Abstract
Exposure to chloromethylisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone (CMIT/MIT) has been associated with allergic contact dermatitis and occupational asthma. Despite this association however, no study has investigated the effects of CMIT/MIT exposure on the development of atopic dermatitis (AD). This study was conducted to investigate the influence of epicutaneous exposure to CMIT/MIT on AD in a mouse model and the underlying biological mechanisms. BALB/C mice were exposed to CMIT/MIT for 3 weeks and AD was developed using ovalbumin (OVA) epidermal sensitization. CMIT/MIT epicutaneous exposure in normal mice significantly enhanced AD-like phenotypes (e.g., transepidermal water loss, clinical score, total serum immunoglobulin E level and infiltration of inflammatory cells). In addition, CMIT/MIT exposure significantly augmented the mRNA expression level of T helper (Th) 2-related cytokines (thymic stromal lymphopoietin, interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-13), Th2 chemokine (chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 17) and the population of CD4+IL-4+ cells in the skin. Moreover, mice exposed to CMIT/MIT in the OVA challenge had greater AD-like phenotypes, higher IL-4 and IL-17A skin mRNA expression levels, and a larger population of CD4+IL-4+- and IL-17A+-producing cells in the skin-draining lymph nodes. Our current findings in a mouse model thus suggest that CMIT/MIT exposure may cause AD symptoms through the dysregulation of Th2/Th17-related immune responses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory skin disease which manifests as eczematous skin including epidermal hyperplasia, spongiosis and immune cell infiltration of the dermis1,2. In recent years, and due to its high susceptibility to environmental exposure, AD has been strongly linked to a number of environmental factors, including exposure to allergens, air pollution and harmful chemical substances3,4. Epidemiological studies have also provided evidence for a possible relationship between environmental pollution exposure, particularly chemical substances, and the risk of AD5,6,7,8. Hence, the causes of the rapid increase in AD are generally thought to be environmental rather than genetic9.
Chloromethylisothiazolinone (CMIT) and methylisothiazolinone (MIT) are chemicals that have been widely used in biocides, paints, and cosmetics such as shampoo, body lotions and skin care products10,11. With the increasing uses of CMIT/MIT however, recent reports have revealed an association of these agents with allergic contact dermatitis, which acts as a sensitizer12,13,14. In addition, CMIT/MIT exposure induces a systemic allergic reaction and decrease in lung function, resulting in occupational asthma15,16,17. A recent experimental study in mice has provided evidence of a biological basis for MIT as a risk factor for allergic sensitization, as indicated by enhanced skin inflammation, immunoglobulin E (IgE) production and immune responsiveness18. Exposure to CMIT/MIT has the potential to enhance the sensitization to allergens, and therefore may play a crucial role in the development of allergic diseases. Despite the growing evidence for a relationship between CMIT/MIT exposure and an allergic immune response however, no previous studies have investigated an association between these chemicals and the development of AD.
Several chemical disinfectants including CMIT/MIT, polyhexamethylene guanidine phosphate and oligo (2-(2-ethoxy) ethoxyethyl guanidinium have been used in recent years in South Korea as humidifier disinfectants (HDs) because of their strong bactericidal activity and low toxicity19. However, HDs were later clinically confirmed in several epidemiologic studies to cause HD-associated lung injury20,21,22,23. In addition, people who were exposed to HDs claim to have subsequently developed allergic diseases after using HDs. Recent evidence has now shown also that HD exposure increases the risk of asthma in children24. However, the possible risk of AD development upon exposure to HDs is not known. We therefore aimed in our current study to investigate whether exposure to CMIT/MIT in normal mice has the ability to induce the major symptoms of AD. We also investigated whether CMIT/MIT exposure affects AD development and immune responses in an AD mouse model.
Results
Epicutaneous exposure of normal mice to CMIT/MIT induces AD-like skin inflammation and a systemic immune response
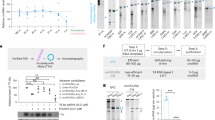
We first investigated whether CMIT/MIT exposure induce AD-like responses in normal mice. The animals were sequentially exposed to epicutaneous CMIT/MIT over 3 weeks (Fig. 1a) which subsequently induced the formation of skin lesions (Fig. 1b). In subsequent histopathological evaluations, the mice exposed to CMIT/MIT showed a higher level of inflammatory cell infiltration and greater epidermis thickness in the skin than the control mice exposed to PBS (Fig. 1c). In addition, the mice exposed to CMIT/MIT had a higher transepidermal water loss (TEWL) (Fig. 1d) and an increase in the total serum IgE level (Fig. 1e) and mast cell number and degranulation in the skin (Fig. 1f–h) than the controls. In assessments of the immune response in these mice, the animals exposed to CMIT/MIT had a higher expression of T helper (Th) 2-related cytokines/chemokines (i.e. thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), interleukin (IL)-6, IL-13 and C-C motif chemokine (CCL)-17) in their skin (Fig. 2a–d), and greater populations of CD4+IL-4+ cells in the skin-draining lymph nodes (Fig. 2e,f) compared to the controls. However, there were no detectable IL-4 and IL-17A transcripts in the skin (data not shown). These findings demonstrated that epicutaneous exposure to CMIT/MIT in normal mice induces a phenotype that is similar to AD and involves Th2 dysfunction.
Effects of CMIT/MIT on skin lesions and histology, the epidermal permeability barrier, total IgE serum levels and the number of mast cells in the skin of normal mice. (a) Experimental protocol for the effects of CMIT/MIT exposure in normal mice. (b) Representative images of typical skin lesions. (c) H&E staining. (d) TEWL measurements. (e) Serum levels of total IgE determined by ELISA. (f) Toluidine Blue staining of skin samples. The numbers of mast cells (g) and degranulated mast cells (h) per high-power field were counted. Statistical significance was determined using a t-test. Red and yellow arrows denote the mast cells within the dermis. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
Effects of CMIT/MIT on Th2-related cytokines (TSLP, IL-6 and IL-13), a Th2-related chemokine (CCL17) and CD4+IL-4+ cell populations in normal mice. Skin mRNA levels of (a) TSLP, (b) IL-6, (c) IL-13 and (d) CCL17 were assessed by real-time PCR. (e,f) Frequency of IL-4 with CD4+ cells was assessed by flow cytometry in the skin-draining lymph nodes. Statistical significance was determined using a t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
Epicutaneous exposure to CMIT/MIT with ovalbumin (OVA) aggravates the level of skin inflammation in the AD mouse model
We investigated whether the epicutaneous exposure to CMIT/MIT during allergen sensitization would enhance the allergic AD-related consequences in the AD mouse model. The mice were exposed to CMIT/MIT during the OVA intraperitoneal sensitization phase (Fig. 3a). OVA application after CMIT/MIT exposure enhanced the formation of AD-like skin lesions (Fig. 3b). Furthermore, the mice exposed to CMIT/MIT during OVA sensitization showed a significant increase in inflammatory cell infiltration, TEWL value, clinical scores and in the number and degranulation of mast cells in skin compared to CMIT/MIT exposed and PBS control treated animals (Fig. 3c–h). In addition, mice exposed to CMIT/MIT with OVA had a greater inflammatory cell infiltration of the skin, and increased TEWL and clinical scores compared to the mice exposed to OVA alone (Fig. 3c–e), although this was not a significant difference. These findings suggested that epicutaneous exposure to CMIT/MIT during allergen sensitization enhances AD-like responses in the mouse.
Effects of CMIT/MIT exposure in an AD mouse model. (a) Experimental protocol for assessing the effects of CMIT/MIT exposure in AD mice. (b) Representative images of typical skin lesions. (c) Histological analysis of H&E-stained skin tissue. (d) TEWL measurements. (e) Clinical score measurements. (f) Toluidine blue staining of skin samples. Numbers of mast cells (g) and degranulated mast cells (h) per high-power field were counted. Red and yellow arrows denote the mast cells within the dermis. Statistical significance was determined using ANOVA and a Newman-Keuls multiple comparison test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. I.P, intraperitoneal; EC, epicutaneous.
Epicutaneous exposure to CMIT/MIT with OVA increases the systemic immune response and the Th2-Th17 response in the AD mouse model
We next investigated whether the epicutaneous exposure to CMIT/MIT during allergen sensitization enhances the systemic immune response in AD mice. We observed that CMIT/MIT exposure during OVA sensitization significantly increased the serum total IgE levels compared with mice exposed to OVA alone (Fig. 4a). In addition, the mice exposed to CMIT/MIT with OVA showed an increased tendency toward OVA-specific IgE compared to the OVA alone animals, although this was not statistically significant (Fig. 4b).
Effects of CMIT/MIT on serum IgE levels and Th2-/Th17-related responses in an AD mouse model. (a,b) ELISA determinations of (a) the total serum IgE levels and (b) the OVA-specific serum IgE levels. (c–f) Skin mRNA expression, assessed by real-time PCR, of (c) TSLP, (d,e) Th2-related cytokines (d, IL-4; e, IL-13) and (f) the Th17-related cytokine, IL-17A. Statistical significance was determined using ANOVA and the Newman-Keuls multiple comparison test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. ND, non-detection.
We next measured the AD-like immune response in both the skin and skin-draining lymph nodes in the mouse model. TSLP expression in the mouse skin was higher following exposure to CMIT/MIT with or without OVA compared to the controls (PBS alone) (Fig. 4c). Furthermore, the animals exposed to CMIT/MIT with OVA showed increased IL-4 and IL-17A expression in skin, although not IL-13, compared to the mice exposed to OVA alone (Fig. 4d–f). In addition, mice exposed to CMIT/MIT with PBS or OVA generated more CD4+IL-4+ and CD4+IL-17A+ producing cells in the skin-draining lymph nodes than the mice exposed to OVA alone (Fig. 5a–c). These findings indicated that CMIT/MIT exposure enhances the allergic systemic response and dysregulation of Th2/Th17 in the AD mouse model.
Discussion
We have here demonstrated that repeated epicutaneous exposure to CMIT/MIT in normal mice significantly enhances AD-like phenotypes, including elevated TEWL, total serum IgE level, infiltration of inflammatory cells in the dermis, and Th2-related response in skin. Moreover, CMIT/MIT epicutaneous exposure worsened the severity of the resulting AD in subsequently OVA-induced mice, including the AD-like phenotypes and Th2/Th17-related responses in skin. Our present findings thus provide strong evidence that repeated epicutaneous exposure to CMIT/MIT may affect the development and aggravation of AD via the modulation of the immune response.
In prior clinical studies, erythema and eczema were observed during physical examinations to occur following epicutaneous airborne exposure to CMIT/MIT10,12,25,26. Notably also, CMIT is categorized as an extreme skin sensitizer and MIT has been proposed as a major contributor to systemic allergic reactions and skin inflammation27,28,29,30. Similarly, our current study using a mouse model has found that the epicutaneous exposure to CMIT/MIT induces AD-like symptoms, as reflected by an elevated TEWL, erythema, scaling, excoriation and skin inflammation. Moreover epicutaneous exposure to CMIT/MIT during allergen sensitization was further found in our analysis to enhance AD-like symptoms (TEWL, clinical score and infiltration of inflammatory cells in the dermis) compared to mice exposed to OVA alone. This further indicated that repeated epicutaneous exposure to CMIT/MIT may induce and enhance AD-like skin lesions and inflammation with/without allergen sensitization.
Additionally, our current results indicated that the total serum IgE levels and the number and degranulation extent of mast cells in the skin became significantly increased in normal mice after repeated epicutaneous exposure to CMIT/MIT. Moreover, this exposure to CMIT/MIT during allergen sensitization enhanced the total serum IgE levels and numbers of mast cells in the skin compared to the mice exposed to OVA alone. Of note in particular, the number of mast cells and the serum IgE levels in the PBS+CMIT/MIT group were still increased at 3 weeks after the last CMIT/MIT treatment compared to the PBS control group. We conducted a non-parametric t-test and found a statistical difference (P-value = 0.008) between the two groups (PBS group vs. PBS+CMIT/MIT group). The functional capacity of IgE plays an essential role in the induction and maintenance of a hypersensitivity reaction in AD. AD patients with high serum IgE levels are more likely to be involved in the development, severity, and skin barrier dysfunction of AD31,32. IgE molecules can trigger allergic responses by binding to their high-affinity Fc receptor (FcεRI) on mast cells33,34. Increased IgE concentrations enhance the IgE-dependent activity of the mast cells35,36. The activation of mast cells by cross-linking, through the binding of IgE to FcεRI, induces degranulation and produces Th2-type cytokines (IL-4 and IL-13) in response to IgE-dependent allergic activation. Furthermore, activated mast cells enhance their own proliferation/survival and also T-cell activation, and modulate IgE production through the secretion of survival/growth factors (IL-13 and IL-4)37,38. Furthermore, even in the absence of allergens, specific IgE molecules can induce some secretion of mediators through the binding to FcεRI of mast cells35,36. Hence, it is possible that epicutaneous exposure to CMIT/MIT contributes to an increase in IgE production and mast cell activation during allergic systemic responses and AD-like inflammation. In addition, the recruitment of mast cells and increase in serum IgE levels after CMIT/MIT exposure are likely to continue to provoke IgE-mediated systemic allergic reactions over time.
Our present study findings also revealed that Th2-related cytokines (TSLP, IL-6 and IL-13), Th2-related chemokine (CCL17) and the Th2 cell population are significantly increased immediately after exposure to CMIT/MIT, even in normal mice. In addition, CMIT/MIT epicutaneous exposure during OVA sensitization was found to increase the expression of Th2/Th17-related cytokines (IL-4 and IL-17A) and the Th2/Th17 cell population in AD mice. However, as shown in the mouse models depicted in Figs. 2 and 4, the expression of IL-13 mRNA and IL-4 and the population of IL-4 cells differ between the PBS group and CMIT/MIT treated groups. In this regard, we considered two possibilities. The first was that the sample collection times had been different. The samples for the mice in Fig. 1a were collected at 24 hours after the last CMIT/MIT treatment, and those related to Fig. 4 at 3 weeks after last CMIT/MIT treatment. The second possibility was that IL-4 and IL-13 can act on different cell types and IL-4 may drive IL-13 independent inflammation in various settings and over time39,40,41,42,43,44.
Interestingly, the expression of IL-4 and IL-17A in normal skin mice was not detected immediately after CMIT/MIT exposure but was increased at 3 weeks after the last CMIT/MIT treatment without OVA sensitization. Th2 cytokines (e.g., IL-4, IL-6 and IL-13) are known to play important roles in orchestrating the inflammation of AD through various routes45,46,47. Generally, allergens induce a Th2 response and subsequent Th2 cell migration by stimulating the expression of Th2 cytokines, which in turn orchestrates the allergic-related responses48.
Th2 cytokines are an important biomarker of prolonged eosinophilia and play a key role in orchestrating the chronic inflammation associated with AD by recruiting, activating and promoting eosinophils in the dermis. Our present study findings have demonstrated that CMIT/MIT epicutaneous exposure increase Th2-related responses. Likewise, a prior experimental study reported that the epicutaneous exposure to MIT induced an increase in T cell proliferation in mice18. Hence, it may be possible that exposure to CMIT/MIT in the mouse induces and enhances allergic AD-like consequences, mediated via Th2-related responses. In addition to Th2 cells, recent studies have reported that Th17 immune responses are also critical for mediating the initiation and progression of AD and differentiation of Th2 cells45,49,50. Several studies have further shown that Th17 responses promote tissue fibrosis, the chronicity of the inflammatory process, and AD severity and are induced by TSLP51,52. Our current study in the mouse has found that the expression of IL-17A and the Th17 cell population in the skin increased following CMIT/MIT epicutaneous exposure combined with OVA. These findings suggest that the exposure to CMIT/MIT during OVA sensitization can induce and enhance skin inflammation and allergic responses via Th2/Th17-mediated pathways.
Our present results have also revealed that Th2-related cytokines and Th2 cell populations are increased immediately after exposure to CMIT/MIT but that Th17 cytokines and cells are only increased at 3 weeks after the last CMIT/MIT treatment without OVA skin sensitization. This suggests that the Th2-related reactions prevail in the early stages of exposure to CMIT/MIT and the Th17-related responses prevail over time. These findings also indicate that the Th17 pathway exacerbates AD by rapidly inducing Th2 responses during OVA skin sensitization after exposure to CMIT/MIT. However, our current analysis did not investigate how increased Th17 responses after CMIT/MIT exposure directly enhances Th2 activity. Further studies are thus needed to confirm this biological relationship.
Our present study had some limitations of note. In the first instance, we could not discriminate whether allergic contact dermatitis or AD was induced by epicutaneous exposure to CMIT/MIT. Allergic contact dermatitis and AD potentially share common cellular mechanisms and it is difficult to distinguish between them in terms of a clinical diagnosis53,54. However, we used a previously established AD mouse model that presents with the classically characterized features of human AD i.e. a disrupted epidermal barrier function, infiltration by inflammatory cells and high serum IgE levels55,56,57. Our results indicated increases in the serum IgE levels and also the TEWL, which are considered to be features of AD after exposure to CMIT/MIT58. The possibility that CMIT/MIT epicutaneous exposure may affect the development of AD can thus be considered. As another limitation of our present analyses, we did not investigate direct changes to Th2-related and other biological mechanisms caused by the CMIT/MIT exposure. Further studies are needed to investigate alterations in the cellular and molecular properties resulting from CMIT/MIT treatment in the AD mouse model.
In summary, our present study has demonstrated the AD-like effects of CMIT/MIT epicutaneous exposure in normal and AD mice and suggests that the possible mechanisms involve Th2/Th17 immune responses. Further studies are needed to confirm this interaction between immune responses and biological mechanisms. Our findings suggest however that epicutaneous exposure to CMIT/MIT can affect the development of AD and can mediate Th2/Th17-related inflammation.
Materials and Methods
Animal experiments
Female BALB/c mice (5 weeks old, n = 5 per group) weighing 16–20 g were purchased from Orient Bio (Seongnam, Korea). All animals were housed at a temperature of 22 ± 2 °C and 40% humidity with a 12-hour light and dark cycle. All animal studies were reviewed and approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Asan Medical Center (authorization no. 2018–14–041), and were performed in accordance with the guidelines and regulations for the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety of South Korea.
Epicutaneous exposure to CMIT/MIT and development of AD in the mouse
In the mouse experiments, the animals were lightly anesthetized with alfaxan (Careside, Korea) and rompun (Bayer Korea, Korea) and their dorsal areas were shaved and treated with CMIT/MIT (1.13% 5-chloro-2-methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, 0.37% 2-methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, 23% inert salts; KATHON™ CG Preservative, DOW) at 0.1875 mg/kg/day, for 5 days/week over 3 weeks. Very limited information is available regarding the disease-causing possibility of CMIT/MIT, so we determined the experimental dose based on Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety (SCCS2009), report59, and considered the following: (1) repeated administration, (2) no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL, ≤0.104 mg/kg/day) and lowest observed adverse effect level (LOAEL, ≥0.104 mg/kg/day) (3) the concentration below threshold of skin sensitization (2.25 ug/cm2 in mice and 1.25 ug/cm2 in human) based on SCCS report contents of skin sensitization and dermal toxicity studies59. Generation of the AD mouse model using OVA sensitization has been previously described55,56,57. Briefly, mice were systemically sensitized via an intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of 10 µg of chicken OVA (grade V; Sigma, St Louis, MO) and 4 mg of aluminum hydroxide (Imject Alum; Pierce, Rockford, IL) 3 times at 1week intervals. The mice were then epicutaneously (EC) sensitized by applying 100 µg OVA (grade V; Sigma, St Louis, MO) to the shaved dorsal skin of for 1week. This epicutaneous sensitization was repeated twice at 1week intervals. All mice were sacrificed at 24 hours after the final OVA sensitization.
Assessment of TEWL and clinical scores
Clinical scores for the skin lesions in the mice were graded for erythema, scaling and excoriation as follows: 0 (no symptoms), 1 (mild), 2 (moderate), and 3 (severe)60. To assess epidermal permeability barrier function, the TEWL was measured using a VapoMeter (SWL-3; Delfin Technologies Ltd., Kuopio, Finland). The clinical scores and TEWL values were evaluated at baseline at the beginning of the experiment and again after each sensitization.
Histology of the skin lesions
For the histologic evaluation of skin tissues, the area of the skin lesion was fixed in 10% formalin and then embedded in paraffin. The paraffin-embedded sections (5 μm thickness) were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and toluidine blue (Sigma Aldrich Chemical Co. St Louis, MO) for the assessment of inflammatory cells. The total (200X magnification) and degranulated (400X magnification) mast cells per 3 high-power fields were counted and averaged per mouse (total 5 mouse) using ImageJ 1.47 software (NIH, Bethesda, MD)61.
Quantitation of the serum levels of immunoglobulin
Serum samples were obtained after sacrifice and stored at −80 °C until analyzed. Total IgE levels in the serum were measured by IgE enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (eBioscience, San Diego, CA). OVA-specific IgE concentrations were also measured using ELISA. Briefly, 96 well plates were coated with 100 µg/mL OVA in coating buffer (Carbonate-Bicarbonate Buffer; Sigma Chemical Co). After an overnight incubation at 4 °C, diluted serum (1:50 in carbonate-bicarbonate buffer) was added to the wells and incubated for 1 h at 37 °C. The plates were washed and 20 ng/100 μℓ anti-mouse IgE (Acris Antibodies, Herford, Germany) was added for a further 1 h at 37 °C. After additional washing, 100 µl of 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) solution (Sigma Chemical Co.) was added to each well and the plate was read at 450 nm.
Real-time PCR
Total RNA from mouse skin was extracted using an RNeasy kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) and cDNA was synthesized from 1 µg aliquots of these preparations using a WizScript cDNA synthesis Kit (Wizbiosolutions, Korea). qPCR was performed on an ABI 7900 system (Applied Biosystems, Piscataway, NJ). The expression level of each gene was normalized to that of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH).
Flow cytometry
Mouse skin-draining lymph nodes (LNs; axillary and brachial lymph nodes) were harvested immediately after sacrifice and dissociated using a 70-um cell strainer (SPL Life Sciences, Pocheon, Korea). LN cells were cultured with 1X Protein Transport Inhibitor Cocktail (500×, eBioscience, San Diego, CA) and 1X Cell Stimulation Cocktail (500×, eBioscience) for 16 hours to stimulate and expand the T cells. Mouse interferon gamma (IFN-γ), IL-4 and IL-17A were subsequently assessed by flow cytometry62. The LNs were then stained using FITC-labeled anti-IFN-γ, PERCP-CY5.5-labeled anti-CD4, APC-labeled anti-IL-4, PE-labeled anti-IL-17A and the respective isotype controls (eBioscience) to analyze CD4+ IFN-γ, IL-4 and IL-17A expression in accordance with the mouse Th1/Th2/Th17 Phenotyping Kit general protocol (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA). The stained cells were then analyzed by FACS Canto with BD FACSDiva 8.0.1 (BD Biosciences, Mountain View, CA).
Statistical analysis
Comparisons between the two groups were conducted using nonparametric tests (Mann Whitney U-test), and the ANOVA and Newman-Keuls multiple comparison tests were used to assess differences in the measurements between multiple groups. Statistical analyses were performed using Graph Pad Prism 4.0 (San Diego, CA). The independent samples t-test was conducted using SPSS version 24.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL).
References
Novak, N., Bieber, T. & Leung, D. Y. Immune mechanisms leading to atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 112, S128–139, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2003.09.032 (2003).
Li, C. et al. Development of atopic dermatitis-like skin disease from the chronic loss of epidermal caspase-8. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 22249–22254, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1009751108 (2010).
Cork, M. J. et al. New perspectives on epidermal barrier dysfunction in atopic dermatitis: gene-environment interactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol 118, 3–21; quiz 22–23, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2006.04.042 (2006).
Kim, K. Influences of Environmental Chemicals on Atopic Dermatitis. Toxicol. Res. 31, 89–96, https://doi.org/10.5487/TR.2015.31.2.089 (2015).
Kathuria, P. & Silverberg, J. I. Association of pollution and climate with atopic eczema in US children. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 27, 478–485, https://doi.org/10.1111/pai.12543 (2016).
Kantor, R. & Silverberg, J. I. Environmental risk factors and their role in the management of atopic dermatitis. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immu 13, 15–26, https://doi.org/10.1080/1744666x.2016.1212660 (2017).
Drasch, G., Schupp, I., Hofl, H., Reinke, R. & Roider, G. Mercury Burden of Human Fetal and Infant Tissues. Eur. J. Pediatr. 153, 607–610, https://doi.org/10.1007/s004310050200 (1994).
Ahn, K. The role of air pollutants in atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin Immunol 134, 993–999; discussion 1000, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2014.09.023 (2014).
Lee, J. Y. et al. Exposure to gene-environment interactions before 1 year of age may favor the development of atopic dermatitis. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 157, 363–371, https://doi.org/10.1159/000328778 (2012).
Lundov, M. D., Thyssen, J. P., Zachariae, C. & Johansen, J. D. Prevalence and cause of methylisothiazolinone contact allergy. Contact Dermat. 63, 164–167, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0536.2010.01774.x (2010).
Flyvholm, M. A. Preservatives in registered chemical products. Contact Dermat. 53, 27–32, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0105-1873.2005.00629.x (2005).
Lundov, M. D., Mosbech, H., Thyssen, J. P., Menne, T. & Zachariae, C. Two cases of airborne allergic contact dermatitis caused by methylisothiazolinone in paint. Contact Dermat. 65, 176–179, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0536.2011.01924.x (2011).
Kaae, J., Menne, T. & Thyssen, J. P. Presumed primary contact sensitization to methylisothiazolinone from paint: a chemical that became airborne. Contact Dermat. 66, 341–342, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0536.2012.02012.x (2012).
Schwensen, J. F. et al. Methylisothiazolinone and benzisothiazolinone are widely used in paint: a multicentre study of paints from five European countries. Contact Dermat. 72, 127–138, https://doi.org/10.1111/cod.12322 (2015).
Kujala, V. & Niinimaki, A. Occupational induction of hypersensitivity after an accidental exposure to chloromethylisothiazolinone and methylisothiazolinone (CMI/MI) in an industrial worker. Occup. Med. 49, 51–53 (1999).
Bourke, S. J., Convery, R. P., Stenton, S. C., Malcolm, R. M. & Hendrick, D. J. Occupational asthma in an isothiazolinone manufacturing plant. Thorax 52, 746–748 (1997).
Spahn, J. D., Cherniack, R., Paull, K. & Gelfand, E. W. Is forced expiratory volume in one second the best measure of severity in childhood asthma? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 169, 784–786, https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200309-1234OE (2004).
Devos, F. C. et al. Methylisothiazolinone: Dermal and respiratory immune responses in mice. Toxicol. Lett. 235, 179–188, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.04.009 (2015).
Park, K. An analysis of a humidifier disinfectant case from a toxicological perspective. Env. Health Toxicol. 31, e2016013, https://doi.org/10.5620/eht.e2016013 (2016).
Lee, E. et al. Two Cases of Chloromethylisothiazolinone and Methylisothiazolinone-associated Toxic Lung Injury. J. Korean Med. Sci. 33, e119, https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e119 (2018).
Kim, W. Y. & Hong, S. B. Humidifier Disinfectant-Associated Lung Injury: Six Years after the Tragic Event. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 80, 351–357, https://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2017.0048 (2017).
Cho, H. J. et al. Effects of a mixture of chloromethylisothiazolinone and methylisothiazolinone on peripheral airway dysfunction in children. PLoS One 12, e0176083, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176083 (2017).
Lee, S. Y., Park, D. U., Do, K. H., Jang, S. J. & Hong, S. J. The Pathological Findings of Chloromethylisothiazolinone and Methylisothiazolinone-associated Lung Injury. J. Korean Med. Sci. 34, e102, https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e102 (2019).
Yoon, J. et al. Exposure to Humidifier Disinfectants Increases the Risk of Asthma in Children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201805-0840LE (2018).
Bregnbak, D. & Johansen, J. D. Airborne sensitization to isothiazolinones observed in a 3-month-old boy. Contact Dermat. 69, 55–56, https://doi.org/10.1111/cod.12079 (2013).
Geier, J., Lessmann, H., Schnuch, A. & Uter, W. Recent increase in allergic reactions to methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone: is methylisothiazolinone the culprit? Contact Dermat. 67, 334–341, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0536.2012.02157.x (2012).
Basketter, D. A., Rodford, R., Kimber, I., Smith, I. & Wahlberg, J. E. Skin sensitization risk assessment: a comparative evaluation of 3 isothiazolinone biocides. Contact Dermat. 40, 150–154 (1999).
Aerts, O., Cattaert, N., Lambert, J. & Goossens, A. Airborne and systemic dermatitis, mimicking atopic dermatitis, caused by methylisothiazolinone in a young child. Contact Dermat. 68, 250–251, https://doi.org/10.1111/cod.12050 (2013).
Garcia-Gavin, J., Vansina, S., Kerre, S., Naert, A. & Goossens, A. Methylisothiazolinone, an emerging allergen in cosmetics? Contact Dermat. 63, 96–101, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0536.2010.01754.x (2010).
Schlichte, M. J. & Katta, R. Methylisothiazolinone: an emergent allergen in common pediatric skin care products. Dermatol. Res. Pract. 2014, 132564, https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/132564 (2014).
Kabashima-Kubo, R. et al. A group of atopic dermatitis without IgE elevation or barrier impairment shows a high Th1 frequency: possible immunological state of the intrinsic type. J. Dermatol. Sci. 67, 37–43, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2012.04.004 (2012).
Sanjuan, M. A., Sagar, D. & Kolbeck, R. Role of IgE in autoimmunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 137, 1651–1661, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2016.04.007 (2016).
Stone, K. D., Prussin, C. & Metcalfe, D. D. IgE, mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 125, S73–80, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2009.11.017 (2010).
Furue, M. et al. Atopic dermatitis: immune deviation, barrier dysfunction, IgE autoreactivity and new therapies. Allergol. Int. 66, 398–403, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alit.2016.12.002 (2017).
Galli, S. J. et al. Mast cells as “tunable” effector and immunoregulatory cells: recent advances. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 23, 749–786, https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.21.120601.141025 (2005).
Kawakami, T. & Galli, S. J. Regulation of mast-cell and basophil function and survival by IgE. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 773–786, https://doi.org/10.1038/nri914 (2002).
Coyle, A. J. et al. Central role of immunoglobulin (Ig) E in the induction of lung eosinophil infiltration and T helper 2 cell cytokine production: inhibition by a non-anaphylactogenic anti-IgE antibody. J. Exp. Med. 183, 1303–1310 (1996).
Mizutani, N., Nabe, T. & Yoshino, S. IgE/antigen-mediated enhancement of IgE production is a mechanism underlying the exacerbation of airway inflammation and remodelling in mice. Immunology 144, 107–115, https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.12355 (2015).
Mentink-Kane, M. M. & Wynn, T. A. Opposing roles for IL-13 and IL-13 receptor alpha 2 in health and disease. Immunol. Rev. 202, 191–202, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.00210.x (2004).
Grunig, G. et al. Requirement for IL-13 independently of IL-4 in experimental asthma. Sci. 282, 2261–2263, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.282.5397.2261 (1998).
Forbes, E., van Panhuys, N., Min, B. & Le Gros, G. Differential requirements for IL-4/STAT6 signalling in CD4 T-cell fate determination and Th2-immune effector responses. Immunol. Cell Biol. 88, 240–243, https://doi.org/10.1038/icb.2009.101 (2010).
Wynn, T. A. IL-13 effector functions. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 21, 425–456, https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.21.120601.141142 (2003).
Junttila, I. S. et al. Tuning sensitivity to IL-4 and IL-13: differential expression of IL-4Ralpha, IL-13Ralpha1, and gammac regulates relative cytokine sensitivity. J. Exp. Med. 205, 2595–2608, https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20080452 (2008).
Perkins, C., Wills-Karp, M. & Finkelman, F. D. IL-4 induces IL-13-independent allergic airway inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 118, 410–419, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2006.06.004 (2006).
Soumelis, V. et al. Human epithelial cells trigger dendritic cell mediated allergic inflammation by producing TSLP. Nat. Immunol. 3, 673–680, https://doi.org/10.1038/ni805 (2002).
Leung, D. Y. & Soter, N. A. Cellular and immunologic mechanisms in atopic dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 44, S1–S12, https://doi.org/10.1067/mjd.2001.109815 (2001).
Valenta, R. et al. Autoallergy: a pathogenetic factor in atopic dermatitis? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 105, 432–437, https://doi.org/10.1067/mai.2000.104783 (2000).
Matsuo, K. et al. A CCR4 antagonist ameliorates atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions induced by dibutyl phthalate and a hydrogel patch containing ovalbumin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 109, 1437–1444, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.194 (2019).
Huang, F. et al. Potentiation of IL-19 expression in airway epithelia by IL-17A and IL-4/IL-13: important implications in asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 121(1415–1421), 1421 e1411–1413, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2008.04.016 (2008).
Ito, T. et al. TSLP-activated dendritic cells induce an inflammatory T helper type 2 cell response through OX40 ligand. J. Exp. Med. 202, 1213–1223, https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20051135 (2005).
Molet, S. et al. IL-17 is increased in asthmatic airways and induces human bronchial fibroblasts to produce cytokines. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 108, 430–438, https://doi.org/10.1067/mai.2001.117929 (2001).
Li, J. et al. T-helper type-2 contact hypersensitivity of Balb/c mice aggravated by dibutyl phthalate via long-term dermal exposure. PLoS One 9, e87887, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0087887 (2014).
Aquino, M. & Fonacier, L. The role of contact dermatitis in patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2, 382–387, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaip.2014.05.004 (2014).
Bains, S. N., Nash, P. & Fonacier, L. Irritant Contact Dermatitis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 56, 99–109, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-018-8713-0 (2019).
Kim, H. J., Lee, E., Lee, S. H., Kang, M. J. & Hong, S. J. Mold elicits atopic dermatitis by reactive oxygen species: Epidemiology and mechanism studies. Clin. Immunol. 161, 384–390, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2015.07.007 (2015).
Kim, H. J. et al. Effects of kestose on gut mucosal immunity in an atopic dermatitis mouse model. J. Dermatol. Sci. 89, 27–32, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2017.10.006 (2018).
Na, K. et al. Bone marrow-derived clonal mesenchymal stem cells inhibit ovalbumin-induced atopic dermatitis. Cell Death Dis. 5, e1345, https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2014.299 (2014).
Gittler, J. K., Krueger, J. G. & Guttman-Yassky, E. Atopic dermatitis results in intrinsic barrier and immune abnormalities: implications for contact dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 131, 300–313, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2012.06.048 (2013).
SCCS report (SCCS123809) OPINION ON the mixture of 5-chloro-2-methylisothiazolin-3(2H)-one and 2-methylisothiazolin-3(2H)-one. 2009.pdf.
Kim, H. J. et al. A novel mouse model of atopic dermatitis with epicutaneous allergen sensitization and the effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus. Exp. Dermatol. 21, 672–675, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0625.2012.01539.x (2012).
Schneider, C. A., Rasband, W. S. & Eliceiri, K. W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 9, 671–675 (2012).
Heesters, B. A., Van der Poel, C. E. & Carroll, M. C. Follicular Dendritic Cell Isolation and Loading of Immune Complexes. Methods Mol. Biol. 1623, 105–112, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7095-7_9 (2017).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from the National Institute of Environment Research (NIER), funded by the Ministry of Environment (MOE) of the Republic of Korea, and by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and future Planning (NRF-2019R1C1C1009114). This study was also supported by a grant of the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant number: HI14C2687).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Han-Na Go and Seung-Hwa Lee designed the experiments, conducted the experiments and data analysis and wrote the manuscript. Jae-Rin Ahn and Mi-Jin Kang performed experiments and contributed to manuscript preparation. Hyun-Ju Cho and So-Yeon Lee wrote, corrected, and revised the entire manuscript. Soo-Jong Hong conceived and designed the experiments, wrote, corrected, and revised the entire manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Go, HN., Lee, SH., Cho, HJ. et al. Effects of chloromethylisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone (CMIT/MIT) on Th2/Th17-related immune modulation in an atopic dermatitis mouse model. Sci Rep 10, 4099 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-60966-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-60966-8
This article is cited by
-
Impact of Air Pollution on Atopic Dermatitis: A Comprehensive Review
Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.