News & Views |
Featured
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Epidemiology, pathogenesis, treatment and outcomes of infection-associated glomerulonephritis
Epidemiology, pathogenesis, treatment and outcomes of infection-associated glomerulonephritis
Staphylococcus infection-associated glomerulonephritis (SAGN) and acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis (APSGN) are the two main types of bacterial infection-associated glomerulonephritis. In this Review, the authors discuss the epidemiology of these diseases, common histopathology findings and the complexities of clinical diagnosis, as well as patient management and renal outcomes.
- Anjali A. Satoskar
- , Samir V. Parikh
- & Tibor Nadasdy
-
Review Article |
 Antimicrobial resistance in nephrology
Antimicrobial resistance in nephrology
Antimicrobial resistance is an emergent global problem and patients with chronic kidney disease have some of the highest rates of colonization and infection with antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARB). This Review focuses on the epidemiology, prevention and treatment of infections with ARB.
- Tina Z. Wang
- , Rosy Priya L. Kodiyanplakkal
- & David P. Calfee
-
-
Correspondence |
Azithromycin decolonization of STEC—a new risk emerges
- Michael E. Seifert
- & Phillip I. Tarr
-
News & Views |
 Azithromycin and decolonization after HUS
Azithromycin and decolonization after HUS
An observational study associates azithromycin use with accelerated stool decolonization in patients infected with Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O104:H4. Even if this association is causal, however, the value of late-in-illness treatment is not established and the results provide no support for early-in-illness treatment of Shiga toxin-producing E. coli infections.
- Michael E. Seifert
- & Phillip I. Tarr
-
-
News & Views |
 Are prophylactic gentamicin catheter locks safe?
Are prophylactic gentamicin catheter locks safe?
Several randomized clinical trials with short-term follow-up have shown that patients on hemodialysis with prophylactic antibiotic catheter locks have reduced catheter-related bacteremia. However, the long-term safety of such locks remains a subject of ongoing debate. Landry et al. now report that prophylactic gentamicin catheter locks can promote the emergence of gentamicin-resistant bacteremia during long-term use.
- Michael Allon
-
News & Views |
The importance of peritoneal catheter exit-site care
The risk of peritonitis associated with infections of the peritoneal catheter exit site can be reduced by the use of proper exit-site care, such as the routine administration of prophylactic antibiotics at the exit site. Studies that demonstrate the efficacy of such an approach or similar approaches continue to be published.
- Beth Piraino
-
Case Study |
 A case of lactic acidosis induced by linezolid
A case of lactic acidosis induced by linezolid
This article reports the case of a 36-year-old man on hemodialysis who presented to an intensive care unit with a large serum anion gap and symptoms such as hypotension and an altered mental state. For the previous 6 weeks, he had received linezolid to treat vancomycin-resistant bacteremia. Discontinuation of linezolid led to resolution of his symptoms and to normalization of the serum anion gap and serum lactate levels. The authors conclude that the patient had suffered from lactic acidosis caused by linezolid.
- Juan Carlos Q. Velez
- & Michael G. Janech
-
Review Article |
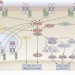 The role of Toll-like receptors in renal diseases
The role of Toll-like receptors in renal diseases
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) have a key role in the regulation of innate immunity by mediating signal transduction pathways that modulate the expression of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines. This Review discusses the potential role of TLRs in the pathogenesis of renal conditions such as acute kidney injury, acute glomerulonephritis, and renal transplant rejection. The authors also describe studies that have used pharmacological inhibition of TLR signaling to modify the response to proinflammatory stimuli.
- Anna Gluba
- , Maciej Banach
- & Jacek Rysz

 High-salt diet aggravates pyelonephritis
High-salt diet aggravates pyelonephritis FGF-23 inhibits neutrophil activation
FGF-23 inhibits neutrophil activation Minocycline–EDTA lock reduces bacteremia in dialysis catheters
Minocycline–EDTA lock reduces bacteremia in dialysis catheters