Abstract
Anatase TiO2 tree-like nanoarrays were prepared on various metal wires (Ti, W, Ni, etc.) through one-step facile hydrothermal reaction. The anatase TiO2 tree-like nanoarrays consist of long TiO2 nanowire trunks with direct charge transport channels and a large number of short TiO2 nanorod branches with large surface areas. Fiber dye-sensitized solar cells (FDSSCs) based on the anatase TiO2 tree-like nanoarrays deposited on Ti wires can achieve outstanding power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 6.32%, while FDSSCs on W wires have lower PCE of 3.24% due to the formation of WO3 layer, which might enhance recombination of charges. When the substrate is changed to a Nicole oxide wire, a novel p-n heterojunction can be obtained. This universal method is simple, facile and low cost for preparing anatase TiO2 treelike-nanoarrays on various metal wires, which may find potential applications in fabrication of optoelectronic devices.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Titanium dioxide (TiO2), one of the most important wide band-gap semiconductors and metal oxides, has attracted great attention due to its excellent optical and electrical properties, high chemical and optical stability, low toxicity and cost and appropriate electronic band structure1,2,3,4. TiO2 plays critical roles in many fields, such as dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs)5, lithium ion batteries6, gas sensors7 and photocatalysts8, etc. The performance of TiO2-based devices is found to be strongly dependent on TiO2 morphology, crystalline phase and structure9,10,11,12,13,14,15. The anatase TiO2 treelike-nanoarrays are of particular interest for large surface areas, suitable porosity and their potential applications as continuous pathway for charge transport. To date, considerable efforts have been devoted to fabricating anatase TiO2 treelike-nanoarrays16,17,18. Normally, the first step of growing anatase TiO2 treelike-nanoarrays is titanium hydrolysis reaction in alkaline solution, which results in one-dimensional (1D) titanate on Ti substrates; the second step is ion-exchange process in acidic solution to obtain 1D titanic acid; the final step is growing anatase TiO2 treelike-nanoarrays. However, the procedures are too complicated and the substrates must be Ti related materials to offer titanium source. Therefore, the controlled growth of anatase TiO2 treelike-nanoarrays on various substrates through a relatively simple method is highly desirable for possible optoelectronic applications with various requirements19,20.
As a cheap, environment-friendly and simple fabrication process, DSSCs have huge potentials for replacing silicon-based solar cells21. Nowadays, the PCE of the traditional plane DSSCs is up to 12.3%22. However, the substrate is rigid fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) conducting glass, which limits transportation and applications of flat DSSCs. Therefore, great attention has been paid to exploring substitutional substrates such as metal, plastic conducting and carbonous substrates. The newly developed FDSSCs can be synthesized based on any flexible conducting wire substrates, such as metal wire23,24,25,26, carbon fiber27,28,29 and optical fiber30, which significantly extend the source of possible substrates. Meanwhile, such structure may find applications in solving electrolyte leakage problems, uncomplicated encapsulation and modularization, omnidirectional light harvesting, weaving materials for clothing and external bond layer of buildings.
TiO2 1D nanoarrays, with continuous pathway for charge transport, have been exploited as excellent photoanodes for FDSSCs. Up to now, TiO2 nanotubes anodised on Ti wires as photoanodes have obtained the highest PCE of nearly 7% after a high concentration of TiCl4 solution processing to achieve sufficient surface areas31. However, only one Ti wire is involved in the reaction for TiO2 nanotube, which is a waste of time and money.
Herein, we report anatase TiO2 treelike-nanoarrays consisting of long TiO2 nanowire trunks and short nanorod branches on various metal wires (Ti, W, Ni. etc.) for possible applications in FDSSCs. The FDSSCs based on Ti wires show outstanding performance of 6.32% PCE. The vertically aligned long TiO2 nanowire trunks enhance the charge transport and the short nanowire branches provide large surface areas for dye loading. Moreover, anatase TiO2 treelike-nanoarrays can be simultaneously synthesized on several metal wires (Ti, W, Ni, etc.) through one-step hydrothermal process in one container. Thus, the hydrothermal method in this study provides large possibilities of growing TiO2 on various metal wires as templates according to the requirements of the TiO2 related devices. This hydrothermal method is the same as growing ZnO nanoarrays on different substrates32,33,34. This method is simple, facile, low cost and suitable for large-scale production, which shows great potentials for future applications.
Results
Structure of anatase TiO2 treelike-nanoarrays
Figure 1(a) shows a bare Ti wire of ~ 500 μm in diameter. The seeded-Ti wires were immersed into a solution containing 1.24 g potassium titanium oxide oxalate dihydrate, 50 mL diethylene glycol and 20 mL water at 180°C for 12 h (see Method Section). The dimension of the wires increases slightly and the surface becomes rough, as shown in Figure 1(b). The morphologies of Ti wire before and after depositing TiO2 are shown in Figure 1S (Supplementary Information) and the later is covered with a white layer of TiO2 film. The phase purity and structure of the hydrothermal sample reacted for 12 h was characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD). Besides the sharp Ti peaks from the substrates of Ti wires, which correspond to (101) and (200) planes of the anatase TiO2 structure, there are obviously several broadened diffraction peaks, as shown in Figure 1(c). The results suggest that the as-products are anatase TiO2 (PCPDFWIN file No. 84-1286). According to the “iii” sample in Figure 1(c), the peaks of anatase TiO2 are much sharper after annealing treatment, which indicates better crystallinity.
Figure 2 shows typical scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the TiO2 nanoarrays with different reaction time (3, 6, 9, 12, 15 h). The reaction temperature is 180°C for each sample deposition. Figures 2 (a) and (b) show SEM images of TiO2 synthesized for 3 h on the Ti wire, with length of about 8 μm. When the reaction time is prolonged to 6 h, there are fractional branches on the trunks of TiO2 nanowire arrays, as shown in Figures 2 (c) and (d). After 9 h of reaction time (Figures 2 (e) and (f)), obvious branches can be observed and the length of the TiO2 nanoarrays increases to about 14 μm. Figures 2 (g) and (h) show the sample morphologies reacted for 12 h. There are a large number of TiO2 nanorod branches on the TiO2 nanowire stems and the length is about 18.5 μm. Figures 2 (i) and (j) show SEM images of TiO2 treelike-nanoarrays deposited on Ti substrate for 15 h. The branches become denser and longer and the length of TiO2 nanowire increases to 22 μm. Therefore, TiO2 nanowire stems grow longer with increasing reaction time and short nanorod branches start to germinate on the surface of TiO2 stems and become denser and longer. In this way, the TiO2 tree-like nanoarrays consisting of long TiO2 nanowire stems and short TiO2 nanorod branches on various wires are successfully obtained with one-step facile hydrothermal reaction.
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) technique was further used to characterize the morphologies and structures of the TiO2 samples, as shown in Figure 3. Figures 3 (a) and (b) are TEM and high-resolution TEM (HRTEM) images of a TiO2 nanowire sample synthesized for 3 h. The interplanar distances of 0.189 and 0.351 nm in the HRTEM image correspond to (200) and (101) planes of the anatase crystal phase of TiO2, respectively (PCPDFWIN file No. 84-1286). The edge of the nanowire is rough, which is beneficial for the regrowth of branches. Figure 3 (c) shows TEM image of a TiO2 nanotree synthesitized for 12 h, in which a large number of branches come out on the stem. The corresponding HRTEM image (Figure 3 (d)) shows interplanar spacing of 0.352 nm, which matches well with the (101) planes of anatase TiO2.
Fabrication of FDSSCs
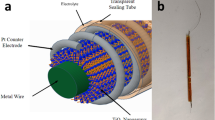
The TiO2 tree-like nanoarrays on metal wires are considered as preferential photoanodes for FDSSCs owing to their superior electron transport capabilities and comparatively large surface areas and the performance of DSSC based on anatase TiO2 is better than that of the rutile one11. The process of fabricating FDSSCs is seen in Method Section. Figures 4 (a) and (b) show the schematic setup and optical image of FDSSC, respectively. The counter electrode is twisted around the dye-sensitized photoanode and then immersed in a transparent tube filled with electrolyte. The FDSSCs is encapsulated in the tube, the end of which is connected to the electrode23,24,25,26,27,28,29. The melted plastic was used to seal the both ends of the tube to finish the fabrication of FDSSCs.
Photovoltaic performance characterization
Figure 5 (a) indicates the current density-voltage (I–V) curves of the FDSSCs fabricated with photoanodes of TiO2 nanoarrays prepared with different reaction time (3, 6, 9, 12, 15 h) on Ti wires. Table 1 summarized the corresponding detailed photovoltaic properties, including the open-circuit voltage (Voc), short-circuit current density (Jsc), fill factor (FF) and PEC. The PCE increases gradually from 2.58% to 6.32% when the hydrothermal reaction time increases from 3 to 12 h and then decreases slightly to 5.50% as the reaction time prolonged to 15 h. The Jsc variation has the same trend as PCE, which increases significantly from 5.42 to 13.95 mA/cm2 and then decreases slightly to 13.15 mA/cm2. Thus, it can be concluded that the differences of the resulting PEC could be mainly attributed to the diverse Jsc. In general, Jsc can be approximated by the following expression35,36:

where q is the elementary charge, ηlh is the light-harvesting efficiency of a cell, ηinj is the charge-injection efficiency, ηcc is the charge-collection efficiency and I0 is the light flux. Among all of these parameters, η1h is mainly related to the amount of adsorbed dye, ηcc is largely dependent on the competition between recombination and charge collection and ηinj is suggested to be of the same value for all the photoelectrodes based on the TiO2 nanoarrays and the N719 dye.
Characteristics of the FDSSCs with TiO2 photoanodes based on Ti wires prepared for different times.
(a) I–V curves. (b) UV-Vis spectra of solutions containing N719 desorbed from sensitized TiO2 nanoarrays. (c) EIS measurements were conducted in the dark under a bias of 0.7 V. (d) an equivalent circuit for fiting Nyquist plots.
The length of nanowire stem and the number of the nanorod branches both increase with prolonged reaction time, which could offer larger surfaces to absorb more dye molecules. Figure 5 (b) shows UV-Vis spectra of solutions containing N719 dye molecules desorbed from sensitized TiO2 nanoarrays synthesized with different reaction time. The corresponding absorbed dye amounts in Table 1 were calculated using Lambert-Beer's law. As the reaction time of TiO2 photoanodes increasing from 3 to 15 h, the amounts of absorbed dye increases from 27.28 to 62.45 nmol/cm2, which results in gradually increasing η1h. Therefore, the Jsc and PCE of the FDSSCs improve with increasing deposition time of TiO2, which could be resulted from the dye adsorption of TiO2 working eletrodes.
However, excessively long TiO2 nanoarrays may lead to decreased Jsc and PCE, which is the case of FDSSCs with the TiO2 photoelectrodes synthesized for 15 h. The corresponding charge-transfer resistance reduces, resulting in a larger recombination rate of photo-induced electrons and holes at the TiO2/dye/electrolyte interfaces. To further elucidate the charge recombination process, electrochemical impedance spectroscopic (EIS) measurements were conducted in the dark under a bias of 0.70 V37. Figures 5 (c) and (d) are the Nyquist plots and the corresponding simplified equivalent circuit for the FDSSCs, respectively. Rs is the series resistance related to the transport resistance of the metal wire substrates. Rct is the charge-transfer resistance accounting for the recombination of photo-induced electrons and holes at the TiO2/dye/electrolyte interfaces, which corresponds to the larger semicircle in the low-frequency region. Rpt is the charge-transfer resistance at the counter electrode/electrolyte interface corresponding to the smaller semicircle in the high-frequency region38. The fitting values of Rct of the TiO2 photoelectrode synthetized for 3, 6, 9, 12 and 15 h are 356.1, 134.9, 103.0, 85.99 and 77.39 Ω, respectively, as listed in Table 1. Nevertheless, the values of Rs and RPt are nearly the same since the Ti wire substrate and the counter electrode/electrolyte interface are the same, as shown in Figure 5 (c). Longer TiO2 nanarrays have smaller Rct values, implying rapid recombination rates of photo-induced electrons and holes at the TiO2/dye/electrolyte interfaces, which may lead to decreased Jsc and PCE of the FDSSC. Both of the Rct and absorbed dye amounts affect the Jsc and PCE of the FDSSC, while both parameters correlate to the length of the TiO2 nanowire arrays and the number of nanorod branches. The TiO2 tree-like nanoarrays synthetized for 12 h possess suitable absorbed dye amounts and recombination rate of generated electrons and holes and achieve the highest Jsc, which ensures excellent photovoltaic performance.
The TiO2 treelike-nanoarrays deposited on W and Ni oxide wires were shown in Figure 2S (Supplementary Information). Figure 6 (a) shows the I–V curve of FDSSCs reacted for 12 h based on a W wire. The corresponding PCE (3.26%) and Jsc (9.91 mA/cm2) are both lower than that based on Ti wire. Annealing of Ti wire leads to the formation of TiO2 anatase phase which has the same band structure as the TiO2 working electrode. Annealing of the W wire, on the other hand, introduces a WO3 layer between the W substrate and the TiO2 photoelectrode. The conduction band level of WO3 is lower than that of TiO239. Thus, electron transfer from the TiO2 layer to the WO3 layer is associated with the dissipation of less amount of energy40,41. To analyse the photovoltaic parameters, EIS measurements were conducted in the dark under a bias of 0.70 V. The Ti and W based FDSSCs showed no noticeable resistance in the first semicircle of EIS data (see Fig. 6 (b)). However, the W based FDSSCs showed a drastic decrease in the internal resistance (Rct = 45.71 Ω), which means a larger recombination rate in photoelectrode and which might be due to the high-level conduction band mismatch between the TiO2 working electrode and the WO3 layer, as shown in Figure 6 (c). Although the W and Ti based FDSSCs have the same interface structures of TiO2/dye/electrolyte, the FDSSCs based on W wires have another interface of TiO2/WO3 labeled as “1” in Figure 6 (c), which enhances the recombination of charges. Thus, the semicircle in the low-frequency region is dependent on both of the interfaces of TiO2/dye/electrolyte and TiO2/WO3 for the FDSSCs based on the W wire substrates. While WO3 is n-type semiconductor, a p-type NiO2 layer was introduced between substrate and TiO2 for comparison. A Ni wire as substrate was heated at 550°C for two hours to introduce a nickel oxide layer on the Ni wire. It was found that the resulting device tested under bias had no efficiency (Figure 3S in Supplementary Information) since the photo-generated electron transfer from the TiO2 to the Ni substrate is hindered by the p-type NiO layer, as schemed in Figure 6 (c) and labeled as “2”. Figure 6 (d) shows that the p-type NiO and n-type TiO2 form a p-n junction (Figure 4S in Supplementary Information). Although the FDDSCs based on the above p-n junction show no performance, they might have potential applications in other photoelectric devices, such as UV-detector, light-emitting diode, etc.
(a) I–V curves of the FDSSCs fabricated with TiO2 photoanodes prepared on W wire for 12 h. (b) EIS measurements were conducted in the dark under a bias of 0.7 V for the FDSSCs based on W and Ti wires with TiO2 photoanodes synsentized for 12 h. (c) Energy states diagram for different metal wire-based FDDSC featuring the operation principle and the dashed line shows the photogenerated electrons can not transfer from TiO2 nanoarray to NiO film (“0”, “1”, “2” note the different oxide layers of TiO2, WO3 and NiO corresponding to the metal wires of Ti, W and Ni, respectively). (d) I–V curve of TiO2 nanoarrays depositing on an oxidized Ni wire for 12 h under bias from −5 V to 5 V and the rectification characteristic indicates a novel p-n junction of NiO/TiO2.
Discussion
Anatase TiO2 tree-like nanoarrays consisting of long TiO2 nanowire trunks and a large number of short TiO2 nanorod branches have been successfully synthesized on various metal wires (Ti, W, Ni, etc.) through one-step facile hydrothermal reaction. The FDSSCs based on anatase TiO2 tree-like nanoarrays on Ti wires show outstanding performance with PCE of 6.32%. The performance of FDSSCs based on a W wire is lower than that based on a Ti wire since the annealing of the WO3 layer enhances charge recombination. If the substrate is an oxidized Ni wire, the cell has no efficiency since the p-type NiO layer prevent electronic transmission, while a novel p-n heterojunction can be obtained. This method is expected to be simple, facile and low cost to prepare anatase TiO2 treelike-nanoarrays on different substrates, which could meet various requirements of optoelectronic applications to the substrates and open up a promising avenue for new TiO2-based applications of nanodevices.
Methods
Materials
Ti (or W, Ni, etc.) wires (99.9%, with the diameter of 0.50 mm) were purchased from China New Metal Materials Technology Co., Ltd. Boric acid (H2BO3, 99.5%), ethanol (99.7%), acetone (99.5%), potassium titanium oxide oxalate dihydrate (C4K2O9Ti·2H2O, 98.5%) and diethylene glycol (DEG) were purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co. Ltd. Ruthenium 535-bisTBA (N719) was purchased from Solaronix. Guanidinium thiocyanate (GuSCN, 99.0%) was from Amresco. Ammonium hexafluorotitanate (IV) ((NH4)2TiF6, 98%), lithium iodide (LiI, 99.999%), iodine (I2, 99.99%), 1-methyl-3- propylimidazolium iodide (PMII, 98%), 4-tert-butylpyridine (TBP, 96%) and tert-butyl alcohol (99.5%) were obtained from Aladdin. Acetonitrile (99.8%) and valeronitrile (99%) were from Alfa Aesar. All solvents and chemicals were reagent grade and were used as received without further purification.
Deposition TiO2 seeds
The metal wires (Ti, W, Ni, etc.) were polished using an abrasive paper, washed using clean water with detergents and subsequently ultrasonicated in deionized water, acetone and ethanol for 20 min, respectively. After dried in air, the Ni wires were placed in a muffle furnace and heated at 550°C for 2 hours. The color of the Ni wires was changed from silver to grey indicating that the surface of the Ni wires was oxidized. The treated-metal wires were immersed into the solution containing 0.1 M (NH4)2TiF6 and 0.2 M H3BO3 at room temperature for 30 min to form a seed layer of TiO2 nanoparticls42.
Synthesis of TiO2 tree-like nanoarrays on metal wires
First, 1.240 g C4O9Ti·2H2O was dissolved in 50 mL DEG by magnetic stirring for 45 min and then 20 mL deionized water added to the solution and stirred for 15 min again. The final solution was transferred to a Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave within a number of seeded-metal wires. Afterward, the autoclave was loaded into an oven at 180°C for different times (3, 6, 9, 12, 15 h) and then cooled down to room temperature naturally. After the hydrothermal reaction, the as-products were collected from the solution, rinsed with deionized water and dried at 80°C over night.
Fabrication of FDSSCs
The as-prepared anatase TiO2 nanoarrays on metal wires were used as photoelectrodes for FDSSCs. Before dye sensitizing, the as-prepared TiO2 nanoarrays were immersed into a 0.12 M TiCl4 solution at 70°C for 40 min. After washing with water and drying in air, the samples were sintered at 500°C for 30 min. After cooling down to about 80°C, the TiO2 electrodes were putted into 0.5 mM N719 dye in acetonitrile/tert-butanol (volume ratio 1:1) and kept for 20 h at room temperature. The sensitized electrodes were then washed in acetonitrile to remove physically-adsorpted dye molecules before the cell assembly. Afterwards, platinum wire with diameter 0.08 mm as the counter electrode was twisted around the dye-sensitized photoanode carefully. Subsequently, the both electrodes were immersed in a transparent plastic tube or a glass tube (Φinner:0.9 mm, Φouter: 1.2 mm) filled with electrolyte. The liquid electrolyte composition was 0.6 M PMII, 0.05 M LiI, 0.03 M I2, 0.1 M GuSCN and 0.5 M TBP in acetonitrile and valeronitrile (V:V = 85:15,)43. The active length of cell was 4.5 cm. The effective active area of the cell is calculated by multiplying the diameter of photoanode and effective length of the cell.
Measurement and characterization
The X-ray diffraction (XRD, PANalytical B.V., The Netherlands) with Cu-Ka radiation measurements were carried out to analyze the phase purity of the samples. The surface morphology of the samples was recorded by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM, FEI NOVA NanoSEM 450). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) images were observed by FEI Titan G2 60–300. The TEM sample was prepared by drop casting ethanolic dispersion of TiO2 samples onto a carbon coated Cu grid. The current density-voltage (I–V) measurements were performed under AM 1.5G (100 mW/cm2, calibrated with a Si photodiode) conditions using a solar simulator illumination (Newport, USA) and an Autolab electrochemic workstation (modelAUT84315, The Netherlands). For testing the adsorbed dye amount of the TiO2 working eletrodes, the sensitized-TiO2 samples desorbed the dye into 0.1 M NaOH solution. UV-Vis absorption spectrometry (UV-2550, Shimadzu) was measured to calculate the amount of the adsorbed dye amount, expressed in terms of moles of dye anchored per projected unit area of the photoelectrode. The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements were scanned in dark condition at a bias of 0.70 V with an amplitude of 10 mV in a frequency range from 100 kHz to 0.1 Hz. The aperture area is equal to the diameter of photoanode multiplied by the active length of the FDSSCs.
References
Chen, X. B. & Mao, S. S. Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, modifications and applications. Chem. Rev. 107, 2891–2959 (2007).
Li, W., Wu, Z. X., Wang, J. X., Elzatahry, A. A. & Zhao, D. Y. A perspective on mesoporous TiO2 materials. Chem. Mater. 10.1021/cm4014859 (2013).
Wold, A. et al. Photocatalytic properties of TiO2 . Chem. Mater. 5, 280–283 (1993).
Wu, H. B., Hng, H. H. & Lou, X. W. Direct synthesis of anatase TiO2 nanowires with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Adv. Mater. 24, 2567–2571 (2012).
O'Regan, B. & Gratzel, M. A low-cost, hight-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 film. Nature 353, 737–740 (1991).
Ren, Y. et al. Nanoparticulate TiO2(B): an anode for lithium-ion batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 2164–2167 (2012).
Wang, C. X. et al. Large scale synthesis and gas-sensing properties of anatase TiO2 three-dimensional hierarchical nanostructures. Langmuir 26(15), 12841–12848 (2010).
Guo, W. X., Zhang, F., Lin, C. J. & Wang, Z. L. Direct growth of TiO2 nanosheet arrays on carbon fibers for highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange. Adv. Mater. 24, 4761–4764 (2012).
Crossland, E. J. W. et al. Mesoporous TiO2 single crystals delivering enhanced mobility and optoelectronic device performance. Nature 495, 215–220 (2013).
Pan, J. H. et al. Large-scale synthesis of urchin-like mesoporous TiO2 hollow spheres by targeted etching and their photoelectrochemical properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 10.1002/adfm.201300946 (2013).
Park, N. G., van de Lagemaat, J. & Frank, A. J. Comparison of Dye-Sensitized Rutile- and Anatase-Based TiO2 Solar Cells. J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 8989–8994 (2000).
Wu, W. Q. et al. Hydrothermal Fabrication of Hierarchically Anatase TiO2 Nanowire arrays on FTO Glass for Dye-sensitized Solar Cells. Sci. Rep. 3, 1352; 10.1038/srep01352 (2013).
Ye, M. D., Xin, X. K., Lin, C. J. & Lin, Z. Q. High efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells based on hierarchically structured nanotubes. Nano Lett. 11, 3214–3220 (2011).
Varghese, O. K., Paulose, M. & Grimes, C. A. Long vertically aligned titania nanotubes on transparent conducting oxide for highly efficient solar cells. Nat. Nanotechnol. 4, 592–597 (2009).
David, O. S. et al. Band alignment of rutile and anatase TiO2 . Nat. Mater. 798–801 (2013).
Shao, F., Sun, J., Gao, L., Yang, S. W. & Luo, J. Q. Forest-like TiO2 hierarchical structures for efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 6824–6830 (2012).
Liao, J. Y., Lei, B. X., Chen, H. Y., Kuang, D. B. & Su, C. Y. Oriented hierarchical single crystalline anatase TiO2 nanowire arrays on Ti-foil substrate for efficient flexible dye-sensitized solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 5, 5750–5757 (2012).
Fonzo, F. D. et al. Hierarchically organized nanostructured TiO2 for photocatalysis applications. Nanotechnology 20, 015604 (2009).
Sakano, T. Okato, T. & Obara, M. Nitrogen-doped TiO2 thin films grown on various substrates. Proc. of SPIE 6106, 610615-1-8 (2006).
Chen, J. S., Chao, S., Kao, J. S., Lai, G. R. & Wang, W. H. Substrate-dependent optical absorption characteristics of titanium dioxide thin films. Appl. Optics 36, 4403–4408 (1997).
Jose, R., Thavasi, V. & Ramakrishna, S. Metal oxides for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92, 289–301 (2009).
Yella, A. et al. Electrolyte exceed 12 percent efficiency based redox-porphyrin-sensitized solar cells with cobalt (II/III). Science 334, 629–634 (2011).
Fan, X. et al. Fibrous flexible solid-type dye-sensitized solar cells without transparent conducting oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 113510-1-3 (2008).
Fan, X. et al. Wire-shaped flexible dye-sensitized solar cells. Adv. Mater. 20, 592–595 (2008).
Liu, Z. Y. & Misra, M. Dye-sensitized photovoltaic wires using highly ordered TiO2 nanotube arrays. ACS Nano 4, 2196–2200 (2010).
Fu, Y. P. et al. TCO-free, flexible and bifacial dye-sensitized solar cell based on low-cost metal wires. Adv. Energy Mater. 2, 37–41 (2012).
Zhang, S. et al. Single-wire dye-sensitized solar cells wrapped by carbon nanotube film electrodes. Nano Lett. 11, 3383–3387 (2011).
Cai, F. J., Chen, T. & Peng, H. S. All carbon nanotube fiber electrode based dye-sensitized photovoltaic wire. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 14856–14860 (2012).
Guo, W. X. et al. Rectangular bunched rutile TiO2 nanorod arrays grown on carbon fiber for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 4437–4441 (2012).
Weintraub, B. et al. Optical fiber/nanowire hybrid structures for efficient three dimensional dye-sensitized solar cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48, 8981–8985 (2009).
Lv, Z. B. et al. Highly efficient and completely flexible fiber-shaped dye-sensitized solar cell based on TiO2 nanotube array. Nanoscale 4, 1248–1253 (2012).
Hassan, J. J. et al. High sensitivity and fast response and recovery times in a ZnO nanorod array/p-Si self-powered ultraviolet detector. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 261108 (2012).
Lu, T. C. et al. Characterizations of low-temperature electroluminescence from ZnO nanowire light-emitting arrays on the p-GaN layer. Optics Lett. 35(24), 4109–4111 (2010).
Abbasi, M. A., Ibupoto, Z. H., Hussain, M., Nur, O. & Willander, M. The fabrication of white light-emitting diodes using the n-ZnO/NiO/p-GaN heterojunction with enhanced luminescence. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 8, 320-1-6 (2013).
Zhu, K., Neale, N. R., Miedaner, A. & Frank, A. J. Enhanced charge-collection efficiencies and light scattering in dye-sensitized solar cells using oriented TiO2 nanotubes arrays. Nano Lett. 7(1), 69–74 (2007).
Liao, J. Y., Lei, B. X., Kuang, D. B. & Su, C. Y. Tri-functional hierarchical TiO2 spheres consisting of anatase nanorods and nanoparticles for high efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 4, 4079–4085 (2011).
Hou, S. C. et al. Flexible conductive threads for wearable dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 6549–6552 (2012).
Liao, J. Y., Lin, H. P., Chen, H. Y., Kuang, D. B. & Su, C. Y. High-performance dye-sensitized solar cells based on hierarchical yolk-shell anatase TiO2 beads. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 1627–1633 (2012).
Miyauchi, M., Nakajima, A., Watanabe, T. & Hashimoto, K. Photocatalysis and photoinduced hydrophilicity of various metal oxide thin films. Chem. Mater. 14, 2812–2816 (2002).
Kang, M. G., Park, N. G., Ryu, K. S., Chang, S. H. & Kim, K. J. Flexible metallic substrates for TiO2 film of dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Lett. 34(6), 804–805 (2005).
Balasingam, S. K., Kang, M. G. & Jun, Y. Metal substrate based electrodes for flexible dye sensitized solar cells: Fabrication methods, progress and challenges. Chem. Comm. 10.1039/C3CC46224B.
Xu, C. K., Wu, J. M., Desai, U. V. & Gao, D. High-efficiency solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells based on TiO2-coated ZnO nanowire arrays. Nano Lett. 12, 2420–2424 (2012).
Wu, W. Q. et al. Hierarchical Oriented Anatase TiO2 Nanostructure arrays on Flexible Substrate for Efficient Dye-sensitized Solar Cells. Sci. Rep. 3, 1892; 10.1038/srep01892 (2013).
Acknowledgements
The current work was supported by the 973 Program of China (2011CB933300), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11074082, 11204093, 11374110, 51371085, 11304106) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (HUST: 2012QN114, 2013TS033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.C. carried out all experiments and wrote the draft of the manuscript; Y.H.G. & L.C. devised the original concept, designed the experiments, discussed the interpretation of results and revised the manuscript; L.Y.L. & J.S. contributed the TEM microstructure experiment; F.F.T. participated in part of experiments; L.Y.L. & L.S.N. revised the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and participated in manuscript revision.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Information
A General Method for Preparing Anatase TiO2 Treelike-Nanoarrays on Various Metal Wires for Fiber Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareALike 3.0 Unported License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, L., Li, L., Su, J. et al. A General Method for Preparing Anatase TiO2 Treelike-Nanoarrays on Various Metal Wires for Fiber Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Sci Rep 4, 4420 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04420
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04420
This article is cited by
-
A photoanode with hierarchical nanoforest TiO2 structure and silver plasmonic nanoparticles for flexible dye sensitized solar cell
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Low-cost photodetector architectures fabricated at room-temperature using nano-engineered silicon wafer and sol-gel TiO2 – based heterostructures
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Growth of black TiO2 nanowire/carbon fiber composites with dendritic structure for efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue
Journal of Materials Science (2019)
-
Synthesis of CeO2-based core/shell nanoparticles with high oxygen storage capacity
International Nano Letters (2017)
-
Significant enhancement of power conversion efficiency for dye sensitized solar cell using 1D/3D network nanostructures as photoanodes
Scientific Reports (2015)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.