Research Highlight |
Featured
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Immune mechanisms of salt-sensitive hypertension and renal end-organ damage
Immune mechanisms of salt-sensitive hypertension and renal end-organ damage
Immune mechanisms have important roles in the development of hypertension and end-organ damage. In this Review, David Mattson discusses these mechanisms with a focus on salt-sensitive hypertension and adaptive immunity.
- David L. Mattson
-
Review Article |
 C3 glomerulopathy — understanding a rare complement-driven renal disease
C3 glomerulopathy — understanding a rare complement-driven renal disease
This Review presents our current understanding of C3 glomerulopathy. Smith et al. discuss the histopathological diagnosis and the crucial pathogenic role of complement dysregulation. Genetic and acquired drivers of C3 glomerulopathy, potential biomarkers and available treatments are highlighted.
- Richard J. H. Smith
- , Gerald B. Appel
- & Carla M. Nester
-
Year in Review |
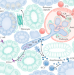 Protecting the kidney against autoimmunity and inflammation
Protecting the kidney against autoimmunity and inflammation
Numerous exciting studies that advanced our understanding of immune-mediated kidney disease were published in 2018. Whereas most of these studies analysed the role of pro-inflammatory mediators, several novel anti-inflammatory mechanisms were discovered that involve immune cells and mediators with previously unrecognized protective roles in renal disease.
- Christian Kurts
- & Catherine Meyer-Schwesinger
-
Review Article |
 Effector and regulatory B cells in immune-mediated kidney disease
Effector and regulatory B cells in immune-mediated kidney disease
Autoimmune diseases and kidney transplantation can result in immune-mediated kidney pathology. In this Review, the authors discuss the roles of effector and regulatory B cells and the efficacy of B cell-targeting therapies in these settings.
- Kristine Oleinika
- , Claudia Mauri
- & Alan D. Salama
-
Review Article |
 HLA in transplantation
HLA in transplantation
Improved understanding of HLAs together with advances in HLA typing and antibody detection techniques have enabled transplantation of sensitized patients. Here, the authors discuss these advances as well as novel approaches to desensitization, immunomodulation and tolerance induction.
- Robert A. Montgomery
- , Vasishta S. Tatapudi
- & Andrea A. Zachary
-
Review Article |
 Angiotensin-converting enzyme in innate and adaptive immunity
Angiotensin-converting enzyme in innate and adaptive immunity
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) not only plays a major part in the regulation of blood pressure but also participates in several other physiological functions, including renal development and male reproduction. Here, Bernstein et al. discuss how ACE enhances both innate and adaptive responses by modulating macrophage and neutrophil function.
- Kenneth E. Bernstein
- , Zakir Khan
- & Xiao Z. Shen
-
Review Article |
 Advances in the understanding and treatment of sepsis-induced immunosuppression
Advances in the understanding and treatment of sepsis-induced immunosuppression
Sepsis induces an initial activation of the immune system, which is often followed by a compensatory anti-inflammatory response that can lead to immunosuppression. In this Review, the authors discuss advances in the understanding of sepsis-induced immunosuppression and how this understanding might lead to new, more effective treatments for sepsis.
- Fabienne Venet
- & Guillaume Monneret
-
News & Views |
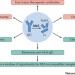 IdeS to desensitize organ allograft recipients
IdeS to desensitize organ allograft recipients
HLA sensitization greatly increases the risk of transplant rejection and failure. An IgG endopeptidase derived from Streptococcus pyogenes (IdeS) may be an attractive new therapy for desensitization. Recent data indicate that IdeS effectively depletes anti-HLA IgG, creating a therapeutic window for successful renal transplantation in sensitized recipients.
- Georg A. Böhmig
- & Lionel Rostaing
-
-
Review Article |
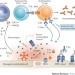 The importance of non-HLA antibodies in transplantation
The importance of non-HLA antibodies in transplantation
Antibodies directed against non-HLA antigens such as angiotensin type 1 receptor, perlecan and collagen have been implicated in antibody-mediated rejection. Here, Elaine Reed and Qiuheng Zhang discuss the clinical relevance and pathogenesis of these non-HLA antibodies in renal, heart and lung transplantation.
- Qiuheng Zhang
- & Elaine F. Reed
-
Review Article |
 Memory T cells in organ transplantation: progress and challenges
Memory T cells in organ transplantation: progress and challenges
Memory T cells and their ability to generate an anamnestic response are vital for protective immunity, but have a potentially detrimental impact on allograft survival. Here, Allan Kirk and colleagues discuss the generation of memory T cells, their role in allograft rejection and therapeutic strategies that target allospecific memory T-cell responses and might improve outcomes in organ transplantation.
- Jaclyn R. Espinosa
- , Kannan P. Samy
- & Allan D. Kirk
-
-
Research Highlight |
IgG reactivity to apoptotic cells—role in presensitization revealed
- Peter Sidaway
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Tolerance: an overview and perspectives
Tolerance: an overview and perspectives
The immune system has evolved to ensure protection against ever changing microbial pathogens. The potential of lymphocytes to recognize 'self' is controlled by a process called 'self tolerance'. Improved understanding of the mechanisms of immunological tolerance is key to understanding the pathogenesis of autoimmune disorders and cancers, and may lead to strategies to harness tolerance to replace the lifelong need for immunosuppressive drugs after organ transplantation. In this Review, Waldmann provides an overview of the mechanisms of self tolerance and assesses the prospects of translating this knowledge to patient care.
- Herman Waldmann

 Induction of immune tolerance in kidney transplant recipients
Induction of immune tolerance in kidney transplant recipients