Research Highlights |
Featured
-
-
-
-
Interview |
 Femtophotography
Femtophotography
A burst-mode camera developed in Japan called STAMP with a femtosecond frame rate could become a powerful tool for studying ultrafast dynamics. Nature Photonics asked Keiichi Nakagawa about the technique.
- Noriaki Horiuchi
-
News & Views |
 High-performance optics
High-performance optics
Developments in optical materials and components for extreme applications such as the James Webb Space Telescope and petawatt laser systems were showcased at CLEO 2014.
- David Pile
-
News & Views |
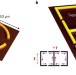 Superconductor photonics
Superconductor photonics
The fields of metamaterials and plasmonics are both set to benefit from the use of superconducting materials.
- Ranjan Singh
- & Nikolay Zheludev
-
Article |
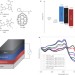 Ternary blend polymer solar cells with enhanced power conversion efficiency
Ternary blend polymer solar cells with enhanced power conversion efficiency
The use of two, rather than one, donor polymers in an organic solar cell is shown to enhance charge separation, transport and recombination.
- Luyao Lu
- , Tao Xu
- & Luping Yu
-
Article |
 Band filling with free charge carriers in organometal halide perovskites
Band filling with free charge carriers in organometal halide perovskites
Femtosecond transient absorption spectroscopy measurements indicate that the dominant relaxation pathway for excited states in perovskite materials is by recombination of free electrons and holes.
- Joseph S. Manser
- & Prashant V. Kamat
-
Article |
 Through-skull fluorescence imaging of the brain in a new near-infrared window
Through-skull fluorescence imaging of the brain in a new near-infrared window
Near-infrared photoluminescence from carbon nanotubes makes it possible to optically image the vasculature in the brain directly through the skull.
- Guosong Hong
- , Shuo Diao
- & Hongjie Dai
-
-
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
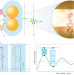 Watching a molecule breathe
Watching a molecule breathe
Marrying the single-molecule detection ability of surface-enhanced Raman scattering with the extreme time resolution of ultrafast coherent spectroscopy enables the vibrations of a single molecule to be observed.
- Lukasz Piatkowski
- , James T. Hugall
- & Niek F. van Hulst
-
Article |
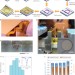 Integrated flexible chalcogenide glass photonic devices
Integrated flexible chalcogenide glass photonic devices
A suite of flexible, integrated, high-index-contrast chalcogenide glass photonic devices, including waveguides, microdisk resonators, add–drop filters and photonic crystals, is reported. The devices are demonstrated to survive repeated bending to a submillimetre radius without any significant degradation in their optical performance.
- Lan Li
- , Hongtao Lin
- & Juejun Hu
-
-
News & Views |
 Materials pushing solar
Materials pushing solar
Rapid developments in perovskite solar cells, photocatalysis and transparent conductors were showcased at the 2014 MRS Spring Meeting.
- David Pile
-
-
Article |
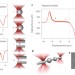 Shape-induced force fields in optical trapping
Shape-induced force fields in optical trapping
Through shaping of colloidal particles, optical traps with prescribed force–displacement profiles are generated and are used to design a microscopic constant-force spring capable of delivering a constant piconewton-scale restoring force for displacements of several micrometres. Potential future applications include the imaging of sensitive biological membranes.
- D. B. Phillips
- , M. J. Padgett
- & S. H. Simpson
-
Article |
 The influence of molecular orientation on organic bulk heterojunction solar cells
The influence of molecular orientation on organic bulk heterojunction solar cells
X-ray scattering experiments indicate that the molecular orientation at the interfaces of bulk heterojunction organic solar cells influences the cells’ fill factor and short-circuit current.
- John R. Tumbleston
- , Brian A. Collins
- & Harald Ade
-
-
News & Views |
 Phosphorescence meets its match
Phosphorescence meets its match
The advent of novel fluorophores that harness thermally activated energy transfer processes is resulting in a new breed of highly efficient organic light-emitting diodes.
- Sebastian Reineke
-
Article |
 Efficient blue organic light-emitting diodes employing thermally activated delayed fluorescence
Efficient blue organic light-emitting diodes employing thermally activated delayed fluorescence
Blue organic light-emitting diodes that harness thermally activated delayed fluorescence are realized with an external quantum efficiency of 19.5% and reduced roll-off at high luminance.
- Qisheng Zhang
- , Bo Li
- & Chihaya Adachi
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Editorial |
 The significance of research
The significance of research
When promoting the value of their research or procuring funding, researchers often need to explain the significance of their work to the community — something that can be just as tricky as the research itself.
-
News & Views |
 Perovskite cells roll forward
Perovskite cells roll forward
Reports of perovskite solar cells fabricated at temperatures compatible with polymer substrates indicate that high-performance flexible cells are now an exciting proposition. However, increasing the cell area and stability and addressing environmental concerns are aspects requiring attention.
- Gary Hodes
- & David Cahen
-
Review Article |
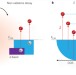 Plasmon-induced hot-electron generation at nanoparticle/metal-oxide interfaces for photovoltaic and photocatalytic devices
Plasmon-induced hot-electron generation at nanoparticle/metal-oxide interfaces for photovoltaic and photocatalytic devices
Optical generation of hot electrons in metallic structures and its potential as an alternative to conventional electron–hole separation in semiconductor devices are reviewed. The possibilities for realizing high conversion efficiencies with low fabrication costs are discussed along with challenges in terms of the materials, architectures and fabrication methods
- César Clavero
-
-
-
Article |
 Perovskite solar cells with a planar heterojunction structure prepared using room-temperature solution processing techniques
Perovskite solar cells with a planar heterojunction structure prepared using room-temperature solution processing techniques
The use of a thin layer of zinc oxide nanoparticles as an electron-transport layer allows flexible perovskite solar cells to be fabricated with a power conversion efficiency as high as 15.7%.
- Dianyi Liu
- & Timothy L. Kelly
-
Letter |
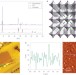 Perovskite solar cells employing organic charge-transport layers
Perovskite solar cells employing organic charge-transport layers
Highly efficient perovskite solar cells have been fabricated by using room-temperature deposition processes. The cells are based on a layer of methylammonium lead iodide perovskite that is prepared by sublimation in a high-vacuum chamber and sandwiched between two thin organic charge-transport layers.
- Olga Malinkiewicz
- , Aswani Yella
- & Henk J. Bolink
-
Letter |
 Tunable lifetime multiplexing using luminescent nanocrystals
Tunable lifetime multiplexing using luminescent nanocrystals
Control over the luminescence lifetimes of upconversion nanocrystals allows a new form of temporal multiplexing for imaging and data-storage applications.
- Yiqing Lu
- , Jiangbo Zhao
- & Dayong Jin
-
Article |
 Triplet–triplet exciton dynamics in single-walled carbon nanotubes
Triplet–triplet exciton dynamics in single-walled carbon nanotubes
Little is known about triplet excitons in semiconducting single-walled nanotubes, despite their importance in various applications. The pump–probe and spin-sensitive photoluminescence of such nanotubes is studied, and the quantum yield of triplet formation, triplet lifetime and triplet exciton size are found to be 5 ± 2%, 30 ± 10 µs and 0.65 nm, respectively.
- Dominik Stich
- , Florian Späth
- & Tobias Hertel
-
-
News & Views |
 Catalysing artificial photosynthesis
Catalysing artificial photosynthesis
Efficient photocatalytic splitting of water to realize carbon-free production of hydrogen from sunlight remains a challenge. New precious-metal-free molecular catalysts in semiconductor-based, visible-light-driven water-splitting systems are promising for realizing practical artificial photosynthesis.
- Samuel S. Mao
- & Shaohua Shen
-
News & Views |
 On-chip synthetic magnetic field
On-chip synthetic magnetic field
The experimental observation of topologically protected photonic edge transport in a silicon chip paves the way to realizing unprecedented control of light using synthetic magnetic fields and opens up new approaches for optical information processing.
- A. B. Khanikaev
-
Letter |
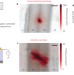 Photocurrent generation in semiconducting and metallic carbon nanotubes
Photocurrent generation in semiconducting and metallic carbon nanotubes
Clear evidence is presented for the origins of photocurrent generation in metallic and semiconducting carbon nanotubes — photocurrent is found to be mainly generated by photothermal and photovoltaic effects in metallic and semiconducting carbon nanotubes, respectively. This finding will enable the engineering of highly efficient carbon-based photodetectors and energy-harvesting devices.
- Maria Barkelid
- & Val Zwiller
-
Article |
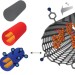 Giant Raman scattering from J-aggregated dyes inside carbon nanotubes for multispectral imaging
Giant Raman scattering from J-aggregated dyes inside carbon nanotubes for multispectral imaging
The use of Raman spectroscopy for high-resolution optical imaging is severely limited by the inherent weakness of the Raman effect. Now, a giant resonant Raman effect is demonstrated from J-aggregated dye molecules encapsulated in single-walled carbon nanotubes, and it is used to realize multispectral Raman imaging.
- E. Gaufrès
- , N. Y.-Wa Tang
- & R. Martel
-
Letter |
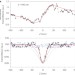 Multiphoton absorption in amyloid protein fibres
Multiphoton absorption in amyloid protein fibres
Two-, three- and higher multiphoton absorption processes are shown to occur in amyloid protein fibres, which are thought to play a role in various diseases, including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. The nonlinear optical behaviour of such proteins may also be useful for fabricating photonics devices.
- Piotr Hanczyc
- , Marek Samoc
- & Bengt Norden
-
News & Views |
 Implantable waveguides
Implantable waveguides
The development of hydrogel patches that both guide light and accommodate optogenetic cells could usher in a new breed of implantable systems for in-body optical sensing and therapy.
- Edward A. Sykes
- , Alexandre Albanese
- & Warren C. W. Chan
-
Article |
 Imaging topological edge states in silicon photonics
Imaging topological edge states in silicon photonics
Topological edge states of light are observed in a two-dimensional array of coupled optical ring resonators, which induce a virtual magnetic field for photons using silicon-on-insulator technology. The edge states are experimentally demonstrated to be robust against intrinsic and introduced disorder, which is a hallmark of topological order.
- M. Hafezi
- , S. Mittal
- & J. M. Taylor
-
Article |
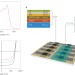 Transparent polymer solar cells employing a layered light-trapping architecture
Transparent polymer solar cells employing a layered light-trapping architecture
Transparent polymer solar cells are demonstrated that can transmit 30% of visible light and operate with a power conversion efficiency of 5.6%. The cells employ photonic crystals to trap ultraviolet and infrared light.
- Rafael Betancur
- , Pablo Romero-Gomez
- & Jordi Martorell
-
-

 Phase-changing pixels
Phase-changing pixels Revealing water's secrets
Revealing water's secrets Photonic sugar detector
Photonic sugar detector Trapping single atoms
Trapping single atoms Self-assembled fibres
Self-assembled fibres Bridging the visible
Bridging the visible