Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Ratiometric fluorescent sensing of pyrophosphate with sp³-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes
Ratiometric fluorescent sensing of pyrophosphate with sp³-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes
Inorganic pyrophosphate is a key molecule in many biological processes. Here, the authors develop an optical sensor that enables its ratiometric detection in the near infrared with functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes.
- Simon Settele
- , C. Alexander Schrage
- & Jana Zaumseil
-
Article
| Open Access Two-photon fluorescence imaging and specifically biosensing of norepinephrine on a 100-ms timescale
Two-photon fluorescence imaging and specifically biosensing of norepinephrine on a 100-ms timescale
Norepinephrine (NE) is a key neurotransmitter in the central nervous system of organisms however specifically tracking the transient NE dynamics with high spatiotemporal resolution in living systems remains a great challenge. Herein, the authors developed a small molecular fluorescent probe that can precisely anchor on neuronal cytomembranes and specifically respond to NE on a 100-ms timescale.
- Leiwen Mao
- , Yujie Han
- & Yang Tian
-
Article
| Open Access 1,2,4,5-Tetrazine-tethered probes for fluorogenically imaging superoxide in live cells with ultrahigh specificity
1,2,4,5-Tetrazine-tethered probes for fluorogenically imaging superoxide in live cells with ultrahigh specificity
Specific detection of cellular superoxide is challenging. Here, the authors designed 1,2,4,5-tetrazine based fluorogenic probes for specific and sensitive imaging of superoxide, and applied them in high throughput screening of modulators of oxidative stress.
- Xuefeng Jiang
- , Min Li
- & Xin Li
-
Article
| Open Access A supramolecular cucurbit[8]uril-based rotaxane chemosensor for the optical tryptophan detection in human serum and urine
A supramolecular cucurbit[8]uril-based rotaxane chemosensor for the optical tryptophan detection in human serum and urine
Sensing small biomolecules in biofluids using host-guest chemosensors remains challenging, in part due to the impact of interfering components. Here, the authors develop a dual-macrocyclic rotaxane for tryptophan detection which can function in biofluids such as human serum and urine.
- Joana Krämer
- , Laura M. Grimm
- & Frank Biedermann
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing inflammation with an M1 macrophage selective probe via GLUT1 as the gating target
Visualizing inflammation with an M1 macrophage selective probe via GLUT1 as the gating target
Studying the specific roles of macrophage subsets has been hampered by a lack of subset-specific probes. Here the authors report an M1 selective fluorescent probe named CDr17, and demonstrate the suitability of this probe for tracking M1 macrophages in vivo.
- Heewon Cho
- , Haw-Young Kwon
- & Young-Tae Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Reaction-based fluorogenic probes for detecting protein cysteine oxidation in living cells
Reaction-based fluorogenic probes for detecting protein cysteine oxidation in living cells
Fluorogenic detection of H2O2 in cells is established, but equivalent tools to monitor its cellular targets remain in their infancy. Here authors develop fluorogenic probes for detecting cysteine sulfenic acid, a redox modification inextricably linked to H2O2 signalling and oxidative stress.
- Renan B. Ferreira
- , Ling Fu
- & Kate S. Carroll
-
Article
| Open Access Bioorthogonally activatable cyanine dye with torsion-induced disaggregation for in vivo tumor imaging
Bioorthogonally activatable cyanine dye with torsion-induced disaggregation for in vivo tumor imaging
Expanding the responsive dyes repertoire is currently a developing field in biorthogonal chemistry. In this article, the authors develop fluorophores that turn on their near-infrared fluorescence upon biorthogonal reaction based on a “torsion-induced disaggregation” approach, allowing for sensitive in vivo imaging of tumors.
- Xianghan Zhang
- , Jingkai Gao
- & Zhongliang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access A synergistic strategy to develop photostable and bright dyes with long Stokes shift for nanoscopy
A synergistic strategy to develop photostable and bright dyes with long Stokes shift for nanoscopy
Super-resolution microscopy is a powerful tool for cellular studies but requires bright and stable fluorescent probes. Here, the authors report on a strategy to introduce quinoxaline motifs to conventional probes to make them brighter, more photostable, larger Stokes shift, and demonstrate the probes for biosensing applications.
- Gangwei Jiang
- , Tian-Bing Ren
- & Lin Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access Extra kinetic dimensions for label discrimination
Extra kinetic dimensions for label discrimination
Label discrimination is challenging in fluorescence microscopy due to broad spectra and narrow lifetime distribution. Here, the authors introduce extra kinetic dimensions by illuminating reversibly photoswitchable fluorophores with different intensities, and discriminate 20 spectrally similar fluorophores.
- Raja Chouket
- , Agnès Pellissier-Tanon
- & Ludovic Jullien
-
Article
| Open Access A prostate-specific membrane antigen activated molecular rotor for real-time fluorescence imaging
A prostate-specific membrane antigen activated molecular rotor for real-time fluorescence imaging
Detection of the tumour boundary in prostate cancer is required for surgery. Here the authors present a fluorescent molecular rotor probe to target a prostate cancer marker, prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA), which they use in a xenograft mouse model to show it can be used for in vivo imaging.
- Jingming Zhang
- , Anastasia Rakhimbekova
- & Xing Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Fluorescence umpolung enables light-up sensing of N-acetyltransferases and nerve agents
Fluorescence umpolung enables light-up sensing of N-acetyltransferases and nerve agents
The electron-withdrawing target (EWT)-induced fluorescence quenching is an unsolved issue in intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) fluorophores that limits their applicability. Here, the authors report a simple and generalizable strategy to reverse the EWT-induced quenching mode into light-up mode, by introducing an indazole building block between the π-bridge and the donor in the ICT scaffold.
- Chenxu Yan
- , Zhiqian Guo
- & Wei-Hong Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Visualising G-quadruplex DNA dynamics in live cells by fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy
Visualising G-quadruplex DNA dynamics in live cells by fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy
Direct observation of G-quadruplexes (G4s) in live cells is challenging. Here the authors report a method to identify G4s within the nuclei of live and fixed cells using a fluorescent probe combined with fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy.
- Peter A. Summers
- , Benjamin W. Lewis
- & Ramon Vilar
-
Article
| Open Access Simultaneous Zn2+ tracking in multiple organelles using super-resolution morphology-correlated organelle identification in living cells
Simultaneous Zn2+ tracking in multiple organelles using super-resolution morphology-correlated organelle identification in living cells
Subcellular Zn2+ compartmentalisation is essential for cell biology. Here the authors make a turn-on fluorescent Zn2+ probe that localises to multiple organelles, and correlate its location using organelle morphology derived from structured illumination microscopy.
- Hongbao Fang
- , Shanshan Geng
- & Jiajie Diao
-
Article
| Open Access Upconversion NIR-II fluorophores for mitochondria-targeted cancer imaging and photothermal therapy
Upconversion NIR-II fluorophores for mitochondria-targeted cancer imaging and photothermal therapy
Currently available mitochondria-targeted fluorescent dyes emit only one color in the visible or NIR-I and their applications are limited. Here, the authors develop upconversion mitochondria-targeted NIR-II fluorophores for synchronous upconversion-mitochondria-targeted cell imaging, in vivo NIR-II osteosarcoma imaging and photothermal efficiency
- Hui Zhou
- , Xiaodong Zeng
- & Yuling Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Remote near infrared identification of pathogens with multiplexed nanosensors
Remote near infrared identification of pathogens with multiplexed nanosensors
Fast and specific detection of pathogenic bacteria is needed to combat infections. Here the authors generate an array of near-infrared biosensors based on carbon nanotubes to detect released metabolites and virulence factors and use them to distinguish pathogens such as S. aureus and P. aeruginosa.
- Robert Nißler
- , Oliver Bader
- & Sebastian Kruss
-
Article
| Open Access NIR-II bioluminescence for in vivo high contrast imaging and in situ ATP-mediated metastases tracing
NIR-II bioluminescence for in vivo high contrast imaging and in situ ATP-mediated metastases tracing
Conventional bioluminescence imaging usually operates in the visible region and its performance is limited by strong tissue absorption and scattering. Here, the authors present bioluminescence probes (BPs) with emission in the second near infrared (NIR-II) region, and show the NIR-II-BPs could sensitively recognize tumor metastasis with a high tumor-to-normal tissue ratio.
- Lingfei Lu
- , Benhao Li
- & Fan Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access A fluorogenic cyclic peptide for imaging and quantification of drug-induced apoptosis
A fluorogenic cyclic peptide for imaging and quantification of drug-induced apoptosis
Programmed cell death or apoptosis is an essential biological process that is impaired in some diseases and can be used to assess the effectiveness of drugs. Here the authors design Apo-15 as a fluorogenic peptide for the detection and real-time imaging of apoptotic cells.
- Nicole D. Barth
- , Ramon Subiros-Funosas
- & Marc Vendrell
-
Article
| Open Access Organic NIR-II molecule with long blood half-life for in vivo dynamic vascular imaging
Organic NIR-II molecule with long blood half-life for in vivo dynamic vascular imaging
Optical bioimaging in the second near-infrared (NIR-II, 1000–1700 nm) window exhibits abundant advantages. Here the authors report an organic NIR-II molecule with long blood circulation half-life time for continuous real-time monitoring of dynamic vascular processes.
- Benhao Li
- , Mengyao Zhao
- & Fan Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Decorating bacteria with self-assembled synthetic receptors
Decorating bacteria with self-assembled synthetic receptors
Cell surface proteins mediate the interactions between cells and their extracellular environment. Here the authors design synthetic biomemetic receptor-like sensors that facilitate programmable interactions between bacteria and their target.
- Naama Lahav-Mankovski
- , Pragati Kishore Prasad
- & David Margulies
-
Article
| Open Access De novo strategy with engineering anti-Kasha/Kasha fluorophores enables reliable ratiometric quantification of biomolecules
De novo strategy with engineering anti-Kasha/Kasha fluorophores enables reliable ratiometric quantification of biomolecules
Fluorescent probes are used in a number of fields but suffer from a lack of quantifiable results due to environmental effects. Here, the authors report on a dual-emission probe which can be used to detect the amount of probe present and the emission from detection applications to allow for quantification.
- Limin Shi
- , Chenxu Yan
- & Wei-Hong Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Chiral recognition and enantiomer excess determination based on emission wavelength change of AIEgen rotor
Chiral recognition and enantiomer excess determination based on emission wavelength change of AIEgen rotor
Artificial receptors for chiral recognition are important in enantiomer excess analysis but current artificial detectors are based on fluorescence intensity changes only. Here the authors propose a different detection mechanism based on change of the fluorescence emission wavelength of an AIEgen rotor.
- Ming Hu
- , Ying-Xue Yuan
- & Yan-Song Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Simultaneous multi-signal quantification for highly precise serodiagnosis utilizing a rationally constructed platform
Simultaneous multi-signal quantification for highly precise serodiagnosis utilizing a rationally constructed platform
Single channel detection methods often suffer from false positives when analysing biological samples. Here, the authors report on the development of a three-channel detection device for measuring hydrogen sulphide in serum and demonstrate application in an in vivo model.
- Yuxin Liu
- , Zheng Wei
- & Zhanfang Ma
-
Article
| Open Access A generic approach towards afterglow luminescent nanoparticles for ultrasensitive in vivo imaging
A generic approach towards afterglow luminescent nanoparticles for ultrasensitive in vivo imaging
Afterglow luminescence is used to reduce background noise and increase sensitivity; however, biocompatible afterglow materials are limited. Here, the authors report on an approach to turn standard optical agents into afterglow nanoparticles and demonstrate the application in tumour imagining in vivo.
- Yuyan Jiang
- , Jiaguo Huang
- & Kanyi Pu
-
Article
| Open Access Small molecule electro-optical binding assay using nanopores
Small molecule electro-optical binding assay using nanopores
Nanopore detection of small molecules can be improved using molecular carriers, but separating a small analyte from the carrier signal can be challenging. Here the authors address this challenge using simultaneous electrical and optical readout in nanopore sensing to detect small molecules and quantify binding affinities.
- Shenglin Cai
- , Jasmine Y. Y. Sze
- & Joshua B. Edel
-
Article
| Open Access Anti-quenching NIR-II molecular fluorophores for in vivo high-contrast imaging and pH sensing
Anti-quenching NIR-II molecular fluorophores for in vivo high-contrast imaging and pH sensing
Fluorophores operating in the second near-infrared window suffer from solvatochromism-caused fluorescence quenching in biological aqueous solution. Here, the authors synthesized a series of pH-responsive pentamethine cyanine fluorophores that afford stable absorption/emission beyond 1000 nm.
- Shangfeng Wang
- , Yong Fan
- & Fan Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Design strategy for serine hydroxymethyltransferase probes based on retro-aldol-type reaction
Design strategy for serine hydroxymethyltransferase probes based on retro-aldol-type reaction
The enzyme serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) has been implicated in several diseases, however is hard to investigate. Here, the authors used a design strategy based on the retro-aldol-type reaction catalyzed by SHMT to develop SHMT-responsive fluorescence and 19F NMR molecular probes.
- Hiroshi Nonaka
- , Yuki Nakanishi
- & Shinsuke Sando
-
Article
| Open Access Highly-sensitive optical organic vapor sensor through polymeric swelling induced variation of fluorescent intensity
Highly-sensitive optical organic vapor sensor through polymeric swelling induced variation of fluorescent intensity
Traditional optical organic vapor sensors with solvatochromic shift mechanisms have lower sensitivity due to weak intermolecular interactions. Here, the authors report a general strategy to prepare a higher sensitivity optical organic vapor sensor through polymeric swelling-induced variation of fluorescent intensity.
- Xiangyu Jiang
- , Hanfei Gao
- & Lei Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Manipulating and visualizing the dynamic aggregation-induced emission within a confined quartz nanopore
Manipulating and visualizing the dynamic aggregation-induced emission within a confined quartz nanopore
The difficulty in recovering the aggregation-induced emission fluorogens (AIEgens) to the initial dispersed state upon illuminating has limited their applications. Here, the authors employ the confined space in the quartz nanopore to achieve a nanopore-size dependent restriction of AIEgens.
- Yi-Lun Ying
- , Yuan-Jie Li
- & He Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Non-contact identification and differentiation of illicit drugs using fluorescent films
Non-contact identification and differentiation of illicit drugs using fluorescent films
Sensitive and rapid identification of illicit drugs in a non-contact mode remains a challenge. Here, the authors report three film-based fluorescent sensors showing remarkable sensitivity, selectivity and response speed to six widely abused illicit drugs in vapor phase.
- Ke Liu
- , Congdi Shang
- & Yu Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasensitive reversible chromophore reaction of BODIPY functions as high ratio double turn on probe
Ultrasensitive reversible chromophore reaction of BODIPY functions as high ratio double turn on probe
BODIPY dyes, though widely explored, have not been pursued as chromophore reaction based chemical probes. Here, the authors synthesize a meso-naked BODIPY core flanked with two electron-withdrawing groups, which undergoes a reversible change in conjugated structure in the presence of base and functions as a dual signal and ultrahigh turn-on ratio chemical probe.
- Dehui Hu
- , Tao Zhang
- & Guoqiang Yang
-
Article
| Open Access A bioreducible N-oxide-based probe for photoacoustic imaging of hypoxia
A bioreducible N-oxide-based probe for photoacoustic imaging of hypoxia
Hypoxia is a hallmark of many diseases including cancer and ischemia, and detection can be invasive and of low resolution and specificity. Here the authors show a hypoxia probe that converts non-ionizing light to ultrasound, which enables the acquisition of high-resolution 3D images in deep tissue.
- Hailey J. Knox
- , Jamila Hedhli
- & Jefferson Chan
-
Article
| Open Access Facile access to potent antiviral quinazoline heterocycles with fluorescence properties via merging metal-free domino reactions
Facile access to potent antiviral quinazoline heterocycles with fluorescence properties via merging metal-free domino reactions
Heterocycles are ubiquitous in bioactive compounds and routes to different substitution patterns are important to access the full substrate space. Here the authors report a route to 4,5,7,8-substituted antiviral fluorescent quinazolines, to allow cellular uptake visualization without external marker.
- Felix E. Held
- , Anton A. Guryev
- & Svetlana B. Tsogoeva
-
Article
| Open Access Development of background-free tame fluorescent probes for intracellular live cell imaging
Development of background-free tame fluorescent probes for intracellular live cell imaging
The success of a fluorescent dye as a molecular probe to monitor the intracellular activity of biomolecules depends on its physicochemical characteristics. Here, the authors use a predictive model to identify key features that allow them to design cell permeable, background-free fluorescent probes.
- Samira Husen Alamudi
- , Rudrakanta Satapathy
- & Young-Tae Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Spacer-free BODIPY fluorogens in antimicrobial peptides for direct imaging of fungal infection in human tissue
Spacer-free BODIPY fluorogens in antimicrobial peptides for direct imaging of fungal infection in human tissue
Functionalizing antimicrobial peptides with fluorescent groups is a useful strategy for imaging infection, but the tag can alter the performance of the probe. Here, the authors report a spacer-free method to directly functionalise an amino acid with a fluorogenic group and prepare peptide-based imaging agents for fungal infection.
- Lorena Mendive-Tapia
- , Can Zhao
- & Marc Vendrell
-
Article
| Open Access Lysosome triggered near-infrared fluorescence imaging of cellular trafficking processes in real time
Lysosome triggered near-infrared fluorescence imaging of cellular trafficking processes in real time
Real time cellular fluorescence imaging requires a probe that displays high degrees of localisation, low toxicity and good photostability. Here, the authors report a near infrared fluorophore that displays pH-sensitive fluorescence based on phenol/phenolate interconversion, showing real time imaging of cellular processes.
- Marco Grossi
- , Marina Morgunova
- & Donal F. O’Shea
-
Article
| Open Access Brightness-equalized quantum dots
Brightness-equalized quantum dots
Quantum dots with different size emit light at different wavelengths but also different brightness, which complicates analysis of fluorescence images. Here, the authors synthesize multicolour brightness-equalized quantum dots by controlling the composition and structure of core-shell HgCdSeS-CdZnS nanocrystals.
- Sung Jun Lim
- , Mohammad U. Zahid
- & Andrew M. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access STED nanoscopy with fluorescent quantum dots
STED nanoscopy with fluorescent quantum dots
STED nanoscopy enables sub-diffraction imaging with a wide range of fluorescent probes. Here, the authors show that a bright and very photostable class of fluorescent quantum dots can be super-resolved with STED as biolabels in cellular contexts.
- Janina Hanne
- , Henning J. Falk
- & Stefan W. Hell
-
Article |
 Locating and classifying fluorescent tags behind turbid layers using time-resolved inversion
Locating and classifying fluorescent tags behind turbid layers using time-resolved inversion
Fluorescent patches can be localized in 3D and identified behind a diffusive layer by use of streak images taken from one horizontal line on the diffusive barrier. Satat et al. show that the time-resolved inversion along with sparse prior can be used to perform this with deeper recovery range.
- Guy Satat
- , Barmak Heshmat
- & Ramesh Raskar
-
Article |
 Rational design of a chalcogenopyrylium-based surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering nanoprobe with attomolar sensitivity
Rational design of a chalcogenopyrylium-based surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering nanoprobe with attomolar sensitivity
Raman imaging offers great potential in biomedical imaging due to the combination of specificity and sensitivity. Here, the authors show nanoparticles functionalized with a chalcogenopyrylium reporter molecule, giving bright probes with low limits of detection for in vivoimaging.
- Stefan Harmsen
- , Matthew A. Bedics
- & Moritz F. Kircher
-
Article |
 Super-resolution surface mapping using the trajectories of molecular probes
Super-resolution surface mapping using the trajectories of molecular probes
Surface characterization of soft materialsin situis challenging due to the importance of non-covalent interactions. Now, a new chemical imaging method is reported that generates images of surface interactions by combining many molecular probe trajectories.
- Robert Walder
- , Nathaniel Nelson
- & Daniel K. Schwartz
-
Article |
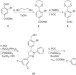 Selective fluorescent probes for live-cell monitoring of sulphide
Selective fluorescent probes for live-cell monitoring of sulphide
Molecular probes that can detect aqueous sulphides could help to elucidate their roles in biological signalling. Qianet al. develop two sulphide-selective fluorescent probes and demonstrate their ability to image free sulphide in living cells.
- Yong Qian
- , Jason Karpus
- & Chuan He

 Early onset diagnosis in Alzheimer’s disease patients via amyloid-β oligomers-sensing probe in cerebrospinal fluid
Early onset diagnosis in Alzheimer’s disease patients via amyloid-β oligomers-sensing probe in cerebrospinal fluid