News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Research Highlights |
 Milestones in laser development
Milestones in laser development
-
News & Views |
 Pyramidal quantum dots
Pyramidal quantum dots
The use of a fabrication scheme for controlling the symmetry, uniformity and location of quantum dots has resulted in a superior source of entangled photon pairs.
- David Gershoni
-
News & Views |
 Nonlinear attraction
Nonlinear attraction
A new femtosecond fibre laser design combines two distinct regimes of nonlinear dynamic attraction within a single cavity to yield robust and low-noise performance.
- John M. Dudley
-
Industry Perspective |
 Enabling optical communication
Enabling optical communication
The semiconductor laser has revolutionized the way the world communicates, and it is continuously evolving with our ever-increasing demand for higher bandwidths.
- Ed Murphy
-
News & Views |
 Sharper focus by random scattering
Sharper focus by random scattering
Contrary to intuition, a disordered scattering medium can be exploited to improve, rather than deteriorate, the focusing resolution of a lens.
- Mathias Fink
-
News & Views |
 Resonant dust
Resonant dust
The optics of disordered materials is rich and full of surprises. Researchers have now found a new form of stochastic resonance in which an image beam is resonantly amplified by noise.
- Diederik S. Wiersma
-
News & Views |
 Yagi–Uda antenna shines bright
Yagi–Uda antenna shines bright
The demonstration of a Yagi–Uda nano-antenna that operates at visible wavelengths gives hope for a convenient means of directing radiation patterns from nanoscale light sources such as single molecules and quantum dots.
- Geoffroy Lerosey
-
Editorial |
 Celebrating the laser
Celebrating the laser
This month sees the 50th anniversary of the laser, with a host of activities taking place in celebration.
-
Profile |
 Making history
Making history
The initial concept of the laser was pioneered at Bell Labs, as were many other technologies that are fundamental to the photonics industry. Nadya Anscombe finds out how the company has changed in recent years and what technologies are being researched at Bell Labs today.
- Nadya Anscombe
-
Industry Perspective |
 Precision engineering
Precision engineering
The excimer laser is synonymous with precision. Today it is enabling the production of integrated circuits and nextgeneration displays, as well as new breakthroughs in eye surgery.
- Ralph Delmdahl
-
Industry Perspective |
 Ready for take-off
Ready for take-off
Since their invention, quantum cascade lasers have made considerable progress in terms of their wavelength range and efficiency. Today, they have important applications in environmental science, process control and medical diagnostics.
- Antoine Müller
- & Jérôme Faist
-
Industry Perspective |
 The flexible research tool
The flexible research tool
When the Ti:Sapphire laser was first invented, it took the research community by storm. Today, it has an important role in imaging, spectroscopy and many other applications.
- Julien Klein
- & James D. Kafka
-
Product Highlights |
 Stacked arrays, direct green diodes and more
Stacked arrays, direct green diodes and more
-
Industry Perspective |
 From a rod to a disk
From a rod to a disk
The Nd:YAG was one of the first ever industrial lasers, and even today it still has many advantages over other laser technologies. Competition from newer laser technologies, however, has made its evolution critical to its survival.
- Paul Seiler
- , Klaus Wallmeroth
- & Kurt Mann
-
Industry Perspective |
 Delivering power
Delivering power
With its high wall-plug efficiency and record-breaking power output, the fibre laser has made the use of lasers in manufacturing more acceptable and cost-effective.
- Bill Shiner
-
Interview |
 Exciting times
Exciting times
Nadya Anscombe talks to Charles Townes, Nobel Prize winner and inventor of the maser, the forerunner to the laser, to find out how the invention of the laser came about and how he struggled to convince people of its importance.
- Nadya Anscombe
-
Research Highlights |
 Our choice from the recent literature
Our choice from the recent literature
-
Business News |
 Laser celebrations
Laser celebrations
-
Commentary |
 Why future supercomputing requires optics
Why future supercomputing requires optics
Could optical technology offer a solution to the heat generation and bandwidth limitations that the computing industry is starting to face? The benefits of energy-efficient passive components, low crosstalk and parallel processing suggest that the answer may be yes.
- H. John Caulfield
- & Shlomi Dolev
-
Letter |
 Ultrafast optical spin echo in a single quantum dot
Ultrafast optical spin echo in a single quantum dot
An ultrafast, all-optical spin echo technique is used to increase the decoherence time of a single quantum dot electron spin from nanoseconds to several microseconds. The ratio of decoherence time to gate time exceeds 105, suggesting strong promise for future photonic quantum information processors and repeater networks.
- David Press
- , Kristiaan De Greve
- & Yoshihisa Yamamoto
-
Letter |
 Room-temperature polariton lasing in an organic single-crystal microcavity
Room-temperature polariton lasing in an organic single-crystal microcavity
Polaritons in organic semiconductors are highly stable at room temperature, but so far nonlinear emission from these structures has not been demonstrated. Here, polariton lasing at room temperature in an organic microcavity composed of a melt-grown anthracene single crystal sandwiched between two dielectric mirrors is reported.
- S. Kéna-Cohen
- & S. R. Forrest
-
Article |
 Room-temperature subwavelength metallo-dielectric lasers
Room-temperature subwavelength metallo-dielectric lasers
Room-temperature lasing from metallo-dielectric cavities that are smaller than their emission wavelength in all three dimensions is reported. The cavity consists of an aluminium/silica bi-layer shield that surrounds an InGaAsP disk. The gain threshold of the laser is minimized by optimizing the thickness of the silica layer.
- Maziar P. Nezhad
- , Aleksandar Simic
- & Yeshaiahu Fainman
-
Letter |
 Exciton–polariton spin switches
Exciton–polariton spin switches
An all-optical spin switch based on exciton–polaritons in a semiconductor microcavity is demonstrated. These results may lead to small and fast spin-based on-chip logic devices.
- A. Amo
- , T. C. H. Liew
- & A. Bramati
-
Letter |
 Experimental quantum-enhanced estimation of a lossy phase shift
Experimental quantum-enhanced estimation of a lossy phase shift
Evidence that appropriately engineered quantum states outperform both standard and N00N states in the precision of phase estimation — even in the presence of losses and decoherence — is presented. The results show that the strategy for realizing the quantum enhancement of metrology is quite distinct from protecting quantum information encoded in light.
- M. Kacprowicz
- , R. Demkowicz-Dobrzański
- & I. A. Walmsley
-
Letter |
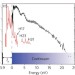 XFROG phase measurement of threshold harmonics in a Keldysh-scaled system
XFROG phase measurement of threshold harmonics in a Keldysh-scaled system
By exploiting the Keldysh scaling — universal wavelength scaling laws in strong-field physics — direct temporal characterization of high-harmonics is demonstrated using sum-frequency-generation cross-correlation frequency-resolved optical gating (SFG XFROG).
- Erik P. Power
- , Anne Marie March
- & Louis F. DiMauro
-
-
Editorial |
 Carbon optimism
Carbon optimism
The use of diamond, graphene and carbon nanotubes is becoming increasingly common in photonic applications, and several recent notable achievements suggest that carbon has a bright future in photonics.
-
Product Focus |
 Optical simulation software
Optical simulation software
The design of complex and high-performance optical assemblies is greatly simplified by the availability of a wide range of sophisticated software packages, reports The Scott Partnership.
-
Interview |
 Waveform analysis
Waveform analysis
Accurate characterization of ultrafast optical pulses is important for applications such as spectroscopy and communications research. S. J. Ben Yoo from the University of California at Davis explains his team's scheme for real-time measurement of the amplitude and phase of arbitrary and non-repetitive waveforms.
- Rachel Won
-
News & Views |
 An incoherent fibre laser
An incoherent fibre laser
The demonstration of a 'mirrorless' ultralong Raman fibre laser that provides stable, spatially incoherent continuous-wave lasing may prove to be an important new light source for applications in nonlinear optics, sensing and telecommunications.
- Andrei A. Fotiadi
-
News & Views |
 A little diamond goes a long way
A little diamond goes a long way
The demonstration of a solid-state yellow laser based on diamond could bring new levels of convenience and capability for biomedical applications.
- Andrew D. Greentree
- & Steven Prawer
-
News & Views |
 Beating the classical camera
Beating the classical camera
By utilizing the spatial quantum correlations of light, Italian researchers have now performed imaging at significantly higher signal-to-noise ratios than those possible through classical techniques.
- Stefanie Barz
- & Philip Walther
-
News & Views |
 Breaking Kasha's rule
Breaking Kasha's rule
The emission of visible light from a dye encapsulated within a carbon nanotube gives great hope and new opportunities for the design of nanoscale optoelectronic devices.
- Kazuhiro Yanagi
- & Hiromichi Kataura
-
News & Views |
 Light storage at record bandwidths
Light storage at record bandwidths
The demonstration of coherent storage and retrieval of subnanosecond light pulses in an atomic vapour opens the door to optical quantum memories with gigahertz bandwidths.
- Hugues de Riedmatten
-
News & Views |
 OPCPA boosts high-field physics
OPCPA boosts high-field physics
Optical parametric chirped pulse amplification is a promising approach for amplifying few-cycle laser pulses to unprecedented powers. However, the future success of the scheme depends on the availability of suitable pump sources.
- Rachel Won
-
Research Highlights |
 Our choice from the recent literature
Our choice from the recent literature
-
Review Article |
 Optomechanical device actuation through the optical gradient force
Optomechanical device actuation through the optical gradient force
- Dries Van Thourhout
- & Joris Roels
-
Letter |
 Graphene photodetectors for high-speed optical communications
Graphene photodetectors for high-speed optical communications
A graphene-based photodetector with unprecedented photoresponsivity and the ability to perform error-free detection of 10 Gbit s−1s data streams is demonstrated. The results suggest that graphene-based photonic devices have a bright future in telecommunications and other optical applications.
- Thomas Mueller
- , Fengnian Xia
- & Phaedon Avouris
-
Article |
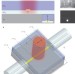 Amplification of long-range surface plasmons by a dipolar gain medium
Amplification of long-range surface plasmons by a dipolar gain medium
Researchers overcome the propagation loss of surface-plasmon polaritons, with this demonstration being the first direct gain measurement of propagating plasmons. Low-loss long-range modes of a metal stripe waveguide are amplified by using optically pumped dye molecules in solution as the gain medium. The mode power gain was measured to be 8.55 dB mm−1.
- Israel De Leon
- & Pierre Berini
-
Letter |
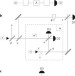 Heralded noiseless linear amplification and distillation of entanglement
Heralded noiseless linear amplification and distillation of entanglement
A noiseless linear amplifier for quantum states of an optical field is demonstrated. The amplifier is also used to enhance entanglement through a technique known as distillation. Such amplification and distillation may be useful for quantum cloning, metrology and communications.
- G. Y. Xiang
- , T. C. Ralph
- & G. J. Pryde
-
Letter |
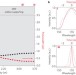 Soliton–similariton fibre laser
Soliton–similariton fibre laser
Scientists report a mode-locking regime of an erbium-doped fibre laser in which the laser pulse evolves as a similariton in the gain segment of the cavity and transforms into a soliton in the rest of the cavity. The findings constitute the first observation of amplifier similaritons in a laser cavity and are likely to be applicable to various other nonlinear systems.
- Bulent Oktem
- , Coşkun Ülgüdür
- & F. Ömer Ilday
-
Article |
 Nonlinear self-filtering of noisy images via dynamical stochastic resonance
Nonlinear self-filtering of noisy images via dynamical stochastic resonance
By exploiting stochastic resonance — in which nonlinear coupling allows signals to grow at the expense of noise — scientists show that they can recover noise-hidden images propagating in a self-focusing medium. The findings pave the way for a variety of nonlinear instability-driven imaging techniques.
- Dmitry V. Dylov
- & Jason W. Fleischer
-
Article |
 Measuring the light emission profile in organic light-emitting diodes with nanometre spatial resolution
Measuring the light emission profile in organic light-emitting diodes with nanometre spatial resolution
Precise spatial characterization of the origin of light emission from organic light-emitting diodes is important for improving the design of future devices and gaining valuable insight into their operation. Here, a characterization scheme that achieves this task with a spatial resolution better than 5 nm is reported.
- S. L. M. van Mensfoort
- , M. Carvelli
- & R. Coehoorn
-
Letter |
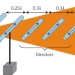 Directional control of light by a nano-optical Yagi–Uda antenna
Directional control of light by a nano-optical Yagi–Uda antenna
A Yagi–Uda directional antenna — the work horse of radiofrequency communications for more than 60 years — has now been demonstrated at visible wavelengths. An array of appropriately tuned nanoparticles replicate the reflecting and directing elements of the original design. Directional control of radiation from the nano-optical Yagi–Uda antenna was experimentally shown.
- Terukazu Kosako
- , Yutaka Kadoya
- & Holger F. Hofmann
-
Letter |
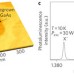 Polarization-entangled photons produced with high-symmetry site-controlled quantum dots
Polarization-entangled photons produced with high-symmetry site-controlled quantum dots
Entangled photons are efficiently generated from highly symmetric, site-controlled InGaAs/GaAs quantum dots grown in inverted pyramids. Fine-structure splitting of the intermediate exciton level is suppressed without the application of electric, magnetic or strain fields. Polarization entanglement is demonstrated by measurements of the two-photon density matrix and the confirmation of several entanglement criteria.
- A. Mohan
- , M. Felici
- & E. Kapon
-
Letter |
 Towards high-speed optical quantum memories
Towards high-speed optical quantum memories
Quantum memories for storing and releasing photons are required for quantum computers and quantum communications. So far, their operational bandwidths have limited data-rates to megahertz. Researchers now demonstrate coherent storage and retrieval of subnanosecond low-intensity light pulses with spectral bandwidths exceeding 1 GHz.
- K. F. Reim
- , J. Nunn
- & I. A. Walmsley
-
Editorial |
Ultrafast photonics
-
-
Editorial |
 Embracing mobility
Embracing mobility
An iPhone application for browsing nature.com content may change the way we access research news.

 The season of inspiration
The season of inspiration Tying knots with light
Tying knots with light Selective disinfection
Selective disinfection