Featured
-
-
Research Briefing |
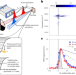 Vibrational optical control via cation motions in perovskite solar cells
Vibrational optical control via cation motions in perovskite solar cells
Hybrid organic–inorganic perovskite materials have promise as the photovoltaic technology of the future. A method for spectroscopic optical control reveals how the structural dynamics and vibrations of a perovskite’s organic cations affect the electronic performance of working photovoltaic devices.
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast vibrational control of organohalide perovskite optoelectronic devices using vibrationally promoted electronic resonance
Ultrafast vibrational control of organohalide perovskite optoelectronic devices using vibrationally promoted electronic resonance
Optically stimulated vibrational control for materials has the potential to improve the performance of optoelectronic devices. The vibrational control of FAPbBr3 perovskite solar cells has been demonstrated, where the fast dynamics of coupling between cations and inorganic sublattice may suppress non-radiative recombinations in perovskites, leading to reduced voltage losses.
- Nathaniel. P. Gallop
- , Dmitry R. Maslennikov
- & Artem A. Bakulin
-
Article |
 Compact angle-resolved metasurface spectrometer
Compact angle-resolved metasurface spectrometer
Employing a miniaturized spectrometer that combines a metasurface-based spectrometer array and a metalens, angle-resolved spectral imaging is achieved with a wavelength accuracy of 0.17 nm, spectral resolution of 0.40 nm and angular resolution of 4.88 × 10−3 rad for a spectrometer with a 4 × 4 μm2 footprint.
- Guiyi Cai
- , Yanhao Li
- & Qinghai Song
-
Article |
 Large-scale optical characterization of solid-state quantum emitters
Large-scale optical characterization of solid-state quantum emitters
Employing a widefield cryogenic microscope to parallelize resonant spectroscopy, chip-scale automated optical characterization of solid-state quantum emitters is demonstrated.
- Madison Sutula
- , Ian Christen
- & Dirk R. Englund
-
News & Views |
 A new spin on impact ionization
A new spin on impact ionization
Quantum dots are engineered to use dopant states to achieve substantially enhanced impact ionization, which is potentially useful for light-harvesting applications.
- Miri Kazes
- & Dan Oron
-
Article
| Open Access Spin-exchange carrier multiplication in manganese-doped colloidal quantum dots
Spin-exchange carrier multiplication in manganese-doped colloidal quantum dots
Carrier multiplication generates multiple excitons for each absorbed photon but is normally limited by fast phonon-assisted relaxation. Here the authors achieve a threefold enhancement in multiexciton yields in Mn-doped PbSe/CdSe quantum dots, due to very fast spin-exchange interactions between Mn ions and the quantum dots that outpace energy losses arising from phonon emission.
- Ho Jin
- , Clément Livache
- & Victor I. Klimov
-
Article |
 Tip-induced excitonic luminescence nanoscopy of an atomically resolved van der Waals heterostructure
Tip-induced excitonic luminescence nanoscopy of an atomically resolved van der Waals heterostructure
Tip-induced excitonic luminescence nanoscopy of an atomically resolved van der Waals heterostructure.
- Luis E. Parra López
- , Anna Rosławska
- & Guillaume Schull
-
Letter |
 Observation of a massive phason in a charge-density-wave insulator
Observation of a massive phason in a charge-density-wave insulator
We report the observation of narrowband terahertz emission from a quasi-one-dimensional charge-density-wave insulator, (TaSe4)2I. The origin of the emitted radiation is interpreted as a phason that obtains mass due to the long-range Coulomb interaction.
- Soyeun Kim
- , Yinchuan Lv
- & Fahad Mahmood
-
-
News & Views |
 Picturing charge carrier diffusion
Picturing charge carrier diffusion
Spectral shifts in transient photoluminescence measurements performed with a confocal microscope allow tracking of charge carrier mobilities in polycrystalline halide perovskites.
- Thomas Kirchartz
-
Article |
 Efficient vertical charge transport in polycrystalline halide perovskites revealed by four-dimensional tracking of charge carriers
Efficient vertical charge transport in polycrystalline halide perovskites revealed by four-dimensional tracking of charge carriers
A discrepancy exists between the low diffusion coefficients and near-unity charge collection efficiencies achieved in practical halide perovskite solar cells. Here, the authors explain this through the discovery of strong heterogeneity in vertical charge diffusivities in a 3D perovskite film.
- Changsoon Cho
- , Sascha Feldmann
- & Neil C. Greenham
-
Article |
 Dielectric control of reverse intersystem crossing in thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters
Dielectric control of reverse intersystem crossing in thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters
The role of the dielectric environment in thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) is not yet fully understood. Here the authors reveal the relevance of environment–emitter interactions in gating the reverse intersystem crossing and its particular relevance in dipolar TADF emitters.
- Alexander J. Gillett
- , Anton Pershin
- & David Beljonne
-
News & Views |
 Twistronics and the small-angle magic
Twistronics and the small-angle magic
Understanding, at the atomic level, the effect of the stacking and twisting of different layered two-dimensional materials is a major challenge for the future of twistronics. Optical excitations evidence twist-angle-dependent whirlpool-shaped distortions in such materials.
- Ado Jorio
-
Article
| Open Access Unconventional excitonic states with phonon sidebands in layered silicon diphosphide
Unconventional excitonic states with phonon sidebands in layered silicon diphosphide
Distinct electronic and optical properties emerge from quantum confinement in low-dimensional materials. Here, combining optical characterization and ab initio calculations, the authors report an unconventional excitonic state and bound phonon sideband in layered silicon diphosphide.
- Ling Zhou
- , Junwei Huang
- & Hongtao Yuan
-
News & Views |
 No free lunch for non-fullerene acceptors
No free lunch for non-fullerene acceptors
Non-fullerene acceptors have successfully overcome energy losses that were thought to be unavoidable in organic solar cells based on fullerene derivatives. However, it is now shown that they have limits too.
- Justin M. Hodgkiss
-
Article |
 Intrinsic efficiency limits in low-bandgap non-fullerene acceptor organic solar cells
Intrinsic efficiency limits in low-bandgap non-fullerene acceptor organic solar cells
A systematic analysis of a series of donor–acceptor organic blends shows that in solar cells based on low-bandgap non-fullerene acceptors an ionization energy offset of about 0.5 eV is required to ensure efficient charge separation.
- Safakath Karuthedath
- , Julien Gorenflot
- & Frédéric Laquai
-
Article |
 Insight into the effects of confined hydrocarbon species on the lifetime of methanol conversion catalysts
Insight into the effects of confined hydrocarbon species on the lifetime of methanol conversion catalysts
The methanol-to-hydrocarbons reaction on zeolites produces olefins from many sources, but catalyst stability is a major challenge. Here, by combining operando measurements and simulations, the formation and identification of deactivating carbonaceous species throughout the reaction are achieved.
- I. Lezcano-Gonzalez
- , E. Campbell
- & A. M. Beale
-
News & Views |
 Shaky lattices for light–matter interactions
Shaky lattices for light–matter interactions
Impulsive Raman spectroscopy reveals how atoms are pushed into action by light absorption. The surprising sensitivity of this behaviour to the polaronic character of 2D perovskites opens up new avenues for tailored light–matter interactions.
- Christoph Schnedermann
- , Akshay Rao
- & Philipp Kukura
-
Letter |
 Simultaneous coherence enhancement of optical and microwave transitions in solid-state electronic spins
Simultaneous coherence enhancement of optical and microwave transitions in solid-state electronic spins
Long coherence times in a subset of states that allows for transitions in both microwave and optical range have been reported using an isotopically purified 171Yb3+:Y2SiO5 crystal, rendering the system suitable for quantum information applications.
- Antonio Ortu
- , Alexey Tiranov
- & Mikael Afzelius
-
Article |
 Continuous-wave infrared optical gain and amplified spontaneous emission at ultralow threshold by colloidal HgTe quantum dots
Continuous-wave infrared optical gain and amplified spontaneous emission at ultralow threshold by colloidal HgTe quantum dots
Stimulated emission under continuous-wave excitation from mercury telluride quantum dots at very low thresholds (compatible with electrical injection) is achieved by exploiting surface traps that render the quantum dots into four-level systems.
- Pieter Geiregat
- , Arjan J. Houtepen
- & Zeger Hens
-
News & Views |
 Enhanced by organic surfaces
Enhanced by organic surfaces
Nanostructured films of organic semiconductors are now shown to enhance the Raman signal of probe molecules, paving the way to the realization of substrates for Raman spectroscopy with molecular selectivity.
- John R. Lombardi
-
News & Views |
 Pushing the knowledge of interfaces
Pushing the knowledge of interfaces
The use of a spectroscopy technique called pump–push–probe electro-absorption provides insight into the energetic landscape of nanostructured donor–acceptor interfaces in bulk-heterojunction organic solar cells.
- Natalie Banerji
-
Article |
 Visualizing excitations at buried heterojunctions in organic semiconductor blends
Visualizing excitations at buried heterojunctions in organic semiconductor blends
A pump–push–probe time-resolved technique is developed to characterize the dynamics of photoexcitations at buried, disordered interfaces. Applied to organic bulk heterojunctions, the method provides insight on charge separation in photovoltaic films.
- Andreas C. Jakowetz
- , Marcus L. Böhm
- & Richard H. Friend
-
News & Views |
 Slow recombination unveiled
Slow recombination unveiled
One of the most salient features of hybrid lead halide perovskites is the extended lifetime of their photogenerated charge carriers. This property has now been shown experimentally to originate from a slow, thermally activated recombination process.
- Jacques-E. Moser
-
Article |
 Direct–indirect character of the bandgap in methylammonium lead iodide perovskite
Direct–indirect character of the bandgap in methylammonium lead iodide perovskite
Time-resolved photo-conductance and microwave conductance investigations reveal that methylammonium lead iodide perovskites have an indirect bandgap at temperatures relevant to photovoltaic applications.
- Eline M. Hutter
- , María C. Gélvez-Rueda
- & Tom J. Savenije
-
News & Views |
 Strong absorption in stiff polymers
Strong absorption in stiff polymers
Greater rigidity of conjugated polymer backbones increases their light-harvesting ability, making them better performers in solar-cell applications.
- John Grey
-
News & Views |
 Probing quantum chaos
Probing quantum chaos
Giant Rydberg excitons reveal signatures of quantum chaotic behaviour in the presence of time-reversal symmetry breaking enforced by the background solid-state lattice, and they provide a new mesoscopic platform for fundamental studies of quantum chaos.
- Elena A. Ostrovskaya
- & Franco Nori
-
Letter |
 Ultrafast energy- and momentum-resolved dynamics of magnetic correlations in the photo-doped Mott insulator Sr2IrO4
Ultrafast energy- and momentum-resolved dynamics of magnetic correlations in the photo-doped Mott insulator Sr2IrO4
The dynamics of the magnetic correlations after photo-doping Sr2IrO4 are studied through ultrafast time-resolved resonant inelastic X-ray spectroscopy. The timescales are found to depend on the dimensionality of the correlations.
- M. P. M. Dean
- , Y. Cao
- & J. P. Hill
-
Article |
 Quantum chaos and breaking of all anti-unitary symmetries in Rydberg excitons
Quantum chaos and breaking of all anti-unitary symmetries in Rydberg excitons
Applying an external magnetic field to cuprous oxide causes the energy spacings in the exciton spectrum to transition from a Poissonian distribution to one governed by the Gaussian unitary ensemble statistics, revealing a signature of quantum chaos.
- Marc Aßmann
- , Johannes Thewes
- & Manfred Bayer
-
-
Article |
 Hydride formation thermodynamics and hysteresis in individual Pd nanocrystals with different size and shape
Hydride formation thermodynamics and hysteresis in individual Pd nanocrystals with different size and shape
The physicochemical properties of nanoparticles can sometimes prove difficult to characterize. Using plasmonic nanospectroscopy, hydride formation thermodynamics in individual Pd nanocrystals are found to be nearly size- and shape-independent.
- Svetlana Syrenova
- , Carl Wadell
- & Christoph Langhammer
-
News & Views |
 Ultrafast exciton dynamics
Ultrafast exciton dynamics
Time-resolved measurements of the exciton dynamics in tungsten diselenide monolayers reveal ultrafast radiative recombination of the exciton ground state (∼150 fs) and the interplay between optically bright and dark excitons.
- Xavier Marie
- & Bernhard Urbaszek
-
-
-
Correspondence |
 Optical excitation of thin magnetic layers in multilayer structures
Optical excitation of thin magnetic layers in multilayer structures
- A. R. Khorsand
- , M. Savoini
- & Th. Rasing
-
Correspondence |
 Reply to 'Optical excitation of thin magnetic layers in multilayer structures'
Reply to 'Optical excitation of thin magnetic layers in multilayer structures'
- A. Eschenlohr
- , M. Battiato
- & C. Stamm
-
-
News & Views |
 A little twist with big consequences
A little twist with big consequences
A study on the subtle interplay between electronic structure and structural defects now explains why the suppression of conduction in the insulating state of bilayer graphene is not as strong as might be expected. It also reveals the possibility of creating graphene-based nanoscale systems with unique electronic properties.
- Philip Hofmann
-
Correspondence |
 Measuring internal quantum efficiency to demonstrate hot exciton dissociation
Measuring internal quantum efficiency to demonstrate hot exciton dissociation
- Markus Scharber
-
Correspondence |
 Measuring internal quantum efficiency to demonstrate hot exciton dissociation
Measuring internal quantum efficiency to demonstrate hot exciton dissociation
- Ardalan Armin
- , Yuliang Zhang
- & Almantas Pivrikas
-
Correspondence |
 Reply to 'Measuring internal quantum efficiency to demonstrate hot exciton dissociation'
Reply to 'Measuring internal quantum efficiency to demonstrate hot exciton dissociation'
- G. Grancini
- , M. Binda
- & G. Lanzani
-
Article |
 Exploring electrolyte organization in supercapacitor electrodes with solid-state NMR
Exploring electrolyte organization in supercapacitor electrodes with solid-state NMR
Supercapacitors are electrochemical energy-storage devices that take advantage of electrostatic interactions between high-surface-area nanoporous electrodes and electrolyte ions. Molecular mechanisms at work inside supercapacitor carbon electrodes are now clarified with solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance.
- Michaël Deschamps
- , Edouard Gilbert
- & François Béguin
-
Letter |
 Experimental realization of optical lumped nanocircuits at infrared wavelengths
Experimental realization of optical lumped nanocircuits at infrared wavelengths
Lumped elements such as resistors, capacitors and inductors play a crucial role in electronic circuits. Now, inspired by metamaterials technology, the experimental realization of lumped circuit elements for optical frequencies provides a standardized platform for applications such as mixing and multiplexing of optical signals.
- Yong Sun
- , Brian Edwards
- & Nader Engheta
-
-
News & Views |
 Deep into the bulk
Deep into the bulk
The electronic structure in the bulk of a crystal can be unveiled by hard X-ray angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy.
- Dong-Lai Feng
-
Letter |
 Direct tomography with chemical-bond contrast
Direct tomography with chemical-bond contrast
Although X-ray tomography has proven to be an efficient tool for three-dimensional imaging, its application to light materials has not been too successful. A new X-ray spectroscopy tomography method has now been developed that allows the mapping of chemical bonding in various types of structures, as well as the imaging of soft materials in three dimensions.
- Simo Huotari
- , Tuomas Pylkkänen
- & Keijo Hämäläinen
-
Letter |
 Infrared-spectroscopic nanoimaging with a thermal source
Infrared-spectroscopic nanoimaging with a thermal source
Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy is a widely used spectroscopic technique, particularly for infrared wavelengths. However, for imaging applications the spatial resolution of FTIR spectrometers is restricted by the diffraction limit. The use of an FTIR spectrometer to pick up the low signal from scanning near-field optical microscopy employing thermal radiation now enables infrared imaging with nanoscale resolution.
- F. Huth
- , M. Schnell
- & R. Hillenbrand
-
News & Views |
 Shape the wave
Shape the wave
Tunnelling and capacitance spectroscopies are able to image the wavefunctions of electrons in atom-like solid-state systems as they are shaped by an external magnetic field.
- Massimo Rontani
-
Letter |
 Scanning tunnelling microscopy and spectroscopy of ultra-flat graphene on hexagonal boron nitride
Scanning tunnelling microscopy and spectroscopy of ultra-flat graphene on hexagonal boron nitride
Using boron nitride as a substrate for graphene has been suggested as a promising way to reduce the disorder in graphene caused by space fluctuations. It is now shown by scanning tunnelling microscopy that graphene conforms perfectly to boron nitride and the charge fluctuations are minimal compared with the conventionally used substrate, silica. Boron nitride could really be the natural graphene substrate.
- Jiamin Xue
- , Javier Sanchez-Yamagishi
- & Brian J. LeRoy

 Elementary excitations of single-photon emitters in hexagonal boron nitride
Elementary excitations of single-photon emitters in hexagonal boron nitride Tiny spectrometers
Tiny spectrometers Cationic vibrations
Cationic vibrations Trapped in a flat dispersion
Trapped in a flat dispersion Fretted diffusion
Fretted diffusion Rapid unfolding
Rapid unfolding