Abstract
The present study explores the preparation of Al–10wt.%Zn alloy by the casting process. Nano CuO was prepared by the Co-precipitation method. The effect of adding nanostructure of (1wt.% CuO) to Al–10Zn alloy was studied the corrosion effects as-cast and with different aging temperatures (423, 443, and 463 K) for 2 h in 3.5% NaCl aqueous solution after homogenized for 2 h at 500 K at room temperature. Electrochemical measurements (OCP, Tafel, and EIS) were performed to determine the corrosion rate (C.R.) and corrosion current density (Icorr.) to find out corrosion behavior. In addition, microstructures of Al–10Zn and Al–10Zn–1CuO were observed using a scanning electron microscope, EDX mapping, and the optical microscope to investigate the effect of the nanoparticle’s addition before and after aging and the corrosion test. The average crystal size and the dislocation density were calculated from the XRD pattern. The results show that the appropriate addition of CuO nanoparticles can refine the Al–10Zn alloy and shift the Al–10Zn alloy to a more noble direction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Aluminum (Al) and its alloys have recently been employed extensively in modern engineering applications due to its high strength and lightweight1,2. Moreover, their hardness, low wear, and chemical resistance limit their use in various automotive, construction, and aerospace applications3,4,5,6. Pure Al has weak mechanical characteristics in engineering applications, whereas alloying and heat treatment can improve it. The proper Al alloys must be chosen for required applications considering their specific rigidity, thermic conductivity, low density, strength, formability, weldability, workability, ductility, wear, and corrosion resistance7.
There are more and more applications for cast alloys made from Al and Zinc (Zn)-based matrices, and their production is rising globally8.
The primary purpose for concentrating on Al–Zn alloys is that adding Zn causes value addition, improves the matrix’s homogeneity, and enhances Al alloys properties9. Zn has a high solubility in the Al matrix; adding Zn causes a low lattice distortion, which almost has no impact on the alloy’s formability10. Al–Zn alloys have high strength, ductility, heat treatability, excellent hot workability/formability, and good welding properties11,12. Al–Zn alloys also have a considerable impact on their microstructure, being a fine-grained industrial alloy used to create high-strength corrosion-proof (verification) structures for aircraft, ships, and vehicle buildings13. Hence, it is necessary to constantly support the Al matrix with suitable Ceramic nano particulate reinforced ceramics such as CuO, TiO2, SiC, SiO2, B4C, and Al2O3 14,15. They are considered the best option for Al as a matrix base metal because they impart high strength and resistance to wear and corrosion16. Ceramic particles play a role in increasing mechanical strength by acting as a nucleation site for solidification, allowing the grain size to be finer. Alloying elements’ function is to form a solid solution of Al alloy, which causes grain size refinement. At the same time, the role of alloying elements is to develop a solid solution of Al alloy which causes grain size refinement. There are different ways to make Al alloys’ nanocomposites, such as stir casting, which mainly works in manufacturing the composites as it produces composites with uniform reinforcement distribution6,17,18,19.
CuO is one of the best choices for Al matrix nanocomposite because it has many advantages; CuO addition in Al matrix material improves corrosion resistance, stability, stiffness structural applications, particularly for aerospace and automobile engineering, and thermal properties20. CuO was chosen in this study for various reasons, including; commercially, CuO particles were used to create Al-based composites due to their superior mechanical and physical properties21. Low-cost, widely available. CuO has received much research attention due to its many valuable uses in electrical equipment, including Solar cells, highly hydrophobic surfaces, and gas detection sensors22. Cu addition lowers the melting point and may cause the creation of the Al2Cu phase, which increases the Al matrix’s tensile strength21. Nano-copper oxide effectively reduces friction and prevents wear on machinery parts because of its hardness23. Al and CuO phases have differing structures and stresses, which makes adding CuO nanoparticles to the Al matrix advantageous. At the point where the Al matrix and CuO reinforcement particles meet, it creates dislocation. The strength of the Al matrix, which is connected to the static dislocations generated during the work hardening (aging) process, is increased due to the created dislocations’ increased surface area and increased grain refinement, which improves corrosion resistance24.
To study the effect of Al–CuO composite on Al sheets, Hamed et al. prepared Al sheets and Al–CuO composite by accumulative roll bonding, adding 0.5 vol.% CuO to pure Al. They reported that the Al–CuO composite showed that microhardness and tensile strength analysis was higher than the pure Al; reinforcing in particles acts like pins on Al24. Usually, heat treatment increases formability. Nonetheless, depending on the heat treatment’s temperature and time, it can result in recovery, recrystallization, or grain growth. Strength and toughness are consequently reduced. Increased work hardening and improved grain refinement are caused by the addition of nanostructure24. Wang et al.25 recently investigated the electrochemical behavior of an Al–Zn alloy. The authors examined the electrochemical corrosion test on Al–20Zn–0.2In alloy and discovered a reduced corrosion rate. Zhao et al.26 used electron back-scattered diffraction to study the microstructural evolutions of an Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy processed by multiaxial forging in various directions (z-axis to the x-axis to the y-axis to z-axis to again x-axis), while rotating the sample 90° each time. All the samples were heating at 573 K and suffered various degrees of deformation. As the number of multiaxial deformations increased, the formed precipitate decreased. Due to precipitates pinning grain development, grain size decreased as multiaxial deformations increased. Hu et al.27 investigated how Ce affected the Al–Zn–Mg alloy’s microstructural changes and corrosion behavior. High-purity Al, Zn, Mg, and Ce ingots and rods were combined to prepare the alloy through the casting process. The casting process was carried out at 1023 K, the cast samples were heated for 4 h at 693 K, and then the specimens were extruded at 733 K using an 11:1 extrusion ratio. The microstructural and stress corrosion cracking was performed to evaluate the alloy performances. The addition of Ce increased homogenous microstructure and corrosion resistance. Pan et al.28 studied two nano-treated AA7075 alloys (Al–Zn–Mg–Cu) cast and extruded were tested for corrosion behavior and microstructure. The results showed that the nano-treated AA7075 (TiC and TiB2) have higher hardness considering the refine grain size. At the same time, the localized electrons at the matrix-nanoparticle interfaces cause reduced electrical conductivity, which might minimize corrosion reactivity. AA7075 nano-treated alloys may exhibit improved corrosion resistance for either of these reasons. Simoes et al.29 studied the microstructural and mechanical characteristics of Al matrix composites produced by the powder metallurgy technique and reinforced with varying amounts of CNTs (0, 0.5, 0.75, 1, and 1.5 vol). The study’s findings demonstrated that nanocomposites with a 1 vol% CNT reinforcement increase their strength due to their strong dispersion efficiency. AbdElRhiem et al.30 studied the Effects of adding TiO2, CuO, and SiO2 nanoparticles on Al–Zn alloy's microstructure and mechanical properties. The study found nanoparticle addition resulted in grain refinement and hardening of the Al–Zn alloy.
The above discussion shows insufficient corrosion behavior, and pit formation data are available. This study has highlighted the significance of Al–10wt.%Zn alloy and the effect of nano 1wt.%CuO addition as a reinforcement to improve and enhance the performance of the alloy (electrochemical behavior and microstructure). 1CuO nanostructure was added to Al–10Zn by the mechanical dispersion method. Electrochemical measurements were performed at room temperature to determine the corrosion behavior before and after different aging temperatures (423, 443, and 463 K) for 2 h.
Materials and methods
Nano CuO preparation
Copper oxide nanostructure was prepared by the co-precipitation method using copper chloride (CuCl2) as a copper source and NaOH as a precipitating agent. Distilled water was used to filter and wash the precipitate. Then the precipitate was grinded and overnight dried at 373 K. Finally, the powder was calcinated at 773 K for 2 h.
Samples fabrication and treatment
In the present study, the base matrix and reinforcement particles are Al–10wt.% Zn and CuO nanostructure addition (Al–10wt.% Zn–1wt.%CuO). Using the raw materials, an Al–10wt.% Zn alloy was created. At 1023 K, Al and Zn were melted and mixed in high-purity graphite crucibles in an Ar atmosphere. The molten alloy was poured into a steel mould to make the cold-cast ingots. Ten millimeter-diameter rod-shaped samples were collected. In addition, reinforcement particles were created by mechanically distributing 1% CuO nanostructure into an Al–10%Zn alloy. The samples were remelted in a vacuum arc furnace at 1050 K under a high-quality argon flow protection and then cast into stainless steel molds to achieve a homogeneous composition, obtaining 10 mm diameter rod-like samples. These rod-shaped samples were swaged and then cold-pulled into sheets that were 1 mm thick. After solidification, the ingots were homogenized for 2 h at 500 K before being cooled slowly to ambient temperature.
The samples were then aged for 2 h at three different temperatures (423, 443, and 463 K) before being quenched in cooled water to room temperature to preserve the structure created at these aging temperatures.
Table 1 displays the investigated samples’ chemical composition (in weight percent). The schematic diagram (Fig. 1) shows the preparation steps of the matrix Al–10wt.% Zn and Al–10wt.% Zn–1wt.%CuO.
Material characterization
Mechanical grinding and polishing were used on the surface samples for the microstructure investigations. Keller’s reagent etching was then applied to reveal their grain boundaries and orientations. (2.5 ml HNO3, 1.5 ml HCl, 1 ml HF, and 95 ml distilled water).
The morphology of the obtained samples was investigated using emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) JOEL, JSM-6700F equipped with an energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), optical microscope (OM) LECO LX 31 with a magnification of up to 500, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEOL JEM_2100). The phase analysis was performed using an X-ray diffractometer (Bruker AXSD8 X-ray diffractometer, ADVANCE, Germany) with Cu Kα radiation at λ = 1.5406 Å.
Corrosion testing
The corrosion test of the samples was studied using a three-electrode system according to ASTM G59-97 using an electrochemical testing station (Origaflex-OGF01A-Origalys, France) at room temperature. Before testing, the samples were subjected to mechanical polishing with 1 cm × 1 cm dimensions. The samples were cleaned with deionized water, then ultrasonically cleaned in acetone and dried. Then, the corrosion test was formed in a solution of NaCl 3.5% concentration. The Pt sheet served as an auxiliary electrode, and an Ag/AgCl was used as the reference electrode.
The electrochemical measurements were done in two steps: (i) obtaining a time dependence of potential over a period of 30 min that allowed for the measurement of the static potential; and (ii) obtaining the curves “corrosion current density (Id)–potential (E) in the potential between −300 and 300 mV with respect to Ecorr, with the scan rate of 2 mV/s.
In addition, use the Tafel extrapolation method to get the Tafel slopes. The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements were performed at a frequency range of 0.1 Hz to 100 kHz at the open circuit potential with an AC sine wave amplitude of 10 mV (ASTM G106-89).
Results and discussion
Microstructural investigations
CuO nanostructure
Figure 2 shows the SEM images of the CuO nanostructure. Nanorod morphology with porous nature can be observed in both SEM (Fig. 2a) and TEM images (Fig. 2b), indicating the successful preparation of the CuO nanostructure.
The XRD pattern of the prepared copper oxide (Fig. 2c) shows peaks at 2θ equal to 32.5°, 35.6°, 38.7°, 38.9°, 46.3°, 48.8°, 51.3°, 53.4°, 58.3°, 61.6°, 66.2° and 68.1° with monoclinic phase31 (card no. 00-005-0661) which confirms the preparation of pure CuO. The XRD shows sharp peaks, revealing the high crystallinity of the prepared CuO22.
Microstructure of the samples
Figure 3 shows The EDX mapping and SEM images of a homogeneous microstructure of A1 and A2, showing two metallurgical phases: an α-Al matrix and β-Zn phase, where the Zn single large particles nucleate at the grain boundary with white color, and the grey color represents Al, as shown in (Fig. 3a). When added to the base alloy, the CuO nanostructure represented the accumulated white particles, as shown in (Fig. 3b). The EDX mapping analysis confirms the chemical compositions of samples A1 and A2, respectively. In addition, Fig. 3 indicates that the CuO nanoparticles had an identical distribution (strong dispersion efficiency). The propensity of zinc to precipitate on the boundaries of the grains enhances the possibility of nanoparticle aggregation on the Zn particles that produce bright grey precipitates on grain boundaries, as shown in (Fig. 3a, b) during aging, which leads to an increase in their strength by acting as a nucleation site for solidification, following the grain size to be finner6,17,18,19.
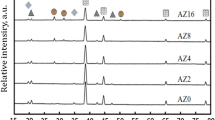
Figure 4a–d, e–h show the XRD patterns of A1 and A2, as-cast and at different aging temperatures of 423 K, 443 K, and 463 K, respectively. The XRD pattern of the as-cast A1 alloy, shown in Fig. 4a, revealed an AlZn anorthic structure with a homogeneity distribution of a single phase, where Zn is completely dissolved in the Al matrix (reference code: 03-065-3358). The addition of nano-CuO to the Al–10Zn alloy appears to have formed CuO peaks, as shown in Fig. 4e (monoclinic CuO, reference code: 00-005-0661)22.
Figure 4b, c show the XRD patterns of A1 alloy after aging at 423 K and 443 K, revealing two phases, α-Al of fcc structure and β-Zn of hexagonal structure, with reference codes of 000030932 and 030653358, respectively. Furthermore, after the 443 K transition temperature, the diffraction peaks for Zn particles completely disappeared at 463 K, as shown in Fig. 4d, where Zn atoms are completely dissolved in the Al matrix and transferred into a single phase32,33.
The average crystal size (D) and the dislocation density (ρ) can be calculated from the XRD pattern by using Williamson-Hall’s calculation (Eq. 1)24.
where θ is the Bragg angle, λ is the x-ray wavelength; β is the broadening of the diffraction line (FWHM). And the dislocation density was obtained for samples using Eq. (2)34.
To understand the evolution of the polarization resistance, dislocation density was calculated, and detailed microstructure characterization was performed on all samples studied. The value of dislocation density obtained from XRD as a function of aging temperature is given in Table 2. The crystal size of A1 was decreased by adding nano CuO at different aging temperatures. Perhaps the formation of dislocations at the interface of the Al matrix and nano-CuO, as reinforcement particles, is caused by strain and different structural properties of the two phases, which improve microstructures and corrosion resistance6,24. The lattice strain and dislocation density decrease as the aging temperature rises, as discussed in Table 2 and as shown by XRD calculations, creating pinned mobile dislocations. This result led to significant refining in the grains of A2 due to their strong dispersion efficiency compared with A1, confirmed by OM and SEM images in Figs. 5 and 6. As a result, the strengthening characteristics of the nano-treated A2 increased and hardened than A124,30.
Optical microscope examinations (grain refinement)
Optical micrographs and SEM of A1 and A2 are shown in Figs. 5 and 6 before and after aging at different temperatures (423, 443, and 463 K), respectively. Grain size calculations using the Image J program showed that fine-refining is performed at all aging temperatures than as-cast one (Figs. 5 and 6a, b). A1 grains size is 168 μm while A2 is 176 μm. While after all aging temperatures, the A2 grains size was refined, as shown in Figs. 5 and 6d, f, h. Moreover, after 443 K, the grains’ size experienced more grain refinement than before. At 423 K, Figs. 5 and 6c, d, the mean grains size of A2 became smaller than A1 alloy, from 77 μm to 75 μm, but after the transformation point, the grains size of A2 became finer than A1 alloy, as shown in Figs.5 and 6e, f, from 102 μm to 63 μm at 443 K and then became more finner from 108 to 58 μm at 463 K, as shown in Figs. 5 and 6g, h. The mean grain size of A1 alloy and A2 was 113 and 93, respectively. Hence, aging resulted in modifying the structure of the aged samples as a consequence of the more uniform distribution of solute, especially for A2 than A1 alloy. Referring to dislocation density, as presented in Table 2, A2 caused an increase in the surface area compared with A1 alloy before and after aging temperatures, fine graining occurred and modifying the structure.
As a result, the grains of the A2 have different orientations than the grains of the A1 alloy, as shown in Figs. 5 and 6. The increasing number of dislocations density, as provided in Table 2 of A2, where the CuO nanostructure interface with metal matrix caused to increase in the surface areas. Adding CuO nanostructure created different structures of Al–Zn and CuO Phases, which caused the creation of dislocations in the interface of the Al matrix and reinforcement nano CuO24. The increased aging temperature caused a significant change in the microstructure besides the grain growth and affected the A2 grains size distribution24.
Corrosion characteristics of the samples
The open circuit potential (OCP) values of A1 and A2 were observed for 2000s while being as-cast and after being aged at different temperatures (423, 443, and 463 K) for 2 h before being submerged in a 3.5% NaCl solution at room temperature, as shown in Fig. 7 a. The OCP of both A1 and A2 increases steadily with increasing aging temperature during the OCP of immersion in NaCl. The potential of the A1 varies from −0.90065 to −0.96697 V vs. Ag/AgCl at aging temperature 423 K, while the potential of the A2 changes from −0.8959 to −0.96072 V vs. Ag/AgCl. The potential of the A1 shifts from −0.96697 to −0.96958 V vs. Ag/AgCl at aging temperature 443 K, while the potential of the A2 shifts from −0.96072 to −0.96141 V vs. Ag/AgCl. The potential of the A1 shifts from −0.96958 to −0.96974 V vs. Ag/AgCl at the aging temperature of 463 K, while the potential of the A2 changes from −0.96141 to −0.97876 V vs. Ag/AgCl. After being submerged in NaCl for longer periods (> 2000s), it is hypothesized that the OCP of the A1 and A2 may undergo an additional positive shift, with the potential shift of the A2 being expected to be greater than that of the A1. Al–10Zn was made better in terms of OCP when nano 1CuO was added, both as-cast and at all aged temperatures. The OCP for A1 and A2 that is optimally aged is at 463 K. OCP tests revealed the potential stability of A2 in 3.5% NaCl solution slowed down due to the addition of nano 1CuO and showed the influence of aging on positive potential shift by increasing temperature, which confirms the Tafel test. (Fig. 7b).
The potentiodynamic polarization was used to investigate the effect of adding 1 nano CuO to an Al–10Zn alloy on corrosion attack in a 3.5% NaCl solution at room temperature. The anodic and cathodic branch slopes are where the Tafel slopes are found. The corrosion parameters can be derived using these slopes.
The corrosion rate of the samples can be determined using the results of the polarization test. The following formula is used to determine the corrosion rate:
where n is the number of charge transfers that occur during the corrosion process, C.R. is the corrosion rate (mpy), Icorr is the current density of corrosion (A cm−2), M.W. is the molecular weight of the corroded material (g/mol), and d is the density of the corroded material (g cm−3)35.
The corrosion rates for the A1 and A2 in NaCl at room temperature, as determined by electrochemical measurements, are shown in Fig. 7b. The Tafel extrapolation measurements show the results of at least three tests for each condition of the as-cast and after-aged samples. It can be noted that the A2 corrosion rate is lower than the A1, and also corrosion current density lowered over the brief testing period.
The Tafel plot yielded corrosion potential (Ecorr), Icorr, and corrosion rate (C.R.). As shown in Fig. 8a, C.R. in as-cast samples decreased from 159 to 79.6 μm/y. C.R. of the aged sample at 423 K decreased from 140.4 to 59.9 μm/year. Also, C.R. reduced for the aged sample at 443 K from 108 to 44.3 μm/year, and the aged sample at 463 K from 95.7 to 26.6 μm/year. According to Fig. 8b, Icorr reduces for A1 alloy by increasing the aging temperature compared with the as-cast one. However, as shown in Fig. 8b, adding nano CuO to Al–10wt.%Zn alloy improved corrosion resistance (reduction of Icorr) over A1. After all aging temperatures, A2 showed better corrosion resistance than A1 samples. By increasing the aging temperature, Icorr of A1 reduces. However, as shown in Fig. 8b, adding 1 nano CuO to A1 improved corrosion resistance (reduction of Icorr) over A1. A2 demonstrated superior corrosion resistance to A1 samples for the as-cast and after-all aging temperatures. Icorr reduced in the as-cast samples from 14.6 to 6.8 μA/cm2, the sample at 423 K reduced from 12.9 to 5.5 μA/cm2, the sample at 443 K reduced from 9.9 to 4 μA/cm2, and the sample at 463 K reduced from 8.8 to 2.4 μA/cm2, as shown in Fig. 8b. Because Icorr is directly proportional to C.R. of the material, the decrease in Icorr reduces the C.R. (As illustrated in Fig. 8)16,36. Furthermore, there is a direct relationship between the addition of hard particles (CuO nanostructure, for instance) to the alloy and the grain size diameter, which is related to the improvement of the electrochemical and mechanical properties due to the uniform distribution of CuO nanostructure20,37,38. Raising the aging temperatures for both A1 and A2 reduces the corrosion rate.
Concerning the electrochemical corrosion tests, a small addition of nano CuO enhanced the surface area, reducing corrosion sites and slowing down the C.R. before and after aging24. The larger specific surface area surface of nano CuO may be responsible for its corrosion resistance. The aged samples appeared with a more uniform distribution of nano CuO in A1, which controls charge transfer in the composite surface regarding better corrosion rate during corrosion testing than A1. Accordingly, sample A2 containing nano CuO exhibits greater corrosion resistance than the other A1.
To obtain superior corrosion resistance both before and after aging, the A2 gives additional stability. EIS was utilized to describe the corrosion behavior of the A1 alloy and A2 in NaCl-based solution, as depicted in Fig. 9a. According to the findings, the A2 exhibits greater corrosion resistance than the A1. A2 may be well protected under corrosive conditions by the dense and stable surface, according to the greater phase angle and larger capacitive response, as shown in Fig. 9b. The phase angle and Bode impedance results match those from Nyquist plots. Because of this, the corrosion product layer on the A1 surface is less dense than on the A2 sample, which has caused A1 to corrode even more.
When A1 and A2 were aged (423, 443, and 463 K), corrosion resistance effectiveness was seen. The effect of nano CuO addition. This outcome was brought about by the condition of the possibility for pitting, cracks, and voids being minimal and smaller particle size. The blocking that turns the surface passive and shields the A2 surface from ionization and dissolution improved the nano sample’s corrosion resistance. This outcome demonstrates how the CuO addition enhances the Al–Zn surface’s ability to resist corrosion in water environments at room temperature23.
Morphology of the corroded surface
The microstructure (SEM micrographs) for A1 and A2 samples are shown in Fig. 10, which were taken of the corroded surface before and after aging. Aging can change the sample surface microstructures, confirming the C.R. results. Figure 10a, c, e, g represent samples A1 and Fig. 10b, d, f, h represent sample A2. As shown in Fig. 10, the sample’s surfaces corroded by NaCl solution have irregular pitting, cracks, and ruptured oxide, which determine the sites of electrochemical activity of A1 and A2. As a result, A2 has a higher corrosion resistance than A1, which was very noticeable and confirmed the values of C.R. and Icorr for both samples, as shown in Fig. 8.
Before and after aging at 423 K, both A1 and A2 showed pits, cracks, and voids; however, above 423 K, nano CuO fractured into minute pieces, and at 443 K and 463 K, the nano CuO started to disappear. This finding is because Al–Zn alloy and CuO are different phases at first, causing incoherency between the two structures. During aging above 423 K, A2 became a single phase, significantly depleting the microcrack’s energy, reducing crack nucleation sites, and arresting its propagation 39,40.
Segregation is reduced when the grain size is smaller, and homogenous corrosion results. Improving grain refining lowers the corrosion rate41,42,43. A fine grain structure is more corrosion-resistant because a high grain boundary density encourages a superior oxide layer conduction rate on surfaces with low to passive corrosion rates. Several researchers have reported that dislocations have an impact on corrosion performance. These findings show that aging temperature has a significant and similar effect on the microstructure and electrochemical properties of the samples. As a result, it has been discovered that raising the aging temperature lowers the corrosion rate.
Conclusions
The results of the study evidenced the following conclusions:
-
The copper oxide was successfully prepared, and TEM analysis confirms it is in the nano-size range.
-
Al–10Zn alloy and Al–10Zn–1CuO were successfully prepared and studied by XRD, SEM, and electrochemical measurements before and after different aging temperatures.
-
Heat treatments offer an elegant way to modify the microstructure; as the aging temperature increased from 423 to 463 K, the addition of nano CuO caused grain refinement.
-
OCP demonstrated that Al–10Zn–1CuO might be stable in 3.5% NaCl solution, nano 1CuO addition slowed down and shifted the potential to positive by increasing the temperature.
-
It was found that polarization testing confirms the results of EIS, and microstructure (SEM & OP images), where Al–10Zn–1CuO revealed better corrosion resistance than Al–10Zn alloy in the 3.5% NaCl solution before and after aging, where the addition of nano CuO obstructed the defects (cracks, developing pits, and ruptured oxide).
-
Aging has a significant influence on reducing the samples’ corrosion rate by increasing temperature.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Mohammed, H. J., Mahmood, I. A. & Al-Jaafari, M. A. An estimation study on fatigue transition life of nanocomposites reinforced by Al2O3. Assoc. Arab Univ. J. Eng. Sci. 25, 185–202 (2018).
Zhang, X., Zhou, X., Nilsson, J.-O., Dong, Z. & Cai, C. Corrosion behaviour of AA6082 Al–Mg–Si alloy extrusion: Recrystallized and non-recrystallized structures. Corros. Sci. 144, 163–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2018.08.047 (2018).
Sun, N., Jones, W. J. & Apelian, D. Friction stir processing of aluminum alloy A206: Part II—Tensile and fatigue properties. Int. J. Metalcast. 13, 244–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-018-0268-6 (2019).
Verma, N. & Vettivel, S. C. Characterization and experimental analysis of boron carbide and rice husk ash reinforced AA7075 aluminium alloy hybrid composite. J. Alloys Compd. 741, 981–998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.185 (2018).
Ashwath, P. & Anthony Xavior, M. in Advances in Micro and Nano Manufacturing and Surface Engineering. (eds. Shunmugam, M. S. & Kanthababu, M.). 19–32 (Springer).
Malaki, M. et al. Advanced metal matrix nanocomposites. Metals 9, 330 (2019).
Nafsin, N. & Rashed, H. Effects of copper and magnesium on microstructure and hardness of Al–Cu–Mg alloys. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. (IJEAT) 2, 533–536 (2013).
Krajewski, P. K., Greer, A. L. & Krajewski, W. K. Main directions of recent works on Al–Zn-based alloys for foundry engineering. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 28, 3986–3993. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04048-5 (2019).
Adeosun, S., Balogun, S., Osoba, L., Ayoola, W. & Oladoye, A. Effect of Cu and Zn addition on the mechanical properties of structural aluminum alloy. J. Mod. Manuf. Technol. 3, 103–110 (2011).
Sivasankaran, S., Al-Mufadi, F., Al-Shataif, Y. & Irfan, O. Development of Al–Zn die-casting alloys and its flexural deformation behavior. Int. J. Mech. Prod. Eng. Res. Dev. (IJMPERD) 10, 14185–14192 (2020).
Sun, X. Y. et al. Correlations between stress corrosion cracking susceptibility and grain boundary microstructures for an Al–Zn–Mg alloy. Corros. Sci. 77, 103–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2013.07.032 (2013).
Liu, T., Si, N.-C., Liu, G.-L., Zhang, R. & Qi, C.-Y. Effects of Si addition on microstructure, mechanical and thermal fatigue properties of Zn–38Al–2.5Cu alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 26, 1775–1782. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64290-5 (2016).
Chuvil'deev, V. N. et al. Investigation of mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of fine-grained aluminum alloys Al–Zn with reduced zinc content. J. Alloys Compd. 891, 162110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162110 (2022).
Węglowski, M. S. Friction stir processing—State of the art. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 18, 114–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2017.06.002 (2018).
Bauri, R., Yadav, D. & Suhas, G. Effect of friction stir processing (FSP) on microstructure and properties of Al–TiC in situ composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 4732–4739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.02.085 (2011).
Arunkumar, T., Pavanan, V., Murugesan, V. A., Mohanavel, V. & Ramachandran, K. Influence of nanoparticles reinforcements on aluminium 6061 alloys fabricated via novel ultrasonic aided rheo-squeeze casting method. Met. Mater. Int. 28, 145–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-021-01036-0 (2022).
Dwivedi, P., Maheshwari, S. & Siddiquee, A. N. Fe–SiC–Sn–Mn reinforced surface composite via FSP: A comprehensive analysis. Mater. Today Commun. 35, 105783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.105783 (2023).
Abbasi, M. & Sajjadi, S. Manufacturing of Al–Al2O3–Mg multilayered nanocomposites by accumulative roll bonding process and study of its microstructure, tensile, and bending properties. J. Compos. Mater. 52, 147–157. https://doi.org/10.1177/0021998317703693 (2018).
Ma, C., Chen, L., Cao, C. & Li, X. Nanoparticle-induced unusual melting and solidification behaviours of metals. Nat. Commun. 8, 14178. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14178 (2017).
Fathy, A., Elkady, O. & Abu-Oqail, A. Synthesis and characterization of Cu–ZrO2 nanocomposite produced by thermochemical process. J. Alloys Compd. 719, 411–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.05.209 (2017).
Msebawi, M. S. et al. The effects of CuO and SiO2 on aluminium AA6061 hybrid nanocomposite as reinforcements: A concise review. Coatings 11, 972 (2021).
Saravanan, M., Nair, S. V. & Rai, A. K. Low temperature synthesis of carbon-wrapped CuO synthesized without using a conventional carbon source for Li ion battery application. Physica E 94, 113–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2017.07.023 (2017).
Mahmood, M. H., Suryanto, S., Al Hazza, M. H. F. & Haidera, F. I. Developing of corrosion resistance nano copper oxide coating on copper using anodization in oxalate solution. Int. J. Eng. 31, 450–455 (2018).
Roghani, H., Borhani, E. & Jafarian, H. R. Effect of a trace amount addition of CuO on aluminum sheet processed by accumulative roll bonding with the common roots and rapid annealing. J. Market. Res. 15, 4257–4271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.10.055 (2021).
Wang, X., Yang, F., Viswanathan, G., Wang, S.-S. & Frankel, G. S. Characterization and electrochemical assessment of Al–Zn–In alloy with trivalent chromium process coating. Corros. Sci. 176, 108933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2020.108933 (2020).
Zhao, J., Deng, Y., Tang, J. & Zhang, J. Effect introduced high density of precipitates on the microstructural evolutions during multi-direction forging of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 798, 139927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.139927 (2020).
Hu, G., Zhu, C., Xu, D., Dong, P. & Chen, K. Effect of cerium on microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion properties of Al–Zn–Mg alloy. J. Rare Earths 39, 208–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2020.07.010 (2021).
Pan, S., Yuan, J., Linsley, C., Liu, J. & Li, X. Corrosion behavior of nano-treated AA7075 alloy with TiC and TiB2 nanoparticles. Corros. Sci. 206, 110479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2022.110479 (2022).
Simões, S., Viana, F., Reis, M. A. L. & Vieira, M. F. Influence of dispersion/mixture time on mechanical properties of Al–CNTs nanocomposites. Compos. Struct. 126, 114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.02.062 (2015).
AbdElRhiem, E. et al. Effects of TiO2, CuO, and SiO2 nanoparticles addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al–10 wt% Zn alloy. Phys. Scr. 98, 065018. https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/acd5b5 (2023).
Etefagh, R., Azhir, E. & Shahtahmasebi, N. Synthesis of CuO nanoparticles and fabrication of nanostructural layer biosensors for detecting Aspergillus niger fungi. Sci. Iran. 20, 1055–1058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scient.2013.05.015 (2013).
Lamrous, D., Debili, M. & Boehm-Courjault, E. Microstructure and phase composition of Al–Zn alloys. J. Adv. Microsc. Res. 8, 266–269 (2013).
Zhang, W., Yi, Y., Huang, S., He, H. & Dong, F. Effects of deformation at high, medium, and cryogenic temperatures on the microstructures and mechanical properties of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys. Materials 15, 6955 (2022).
Thirathipviwat, P. et al. Compositional complexity dependence of dislocation density and mechanical properties in high entropy alloy systems. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 30, 545–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2020.07.002 (2020).
Oraei, M., Mostaan, H. & Rafiei, M. The effect of Al2O3 reinforcement particles on the corrosion behavior of Al(Zn) solid solution matrix. Int. J. Mater. Res. 109, 1020–1026. https://doi.org/10.3139/146.111704 (2018).
El-Sayed, A.-R., Mohran, H. S. & Abd El-Lateef, H. M. Corrosion study of zinc, nickel, and zinc–nickel alloys in alkaline solutions by Tafel plot and impedance techniques. Metallur. Mater. Trans. A 43, 619–632. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0908-4 (2012).
Padmavathy, S., Kamalakannan, R. & Manikandan, A. Tribological and mechanical properties of AA6061 reinforced with SiC and graphite for automobile applications. Mater. Today Proc. 21, 24–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.05.354 (2020).
Zhu, J., Liu, L., Zhao, H., Shen, B. & Hu, W. Microstructure and performance of electroformed Cu/nano-SiC composite. Mater. Des. 28, 1958–1962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2006.04.021 (2007).
Safarabadi, M., Khansari, N. & Rezaei, A. An experimental investigation of HA/Al2O3 nanoparticles on mechanical properties of restoration materials. Eng. Solid Mech. 2, 173–182 (2014).
Ahmed, M. A., El-Shennawy, M., Althomali, Y. M. & Omar, A. A. Effect of titanium dioxide nano particles incorporation on mechanical and physical properties on two different types of acrylic resin denture base. World J. Nano Sci. Eng. 6, 111–119 (2016).
op't Hoog, C., Birbilis, N. & Estrin, Y. Corrosion of pure Mg as a function of grain size and processing route. Adv. Eng. Mater. 10, 579–582. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.200800046 (2008).
Jang, Y. H., Kim, S. S., Yim, C. D., Lee, C. G. & Kim, S. J. Corrosion behaviour of friction stir welded AZ31B Mg in 3.5%NaCl solution. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 42, 119–122. https://doi.org/10.1179/174327807X196834 (2007).
Sikora, E., Wei, X. & Shaw, B. Corrosion behavior of nanocrystalline bulk Al–Mg-based alloys. Corrosion 60, 4 (2004).
Acknowledgements
Tabbin Institute for Metallurgical Studies and Physics Department, Faculty of Education, Ain Shams University are gratefully appreciated by the authors for providing the necessary resources to complete this study.
Funding
Open access funding provided by The Science, Technology & Innovation Funding Authority (STDF) in cooperation with The Egyptian Knowledge Bank (EKB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.A.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal Analysis, Data curation, Investigation, Writing-original draft, Writing-review & editing. S.G.M.: Formal Analysis, Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Supervision, Writing-review & editing. Y.F.B.: Investigation, Supervision, Writing-review & editing. M.M.M.: Investigation, Supervision, Validation. R.H.N.: Investigation, Supervision, Validation. S.M.A.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Validation, Writing-review & editing. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
AbdElRhiem, E., Mohamed, S.G., Barakat, Y.F. et al. Corrosion behavior and microstructure of Al–10Zn alloy with nano CuO addition. Sci Rep 13, 12855 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-39515-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-39515-6
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.