Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Shape memory in self-adapting colloidal crystals
Shape memory in self-adapting colloidal crystals
Preparing crystals held together with macromolecular bonds can create shape memory materials that can be engineered to exhibit a wide range of reversible changes useful for chemical sensing, optics and robotics.
- Seungkyu Lee
- , Heather A. Calcaterra
- & Chad A. Mirkin
-
Article
| Open Access Live-seq enables temporal transcriptomic recording of single cells
Live-seq enables temporal transcriptomic recording of single cells
Live-seq, a single-cell transcriptome profiling approach that preserves cell viability during RNA extraction using fluidic force microscopy, can address a range of biological questions by transforming scRNA-seq from an end-point to a temporal analysis approach.
- Wanze Chen
- , Orane Guillaume-Gentil
- & Bart Deplancke
-
Article |
 Imaging of isotope diffusion using atomic-scale vibrational spectroscopy
Imaging of isotope diffusion using atomic-scale vibrational spectroscopy
Vibrational electron energy-loss spectroscopy is used to distinguish two stable isotopes of carbon and to monitor their diffusion with subnanometre spatial resolution.
- Ryosuke Senga
- , Yung-Chang Lin
- & Kazu Suenaga
-
Article |
 De novo design of modular and tunable protein biosensors
De novo design of modular and tunable protein biosensors
A modular de novo designed biosensor platform consisting of a cage and key molecule is developed, and used to create sensors for seven distinct proteins including the spike protein from SARS-CoV-2 and anti-SARS antibodies.
- Alfredo Quijano-Rubio
- , Hsien-Wei Yeh
- & David Baker
-
Article |
 Spin-enhanced nanodiamond biosensing for ultrasensitive diagnostics
Spin-enhanced nanodiamond biosensing for ultrasensitive diagnostics
Lateral-flow in vitro diagnostic assays based on fluorescent nanodiamonds, in which microwave-based spin manipulation is used to increase sensitivity, are demonstrated using the biotin–avidin model and by the single-copy detection of HIV-1 RNA.
- Benjamin S. Miller
- , Léonard Bezinge
- & Rachel A. McKendry
-
Article |
 Reverse and forward engineering of Drosophila corneal nanocoatings
Reverse and forward engineering of Drosophila corneal nanocoatings
The building blocks of the nanostructures observed on Drosophila corneas are determined, and then used to create artificial nanostructures with anti-reflective and anti-adhesive properties.
- Mikhail Kryuchkov
- , Oleksii Bilousov
- & Vladimir L. Katanaev
-
Letter |
 Evolution of a designed protein assembly encapsulating its own RNA genome
Evolution of a designed protein assembly encapsulating its own RNA genome
Computationally designed icosahedral protein-based assemblies can protect their genetic material and evolve in biochemical environments, suggesting a route to the custom design of synthetic nanomaterials for non-viral drug delivery.
- Gabriel L. Butterfield
- , Marc J. Lajoie
- & David Baker
-
Letter |
 Gigadalton-scale shape-programmable DNA assemblies
Gigadalton-scale shape-programmable DNA assemblies
By using DNA sequence information to encode the shapes of DNA origami building blocks, shape-programmable assemblies can be created, with sizes and complexities similar to those of viruses.
- Klaus F. Wagenbauer
- , Christian Sigl
- & Hendrik Dietz
-
Letter |
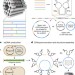 Biotechnological mass production of DNA origami
Biotechnological mass production of DNA origami
All necessary strands for DNA origami can be created in a single scalable process by using bacteriophages to generate single-stranded precursor DNA containing the target sequences interleaved with self-excising DNA enzymes.
- Florian Praetorius
- , Benjamin Kick
- & Hendrik Dietz
-
Letter |
 Molecular machines open cell membranes
Molecular machines open cell membranes
Rotary molecular machines, activated by ultraviolet light, are able to perturb and drill into cell membranes in a controllable manner, and more efficiently than those exhibiting flip-flopping or random motion.
- Víctor García-López
- , Fang Chen
- & James M. Tour
-
Letter |
 Nanoparticle biointerfacing by platelet membrane cloaking
Nanoparticle biointerfacing by platelet membrane cloaking
The authors report a new biomimetic nanodelivery platform in which polymeric nanoparticles enclosed in the plasma membrane of human platelets are used for disease-relevant targeting, and the therapeutic potential of the concept is demonstrated in animal models of coronary restenosis and systemic bacterial infection.
- Che-Ming J. Hu
- , Ronnie H. Fang
- & Liangfang Zhang
-
Letter |
 Shape-changing magnetic assemblies as high-sensitivity NMR-readable nanoprobes
Shape-changing magnetic assemblies as high-sensitivity NMR-readable nanoprobes
A shape-changing sensor made of pairs of magnetic disks spaced by swellable hydrogel material removes all need for optical access by operating in the nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) radio-frequency spectrum.
- G. Zabow
- , S. J. Dodd
- & A. P. Koretsky
-
Letter |
 Stochastic transport through carbon nanotubes in lipid bilayers and live cell membranes
Stochastic transport through carbon nanotubes in lipid bilayers and live cell membranes
Short carbon nanotubes spontaneously insert into lipid bilayers and live cell membranes to form channels with useful and tunable transport properties that make them a promising biomimetic nanopore platform for developing cell interfaces, studying nanofluidic transport in biological channels, and creating stochastic sensors.
- Jia Geng
- , Kyunghoon Kim
- & Aleksandr Noy
-
Letter |
 Structural and mechanistic insights into the bacterial amyloid secretion channel CsgG
Structural and mechanistic insights into the bacterial amyloid secretion channel CsgG
CsgG and CgsE form an encaging translocon for selective, iterative diffusion of curli subunits across the non-energized bacterial outer membrane.
- Parveen Goyal
- , Petya V. Krasteva
- & Han Remaut
-
Outlook |
 Nanotechnology: Deliver on a promise
Nanotechnology: Deliver on a promise
Effective treatment of cancer requires getting the drugs precisely to the target. Enter the nanoparticle.
- Jessica Wright
-
Outlook |
 Drug discovery: Leaving no stone unturned
Drug discovery: Leaving no stone unturned
New antibiotic treatments could be found by combining novel and existing drugs, in drug-free nanoparticles, or at the bottom of the sea.
- Katharine Gammon
-
Letter |
 Stabilizing the magnetic moment of single holmium atoms by symmetry
Stabilizing the magnetic moment of single holmium atoms by symmetry
Single magnetic atoms on non-magnetic surfaces have magnetic moments that are usually destabilized within a microsecond, too speedily to be useful, but here the magnetic moments of single holmium atoms on a highly conductive metallic substrate can reach lifetimes of the order of minutes.
- Toshio Miyamachi
- , Tobias Schuh
- & Wulf Wulfhekel
-
Letter |
 Nanometre-scale thermometry in a living cell
Nanometre-scale thermometry in a living cell
A nanoscale thermometry technique that uses coherent manipulation of the electronic spin associated with nitrogen–vacancy colour centres in diamond makes it possible to detect temperature variations as small as 1.8 millikelvin in ultrapure samples and to control and map temperature gradients within living cells.
- G. Kucsko
- , P. C. Maurer
- & M. D. Lukin
-
Research Highlights |
 Pulsating tubes act as pumps
Pulsating tubes act as pumps
-
News & Views |
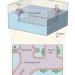 Blood vessels on a chip
Blood vessels on a chip
To understand how blood vessels form and function, scientists require reproducible systems that mimic living tissues. An innovative approach based on microfabricated vessels provides a key step towards this goal.
- Claudio Franco
- & Holger Gerhardt
-
Letter |
 Structured spheres generated by an in-fibre fluid instability
Structured spheres generated by an in-fibre fluid instability
Uniformly sized, structured spherical particles can be made in large quantities and across a wide range of sizes by an ingenious technique involving heating and drawing out multi-component fibres.
- Joshua J. Kaufman
- , Guangming Tao
- & Ayman F. Abouraddy
-
Research Highlights |
 Nanoparticles home in to clear clots
Nanoparticles home in to clear clots
-
Letter |
 SbsB structure and lattice reconstruction unveil Ca2+ triggered S-layer assembly
SbsB structure and lattice reconstruction unveil Ca2+ triggered S-layer assembly
Nanobody-aided X-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy are used to describe the Ca2+-dependent polymerization dynamics of the S-layer of the Geobacillus stearothermophilus cell wall.
- Ekaterina Baranova
- , Rémi Fronzes
- & Han Remaut
-
Research Highlights |
Radio remote control of genes
-
Research Highlights |
High-throughput cell stretcher
-
Research Highlights |
On-demand drug release
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 Nanostructure-enhanced atomic line emission
Nanostructure-enhanced atomic line emission
- M. Sivis
- , M. Duwe
- & C. Ropers
-
Letter |
 Patterning by controlled cracking
Patterning by controlled cracking
Propagating cracks—normally associated with material failure and viewed as undesirable—can be controlled in a film/substrate system, opening up new possibilities for nanofabrication and atomic-scale patterning.
- Koo Hyun Nam
- , Il H. Park
- & Seung Hwan Ko
-
News |
 Remote-controlled genes trigger insulin production
Remote-controlled genes trigger insulin production
Nanoparticles heated by radio waves switch on genes in mice
- Helen Shen
-
Research Highlights |
 Injectable protein nanofactories
Injectable protein nanofactories
-
News |
 Nanomaterials offer hope for cerebral palsy
Nanomaterials offer hope for cerebral palsy
Rabbits with brain injuries hop again after treatment with dendrimers.
- Amy Maxmen
-
Letter |
 Field-driven photoemission from nanostructures quenches the quiver motion
Field-driven photoemission from nanostructures quenches the quiver motion
Experiments using ultrafast mid-infrared light pulses on nanostructures access a new regime in photoelectron emission, revealing classical sub-cycle electron dynamics in optical near-fields and breaking a diffraction limit in strong-field physics.
- G. Herink
- , D. R. Solli
- & C. Ropers
-
News & Views |
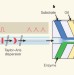 Analog-to-digital drug screening
Analog-to-digital drug screening
Current methods for screening libraries of compounds for biological activity are rather cumbersome, slow and imprecise. A method that breaks up a continuous flow of a compound's solution into droplets offers radical improvements.
- Robert C. R. Wootton
- & Andrew J. deMello
-
News Explainer |
 Say hello to intelligent pills
Say hello to intelligent pills
Digital system tracks patients from the inside out.
- Daniel Cressey
-
Article |
 A sensing array of radically coupled genetic ‘biopixels’
A sensing array of radically coupled genetic ‘biopixels’
Thousands of quorum-sensing Escherichia coli colonies are synchronized over centimetres using redox signalling to create ‘biopixels’ that can sense trace amounts of arsenic in water.
- Arthur Prindle
- , Phillip Samayoa
- & Jeff Hasty
-
Research Highlights |
 Recharge through the skin
Recharge through the skin
-
Letter |
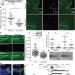 Lyn is a redox sensor that mediates leukocyte wound attraction in vivo
Lyn is a redox sensor that mediates leukocyte wound attraction in vivo
The Src family kinase Lyn is identified as a physiological redox sensor that mediates the initial attraction of leukocytes to wounds in zebrafish larvae.
- Sa Kan Yoo
- , Taylor W. Starnes
- & Anna Huttenlocher
-
News & Views |
 A molecular four-wheel drive
A molecular four-wheel drive
Nanoscale systems designed to imitate functions from the macroscopic world lead to a new appreciation of the complexity needed to actuate motion at the limits of miniaturization. A nanoscale 'car' is the latest example. See Letter p.208
- Paul S. Weiss
-
News |
 Draft guidelines for nanomedicine unveiled
Draft guidelines for nanomedicine unveiled
With hundreds of nanoproducts currently being tested in humans, recommendations aim to safeguard trial participants.
- Jessica Marshall
-
News |
 Nanoparticles hit tumours with one-two punch
Nanoparticles hit tumours with one-two punch
Using scout particles to pave the way makes drug delivery more effective.
- Corie Lok
-
Letter |
 Modular and predictable assembly of porous organic molecular crystals
Modular and predictable assembly of porous organic molecular crystals
- James T. A. Jones
- , Tom Hasell
- & Andrew I. Cooper
-
-
Research Highlights |
 Slip and slide pores for sensors
Slip and slide pores for sensors
-
Letter |
 Programming the magnitude and persistence of antibody responses with innate immunity
Programming the magnitude and persistence of antibody responses with innate immunity
Here it is shown that nanoparticles containing two Toll-like receptor ligands can boost the magnitude and persistence of vaccine-elicited antibody responses in primates, improving vaccine-mediated protection against influenza virus.
- Sudhir Pai Kasturi
- , Ioanna Skountzou
- & Bali Pulendran
-
News & Views |
 Peptides as biological semiconductors
Peptides as biological semiconductors
A simple peptide that assembles into desirable nanoscale structures is a striking example of how the whole can be greater than the sum of its parts. What's more, the assembly process is controllably reversible.
- Charlotte A. E. Hauser
- & Shuguang Zhang
-
Research Highlights |
Biophysics: DNA replication control
-
News & Views |
 Dark-hot resonances
Dark-hot resonances
The resonant behaviour of clusters of gold nanoparticles has been tuned by gradually bringing the particles together. The approach could have many applications, including chemical and biological sensing.
- Mark I. Stockman
-
News & Views |
 Beyond fluorescence
Beyond fluorescence
Nanoparticles that generate light through a mechanism known as second harmonic generation have been used to image live tissue. The particles overcome many problems associated with fluorescent probes for bioimaging.
- Bruce E. Cohen
-
News |
 Electron microscopy gets twisted
Electron microscopy gets twisted
Spiralling electron beams have the potential to measure and manipulate the properties of single atoms.
- Zeeya Merali

 A microfluidic transistor for automatic control of liquids
A microfluidic transistor for automatic control of liquids