Featured
-
-
-
Article |
 Wittig reagents for chemoselective sulfenic acid ligation enables global site stoichiometry analysis and redox-controlled mitochondrial targeting
Wittig reagents for chemoselective sulfenic acid ligation enables global site stoichiometry analysis and redox-controlled mitochondrial targeting
Triphenylphosphonium ylides (Wittig reagents) that selectively react with sulfenic acids—a pivotal post-translational cysteine modification in redox biology—are developed. This bioconjugation method enables a site-specific proteome-wide stoichiometry analysis of S-sulfenylation, and visualization of redox-dependent changes in mitochondrial cysteine oxidation and the redox-triggered generation of triphenylphosphonium for the controlled delivery of small molecules to mitochondria.
- Yunlong Shi
- , Ling Fu
- & Kate S. Carroll
-
Article |
 Deep learning to design nuclear-targeting abiotic miniproteins
Deep learning to design nuclear-targeting abiotic miniproteins
Machine learning has now been shown to enable the de novo design of abiotic nuclear-targeting miniproteins. To achieve this, high-throughput experimentation was combined with a directed evolution-inspired deep-learning approach in which the molecular structures of natural and unnatural residues are represented as topological fingerprints. The designed miniproteins, called Mach proteins, are non-toxic and can efficiently deliver antisense cargo in mice.
- Carly K. Schissel
- , Somesh Mohapatra
- & Bradley L. Pentelute
-
Review Article |
 The synthesis, properties and potential applications of cyclic polymers
The synthesis, properties and potential applications of cyclic polymers
Cyclic polymers have a ring-like architecture and one of the most important consequences of this topology is the absence of any chain ends, which typically have a substantial impact on the physical properties of macromolecules. This Review Article discusses advances in the synthesis, purification and characterization of cyclic polymers and the potential applications they may prove useful for.
- Farihah M. Haque
- & Scott M. Grayson
-
News & Views |
 Foldamers wave to the ribosome
Foldamers wave to the ribosome
Ribosomes have now been shown to accept certain initiator tRNAs acylated with aromatic foldamer–dipeptides thereby enabling the translation of a peptide or protein with a short aromatic foldamer at the N-terminus. Some foldamer–peptide hybrids could be cyclized to generate macrocycles that present conformationally restricted peptide loops.
- Alanna Schepartz
-
Article |
 Engineering live cell surfaces with functional polymers via cytocompatible controlled radical polymerization
Engineering live cell surfaces with functional polymers via cytocompatible controlled radical polymerization
A cytocompatible controlled radical polymerization method has now been developed that initiates polymer synthesis directly on the surface of living cells. This method achieves significantly enhanced polymer grafting and enables active manipulation of cellular phenotypes.
- Jia Niu
- , David J. Lunn
- & Craig J. Hawker
-
Perspective |
 Recent advances in the construction of antibody–drug conjugates
Recent advances in the construction of antibody–drug conjugates
Antibody–drug conjugates have shown considerable promise for treating disease. However, in order to deliver their full potential, sophisticated site-specific conjugation technologies are needed. This Perspective provides an overview of the different methods used for the site-specific attachment of cytotoxic agents to antibodies.
- Vijay Chudasama
- , Antoine Maruani
- & Stephen Caddick
-
Article |
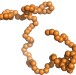 Structure of a PEGylated protein reveals a highly porous double-helical assembly
Structure of a PEGylated protein reveals a highly porous double-helical assembly
Protein PEGylation is routinely used to produce molecules with improved pharmacokinetic properties. However, despite their importance, the structure of PEGylated proteins has remained elusive. Now, the first crystal structure of a model β-sheet protein modified with a single PEG chain has been reported. NMR spectroscopy data indicates that the protein and PEG behave as independent domains.
- Giada Cattani
- , Lutz Vogeley
- & Peter B. Crowley
-
News & Views |
 Proteins in a pill
Proteins in a pill
Protein drugs are important therapies for many different diseases, but very few can be administered orally. Now, a cationic dendronized polymer has been shown to stabilize a therapeutic protein for delivery to the gut.
- Heather D. Maynard
-
Article |
 Sustained gastrointestinal activity of dendronized polymer–enzyme conjugates
Sustained gastrointestinal activity of dendronized polymer–enzyme conjugates
Methods for stabilizing enzymatic activity in the gastrointestinal tract are rarely investigated because of the difficulty in protecting proteins from an environment that promotes their digestion. Now, functionally diverse polymers have been conjugated to therapeutic enzymes, which lead to a substantial enhancement of their in vivo activity in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Gregor Fuhrmann
- , Andrea Grotzky
- & Jean-Christophe Leroux
-
Article |
 A heparin-mimicking polymer conjugate stabilizes basic fibroblast growth factor
A heparin-mimicking polymer conjugate stabilizes basic fibroblast growth factor
Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) is crucial for a range of diverse cellular processes, from wound healing to bone regeneration, yet is inherently unstable. This important biologic has now been covalently linked to a polymer that mimics the polysaccharide heparin to produce a conjugate that shows remarkable stability to a wide range of therapeutically and environmentally relevant stressors.
- Thi H. Nguyen
- , Sung-Hye Kim
- & Heather D. Maynard
-
News & Views |
 Relieving PEGylation
Relieving PEGylation
A new type of protein–polymer conjugate provides improved stability without detrimentally affecting bioactivity, and thus offers great potential for the development of new peptide-based drugs.
- Matthew C. Parrott
- & Joseph M. DeSimone

 Discovering covalent inhibitors of protein–protein interactions from trillions of sulfur(VI) fluoride exchange-modified oligonucleotides
Discovering covalent inhibitors of protein–protein interactions from trillions of sulfur(VI) fluoride exchange-modified oligonucleotides Chemistry just a click away
Chemistry just a click away