Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Engineering cyanine cyclizations for new fluorogenic probes
Engineering cyanine cyclizations for new fluorogenic probes
As the need for specific fluorescent probes that enable high sensitivity and super-resolution imaging experiments continues to grow, it is imperative to develop new, well-characterized methods to modulate the emission of fluorophores. Now, a general platform affords visible-to-NIR fluorogenic fluorophores by engineering a simple cyclization event into cyanine dyes.
- Quintashia D. Wilson
- & Ellen M. Sletten
-
Article |
 Electrochemical labelling of hydroxyindoles with chemoselectivity for site-specific protein bioconjugation
Electrochemical labelling of hydroxyindoles with chemoselectivity for site-specific protein bioconjugation
Current electrochemical-based protein labelling methods suffer from limited site-selectivity and off-target reactivity owing to required radical/electrophilic reagents. Now an electrochemical strategy enables chemoselective labelling of proteins at a site-specifically incorporated 5-hydroxytryptophan residue using aromatic amines as coupling partners. This approach works on various proteins, including a full-length antibody, and is compatible with established click reactions.
- Conor Loynd
- , Soumya Jyoti Singha Roy
- & Abhishek Chatterjee
-
Article
| Open Access A general strategy to develop fluorogenic polymethine dyes for bioimaging
A general strategy to develop fluorogenic polymethine dyes for bioimaging
Polymethine dyes are bright and red-shifted fluorophores that lack an intrinsic turn-on mechanism, which leads to non-specific staining when applied to biological samples. Now the fluorescence of polymethine dyes was masked through an intracellular cyclization strategy that gets reversed upon binding an intended macromolecular target, providing specificity for live-cell imaging.
- Annabell Martin
- & Pablo Rivera-Fuentes
-
Research Briefing |
 In vitro selection of covalent aptamers with sulfur(VI) fluoride exchange chemistry
In vitro selection of covalent aptamers with sulfur(VI) fluoride exchange chemistry
To develop covalent inhibitors with high potency and low off-target effects, combinatorial approaches that search for candidates from large libraries are desired. Here, sulfur(VI) fluoride exchange (SuFEx) in vitro selection is established for the evolution of covalent aptamers from trillions of SuFEx-modified oligonucleotides. Through this technique, covalent aptamers with optimally balanced selectivity and reactivity are identified.
-
News & Views |
 RNA as an off-target for FDA-approved drugs
RNA as an off-target for FDA-approved drugs
Medicinal chemistry efforts typically focus on drug–protein interactions and overlook RNA binding as a source of off-target pharmacology. Now, a new method has been developed to map the interactions of small-molecule drugs with RNA in cells and characterize how these interactions can exert functional effects.
- Christopher R. Fullenkamp
- & John S. Schneekloth Jr
-
Article |
 Pervasive transcriptome interactions of protein-targeted drugs
Pervasive transcriptome interactions of protein-targeted drugs
Now a reactivity-based RNA profiling strategy can measure the global off-target transcriptome interactions of small-molecule drugs at single-nucleotide resolution. Using this approach, three FDA-approved drugs were evaluated, uncovering pervasive drug–RNA interactions and interactions that perturb RNA functions in cells.
- Linglan Fang
- , Willem A. Velema
- & Eric T. Kool
-
Article |
 Direct mapping of ligandable tyrosines and lysines in cells with chiral sulfonyl fluoride probes
Direct mapping of ligandable tyrosines and lysines in cells with chiral sulfonyl fluoride probes
Most chemoproteomic screening approaches are indirect. Now, a chemoproteomic platform based on chiral sulfonyl fluoride probes has been developed for the direct identification of probe-modified tyrosines and lysines in live cells. Stereoselective modification by structurally diverse probes was observed for 634 tyrosines and lysines across functionally diverse protein sites.
- Ying Chen
- , Gregory B. Craven
- & Jack Taunton
-
Article |
 Reversible 2′-OH acylation enhances RNA stability
Reversible 2′-OH acylation enhances RNA stability
Stabilization of RNAs for storage, transport and biological application remains a profound challenge. Now, it has been shown that reversible 2′-OH acylation with easily accessible acylimidazoles unlocks efficient protection of RNA. RNA can be deprotected by non-basic nucleophiles or spontaneously in cells to restore RNA functions.
- Linglan Fang
- , Lu Xiao
- & Eric T. Kool
-
Article
| Open Access A locally activatable sensor for robust quantification of organellar glutathione
A locally activatable sensor for robust quantification of organellar glutathione
Fluorescent sensors that are responsive only in a specific subcellular location have remained elusive. Now, a chemogenetic sensing platform has been developed to sense glutathione in a user-defined organelle of interest. These tools enable quantitative studies of subcellular glutathione homeostasis using visible or near-infrared wavelengths.
- Sarah Emmert
- , Gianluca Quargnali
- & Pablo Rivera-Fuentes
-
Article |
 Isomerization of bioactive acylhydrazones triggered by light or thiols
Isomerization of bioactive acylhydrazones triggered by light or thiols
Acylhydrazones are often found in compounds across screening databases, and numerous bioactive acylhydrazones exist. This functional group can isomerize between E and Z in response to light or upon exposure to thiols. Now, E/Z isomerization is found to impact activities of bioactive acylhydrazones and should be routinely analysed.
- Zhiwei Zhang
- , Giang N. T. Le
- & G. Andrew Woolley
-
Article |
 Spatiotemporal and global profiling of DNA–protein interactions enables discovery of low-affinity transcription factors
Spatiotemporal and global profiling of DNA–protein interactions enables discovery of low-affinity transcription factors
Precise analysis of DNA–protein interactions can help to better understand various biological processes. Now, the ‘light-induced lysine (K) enabled crosslinking’ strategy (shortened to ‘LIKE-XL’) has been developed for spatiotemporal and global profiling of DNA–protein interactions, affording the discovery of low-affinity interactions between transcription factors and DNA using sequence-specific DNA baits.
- An-Di Guo
- , Ke-Nian Yan
- & Xiao-Hua Chen
-
Article |
 Genetically encoded chemical crosslinking of carbohydrate
Genetically encoded chemical crosslinking of carbohydrate
Protein–carbohydrate interactions remain challenging to study due to their low binding affinity and non-covalent nature. Now, a genetically encoded bioreactive unnatural amino acid containing sulfonyl fluoride has been shown to crosslink a protein with its bound glycan, offering a solution to probe and exploit protein–carbohydrate interactions.
- Shanshan Li
- , Nanxi Wang
- & Lei Wang
-
Article |
 Targeted activation in localized protein environments via deep red photoredox catalysis
Targeted activation in localized protein environments via deep red photoredox catalysis
Technologies for profiling biological environments with high spatiotemporal resolution are in demand to enable the discovery of new targets for addressing unmet clinical needs. Now, a deep red light-mediated photocatalytic strategy for the targeted activation of aryl azides has been developed. This platform enables mapping of protein microenvironments in physiologically relevant systems.
- Nicholas Eng Soon Tay
- , Keun Ah Ryu
- & Tomislav Rovis
-
Article |
 Structure-specific amyloid precipitation in biofluids
Structure-specific amyloid precipitation in biofluids
The composition of toxic protein aggregates associated with neurodegenerative diseases is difficult to determine. Now, a method has been developed that can capture amyloid-containing aggregates in human biofluids using a structure-specific chemical dimer. This method—known as amyloid precipitation—enables unbiased determination of the molecular composition and structural features of the in vivo aggregates.
- M. Rodrigues
- , P. Bhattacharjee
- & D. Klenerman
-
Article |
 Light-activated tetrazines enable precision live-cell bioorthogonal chemistry
Light-activated tetrazines enable precision live-cell bioorthogonal chemistry
Developing stimuli-responsive bioorthogonal tetrazine ligations remains highly challenging, but a versatile approach that uses photocaged dihydrotetrazines has now been developed. Photouncaging results in the spontaneous formation of reactive tetrazines that rapidly react with dienophiles such as trans-cyclooctenes. As a demonstration, the method was used for live-cell labelling with single-cell precision and light-triggered drug delivery.
- Luping Liu
- , Dongyang Zhang
- & Neal K. Devaraj
-
Article |
 Native mass spectrometry-based metabolomics identifies metal-binding compounds
Native mass spectrometry-based metabolomics identifies metal-binding compounds
The systemic discovery of metal–small-molecule complexes from biological samples is a difficult challenge. Now, a method based on liquid chromatography and native electrospray ionization mass spectrometry has been developed. The approach uses post-column pH adjustment and metal infusion combined with ion identity molecular networking, and a rule-based informatics workflow, to interrogate small-molecule–metal binding.
- Allegra T. Aron
- , Daniel Petras
- & Pieter C. Dorrestein
-
Article |
 Photoacoustic imaging of elevated glutathione in models of lung cancer for companion diagnostic applications
Photoacoustic imaging of elevated glutathione in models of lung cancer for companion diagnostic applications
Imaging-based companion diagnostics can provide real-time information to match therapies to patients; however, glutathione is abundant in most cells, making it an unlikely candidate for companion diagnosis. Now, a chemical probe has been developed that can detect elevated glutathione concentrations via photoacoustic imaging. Using this probe enables normal and pathological states in a lung cancer model to be distinguished.
- Melissa Y. Lucero
- & Jefferson Chan
-
Article |
 Wittig reagents for chemoselective sulfenic acid ligation enables global site stoichiometry analysis and redox-controlled mitochondrial targeting
Wittig reagents for chemoselective sulfenic acid ligation enables global site stoichiometry analysis and redox-controlled mitochondrial targeting
Triphenylphosphonium ylides (Wittig reagents) that selectively react with sulfenic acids—a pivotal post-translational cysteine modification in redox biology—are developed. This bioconjugation method enables a site-specific proteome-wide stoichiometry analysis of S-sulfenylation, and visualization of redox-dependent changes in mitochondrial cysteine oxidation and the redox-triggered generation of triphenylphosphonium for the controlled delivery of small molecules to mitochondria.
- Yunlong Shi
- , Ling Fu
- & Kate S. Carroll
-
Article |
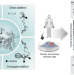 A proteome-wide atlas of lysine-reactive chemistry
A proteome-wide atlas of lysine-reactive chemistry
A deep chemical proteomic investigation of diverse aminophilic electrophiles has identified ligandable lysines across a wide range of human proteins. The proteins cover different functional and structural classes, and the aminophilic electrophiles include compounds that disrupt protein–protein and protein–RNA interactions. This dataset provides a proteome-wide atlas of lysine-reactive chemistry.
- Mikail E. Abbasov
- , Madeline E. Kavanagh
- & Benjamin F. Cravatt
-
Article |
 Deep learning to design nuclear-targeting abiotic miniproteins
Deep learning to design nuclear-targeting abiotic miniproteins
Machine learning has now been shown to enable the de novo design of abiotic nuclear-targeting miniproteins. To achieve this, high-throughput experimentation was combined with a directed evolution-inspired deep-learning approach in which the molecular structures of natural and unnatural residues are represented as topological fingerprints. The designed miniproteins, called Mach proteins, are non-toxic and can efficiently deliver antisense cargo in mice.
- Carly K. Schissel
- , Somesh Mohapatra
- & Bradley L. Pentelute
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical profiling of DNA G-quadruplex-interacting proteins in live cells
Chemical profiling of DNA G-quadruplex-interacting proteins in live cells
DNA–protein interactions are essential to genome function, but they are challenging to map in a cellular environment. Now, a chemical proteomics approach, which uses DNA G-quadruplex-specific ligands containing a photocrosslinking motif, has enabled the systematic identification of DNA G-quadruplex-binding proteins in live cells.
- Xiaoyun Zhang
- , Jochen Spiegel
- & Shankar Balasubramanian
-
Article |
 Cellular uptake of large biomolecules enabled by cell-surface-reactive cell-penetrating peptide additives
Cellular uptake of large biomolecules enabled by cell-surface-reactive cell-penetrating peptide additives
Robust delivery of proteins into cells is challenging, but it has now been shown that by conjugating arginine-rich cell-penetrating peptides to the surface of cells, proteins containing a cell-penetrating peptide can be delivered efficiently into them. Using a thiol-reactive cell-penetrating peptide enables thiol-containing proteins to be delivered by simple co-incubation.
- Anselm F. L. Schneider
- , Marina Kithil
- & Christian P. R. Hackenberger
-
Article |
 A far-red hybrid voltage indicator enabled by bioorthogonal engineering of rhodopsin on live neurons
A far-red hybrid voltage indicator enabled by bioorthogonal engineering of rhodopsin on live neurons
Voltage imaging is a powerful technique for studying electrical signalling in neurons. A palette of bright and sensitive voltage indicators has now been developed via enzyme-mediated ligation and Diels–Alder cycloaddition. Among these, a far-red indicator faithfully reports neuronal action potential dynamics with an excitation spectrum orthogonal to optogenetic actuators and green/red-emitting biosensors.
- Shuzhang Liu
- , Chang Lin
- & Peng Zou
-
News & Views |
 Fishing for nucleic acid with a coiled hook
Fishing for nucleic acid with a coiled hook
Site-specific attachment of a programmable motif, such as a synthetic nucleic acid tag, on a target protein can facilitate functional studies of proteins in cells or modulation of protein activity. Now, a small genetically encoded peptide enables the templated incorporation of a peptide nucleic acid tag onto membrane proteins in live cells.
- Jerrin Thomas George
- & Sarit S. Agasti
-
Article |
 Live cell PNA labelling enables erasable fluorescence imaging of membrane proteins
Live cell PNA labelling enables erasable fluorescence imaging of membrane proteins
A method for the covalent labelling of proteins by installing a biostable peptide nucleic acid (PNA) tag has now been developed. The PNA label serves as a generic landing platform that enables the recruitment of fluorescent dyes via nucleic acid hybridization and fluorophore removal by toehold-mediated strand displacement. Imaging of cell surface receptors, including internalized receptors, has been demonstrated using this approach.
- Georgina C. Gavins
- , Katharina Gröger
- & Oliver Seitz
-
News & Views |
 Decorating proteins with LACE
Decorating proteins with LACE
Labelling proteins at internal sites holds promise for generating novel protein conjugates in a programmable fashion. Now, a chemoenzymatic approach, dubbed LACE, enables the site-specific modification of recombinant proteins that contain a short genetically encoded tag.
- Maximilian Fottner
- & Kathrin Lang
-
Article |
 Shortwave infrared polymethine fluorophores matched to excitation lasers enable non-invasive, multicolour in vivo imaging in real time
Shortwave infrared polymethine fluorophores matched to excitation lasers enable non-invasive, multicolour in vivo imaging in real time
Conducting high-resolution, multiplexed imaging in living mammals is challenging because of considerable scattering and autofluorescence in tissue at visible and near-infrared wavelengths. Now, real-time, non-invasive multicolour imaging experiments in live animals have been achieved through the design of optical contrast agents for the shortwave infrared (SWIR, 1,000–2,000 nm) region and the introduction of excitation multiplexing with single-channel SWIR detection.
- Emily D. Cosco
- , Anthony L. Spearman
- & Ellen M. Sletten
-
News & Views |
 Protein targeting with SAF(er) electrophiles
Protein targeting with SAF(er) electrophiles
Electrophilic groups that undergo sulfur-exchange chemistry with protein nucleophiles can serve as the functional basis of chemical proteomic probes. A new addition to this class, sulfuramidimidoyl fluoride (SAF), which can be included in an array of covalent small molecule probes, exhibits a unique reactivity profile with proteins.
- Thomas E. Speltz
- & Raymond E. Moellering
-
Article |
 Using sulfuramidimidoyl fluorides that undergo sulfur(vi) fluoride exchange for inverse drug discovery
Using sulfuramidimidoyl fluorides that undergo sulfur(vi) fluoride exchange for inverse drug discovery
Latent functional groups—typically unreactive unless activated by protein binding—can provide additional selectivity to covalent drugs. Now, compounds containing the weakly electrophilic sulfuramidimidoyl fluoride group, capable of undergoing sulfur(vi) fluoride exchange, have been used to identify reactive proteins in human cell lysate. This approach has identified a compound that conjugates to and inhibits an important anticancer target.
- Gabriel J. Brighty
- , Rachel C. Botham
- & Jeffery W. Kelly
-
Article |
 In situ chromatin interactomics using a chemical bait and trap approach
In situ chromatin interactomics using a chemical bait and trap approach
Proteins that interact with histone post-translational modifications have now been identified using an approach based on split-intein mediated histone semisynthesis. Histone modifications and disease-relevant mutations were installed into native chromatin with an adjacent photocross-linker to enable in situ cross-linking. This strategy enabled the determination of chromatin-relevant interactomes and represents a powerful tool for exploring epigenetic regulation and dysregulation at the molecular level.
- Antony J. Burton
- , Michael Haugbro
- & Tom W. Muir
-
Q&A |
 A dream to sequence life
A dream to sequence life
Yujia Qing, an early-career researcher at the University of Oxford, talks to Nature Chemistry about winning the Dream Chemistry Award 2019, her chemistry dream of ‘Sequencing Life’, and the challenge this represents.
- Russell Johnson
-
Article |
 A general strategy to develop cell permeable and fluorogenic probes for multicolour nanoscopy
A general strategy to develop cell permeable and fluorogenic probes for multicolour nanoscopy
It is difficult to develop suitable fluorescent probes for live-cell nanoscopy, but a general strategy is now reported that can transform regular fluorophores into fluorogenic probes with excellent cell permeability and low unspecific background signals. Using this approach, probes in a variety of colours were developed for different cellular targets and used for wash-free, multicolour, live-cell confocal and STED microscopy.
- Lu Wang
- , Mai Tran
- & Kai Johnsson
-
News & Views |
 A chiral trick to map protein ligandability
A chiral trick to map protein ligandability
Biological receptors distinguish between S- and R-enantiomers and these subtle differences in chirality can lead to vastly different protein affinities. Now, a proteomics approach has been developed that capitalizes on chirality to map enantiomeric probe pairs and provides a rapid and global view of protein ligandability within the cell.
- Yuka Amako
- & Christina M. Woo
-
Review Article |
 Computational advances in combating colloidal aggregation in drug discovery
Computational advances in combating colloidal aggregation in drug discovery
Biochemical and cellular assays are often plagued by false positive readouts elicited by nuisance compounds. A significant proportion of those compounds are aggregators. This Review discusses the basis for colloidal aggregation, experimental methods for detecting aggregates and analyses recent progress in computer-based systems for detecting colloidal aggregation with particular emphasis on machine learning [In the online version of this Review originally published, the graphical abstract image was incorrectly credited to ‘Reven T.C. Wurman / Alamy Stock Photo’ this has now been corrected].
- Daniel Reker
- , Gonçalo J. L. Bernardes
- & Tiago Rodrigues
-
Article |
 Dual chemical probes enable quantitative system-wide analysis of protein prenylation and prenylation dynamics
Dual chemical probes enable quantitative system-wide analysis of protein prenylation and prenylation dynamics
Two chemical probes, YnF and YnGG, that enable the identification of prenylated peptides and global analysis of protein prenylation using quantitative chemical proteomics have now been developed. Prenylation dynamics in response to pharmacological inhibition of prenyl-transferase enzymes were also studied. As a final demonstration, defective Rab prenylation in a model of the retinal degenerative disease choroideremia was also quantified.
- Elisabeth M. Storck
- , Julia Morales-Sanfrutos
- & Edward W. Tate
-
Article |
 Fluorogenic d-amino acids enable real-time monitoring of peptidoglycan biosynthesis and high-throughput transpeptidation assays
Fluorogenic d-amino acids enable real-time monitoring of peptidoglycan biosynthesis and high-throughput transpeptidation assays
Biosynthesis of peptidoglycan requires carefully orchestrated transpeptidation reactions to maintain the structural integrity of this essential component of the bacterial cell wall. Now, rotor-fluorescent d-amino acids have been shown to enable real-time tracking of these transpeptidation reactions in live bacterial cells. These powerful tools allow visualization of peptidoglycan biosynthesis with high spatiotemporal resolution.
- Yen-Pang Hsu
- , Edward Hall
- & Michael S. VanNieuwenhze
-
Article |
 Mining the cellular inventory of pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzymes with functionalized cofactor mimics
Mining the cellular inventory of pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzymes with functionalized cofactor mimics
A chemical proteomic strategy has now been developed for profiling pyridoxal-phosphate dependent enzymes (PLP-DEs) in cells. Pyridoxal-based probes are phosphorylated in situ and bind to cellular PLP-DEs as cofactor mimics. The method accessed 73% of the Staphylococcus aureus PLP-dependent proteome and annotated uncharacterized proteins as novel PLP-DEs.
- Annabelle Hoegl
- , Matthew B. Nodwell
- & Stephan A. Sieber
-
Article |
 A fluorescent membrane tension probe
A fluorescent membrane tension probe
Lipid membranes—which separate cells and organelles from their environment—experience tension during various cell processes; however, measuring membrane tension is notoriously difficult. Now, a new fluorescent, mechanosensitive membrane probe called FliptR has been developed. FliptR enables simple, direct membrane tension measurements in cellular and artificial membranes.
- Adai Colom
- , Emmanuel Derivery
- & Aurélien Roux
-
Article |
 Enrichment-triggered prodrug activation demonstrated through mitochondria-targeted delivery of doxorubicin and carbon monoxide
Enrichment-triggered prodrug activation demonstrated through mitochondria-targeted delivery of doxorubicin and carbon monoxide
A new concept for targeted drug delivery based on enrichment triggered prodrug activation has been developed. Without enrichment, the activation reaction is sluggish; however, following enrichment, the increased concentration enhances the activation reaction rate, thereby leading to the release of the payload. The same approach can be used in antibody–drug conjugate applications.
- Yueqin Zheng
- , Xingyue Ji
- & Binghe Wang
-
Article |
 Fragment-derived inhibitors of human N-myristoyltransferase block capsid assembly and replication of the common cold virus
Fragment-derived inhibitors of human N-myristoyltransferase block capsid assembly and replication of the common cold virus
An effective antiviral against the common cold could prevent exacerbations in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, but the diversity and adaptability of the virus makes it a highly challenging target. Now, picomolar inhibitors of a human lipid transferase have been developed. Targeting this human lipid transferase could provide an effective and broad-spectrum approach to block viral replication in the host.
- Aurélie Mousnier
- , Andrew S. Bell
- & Edward W. Tate
-
Article |
 Single helically folded aromatic oligoamides that mimic the charge surface of double-stranded B-DNA
Single helically folded aromatic oligoamides that mimic the charge surface of double-stranded B-DNA
Molecules that mimic the charge surface of B-DNA could enable the inhibition of DNA processive enzymes. Now, helically folded aromatic oligoamide scaffolds have been synthesized that display anions at positions similar to that of B-DNA phosphates. These foldamer mimics can recognize some DNA binding proteins and inhibit enzymes such as HIV integrase and topoisomerase 1.
- Krzysztof Ziach
- , Céline Chollet
- & Ivan Huc
-
Article |
 Versatile protein recognition by the encoded display of multiple chemical elements on a constant macrocyclic scaffold
Versatile protein recognition by the encoded display of multiple chemical elements on a constant macrocyclic scaffold
Encoded display of multiple chemical elements on a constant macrocyclic scaffold could mimick antibody–antigen recognition. A chemical library constructed using this approach enabled the identification of specific binders against a variety of protein targets, including difficult targets, such as TNF.
- Yizhou Li
- , Roberto De Luca
- & Dario Neri
-
News & Views |
 Making your mark on DNA
Making your mark on DNA
Understanding the biological roles of modifications to DNA, RNA and proteins is critical to revealing how cells regulate gene expression in development and disease. Two papers now present a combination of new tools and discoveries that could enable biologists and chemical biologists to better study epigenetic regulation in mammals.
- Bryan T. Harada
- & Chuan He
-
Review Article |
 Fluorescent nucleobases as tools for studying DNA and RNA
Fluorescent nucleobases as tools for studying DNA and RNA
The emergence of synthetic fluorescent nucleobases that can be incorporated into DNA and RNA in place of their natural counterparts has enabled new tools and technologies with applications in chemistry, biology and biomedicine. This Review discusses chemical insights into canonical and non-canonical nucleobase designs, relating structure to properties.
- Wang Xu
- , Ke Min Chan
- & Eric T. Kool
-
Article |
 Global profiling of lysine reactivity and ligandability in the human proteome
Global profiling of lysine reactivity and ligandability in the human proteome
A chemical proteomic strategy has now been reported for the global profiling of lysine reactivity and ligandability. Using this approach, >9000 lysines in the human proteome were evaluated, leading to the discovery of hyper-reactive lysines, and lysines that can be targeted by electrophilic small molecules to perturb enzyme function and protein–protein interactions.
- Stephan M. Hacker
- , Keriann M. Backus
- & Benjamin F. Cravatt
-
Review Article |
 The versatility of boron in biological target engagement
The versatility of boron in biological target engagement
Recent years have witnessed a surge of interest in targeted covalent inhibition of disease-associated proteins. Among the electrophiles used to interact with nucleophilic residues in protein structures, boron is unique for its chameleonic ability to display a range of coordination modes upon interaction with protein targets.
- Diego B. Diaz
- & Andrei K. Yudin
-
Article |
 Cell-permeable nanobodies for targeted immunolabelling and antigen manipulation in living cells
Cell-permeable nanobodies for targeted immunolabelling and antigen manipulation in living cells
Delivery of antibodies into living cells enables the labelling and manipulation of intracellular antigens; however, transporting antibodies into the cytosol in a functional state is difficult. Now, a modular strategy for creating cell-permeable nanobodies capable of targeting intracellular antigens has been developed. The cell-permeable nanobodies are formed by site-specific attachment of cyclic arginine-rich cell-penetrating peptides to camelid-derived single-chain antibody fragments.
- Henry D. Herce
- , Dominik Schumacher
- & Christian P. R. Hackenberger
-
Article |
 Rational design of reversible fluorescent probes for live-cell imaging and quantification of fast glutathione dynamics
Rational design of reversible fluorescent probes for live-cell imaging and quantification of fast glutathione dynamics
Reversible fluorescent probes for intracellular glutathione (GSH) imaging have now been designed and synthesized based on Si-rhodamine fluorophores. These probes are shown to be capable of quantifying the GSH concentration in various living cell types and also for monitoring real-time live-cell imaging of GSH dynamics with a temporal resolution of seconds.
- Keitaro Umezawa
- , Masafumi Yoshida
- & Yasuteru Urano
-
Article |
 Chemoproteomic profiling and discovery of protein electrophiles in human cells
Chemoproteomic profiling and discovery of protein electrophiles in human cells
A chemical proteomic strategy is described for the discovery of protein-bound electrophilic groups in human cells. Using this approach, the dynamic regulation of the pyruvoyl catalytic cofactor in S-adenosyl-L-methionine decarboxylase was characterized and an N-terminal glyoxylyl modification on secernin proteins was discovered.
- Megan L. Matthews
- , Lin He
- & Benjamin F. Cravatt

 Bioorthogonal masked acylating agents for proximity-dependent RNA labelling
Bioorthogonal masked acylating agents for proximity-dependent RNA labelling