactor binding
Mass spectrometry locates local and allosteric conformational changes that occur on cofactor binding
The decarboxylate enzyme Fdc1 requires a prenylated flavin mononucleotide co-factor for activity. Here, the authors use a variety of mass spectrometric techniques to observe the structural changes in this protein in response to co-factor binding.
- Rebecca Beveridge
- , Lukasz G. Migas
- & Perdita E. Barran
-
Article
| Open Access Photo-induced enhanced Raman spectroscopy for universal ultra-trace detection of explosives, pollutants and biomolecules
Photo-induced enhanced Raman spectroscopy for universal ultra-trace detection of explosives, pollutants and biomolecules
Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy is a sensitive technique capable of detecting single molecules via their vibrational fingerprints. Here, the authors demonstrate improved sensitivity with photo-induced enhanced Raman spectroscopy applied to trace-level detection of explosives and other analytes.
- Sultan Ben-Jaber
- , William J. Peveler
- & Ivan P. Parkin
-
Article
| Open Access Bottom-up synthesis of chiral covalent organic frameworks and their bound capillaries for chiral separation
Bottom-up synthesis of chiral covalent organic frameworks and their bound capillaries for chiral separation
Porous materials can be used in columns for gas separation applications. Here, Yan and co-workers from a bottom-up method have produced chiral covalent organic frameworks and from an in situ strategy formed capillary columns for chiral gas chromatography.
- Hai-Long Qian
- , Cheng-Xiong Yang
- & Xiu-Ping Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Gelation process visualized by aggregation-induced emission fluorogens
Gelation process visualized by aggregation-induced emission fluorogens
Chitosan hydrogel materials have unique properties, but understanding the gelation process these materials undergo has been problematic. Here, Wang and co-workers have visualised the entire gelation process of a chitosan LiOH-urea aqueous system by aggregation induced emission fluorescent imaging.
- Zhengke Wang
- , Jingyi Nie
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Programming a topologically constrained DNA nanostructure into a sensor
Programming a topologically constrained DNA nanostructure into a sensor
DNA nanostructures with interlocked topologies will tend to display different behaviour to the linear counterparts. Here, the authors show a DNA catenane that is inactive for rolling circle amplification but is activated upon cleavage of one ring, and exploit this for the development of a biosensing system.
- Meng Liu
- , Qiang Zhang
- & Yingfu Li
-
Article
| Open Access Development of background-free tame fluorescent probes for intracellular live cell imaging
Development of background-free tame fluorescent probes for intracellular live cell imaging
The success of a fluorescent dye as a molecular probe to monitor the intracellular activity of biomolecules depends on its physicochemical characteristics. Here, the authors use a predictive model to identify key features that allow them to design cell permeable, background-free fluorescent probes.
- Samira Husen Alamudi
- , Rudrakanta Satapathy
- & Young-Tae Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Operando NMR spectroscopic analysis of proton transfer in heterogeneous photocatalytic reactions
Operando NMR spectroscopic analysis of proton transfer in heterogeneous photocatalytic reactions
Identifying proton transfer processes in catalytic reactions is a technically challenging task. Here, the authors employ operando nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to study the reaction mechanism and intermediates of the photocatalytic hydrogen evolution, and to identify the proton sources.
- Xue Lu Wang
- , Wenqing Liu
- & Hua Gui Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Structural identification of electron transfer dissociation products in mass spectrometry using infrared ion spectroscopy
Structural identification of electron transfer dissociation products in mass spectrometry using infrared ion spectroscopy
Mass spectrometry is a leading method used for sequencing peptides and proteins by fragmentation followed by analysis of the sequence fragments. Here, the authors use infrared spectroscopy to characterize the structures of peptide fragments formed during electron transfer dissociation.
- Jonathan Martens
- , Josipa Grzetic
- & Jos Oomens
-
Article
| Open Access Fluorescence microscopy as an alternative to electron microscopy for microscale dispersion evaluation of organic–inorganic composites
Fluorescence microscopy as an alternative to electron microscopy for microscale dispersion evaluation of organic–inorganic composites
Imaging of inorganic dispersions in organic-inorganic composites is typically performed using electron microscopy. Here, the authors show that surfactants with attached aggregation-induced emission fluorophores allow simple fluorescence imaging of the spatial distribution of the inorganic filler dispersion.
- Weijiang Guan
- , Si Wang
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access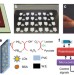 A wearable chemical–electrophysiological hybrid biosensing system for real-time health and fitness monitoring
A wearable chemical–electrophysiological hybrid biosensing system for real-time health and fitness monitoring
Wearable sensors can provide continuous, convenient feedback for users but typically focus on a small number of physiological parameters. Here, the authors report a skin-worn sensing system that combines a biosensor for lactate detection with an electrocardiogram in one patch, with applications for exercise monitoring.
- Somayeh Imani
- , Amay J. Bandodkar
- & Patrick P. Mercier
-
Article
| Open Access Message in a molecule
Message in a molecule
Although historically common chemicals were frequently used as secret inks, the ease of readout could not prevent unauthorized reading. Here, the authors report a multi-analyte sensor that can conceal and encrypt messages by responding to simple chemicals, demonstrating a chemical means to secure communication.
- Tanmay Sarkar
- , Karuthapandi Selvakumar
- & David Margulies
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding silicate hydration from quantitative analyses of hydrating tricalcium silicates
Understanding silicate hydration from quantitative analyses of hydrating tricalcium silicates
Despite its importance to the cement industry, tricalcium silicate hydration, with its sequence of induction, acceleration and deceleration steps, still hosts many open questions. Here, 29Si nuclear magnetic resonance provides new information on the silicate polymerization mechanism and its kinetics.
- Elizaveta Pustovgar
- , Rahul P. Sangodkar
- & Jean-Baptiste d’Espinose de Lacaillerie
-
Article
| Open Access Spacer-free BODIPY fluorogens in antimicrobial peptides for direct imaging of fungal infection in human tissue
Spacer-free BODIPY fluorogens in antimicrobial peptides for direct imaging of fungal infection in human tissue
Functionalizing antimicrobial peptides with fluorescent groups is a useful strategy for imaging infection, but the tag can alter the performance of the probe. Here, the authors report a spacer-free method to directly functionalise an amino acid with a fluorogenic group and prepare peptide-based imaging agents for fungal infection.
- Lorena Mendive-Tapia
- , Can Zhao
- & Marc Vendrell

 Atmospheric pressure mass spectrometric imaging of live hippocampal tissue slices with subcellular spatial resolution
Atmospheric pressure mass spectrometric imaging of live hippocampal tissue slices with subcellular spatial resolution