Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 A thicker skin for better immune evasion
A thicker skin for better immune evasion
Cancer cells adjust the composition of their glycocalyx to increase its thickness and create a physical barrier that shields them from immune recognition and engagement.
- Edward N. Schmidt
- & Matthew S. Macauley
-
Article |
 Compensating losses in polariton propagation with synthesized complex frequency excitation
Compensating losses in polariton propagation with synthesized complex frequency excitation
Propagation losses have limited the practical use of polaritons in photonic applications. Here the authors demonstrate a substantial enhancement in the propagation distance of phonon polaritons, employing synthetic optical excitation of complex frequency with virtual gain synthesized by combining multiple real frequency measurements.
- Fuxin Guan
- , Xiangdong Guo
- & Shuang Zhang
-
Research Briefing |
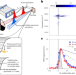 Vibrational optical control via cation motions in perovskite solar cells
Vibrational optical control via cation motions in perovskite solar cells
Hybrid organic–inorganic perovskite materials have promise as the photovoltaic technology of the future. A method for spectroscopic optical control reveals how the structural dynamics and vibrations of a perovskite’s organic cations affect the electronic performance of working photovoltaic devices.
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast vibrational control of organohalide perovskite optoelectronic devices using vibrationally promoted electronic resonance
Ultrafast vibrational control of organohalide perovskite optoelectronic devices using vibrationally promoted electronic resonance
Optically stimulated vibrational control for materials has the potential to improve the performance of optoelectronic devices. The vibrational control of FAPbBr3 perovskite solar cells has been demonstrated, where the fast dynamics of coupling between cations and inorganic sublattice may suppress non-radiative recombinations in perovskites, leading to reduced voltage losses.
- Nathaniel. P. Gallop
- , Dmitry R. Maslennikov
- & Artem A. Bakulin
-
Article |
 Compact angle-resolved metasurface spectrometer
Compact angle-resolved metasurface spectrometer
Employing a miniaturized spectrometer that combines a metasurface-based spectrometer array and a metalens, angle-resolved spectral imaging is achieved with a wavelength accuracy of 0.17 nm, spectral resolution of 0.40 nm and angular resolution of 4.88 × 10−3 rad for a spectrometer with a 4 × 4 μm2 footprint.
- Guiyi Cai
- , Yanhao Li
- & Qinghai Song
-
News & Views |
 A new spin on impact ionization
A new spin on impact ionization
Quantum dots are engineered to use dopant states to achieve substantially enhanced impact ionization, which is potentially useful for light-harvesting applications.
- Miri Kazes
- & Dan Oron
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-exchange carrier multiplication in manganese-doped colloidal quantum dots
Spin-exchange carrier multiplication in manganese-doped colloidal quantum dots
Carrier multiplication generates multiple excitons for each absorbed photon but is normally limited by fast phonon-assisted relaxation. Here the authors achieve a threefold enhancement in multiexciton yields in Mn-doped PbSe/CdSe quantum dots, due to very fast spin-exchange interactions between Mn ions and the quantum dots that outpace energy losses arising from phonon emission.
- Ho Jin
- , Clément Livache
- & Victor I. Klimov
-
-
Article |
 Dielectric control of reverse intersystem crossing in thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters
Dielectric control of reverse intersystem crossing in thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters
The role of the dielectric environment in thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) is not yet fully understood. Here the authors reveal the relevance of environment–emitter interactions in gating the reverse intersystem crossing and its particular relevance in dipolar TADF emitters.
- Alexander J. Gillett
- , Anton Pershin
- & David Beljonne
-
News & Views |
 Twistronics and the small-angle magic
Twistronics and the small-angle magic
Understanding, at the atomic level, the effect of the stacking and twisting of different layered two-dimensional materials is a major challenge for the future of twistronics. Optical excitations evidence twist-angle-dependent whirlpool-shaped distortions in such materials.
- Ado Jorio
-
News & Views |
 Busting through quantum dot barriers
Busting through quantum dot barriers
Early time transient absorption microscopy in quantum dot solids reveals anomalous exciton transport with multiple different temporal regimes within hundreds of femtoseconds after photoexcitation.
- Naomi S. Ginsberg
- & William A. Tisdale
-
News & Views |
 Volume imaging of anisotropic materials
Volume imaging of anisotropic materials
Revealing the molecular orientations of anisotropic materials is desired in materials science and soft-matter physics. Now, an optical diffraction tomographic approach enables the direct reconstruction of dielectric tensors of anisotropic structures in three dimensions.
- Anne Sentenac
- , Guillaume Maire
- & Patrick C. Chaumet
-
Article |
 Tomographic measurement of dielectric tensors at optical frequency
Tomographic measurement of dielectric tensors at optical frequency
Measuring three-dimensional dielectric tensors is desired for applications in material and soft matter physics. Here, the authors use a tomographic approach and inversely solve the vectorial wave equation to directly reconstruct dielectric tensors of anisotropic structures.
- Seungwoo Shin
- , Jonghee Eun
- & YongKeun Park
-
Article |
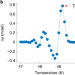 Three-state nematicity in the triangular lattice antiferromagnet Fe1/3NbS2
Three-state nematicity in the triangular lattice antiferromagnet Fe1/3NbS2
A spatially resolved optical polarimetry technique is used to identify a three-state Potts-nematic order parameter in a triangular lattice antiferromagnetic material.
- Arielle Little
- , Changmin Lee
- & Joseph Orenstein
-
Article |
 Ultrafast generation and control of an electron vortex beam via chiral plasmonic near fields
Ultrafast generation and control of an electron vortex beam via chiral plasmonic near fields
By exciting chiral plasmons within a nanohole by means of circularly polarized light pulses, orbital angular momentum can be imparted onto charged matter waves (here, electrons) and controlled at terahertz speed (femtosecond intervals).
- G. M. Vanacore
- , G. Berruto
- & F. Carbone
-
Article |
 Deterministic optical control of room temperature multiferroicity in BiFeO3 thin films
Deterministic optical control of room temperature multiferroicity in BiFeO3 thin films
The remote, non-volatile and reversible optical control of ferroic orders is challenging. Here, using laser illumination, multiple orders in epitaxial mixed-phase BiFeO3 are manipulated deterministically using a thermally driven flexoelectric effect.
- Yi-De Liou
- , Yu-You Chiu
- & Jan-Chi Yang
-
Letter |
 Simultaneous coherence enhancement of optical and microwave transitions in solid-state electronic spins
Simultaneous coherence enhancement of optical and microwave transitions in solid-state electronic spins
Long coherence times in a subset of states that allows for transitions in both microwave and optical range have been reported using an isotopically purified 171Yb3+:Y2SiO5 crystal, rendering the system suitable for quantum information applications.
- Antonio Ortu
- , Alexey Tiranov
- & Mikael Afzelius
-
Article |
 Resolving ultrafast exciton migration in organic solids at the nanoscale
Resolving ultrafast exciton migration in organic solids at the nanoscale
Time-resolved ultrafast spectroscopy is combined with stimulated emission depletion microscopy to observe exciton migration in conjugated polymer films with nanometre and picosecond resolution.
- Samuel B. Penwell
- , Lucas D. S. Ginsberg
- & Naomi S. Ginsberg
-
Article |
 Visualizing excitations at buried heterojunctions in organic semiconductor blends
Visualizing excitations at buried heterojunctions in organic semiconductor blends
A pump–push–probe time-resolved technique is developed to characterize the dynamics of photoexcitations at buried, disordered interfaces. Applied to organic bulk heterojunctions, the method provides insight on charge separation in photovoltaic films.
- Andreas C. Jakowetz
- , Marcus L. Böhm
- & Richard H. Friend
-
Article |
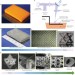 Multiscale metallic metamaterials
Multiscale metallic metamaterials
A large-area fabrication approach to achieve three-dimensional architectured metamaterials, with structural features spanning seven orders of magnitude, results in advanced mechanical properties, including high elasticity.
- Xiaoyu Zheng
- , William Smith
- & Christopher M. Spadaccini
-
News & Views |
 Probing quantum chaos
Probing quantum chaos
Giant Rydberg excitons reveal signatures of quantum chaotic behaviour in the presence of time-reversal symmetry breaking enforced by the background solid-state lattice, and they provide a new mesoscopic platform for fundamental studies of quantum chaos.
- Elena A. Ostrovskaya
- & Franco Nori
-
Letter |
 Ultrafast energy- and momentum-resolved dynamics of magnetic correlations in the photo-doped Mott insulator Sr2IrO4
Ultrafast energy- and momentum-resolved dynamics of magnetic correlations in the photo-doped Mott insulator Sr2IrO4
The dynamics of the magnetic correlations after photo-doping Sr2IrO4 are studied through ultrafast time-resolved resonant inelastic X-ray spectroscopy. The timescales are found to depend on the dimensionality of the correlations.
- M. P. M. Dean
- , Y. Cao
- & J. P. Hill
-
Article |
 Quantum chaos and breaking of all anti-unitary symmetries in Rydberg excitons
Quantum chaos and breaking of all anti-unitary symmetries in Rydberg excitons
Applying an external magnetic field to cuprous oxide causes the energy spacings in the exciton spectrum to transition from a Poissonian distribution to one governed by the Gaussian unitary ensemble statistics, revealing a signature of quantum chaos.
- Marc Aßmann
- , Johannes Thewes
- & Manfred Bayer
-
Article |
 A small-molecule dye for NIR-II imaging
A small-molecule dye for NIR-II imaging
A renally cleared, water-soluble dye emitting in the near-infrared-imaging (NIR)-II window outperforms a clinically approved NIR-I dye in the in vivo imaging of tumours and their nearby blood and lymphatic vasculatures.
- Alexander L. Antaris
- , Hao Chen
- & Hongjie Dai
-
Article |
 Hydride formation thermodynamics and hysteresis in individual Pd nanocrystals with different size and shape
Hydride formation thermodynamics and hysteresis in individual Pd nanocrystals with different size and shape
The physicochemical properties of nanoparticles can sometimes prove difficult to characterize. Using plasmonic nanospectroscopy, hydride formation thermodynamics in individual Pd nanocrystals are found to be nearly size- and shape-independent.
- Svetlana Syrenova
- , Carl Wadell
- & Christoph Langhammer
-
-
News & Views |
 Mid-infrared nanophotonics
Mid-infrared nanophotonics
The confinement and scattering lifetimes of graphene plasmons are improved when graphene is sandwiched between layers of thin hexagonal boron nitride. This finding should pave the way for nanophotonic applications in the low-loss regime.
- Joshua D. Caldwell
- & Kostya S. Novoselov
-
-
-
Letter |
 Cinnamate-based DNA photolithography
Cinnamate-based DNA photolithography
A highly selective and efficient approach to covalently bond complementary DNA strands in solution and on surfaces on demand is shown. The approach involves the substitution of a pair of complementary bases by cinnamate-based crosslinks, which can be activated on exposure to ultraviolet light, and allows chemical patterning of flat and curved surfaces down to micrometre and potentially submicrometre resolutions.
- Lang Feng
- , Joy Romulus
- & Paul Chaikin

 Elementary excitations of single-photon emitters in hexagonal boron nitride
Elementary excitations of single-photon emitters in hexagonal boron nitride Tiny spectrometers
Tiny spectrometers Trapped in a flat dispersion
Trapped in a flat dispersion