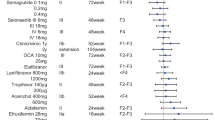
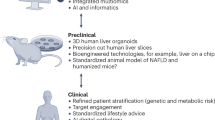
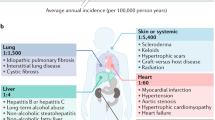
Abstract
The emergence of novel pharmacologic therapies for hepatic fibrosis holds promise for the management of this condition. Furthermore, novel, biological indices—in addition to liver biopsy—may improve our ability to assess the unique pharmacological effects generated by these agents. This article will attempt to highlight the potential for emerging biomarkers to serve as end points in clinical studies that target salient features of hepatic fibrogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghiassi-Nejad, Z. & Friedman, S. L. Advances in antifibrotic therapy. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2, 803–816 (2008).
Friedman, S. L. Molecular regulation of hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 2247–2250 (2000).
Shiratori, Y. et al. Histologic improvement of fibrosis in patients with hepatitis C who have sustained response to interferon therapy. Ann. Intern. Med. 132, 517–524 (2000).
Bedossa, P. & Carrat, F. Liver biopsy: the best, not the gold standard. J. Hepatol. 50, 1–3 (2009).
Manning, D. S. & Afdhal, N. H. Diagnosis and quantitation of fibrosis. Gastroenterology 134, 1670–1681 (2008).
Fontana, R. J. et al. Serum fibrosis marker levels decrease after successful antiviral treatment in chronic hepatitis C patients with advanced fibrosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 7, 219–226 (2009).
Talwalkar, J. A. et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of hepatic fibrosis: emerging clinical applications. Hepatology 47, 332–342 (2008).
Lim, A. K. et al. Hepatic vein transit times using a microbubble agent can predict disease severity non-invasively in patients with hepatitis C. Gut 54, 128–133 (2005).
Castera, L., Forns, X. & Alberti, A. Non-invasive evaluation of liver fibrosis using transient elastography. J. Hepatol. 48, 835–847 (2008).
Talwalkar, J. A., Kurtz, D. M., Schoenleber, S. J., West, C. P. & Montori, V. M. Ultrasound-based transient elastography for the detection of hepatic fibrosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 5, 1214–1220 (2007).
Yin, M. et al. Assessment of hepatic fibrosis with magnetic resonance elastography. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 5, 1207–1213 (2007).
Huwart, L. et al. Magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 135, 32–40 (2008).
Vizzutti, F., Arena, U., Marra, F. & Pinzani, M. Elastography for the non-invasive assessment of liver disease: limitations and future developments. Gut 58, 157–160 (2009).
Girometti, R. et al. Relevance of b-values in evaluating liver fibrosis: a study in healthy and cirrhotic subjects using two single-shot spin-echo echo-planar diffusion-weighted sequences. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 28, 411–419 (2008).
Strijbos, M. H. et al. Circulating endothelial cells in oncology: pitfalls and promises. Br. J. Cancer 98, 1731–1735 (2008).
Boos, C. J., Lip, G. Y. & Blann, A. D. Circulating endothelial cells in cardiovascular disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 48, 1538–1547 (2006).
Dome, B. et al. Identification and clinical significance of circulating endothelial progenitor cells in human non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 66, 7341–7347 (2006).
Corretti, M. C. et al. Guidelines for the ultrasound assessment of endothelial-dependent flow-mediated vasodilation of the brachial artery: a report of the International Brachial Artery Reactivity Task Force. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 39, 257–265 (2002).
Wright, S. A. et al. A randomised interventional trial of omega-3-polyunsaturated fatty acids on endothelial function and disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 67, 841–848 (2008).
Chong, A. Y. et al. Endothelial dysfunction and damage in congestive heart failure: relation of flow-mediated dilation to circulating endothelial cells, plasma indexes of endothelial damage, and brain natriuretic peptide. Circulation 110, 1794–1798 (2004).
Fernández, M. et al. Angiogenesis in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 50, 604–620 (2009).
Assy, N., Paizi, M., Gaitini, D., Baruch, Y. & Spira, G. Clinical implication of VEGF serum levels in cirrhotic patients with or without portal hypertension. World J. Gastroenterol. 5, 296–300 (1999).
O'Connor, J. P., Jackson, A., Parker, G. J. & Jayson, G. C. DCE-MRI biomarkers in the clinical evaluation of antiangiogenic and vascular disrupting agents. Br. J. Cancer 96, 189–195 (2007).
Textor, S. C. et al. The use of magnetic resonance to evaluate tissue oxygenation in renal artery stenosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 19, 780–788 (2008).
Diab, D. L. et al. Cytokeratin 18 fragment levels as a noninvasive biomarker for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in bariatric surgery patients. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 6, 1249–1254 (2008).
Blankenberg, F. G. In vivo detection of apoptosis. J. Nucl. Med. 49 (Suppl. 2), 81S–95S (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares that he receives grant/research support from Salix and Merck.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Talwalkar, J. Antifibrotic therapies—emerging biomarkers as treatment end points. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 7, 59–61 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2009.197
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2009.197
This article is cited by
-
Kinin B1 receptor blockade attenuates hepatic fibrosis and portal hypertension in chronic liver diseases in mice
Journal of Translational Medicine (2022)
-
Real-time monitoring of liver fibrosis through embedded sensors in a microphysiological system
Nano Convergence (2021)
-
Non-Invasive markers for hepatic fibrosis
BMC Gastroenterology (2011)
-
Circulating CO3-610, a degradation product of collagen III, closely reflects liver collagen and portal pressure in rats with fibrosis
Fibrogenesis & Tissue Repair (2011)
-
Evolving challenges in hepatic fibrosis
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology (2010)