Featured
-
-
News & Views |
The importance of peritoneal catheter exit-site care
The risk of peritonitis associated with infections of the peritoneal catheter exit site can be reduced by the use of proper exit-site care, such as the routine administration of prophylactic antibiotics at the exit site. Studies that demonstrate the efficacy of such an approach or similar approaches continue to be published.
- Beth Piraino
-
News & Views |
 Kidney biopsy and HIV: weighing the risks and benefits
Kidney biopsy and HIV: weighing the risks and benefits
Results of a recent case–control study confirm that HIV positivity is far from a contraindication for performing a kidney biopsy. Nevertheless, this procedure is not without risk of complications, and, regardless of HIV status, the decision of whether to perform it must be made keeping in mind the therapeutic benefits the individual patient is likely to obtain.
- Zygimantas C. Alsauskas
- & Jonathan Winston
-
Case Study |
 A case of lactic acidosis induced by linezolid
A case of lactic acidosis induced by linezolid
This article reports the case of a 36-year-old man on hemodialysis who presented to an intensive care unit with a large serum anion gap and symptoms such as hypotension and an altered mental state. For the previous 6 weeks, he had received linezolid to treat vancomycin-resistant bacteremia. Discontinuation of linezolid led to resolution of his symptoms and to normalization of the serum anion gap and serum lactate levels. The authors conclude that the patient had suffered from lactic acidosis caused by linezolid.
- Juan Carlos Q. Velez
- & Michael G. Janech
-
Review Article |
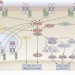 The role of Toll-like receptors in renal diseases
The role of Toll-like receptors in renal diseases
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) have a key role in the regulation of innate immunity by mediating signal transduction pathways that modulate the expression of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines. This Review discusses the potential role of TLRs in the pathogenesis of renal conditions such as acute kidney injury, acute glomerulonephritis, and renal transplant rejection. The authors also describe studies that have used pharmacological inhibition of TLR signaling to modify the response to proinflammatory stimuli.
- Anna Gluba
- , Maciej Banach
- & Jacek Rysz
-
News & Views |
Cytomegalovirus prophylaxis: how long is enough?
Extending the duration of cytomegalovirus prophylaxis to 6 months in virus-seronegative organ recipients who receive transplants from seropositive donors decreases the risk of cytomegalovirus disease. But is prophylaxis extension the best approach to preventing late-onset cytomegalovirus disease?
- Deepali Kumar
- & Atul Humar

 A case of rare, fungal peritonitis caused by Histoplasma capsulatum in a patient on CAPD
A case of rare, fungal peritonitis caused by Histoplasma capsulatum in a patient on CAPD