News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Industry Perspective |
 Ultrafast lasers yield X-rays
Ultrafast lasers yield X-rays
Table-top sources that generate both extreme ultraviolet light and soft X-rays through high-harmonic generation of ultrafast infrared laser pulses look set to perform tasks previously accessible using only large-scale synchrotrons.
- Iain McKinnie
- & Henry Kapteyn
-
News & Views |
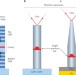 Towards efficient quantum sources
Towards efficient quantum sources
On-demand single-photon sources with high efficiency are required to realize many of the applications of quantum optics. By exploiting photonic mode transformation in a tapered nanowire, researchers have created a source that has an unprecedented extraction efficiency over an extremely broad spectral range.
- Stefan Strauf
-
News & Views |
 Ferroelectric photovoltaics
Ferroelectric photovoltaics
Ferroelectrics may have a bright future for solar-energy generation, following the report that the domain walls of such materials can be engineered to exhibit a photovoltaic effect with an impressively high voltage output.
- Haitao Huang
-
News & Views |
 Terahertz Kerr effect
Terahertz Kerr effect
The optical Kerr effect is a well-known phenomenon in which an electric field creates birefringence in a material. Researchers have now demonstrated this effect using single-cycle terahertz pulses — instead of optical pulses — in a variety of liquids.
- Eric Freysz
- & Jérôme Degert
-
Industry Perspective |
 Image intensification
Image intensification
Cameras equipped with an image intensifier make it possible to image ultrafast and low-light events and are proving of particular importance for combustion studies.
- Jeroen Wehmeijer
- & Bert van Geest
-
Interview |
 Femtosecond future
Femtosecond future
Andreas Stingl, CEO of Austrian company Femtolasers, talks to Nadya Anscombe about the market for femtosecond lasers and their wide variety of applications.
- Nadya Anscombe
-
Product Highlights |
 Real-time pulse characterization and more
Real-time pulse characterization and more
-
Interview |
 Volume optics
Volume optics
A new method for designing aperiodic volume optical elements will offer researchers more degrees of freedom in the design of optical devices. Rafael Piestun explained to Nature Photonics how this method may lead to a myriad of applications in beam-shaping and imaging.
- Rachel Won
-
News & Views |
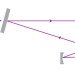 Enhanced quantum light generation
Enhanced quantum light generation
The use of a specially designed cavity to enhance the intensity of femtosecond ultraviolet pulses dramatically increases the rate at which non-classical states of light can be produced.
- R. Jason Jones
-
News & Views |
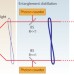 Repairing quadrature entanglement
Repairing quadrature entanglement
Optical loss degrades quantum correlations, hindering the use of quantum quadrature entanglement for many applications. Researchers have now experimentally demonstrated that this entanglement can be recovered using photon subtraction.
- Alexei Ourjoumtsev
-
Profile |
 Optics made to measure
Optics made to measure
Researchers in Germany have set up a company to manufacture custom-made optics for ultrafast applications. Nadya Anscombe finds out about the company's products and its plans for the future.
- Nadya Anscombe
-
Industry Perspective |
 Shaping up
Shaping up
The use of pulse-shaping technology to optimize the temporal and spectral properties of ultrashort light pulses can enhance their utility in many applications.
- Nicolas Forget
-
Research Highlights |
 Our choice from the recent literature
Our choice from the recent literature
-
Research Highlights |
 Our choice from the recent literature
Our choice from the recent literature
-
Business News |
 Ultrafast networks gear-up for deployment
Ultrafast networks gear-up for deployment
-
Letter |
 Experimental realization of sub-shot-noise quantum imaging
Experimental realization of sub-shot-noise quantum imaging
Sub-shot-noise imaging using spatial quantum correlations between parametric down-conversion light beams is demonstrated. The scheme exhibits a larger signal-to-noise ratio than is possible through classical imaging methods.
- G. Brida
- , M. Genovese
- & I. Ruo Berchera
-
Article |
 Real-time full-field arbitrary optical waveform measurement
Real-time full-field arbitrary optical waveform measurement
A measurement scheme that is capable of recording the amplitude and phase of arbitrary shaped optical waveforms with a bandwidth of up to 160 GHz is presented. The approach is compatible with integration on a silicon photonic chip and could aid the study of transient ultrafast phenomena.
- Nicolas K. Fontaine
- , Ryan P. Scott
- & S. J. B. Yoo
-
Letter |
 Light extraction from organic light-emitting diodes enhanced by spontaneously formed buckles
Light extraction from organic light-emitting diodes enhanced by spontaneously formed buckles
Organic light-emitting diodes featuring layers with a spontaneously formed buckled geometry are demonstrated to offer at least a twofold improvement in light extraction efficiency across the entire visible spectrum.
- Won Hoe Koo
- , Soon Moon Jeong
- & Hideo Takezoe
-
Letter |
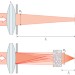 Exploiting disorder for perfect focusing
Exploiting disorder for perfect focusing
Light is scattered out of a focusing beam when an inhomogeneous medium is placed between the lens and the focal plane. Now, scientists experimentally demonstrate that scattering can be exploited to improve, rather than deteriorate, the focusing resolution of a lens by using wavefront shaping to compensate for scattering.
- I. M. Vellekoop
- , A. Lagendijk
- & A. P. Mosk
-
Article |
 Quantum-optical state engineering up to the two-photon level
Quantum-optical state engineering up to the two-photon level
Tailoring of arbitrary single-mode states of travelling light up to the two-photon level is proposed and demonstrated. The desired state is remotely prepared in the signal channel of spontaneous parametric down-conversion by means of conditional measurements on the idler channel.
- Erwan Bimbard
- , Nitin Jain
- & A. I. Lvovsky
-
Article |
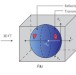 Aperiodic volume optics
Aperiodic volume optics
Fine control over the material structure within a volume gives rise to new physical phenomena and more freedom for designing spatial, spectral and temporal functions. A three-dimensional scattering approach to the design of aperiodic volume optical elements is presented, expanding the traditional capabilities of volume holography, photonic crystals and diffractive optics.
- Tim D. Gerke
- & Rafael Piestun
-
Letter |
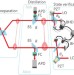 Entanglement distillation from Gaussian input states
Entanglement distillation from Gaussian input states
Distillation of entangled photons is essential for applications such as long-distance quantum communication and high-fidelity quantum teleportation. Distillation from Gaussian input states is experimentally realized, resulting in a large gain in entanglement.
- Hiroki Takahashi
- , Jonas S. Neergaard-Nielsen
- & Masahide Sasaki
-
Article |
 Coherent mixing of mechanical excitations in nano-optomechanical structures
Coherent mixing of mechanical excitations in nano-optomechanical structures
Nanocavity optomechanical systems can exhibit strong dynamical back-action between mechanical motion and the cavity light field. Here, optical control of mechanical motion within two different nanocavity structures is demonstrated. A form of optically controlled mechanical transparency is also demonstrated, which is analogous to electromagnetically induced transparency.
- Qiang Lin
- , Jessie Rosenberg
- & Oskar Painter
-
Article |
 Random distributed feedback fibre laser
Random distributed feedback fibre laser
The combination of distributed Rayleigh back-scatter and Raman gain in an optical fibre yields an open cavity, mirror-less fibre laser that offers stable operation at the telecommunications wavelength of 1.5 µm.
- Sergei K. Turitsyn
- , Sergey A. Babin
- & Evgenii V. Podivilov
-
-
Out of the lab |
 Solar-powered lasers
Solar-powered lasers
Could lasers directly driven by sunlight help address the planet's energy generation problems? Japanese scientists are optimistic, reports Duncan Graham-Rowe.
- Duncan Graham-Rowe
-
News & Views |
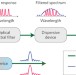 Arbitrary waveform generation
Arbitrary waveform generation
The use of silicon photonics has now enabled the creation of 60-GHz microwave waveforms with programmable amplitude, frequency and phase.
- Jianping Yao
-
News & Views |
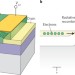 A brighter future
A brighter future
The demonstration of an LED made from a single electrostatically doped carbon nanotube p–n junction with dramatically improved light-emission efficiency marks an important advance for carbon nanotube photonics.
- Tobias Hertel
-
News & Views |
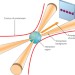 Probing the quantum vacuum
Probing the quantum vacuum
Researchers are proposing a new experiment that will probe fundamental aspects of the quantum vacuum by searching for highly elusive photon–photon scattering events.
- Mattias Marklund
-
News & Views |
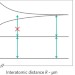 Tubes for quantum electronics
Tubes for quantum electronics
Micrometre-sized atomic vapour cells hosting robust entangled atomic states at room temperature offer a promising route to the realization of quantum photonic devices such as quantum gates and single-photon sources.
- Jan-Michael Rost
-
Interview |
 Generating light bullets
Generating light bullets
Generating 3D light packets that propagate without dispersing in time or space is not an easy task. Andy Chong from Cornell University told Nature Photonics how he and his co-workers came up with a simple and versatile approach to this problem.
- Rachel Won
-
News & Views |
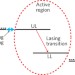 A glass half full
A glass half full
Researchers from Princeton and Northwestern Universities have independently demonstrated, through different design strategies, mid-infrared quantum cascade lasers with wall-plug efficiencies reaching 50%. The result is a quantum cascade laser so efficient that it generates more light than heat, albeit at low temperatures of operation.
- Hui Chun Liu
-
News & Views |
 Magnet-controlled plasmons
Magnet-controlled plasmons
Surface plasmons hold great promise for on-chip miniaturization of all-optical circuits, but practical methods of switching them are needed. Researchers have now demonstrated strong — and potentially fast — modulation of plasmons using a magnet.
- Shanhui Fan
-
Product Focus |
 Optical parametric oscillators
Optical parametric oscillators
Optical parametric oscillators simultaneously generate two beams of coherent light that are widely tunable in wavelength. This flexibility makes them a popular tool in various areas of scientific research, reports Neil Savage.
- Neil Savage
-
News & Views |
 Budget cuts impact photonics
Budget cuts impact photonics
Japan's new government has reversed its decision for research funding and angered many scientists in the process as budgets — including those for photonics research — get cut.
- Ichiko Fuyuno
-
News & Views |
 A question of cost
A question of cost
The adoption of sophisticated phase-shift modulation schemes could make optical communication at 100 Gbit s−1 a reality within the next couple of years, but this is ultimately dependent on the deployment costs involved.
- Rachel Won
-
Research Highlights |
 Our choice from the recent literature
Our choice from the recent literature
-
Letter |
 Ultraviolet enhancement cavity for ultrafast nonlinear optics and high-rate multiphoton entanglement experiments
Ultraviolet enhancement cavity for ultrafast nonlinear optics and high-rate multiphoton entanglement experiments
The first enhancement cavity for femtosecond ultraviolet pulses is demonstrated. More than 7 W of average ultraviolet power at an 81 MHz repetition rate, available to pump a nonlinear crystal inside the cavity, is exploited in an implementation of a powerful source for high-rate experiments with entangled multiphoton states.
- Roland Krischek
- , Witlef Wieczorek
- & Harald Weinfurter
-
Review Article |
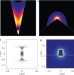 Plasmonics beyond the diffraction limit
Plasmonics beyond the diffraction limit
- Dmitri K. Gramotnev
- & Sergey I. Bozhevolnyi
-
Article |
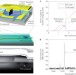 An ultra-small, low-power, all-optical flip-flop memory on a silicon chip
An ultra-small, low-power, all-optical flip-flop memory on a silicon chip
Scientists demonstrate that a single 7.5-μm-diameter microdisk laser coupled to a silicon-on-insulator wire waveguide can work as an all-optical flip-flop memory. Under a continuous bias of 3.5 mA, flip-flop operation is demonstrated using optical triggering pulses of 1.8 fJ and with a switching time of 60 ps. This device is attractive for on-chip all-optical signal buffering, switching, and processing.
- Liu Liu
- , Rajesh Kumar
- & Geert Morthier
-
Letter |
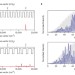 Quasi-periodic distributed feedback laser
Quasi-periodic distributed feedback laser
Researchers have constructed a terahertz quantum cascade laser using quasi-periodic distributed feedback gratings based on the Fibonacci sequence. Features that go beyond traditional distributed feedback lasers are demonstrated, such as directional output independent of the emission frequency and multicolour operation.
- Lukas Mahler
- , Alessandro Tredicucci
- & Diederik S. Wiersma
-
Letter |
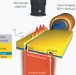 Active magneto-plasmonics in hybrid metal–ferromagnet structures
Active magneto-plasmonics in hybrid metal–ferromagnet structures
Active switching of plasmons by an external magnetic field is demonstrated in a metal–ferromagnet–metal structure. The strong modulation, combined with possible all-optical magnetization reversal induced by femtosecond light pulses, opens the door to ultrafast magneto-plasmonic switching.
- Vasily V. Temnov
- , Gaspar Armelles
- & Rudolf Bratschitsch
-
Article |
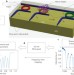 Ultrabroad-bandwidth arbitrary radiofrequency waveform generation with a silicon photonic chip-based spectral shaper
Ultrabroad-bandwidth arbitrary radiofrequency waveform generation with a silicon photonic chip-based spectral shaper
Ultrabroad-bandwidth radiofrequency pulses that increase data transmission rate and allow multipath tolerance in wireless communications are difficult to generate using chip-based electronics. Now, a chip-scale fully programmable spectral shaper consisting of cascaded multichannel micro-ring resonators is demonstrated as a solution.
- Maroof H. Khan
- , Hao Shen
- & Minghao Qi
-
Letter |
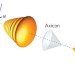 Airy–Bessel wave packets as versatile linear light bullets
Airy–Bessel wave packets as versatile linear light bullets
The generation of spatiotemporal optical wave packets that are resistant to both dispersion and diffraction are attractive for bioimaging applications and plasma physics. By combining Bessel beams in the transverse plane with temporal Airy pulses, scientists now report the first observation of a class of versatile three-dimensional linear light ‘bullets’.
- Andy Chong
- , William H. Renninger
- & Frank W. Wise
-
Letter |
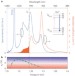 Laser cooling of solids to cryogenic temperatures
Laser cooling of solids to cryogenic temperatures
By exploiting the Stark manifold resonance in a crystalline host, scientists report laser cooling of ytterbium-doped LiYF4 crystals from room temperature to ∼155 K, with a cooling power of 90 mW. This is the lowest temperature achieved without using cryogens or mechanical refrigeration, surpassing the performance of multistage Peltier coolers.
- Denis V. Seletskiy
- , Seth D. Melgaard
- & Mansoor Sheik-Bahae
-
Article |
 Coherent excitation of Rydberg atoms in micrometre-sized atomic vapour cells
Coherent excitation of Rydberg atoms in micrometre-sized atomic vapour cells
Rydberg blockade — the suppression of excitation of more than one Rydberg atom within a blockade volume — has so far been realized using ultracold atoms. Now, scientists show that coherence times of >100 ns are achievable with coherent Rydberg atomic spectroscopy in micrometre-sized thermal vapour cells, making them good candidates for investigating low-dimensional strongly interacting Rydberg gases, constructing quantum gates and building single-photon sources.
- H. Kübler
- , J. P. Shaffer
- & T. Pfau
-
Letter |
 Highly power-efficient quantum cascade lasers
Highly power-efficient quantum cascade lasers
A quantum cascade laser with a wall-plug efficiency of up to 50% is experimentally realized when operated at low temperatures and in pulsed mode. The high-efficiency performance is achieved by implementing an ultrastrong coupling between the injector and active regions.
- Peter Q. Liu
- , Anthony J. Hoffman
- & Claire F. Gmachl
-
Letter |
 A matterless double slit
A matterless double slit
A matterless double-slit scenario is proposed, in which photons generated from head-on collisions between a probe laser field and two ultraintense laser beams form a double-slit interference pattern. Such electromagnetic fields are predicted to induce material-like behaviour in a vacuum, supporting elastic scattering between photons.
- Ben King
- , Antonino Di Piazza
- & Christoph H. Keitel
-
Letter |
 Quantum cascade lasers that emit more light than heat
Quantum cascade lasers that emit more light than heat
A mid-infrared quantum cascade laser that emits more light than heat and features a high wall-plug efficiency of up to 53% when operated a temperature of 40 K is reported. The device utilizes a single-well injector design.
- Yanbo Bai
- , Steven Slivken
- & Manijeh Razeghi

 Endless applications
Endless applications The fluorescence of fraud
The fluorescence of fraud