Research Briefing |
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Scalar topological photonic nested meta-crystals and skyrmion surface states in the light cone continuum
Scalar topological photonic nested meta-crystals and skyrmion surface states in the light cone continuum
Employing connected coaxial waveguides on a nested meta-crystal configuration, the authors design photonic crystals with scalar-wave-like band dispersions, facilitating the search for topological phases in three-dimensional photonic crystals.
- Biao Yang
- , Qinghua Guo
- & C. T. Chan
-
News & Views |
 Writing above the bandgap
Writing above the bandgap
Above-bandgap, nanosecond laser pulses enable the localized in situ writing of spin defects in prefabricated nanophotonic cavities. The approach preserves defect and cavity mode properties, key requirements towards cavity–emitter coupling in quantum networks.
- Sridhar Majety
- & Marina Radulaski
-
Article |
 Strongly enhanced light–matter coupling of monolayer WS2 from a bound state in the continuum
Strongly enhanced light–matter coupling of monolayer WS2 from a bound state in the continuum
Combining a tungsten disulfide monolayer and a topologically protected bound state in the continuum formed by a one-dimensional photonic crystal, strong light–matter interaction enhancement and large exciton–polariton nonlinearities at room temperature are demonstrated.
- Eugenio Maggiolini
- , Laura Polimeno
- & Dario Ballarini
-
Letter |
 Laser writing of spin defects in nanophotonic cavities
Laser writing of spin defects in nanophotonic cavities
Using direct laser writing with a nanosecond pulsed laser operating at above-bandgap photon energies, we demonstrate the selective formation of spin defects in photonic crystal cavities in 4H-silicon carbide and their in situ characterization.
- Aaron M. Day
- , Jonathan R. Dietz
- & Evelyn L. Hu
-
Letter |
 Scalable optical manufacture of dynamic structural colour in stretchable materials
Scalable optical manufacture of dynamic structural colour in stretchable materials
Desired for optical sensing or visual communications, structural colour-changing materials are hindered by the lack of scalable manufacturing. Here, by adapting Lippmann photography, large-area manufacturing of colour patterns in photosensitive elastomers is realized.
- Benjamin Harvey Miller
- , Helen Liu
- & Mathias Kolle
-
Article |
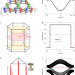 Higher-order topological semimetal in acoustic crystals
Higher-order topological semimetal in acoustic crystals
A second-order topological Weyl semimetal based on a 3D-printed acoustic crystal, exhibiting Weyl points, Fermi arc surface states, and hinge states, has been experimentally demonstrated.
- Qiang Wei
- , Xuewei Zhang
- & Suotang Jia
-
News & Views |
 Electroshock tuning of photonic crystals
Electroshock tuning of photonic crystals
Photonic crystals with optical bandgaps across the entire visible spectrum are generated by reconfiguring three-dimensional blue phase liquid crystalline lattices into long-lived metastable non-cubic structures using sequences of electric pulses.
- Slobodan Žumer
-
Article |
 Reconfiguration of three-dimensional liquid-crystalline photonic crystals by electrostriction
Reconfiguration of three-dimensional liquid-crystalline photonic crystals by electrostriction
Repetitive electrical pulse stimulation of blue-phase liquid crystals promotes their reconfiguration into stable non-cubic structures with promising electro-optical responses for display technologies.
- Duan-Yi Guo
- , Chun-Wei Chen
- & Tsung-Hsien Lin
-
News & Views |
 Lasers that shine brighter
Lasers that shine brighter
A photonic crystal design, consisting of two separated lattices arranged in a specific way, forms the base of high-brightness semiconductor lasers, with a very narrow beam divergence angle.
- L. Kuipers
-
Article |
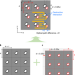 Double-lattice photonic-crystal resonators enabling high-brightness semiconductor lasers with symmetric narrow-divergence beams
Double-lattice photonic-crystal resonators enabling high-brightness semiconductor lasers with symmetric narrow-divergence beams
An optimized design for a broad-area surface-emitting photonic-crystal laser leads to high brightness of over 300 MW cm–2 sr–1 and an output power of 10 W under pulsed excitation.
- Masahiro Yoshida
- , Menaka De Zoysa
- & Susumu Noda
-
News & Views |
 Electrifying quantum dots for lasers
Electrifying quantum dots for lasers
Compositional grading of colloidal quantum dots enables electrically driven amplification of light, bringing electrically driven lasers from these materials very close.
- Ifor Samuel
-
Letter |
 Valley photonic crystals for control of spin and topology
Valley photonic crystals for control of spin and topology
A theoretically proposed photonic crystal design with valley-dependent spin-split bulk bands allows for the independent control of valley and topology in a single system.
- Jian-Wen Dong
- , Xiao-Dong Chen
- & Xiang Zhang
-
News & Views |
 Ultrafast dynamic control
Ultrafast dynamic control
Control of thermal emission with microsecond switching times has been achieved by using sub-band transitions in composite quantum-well and photonic-crystal structures.
- Ognjen Ilic
- & Marin Soljačić
-
Letter |
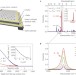 Realization of dynamic thermal emission control
Realization of dynamic thermal emission control
The dynamic control of thermal emission via the control of emissivity through intersubband absorption in n-type quantum wells, at a speed four orders of magnitude faster than is currently possible, is now demonstrated.
- Takuya Inoue
- , Menaka De Zoysa
- & Susumu Noda
-
Letter |
 Stretchable liquid-crystal blue-phase gels
Stretchable liquid-crystal blue-phase gels
Liquid-crystalline elastomers combine rubber-like elasticity with the optical properties of liquid crystals, yet some of their properties depend on the particular liquid-crystal phase. Now, stretchable gels of the liquid-crystalline blue-phase I are reported. The blue-phase gels are electro-optically switchable under a moderate applied voltage, and their optical properties can be manipulated by an applied strain.
- F. Castles
- , S. M. Morris
- & H. J. Coles
-
Article |
 Engineering of light confinement in strongly scattering disordered media
Engineering of light confinement in strongly scattering disordered media
Disordered photonic materials have the ability to control the flow of light through random multiple scattering. This has the drawback of randomizing both the direction and phase of the propagating light. Now, confined and interacting light modes are demonstrated for a two-dimensional disordered photonic structure.
- Francesco Riboli
- , Niccolò Caselli
- & Diederik S. Wiersma
-
Article |
 The in vivo activation of persistent nanophosphors for optical imaging of vascularization, tumours and grafted cells
The in vivo activation of persistent nanophosphors for optical imaging of vascularization, tumours and grafted cells
The use of persistent luminescence nanoparticles for in vivo optical imaging commonly requires ex vivo activation before systemic administration, hampering longer-term imaging capabilities. Now, it is shown that near-infrared emitting nanoprobes based on chromium-doped zinc gallate can be activated in vivo using low-energy red light and used for tumour-targeted imaging and cell tracking experiments.
- Thomas Maldiney
- , Aurélie Bessière
- & Cyrille Richard
-
Article |
 Movable high-Q nanoresonators realized by semiconductor nanowires on a Si photonic crystal platform
Movable high-Q nanoresonators realized by semiconductor nanowires on a Si photonic crystal platform
Confining light in subwavelength nanowires has posed a challenge to harnessing their potential for integrated photonic devices. Now, it is shown that a high-Q cavity can be achieved by placing a single nanowire into a groove in a photonic crystal resonator.
- Muhammad Danang Birowosuto
- , Atsushi Yokoo
- & Masaya Notomi
-
Article |
 Observation of unconventional edge states in ‘photonic graphene’
Observation of unconventional edge states in ‘photonic graphene’
The propagation of light in photonic crystals with a honeycomb structure mirrors the behaviour of charges in graphene, therefore allowing for the investigation of electronic properties that cannot otherwise be accessed in graphene itself. This approach is now used to predict unexpected edge states that localize in the bearded edges of hexagonal lattices.
- Yonatan Plotnik
- , Mikael C. Rechtsman
- & Mordechai Segev
-
Commentary |
 Unidirectional light propagation at exceptional points
Unidirectional light propagation at exceptional points
Unique opportunities arise from exceptional points that coalesce states of an open system in synthetic photonic media, where delicately balanced complex dielectric functions produce unprecedented optical properties.
- Xiaobo Yin
- & Xiang Zhang
-
News & Views |
 Sustainable sensors from silk
Sustainable sensors from silk
A biocompatible method for fabricating three-dimensional photonic crystals opens up unique opportunities for structurally coloured biodegradable materials, but also for implantable biosensing and targeted therapeutics on the microscale.
- Jennifer MacLeod
- & Federico Rosei
-
Editorial |
 Early lights
Early lights
This year marks a quarter of a century since the birth of photonic crystals. Overcoming early difficulties, the field has made a range of technological developments possible as well as the emergence of new science at the interface between condensed-matter physics and photonics.
-
Interview |
 In the limelight
In the limelight
Twenty five years since the birth of the field of photonic crystals, Eli Yablonovitch talks to Nature Materials about his pioneering contributions to the field and his vision for nanophotonics.
- Kosmas Tsakmakidis
-
Commentary |
 Why trap light?
Why trap light?
The field of photonic crystals has become one of the most influential and wide-ranging realms of contemporary electromagnetics and optics, with numerous more opportunities on the horizon.
- Sajeev John
-
Article |
 Second-harmonic generation in silicon waveguides strained by silicon nitride
Second-harmonic generation in silicon waveguides strained by silicon nitride
Photonic devices on silicon offer the benefit of combining advanced electronic functionality with the high bandwidth of silicon photonics. Now, efficient second-order nonlinear activity in silicon waveguides strained by a silicon nitride top layer considerably advances the potential of all-optical data management on a silicon platform.
- M. Cazzanelli
- , F. Bianco
- & L. Pavesi
-
Letter |
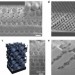 Epitaxial growth of three-dimensionally architectured optoelectronic devices
Epitaxial growth of three-dimensionally architectured optoelectronic devices
Three-dimensional photonic devices are of interest as light emitters, detectors or waveguides. However, so far their fabrication has remained a challenge. The template-directed epitaxy of three-dimensional semiconductor structures now offers a new strategy for the realization of photonic devices, demonstrated by the realization of a three-dimensional photonic crystal light-emitting diode.
- Erik C. Nelson
- , Neville L. Dias
- & Paul V. Braun
-
Letter |
 Dirac cones induced by accidental degeneracy in photonic crystals and zero-refractive-index materials
Dirac cones induced by accidental degeneracy in photonic crystals and zero-refractive-index materials
Materials with zero refractive index show unusual waveguiding properties and, for example, can squeeze light through narrow passages. It is now suggested that such properties can also be realized in a non-metallic photonic crystal. Furthermore, such photonic crystals can also show a Dirac point in the band structure—offering further possibilities, such as guiding waves unperturbed around bends and obstacles.
- Xueqin Huang
- , Yun Lai
- & C. T. Chan

 Scalar photonic crystals with non-radiative topological surface modes
Scalar photonic crystals with non-radiative topological surface modes