Featured
-
-
-
-
Article |
 Colloidal-quantum-dot photovoltaics using atomic-ligand passivation
Colloidal-quantum-dot photovoltaics using atomic-ligand passivation
Organic ligands enhance the stability and the solution processability of semiconductor quantum dots, but they can impede charge transport in films of such nanoparticles. Passivation with atomic ligands now offers an alternative strategy that enables the fabrication of PbS colloidal-quantum-dot solar cells with power-conversion efficiencies of up to 6%.
- Jiang Tang
- , Kyle W. Kemp
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
-
Letter |
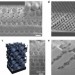 Epitaxial growth of three-dimensionally architectured optoelectronic devices
Epitaxial growth of three-dimensionally architectured optoelectronic devices
Three-dimensional photonic devices are of interest as light emitters, detectors or waveguides. However, so far their fabrication has remained a challenge. The template-directed epitaxy of three-dimensional semiconductor structures now offers a new strategy for the realization of photonic devices, demonstrated by the realization of a three-dimensional photonic crystal light-emitting diode.
- Erik C. Nelson
- , Neville L. Dias
- & Paul V. Braun
-
News & Views |
 Hydrogen caught red-faced
Hydrogen caught red-faced
A single nanodevice that detects the presence of a single molecule would perhaps be the ultimate sensor. The demonstration of hydrogen sensing based on a single gold nanoaerial brings that possibility nearer.
- Roy Sambles
-
News & Views |
 Neither solid nor liquid
Neither solid nor liquid
A new design for elastic metamaterials that can behave either as liquids or solids over a limited frequency range may enable new applications based on the control of acoustic, elastic and seismic waves.
- John Page
-
Letter |
 Tailoring hot-exciton emission and lifetimes in semiconducting nanowires via whispering-gallery nanocavity plasmons
Tailoring hot-exciton emission and lifetimes in semiconducting nanowires via whispering-gallery nanocavity plasmons
Typically, the light-emission of semiconductors always occurs from thermalized electrons, as electrons excited above the bandgap energy relax quickly. In contrast, non-thermalized excitonic light emission has now been observed in nanowires using resonant plasmonic nanocavities. The much higher radiative light-emission rates of the hot excitons suggest their use for ultrafast nanophotonic devices.
- Chang-Hee Cho
- , Carlos O. Aspetti
- & Ritesh Agarwal
-
Letter |
 Arrays of indefinitely long uniform nanowires and nanotubes
Arrays of indefinitely long uniform nanowires and nanotubes
Nanowires have many applications across a number of disciplines. So far, their length has been largely limited to mesoscale dimensions. Through the adaption of an iterative fibre-drawing process it is now possible to fabricate millions of ordered nanowires and nanotubes of almost infinite length.
- Mecit Yaman
- , Tural Khudiyev
- & Mehmet Bayindir
-
Letter |
 Dirac cones induced by accidental degeneracy in photonic crystals and zero-refractive-index materials
Dirac cones induced by accidental degeneracy in photonic crystals and zero-refractive-index materials
Materials with zero refractive index show unusual waveguiding properties and, for example, can squeeze light through narrow passages. It is now suggested that such properties can also be realized in a non-metallic photonic crystal. Furthermore, such photonic crystals can also show a Dirac point in the band structure—offering further possibilities, such as guiding waves unperturbed around bends and obstacles.
- Xueqin Huang
- , Yun Lai
- & C. T. Chan
-
Article |
 Nanoantenna-enhanced gas sensing in a single tailored nanofocus
Nanoantenna-enhanced gas sensing in a single tailored nanofocus
Plasmonic resonances are widely used for sensing applications. The plasmon resonance of a single nanoantenna structure is now used to detect changes in the dielectric properties of a nearby palladium nanoparticle exposed to hydrogen gas, enabling highly sensitive sensing in ultrasmall volumes. The approach can be easily extended to other sensing and catalysis schemes.
- Na Liu
- , Ming L. Tang
- & A. Paul Alivisatos
-
Letter |
 Localized surface plasmon resonances arising from free carriers in doped quantum dots
Localized surface plasmon resonances arising from free carriers in doped quantum dots
Plasmonic resonances are often associated with metals, but can also be realized in semiconductors. The observation of plasmon resonances at near-infrared wavelengths in semiconductor quantum dots in particular, offers the possibility to actively control plasmonic properties through quantum-size effects within the dots.
- Joseph M. Luther
- , Prashant K. Jain
- & A. Paul Alivisatos
-
Article |
 An octave-bandwidth negligible-loss radiofrequency metamaterial
An octave-bandwidth negligible-loss radiofrequency metamaterial
Metamaterials show many intriguing properties, which are often limited to a narrow range of frequencies. The demonstration of a low-loss broadband metamaterial at radiofrequencies promises applications as enhanced antennas, for example.
- Erik Lier
- , Douglas H. Werner
- & Jeremy A. Bossard
-
Letter |
 Room-temperature sub-diffraction-limited plasmon laser by total internal reflection
Room-temperature sub-diffraction-limited plasmon laser by total internal reflection
Plasmon lasers can operate at dimensions well below the diffraction limit. Their small size promises uses in nanophotonic circuits and for other size-critical applications. The demonstration of a sub-diffraction-limited plasmon laser with low losses, which enables its room-temperature operation, takes a significant step towards realizing the potential of these lasers.
- Ren-Min Ma
- , Rupert F. Oulton
- & Xiang Zhang
-
News & Views |
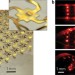 Tiny lamps to illuminate the body
Tiny lamps to illuminate the body
Biocompatible light-emitting structures based on high-performance inorganic compound semiconductors on flexible substrates open the path to futuristic therapeutic devices, instrumented surgical gloves and many other applications.
- Takao Someya
-
Article |
 Waterproof AlInGaP optoelectronics on stretchable substrates with applications in biomedicine and robotics
Waterproof AlInGaP optoelectronics on stretchable substrates with applications in biomedicine and robotics
Flexible electronic devices that can be stretched without losing performance have seen increasing functionality. In particular, the demonstration of light-emitting diodes and photodetectors on flexible electronic substrates now opens the door to applications of flexible optoelectronic sheets in biomedicine and robotics.
- Rak-Hwan Kim
- , Dae-Hyeong Kim
- & John A. Rogers
-
Article |
 Exciton antennas and concentrators from core–shell and corrugated carbon nanotube filaments of homogeneous composition
Exciton antennas and concentrators from core–shell and corrugated carbon nanotube filaments of homogeneous composition
Using optical antennas in optoelectronic devices could lead to improved device performance. Photoemission from the inner core of core–shell single-walled nanotube structures where the optical bandgap of the core is smaller than that of the outer shells demonstrates that these structures channel excitons thereby acting as optical concentrators.
- Jae-Hee Han
- , Geraldine L. C. Paulus
- & Michael S. Strano
-
Review Article |
 The Fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials
The Fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials
- Boris Luk'yanchuk
- , Nikolay I. Zheludev
- & Chong Tow Chong
-
Article |
 Photon-enhanced thermionic emission for solar concentrator systems
Photon-enhanced thermionic emission for solar concentrator systems
The conversion of solar energy into electricity usually occurs either electrically or through thermal conversion. A new mechanism, photon-enhanced thermionic emission, which combines electric as well as thermal conversion mechanisms, is now shown to lead to enhanced conversion efficiencies that potentially could even exceed the theoretical limits of conventional photovoltaic cells.
- Jared W. Schwede
- , Igor Bargatin
- & Nicholas A. Melosh
-
Letter |
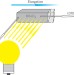 Light-induced size changes in BiFeO3 crystals
Light-induced size changes in BiFeO3 crystals
In magnetoelectric compounds, magnetism and ferroelectricity are coupled. The observation of light-induced size changes in the room-temperature magnetoelectric BiFeO3 now adds optical functionality to magnetoelectric devices that may lead to new applications arising from the coupling of light, electric and magnetic fields.
- B. Kundys
- , M. Viret
- & D. O. Kundys
-
News & Views |
 Enlightened organic transistors
Enlightened organic transistors
Organic light-emitting field-effect transistors surpass the external quantum efficiency of analogous organic light-emitting diodes.
- Christian Melzer
- & Heinz von Seggern
-
Article |
 Organic light-emitting transistors with an efficiency that outperforms the equivalent light-emitting diodes
Organic light-emitting transistors with an efficiency that outperforms the equivalent light-emitting diodes
An organic light-emitting transistor has now been fabricated with a trilayer heterostructure. This architecture is shown to prevent both photon loss at the electrodes and exciton-charge quenching, thereby dramatically improving device efficiency and establishing these types of transistor as a promising alternative to organic light-emitting diodes.
- Raffaella Capelli
- , Stefano Toffanin
- & Michele Muccini
-
Editorial |
 Fifty brilliant years
Fifty brilliant years
The first demonstration of the laser has not only led to a myriad of commercial applications, but fifty years on basic research continues to rejuvenate the fundamental physics of the laser.
-
Interview |
 From the maser to the laser
From the maser to the laser
Charles Townes played a crucial role in the invention and realization of the first masers and lasers, for which he shared the 1964 Nobel Prize in Physics. Nature Materials speaks to him about his historic contributions.
- Joerg Heber
-
Interview |
 Coherence comes full circle
Coherence comes full circle
Coherent synchrotron radiation has revolutionized the study of molecules and materials. Talking to Nature Materials, Gerhard Materlik, CEO of the Diamond Light Source, discusses the many uses of synchrotron sources and free electron lasers.
- Joerg Heber
-
Interview |
 The staircase to flexibility
The staircase to flexibility
The quantum cascade laser has liberated laser properties from materials limitations, enabling light emission to be tailored over a broad spectral range. Nature Materials talks to Federico Capasso about the development of these lasers in his laboratory.
- Joerg Heber
-
Interview |
 The rise of the laser
The rise of the laser
It was the realization of semiconductor lasers that led to the commercial success of lasers. Herbert Kroemer explains to Nature Materials his contributions to the design principle of these lasers, for which he shared the 2000 Nobel Prize in Physics.
- Joerg Heber
-
Review Article |
 Transformation optics and metamaterials
Transformation optics and metamaterials
Transformation optics describes the capability to design the path of light waves almost at will through the use of metamaterials that control effective materials properties on a subwavelength scale. In this review, the physics and applications of transformation optics are discussed.
- Huanyang Chen
- , C. T. Chan
- & Ping Sheng
-
Letter |
 A single-layer wide-angle negative-index metamaterial at visible frequencies
A single-layer wide-angle negative-index metamaterial at visible frequencies
So far, the realization of negative-refractive-index materials has required the use of resonating metallic structures, leading to an inherently narrowband operation around those resonances. Here, negative-refractive-index materials are proposed that consist of single coaxial waveguide layers, with a negative refractive index at a broad range of visible wavelengths.
- Stanley P. Burgos
- , Rene de Waele
- & Harry A. Atwater
-
Editorial |
 A small world full of opportunities
A small world full of opportunities
Light-concentration effects in photonic nanostructures, reviewed in this issue, promise new applications ranging from tumour therapy to catalysis and enhanced solar cells.
-
News & Views |
 Ferromagnets stirred up
Ferromagnets stirred up
Conflicting observations of the speed at which various ferromagnetic materials respond to an external femtosecond laser excitation have generated considerable controversy. It is now shown that ferromagnets can be divided in two categories, according to the values of specific magnetic parameters.
- Markus G. Münzenberg
-
Review Article |
 Plasmonics for extreme light concentration and manipulation
Plasmonics for extreme light concentration and manipulation
Plasmonic structures are ideally suited to manipulate light on a scale that is much smaller than the wavelength of the plasmon resonance. This review discusses the applications arising from such extreme light concentration, which range from photonic devices and photovoltaics to localized thermal effects.
- Jon A. Schuller
- , Edward S. Barnard
- & Mark L. Brongersma
-
Review Article |
 Plasmonics for improved photovoltaic devices
Plasmonics for improved photovoltaic devices
This review article surveys the potential of using plasmonic nanostructures to enhance the absorption of photovoltaic devices. As a result, the physical thickness of solar cells can be reduced, leading to new photovoltaic-device designs.
- Harry A. Atwater
- & Albert Polman
-
News & Views |
 Defects dictated
Defects dictated
Stable particle-like molecular architectures are written in a frustrated chiral-nematic liquid crystal using a vortex laser beam. This fundamentally new mechanism to form toroidal features with anisotropic optical properties has great potential to create new applications in liquid-crystal photonics.
- Dirk J. Broer
-
News & Views |
 Electrifying plasmonics on silicon
Electrifying plasmonics on silicon
The realization of electrical sources of surface plasmon polaritons using complementary metal oxide semiconductor technology is a significant step towards silicon-compatible nanoscale photonic devices.
- Aaron Hryciw
- , Young Chul Jun
- & Mark L. Brongersma
-
Editorial |
 Applied research deserves Nobel prizes
Applied research deserves Nobel prizes
Nobel prizes for applied research provide recognition for innovations with profound impact, fully in tune with the intentions of Alfred Nobel.

 Optical negative refraction by four-wave mixing in thin metallic nanostructures
Optical negative refraction by four-wave mixing in thin metallic nanostructures