Abstract
The patterns of evolution and expression of tissue-specific genes are poorly understood beyond sex-specific genes. Accordingly, we identified 3,191 tissue-specific genes and 38,745 common genes using 22 RNA-seq datasets from cultivated peanut. The expression levels of tissue-specific genes were significantly lower than those of common genes. Further, the expression levels of sex-specific genes were significantly higher than those of somatic tissue-specific genes. Among sex-specific genes, the expression levels of gynoecium-specific genes were significantly higher than those of androecium-specific genes. Function-specific genes were lacking among tissue-specific genes, and tissue-specific gene annotations overlapped among different tissues. Duplicate gene pairs were classified as homogeneous pairs expressed within the same tissue or heterogeneous pairs expressed in different tissues. Heterogeneous gene pairs evolved more rapidly than homogeneous gene pairs. In addition, somatic tissue-specific genes evolved faster than sex-specific genes. Molecular signatures of selection indicated that somatic tissue-specific genes have mainly experienced relaxed selection, while sex-specific genes have been under stronger selective constraint. Somatic tissue-specific genes had higher codon usage bias than sex-specific genes. These contrasting patterns between somatic tissue-specific and sex-specific genes provide new insights into the basic biology and evolution of peanut, an important crop.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Since the publication of the Arabidopsis thaliana genome, many genomic sequences and RNA-seq datasets of other plants have been released. Subsequently, researchers have used these datasets to gain insight into plant growth and development as well as other biological processes. In recent studies, sex-biased genes that are more highly expressed in sexual tissue, including female-biased and male-biased genes, have attracted the interest of researchers because sex-biased expression is fundamentally linked to gene regulation, epigenetics, developmental biology, and sexual antagonism1. Sex-biased studies have been reported in humans and animals such as mammals, birds, fish, and fruit flies1, 2. Similar studies have been lacking in plants. However, studies examining the evolutionary patterns and expression levels of sex-biased genes have been reported for A. thaliana 3, Capsella grandiflora 4, Collinsia heterophylla 5, Ectocarpus spp.6, and Silene latifolia 7. Some consistent conclusions have arisen from these analyses of sex-biased genes in plants. First, sex-biased genes tend to evolve more rapidly than unbiased genes4, 6. Second, sex-biased genes have mainly experienced adaptive evolution3, 6, 8. Third, female-biased gene expression is higher than male-biased gene expression3. In addition, female-biased genes tend to be highly expressed in specific tissues, while male-biased genes tend to be expressed at low levels in the same tissues6, 7. These findings support the hypothesis that differential expression of female-biased and male-biased genes may resolve sexual antagonism under natural selection and sexual selection1, 2, 7. Fourth, a greater bias in codon usage has been observed among female tissues relative to male tissues in Zea mays and Triticum aestivum 9.
However, little is known about the evolutionary patterns and expression levels of tissue-specific genes in plants. There has been a particular lack in comparisons of these two aspects between sex-specific and somatic tissue-specific genes. These comparisons could not be made without RNA-seq datasets of both somatic tissue-specific and sex-specific tissue, especially datasets that focus on male-specific and female-specific tissues. To date, RNA-seq datasets based on cultivated peanut have examined 22 different tissues, including both sexual and somatic tissues10. These datasets are a powerful resource for research into the evolutionary patterns and gene expression levels exhibited in sex-specific and somatic tissue-specific genes. We found that different evolutionary patterns and gene expression levels are observed between sex-specific and somatic tissue-specific genes based on these RNA-seq datasets. Overall sex-specific genes were expressed at higher levels than somatic tissue-specific genes. Furthermore, somatic tissue-specific genes experienced relaxed selection, while sex-specific genes have been subject to stronger selective constraint.
Results
Tissue-specific genes in cultivated peanut
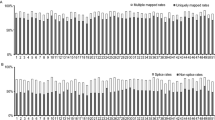
A total of 3,191 tissue-specific genes were identified from 22 RNA-seq datasets for cultivated peanut (Table S1). The largest number of tissue-specific genes were expressed in gynoecium tissue, while the fewest tissue-specific genes were expressed in seedling leaf tissue (Fig. 1). The descending order of tissues ranked by number of tissue-specific genes expressed in them was gynoecium, root, nodule, Pattee 5 seed, reproductive shoot, Pattee 6 seed, main stem leaf, later leaf, Pattee 8 seed, perianth, stalk, Pattee 7 seed, Pattee 3 pod, aerial gynophores, Pattee 5 pericarp, vegetative shoot, androecium, subterranean gynophore, Pattee 6 pericarp, Pattee 1 pod, Pattee 10 seed, and seedling leaf tissue (Fig. 1). RNA-seq data for the leaf, shoot, gynophore, pod, pericarp, and seed can be classified into three, two, two, three, two, and five developmental stages, respectively (Fig. 1 and Table S1). If different developmental stages were considered as individual tissues, we could obtain nine leaf-specific, seventeen shoot-specific, two gynophore-specific, four pod-specific, three pericarp-specific, and twenty-five seed-specific genes, respectively (Table S2). In this study, we used different developmental stages of tissues as the level of analysis because genes can vary in spatial and temporal expression. Sex-specific genes can be expressed at a particular developmental stage without being expressed in later stages1. (These genes are available as supplemental material in Table S2 and may be helpful for research on spatial and temporal gene expression patterns in cultivated peanut).
In contrast, we found 38,745 genes expressed simultaneously among 22 tissues, considered common genes hereafter. The cultivated peanut has about 78,574 coding sequences (CDSs) based on the number of genes of its two ancestors, Arachis duranensis (36,734 genes) and Arachis ipaënsis (41,840 genes)11. Therefore, tissue-specific genes account for 4.06% of the total number of genes (3,191 out of 78,574), and commonly expressed genes account for 49.31% of the total number of genes (38,745 out of 78,574) in cultivated peanut. Further, 1,357 tissue-specific genes and 18,627 common genes were derived from A. duranensis, accounting for 1.73% (1,357 out of 78,574) and 23.71% (18,627 out of 78,574) of cultivated peanut genes. Similarly, 1,834 tissue-specific genes and 20,117 common genes were derived from A. ipaënsis, accounting for 2.32% (1,834 out of 78,574) and 25.60% (20,117 out of 78,574) of cultivated peanut genes. The tissue-specific and common genes from A. ipaënsis outnumbered those from A. duranensis. This is consistent with more gene duplication events having occurred in A. ipaënsis than in A. duranensis 11. Tissue-specific genes were further classified into sex-specific and somatic tissue-specific genes. In this study, sex-specific genes were expressed specifically in gynoecium and androecium tissues, while somatic tissue-specific genes were expressed specifically in one of the other 20 tissues. Sex-specific and somatic tissue-specific genes accounted for 0.66% (522 out of 78,574) and 3.40% (2,669 out of 78,574) of cultivated peanut genes. The sex-specific and somatic-specific genes from A. duranensis accounted for 0.28% (218 out of 78,574) and 1.45% (1,139 out of 78,574) of cultivated peanut genes, respectively. The sex-specific and somatic-specific genes from A. ipaënsis accounted for 0.39% (304 out of 78,574) and 1.95% (1530 out of 78,574) of cultivated peanut genes, respectively.
Gene expression levels of tissue-specific genes were significantly lower than those of common genes (Mann–Whitney U test, P < 0.01). The gene expression levels differed significantly among the 22 tissues (Kruskal–Wallis test, Chi-square = 486.63, P < 0.05). It should also be noted that the sex-specific gene expression levels were significantly higher than those of somatic tissue-specific genes (Mann–Whitney U test, P < 0.01). Gynoecium-specific gene expression levels were higher than those of androecium-specific genes (Mann–Whitney U test, P < 0.01). Tissue-specific genes also overlapped among annotations for different tissues (Fig. S1). These analyses revealed a lack of function-specific genes among tissue-specific genes. Further, gene ontology (GO) analyses revealed that although one tissue may exhibit gene expression across different developmental stages for genes involved in different biological processes, the same biological processes may be shared among different tissues (Fig. S1). We found the most common GO categories to be 0008270 (zinc ion binding), 0006355 (regulation of transcription), 0016021 (transmembrane), 0003676 (nucleic acid binding), 0005524 (ATP binding), 0055114 (oxidation-reduction process), 0005515 (protein binding), and 006508 (proteolysis; Fig. 2). The detailed GO annotation listed in Table S3.
Identification of GO items in tissue-specific genes. The detailed GO annotation listed in Table S3.
Evolutionary divergence between tissue-specific duplicated genes
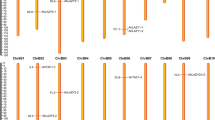
A total of 274 full-length duplicated gene pairs were detected from the cultivated peanut RNA-seq data. K a, K s, and K a/K s values were calculated between 232 duplicated gene pairs, and 42 duplicated gene pairs were removed because their K s values were less than 0.01 or larger than 0.30. The average values of K a, K s, and K a/K s were 0.08, 0.21, and 0.56, respectively. Purifying selection predominated the molecular evolution of 207 duplicate gene pairs with K a/K s values less than 1. In contrast, positive selection played a crucial force in 25 duplicate gene pairs with K a/K s values larger than 1. It should be noted that these duplicate gene pairs possibly underwent adaptive evolution as suggested by their higher average K a/K s values. Similarly, adaptive evolution was detected among sex-biased genes in Ectocarpus spp. because their corresponding average K a/K s value exceeded 0.56, 8.
Among duplicate gene pairs that underwent purifying selection, 167 and 40 were heterogeneous gene pairs and homogeneous gene pairs, respectively. Among duplicate gene pairs predominantly shaped by positive selection, 16 and 9 were heterogeneous gene pairs and homogeneous gene pairs, respectively. The average K a and K s values for homogeneous gene pairs were lower than those for heterogeneous gene pairs (Mann–Whitney U test, P < 0.05), indicating the heterogeneous gene pairs evolved more rapidly than homogeneous gene pairs. The average K a/K s values of homogeneous gene pairs were larger than those of heterogeneous gene pairs, but this difference was not statistically significant (Mann-Whitney U test, P > 0.05). Further, 176 and 19 duplicate gene pairs consisted of somatic tissue-specific genes and sex-specific genes, respectively, while 37 duplicate gene pairs consisted of one somatic tissue-specific gene and one sex-specific gene (somatic-sex-specific gene pair). The K a and K s values of somatic-sex-specific duplicate genes exceeded those of both somatic tissue-specific genes and sex-specific genes (Fig. 3). This again indicates that heterogeneous gene pairs appear to evolve more rapidly than homogeneous gene pairs. In addition, the average K s value was similar between sex-specific and somatic tissue-specific genes, but the average K a value of somatic tissue-specific genes exceeded that of sex-specific genes (Fig. 3). The synonymous substitution rate was similar between sex-specific and somatic tissue-specific genes, while the nonsynonymous evolutionary rate of somatic tissue-specific genes was more rapid than that of sex-specific genes. However, the average K a/K s value of somatic tissue-specific genes and somatic-sex-specific genes exceeded that of sex-specific genes, but this difference was not statistically significant (Fig. 3; Mann–Whitney U test, P > 0.05). Nevertheless, the average K a/K s values of somatic tissue-specific genes, somatic-sex-specific genes, and sex-specific genes were 0.59, 0.50, and 0.46, respectively. Overall, somatic tissue-specific genes and somatic-sex-specific genes mainly underwent relaxed selection, while sex-specific genes experienced stronger selective constraint.
Codon usage bias in tissue-specific genes
After filtering criteria were applied, a total of 2,756 sequences were used to analyze codon usage bias. Although frequency of optimal codons (Fop) was not significantly different among different tissue types (Kruskal–Wallis test, Chi-square = 22.68, P > 0.05), the Fop value of somatic tissue-specific genes was significantly higher than that of sex-specific genes (Mann–Whitney U test, P < 0.05). Moreover, Fop values of gynoecium-specific genes were slightly but not significantly higher than those of androecium-specific genes (Mann–Whitney U test, P > 0.05). These results indicated that codon usage bias in somatic tissue-specific genes was higher than that in sex-specific genes. In addition, amino acid sequence length was significantly different across the various tissues (Kruskal–Wallis test, Chi-square = 36.62, P < 0.05). The amino acid sequences of sex-specific genes were longer than those of somatic tissue-specific genes (Mann–Whitney U test, P < 0.05), while the amino acid sequences of gynoecium-specific genes were non-significantly longer than those of androecium-specific genes (Mann–Whitney U test, P > 0.05).
Discussion
Cultivated peanut is one of the most important oil and protein crops. To elucidate the developmental processes and physiological changes involved in stress responses, many cultivated peanut RNA-seq datasets have been produced. Comparisons of genes differentially expressed between aerial gynophores and subterranean gynophores using RNA-seq data have revealed the involvement of genes that respond to hormones, the ubiquitin proteasome system, oxidative stress, and light signalling12,13,14. The cultivated peanut has been shown to have 842 potential defense-related genes involved in resistance to Aspergillus flavus based on RNA-seq data15. However, research has not been focused on patterns in the evolution and expression of tissue-specific genes in peanut, especially comparisons between sex-specific and somatic tissue-specific genes. The genomes of the cultivated peanut progenitor species, A. duranensis and A. ipaënsis, have recently been completed11. Additionally, 22 RNA-seq datasets distributed across different tissues of cultivated peanut have been assembled based on the A. duranensis and A. ipaënsis genomes10. We used these resources to identify tissue-specific genes and then analyzed the evolutionary pattern and gene expression level of these genes. There were five key findings. (1) The expression levels of sex-specific genes were significantly higher than those of somatic tissue-specific genes. Among sex-specific genes, the expression levels of gynoecium-specific genes were significantly higher than those of androecium-specific genes. (2) The functions of tissue-specific genes overlapped among the different tissues. (3) Heterogeneous gene pairs evolved more rapidly than homogeneous gene pairs. (4) The evolutionary rate of somatic tissue-specific genes exceeded that of sex-specific genes. Molecular signatures of selective pressure indicated that somatic tissue-specific genes mainly experienced relaxed selection, while sex-specific genes were subject to stronger selective constraint. (5) Somatic tissue-specific genes had higher codon usage bias than sex-specific genes.
There are at less two possible explanations for the difference in gene expression level among tissue-specific genes. First, these results are supported by the gene expression and rate of sequence evolution anticorrelation model (E-R anticorrelation model)16. Under this model, the most highly expressed genes are also subject to the strongest selective constraint17. In this study, sex-specific genes experienced stronger selective constraint than somatic tissue-specific genes, and the expression levels of sex-specific genes were higher than those of somatic tissue-specific genes. However, we cannot use E-R anticorrelation to explain the different gene expression levels exhibited between gynoecium-specific genes and androecium-specific genes because we were unable to estimate the selective pressures on androecium-specific genes (there was only one duplicated gene pair). Nevertheless, previous studies have demonstrated that more selective constraint has acted on male-specific genes relative to female-specific genes3. If the same pattern is found in cultivated peanut, the E-R anticorrelation model may explain why the significant difference in expression level between gynoecium-specific genes and androecium-specific genes. Second, different tissue-specific genes had different ages. Gossmann, et al.3 found that female genes were younger than male genes and that the gene expression levels of female genes were higher than those of male genes in A. thaliana. A significant shift in gene expression occurs during gametogenesis in A thaliana, Oryza sativa, and Glycine max, in which younger genes than those typically expressed in sporophytes18. We therefore suggest that the sex-specific genes may be younger than somatic tissue-specific genes.
The biological function of various tissue-specific genes lacked function-specificity. This contrasts with a previous study focused on tissue-biased genes. Shi, et al.19 found that root-biased, leaf-biased, and pistil-biased genes mainly participated in stress responses, photosynthesis, and meiotic cell cycles in barley. Though we cannot explain the non-specificity of the functions of tissue-specific genes, we suggest that the origin of tissue-specific genes precedes those of other genes in evolutionary time. Thus, tissue-specific genes have had longer to diverge in function. Accordingly, newer genes were likely progeny of tissue-specific genes. However, there is a lack of research on the relationship between tissue-specific and constitutively expressed genes in cultivated peanut.
Male-biased genes have evolved more rapidly than female-biased genes in many species1, 2. However, little is known about the difference between the evolutionary rates of somatic tissue-specific and sex-specific genes. A single published study about barley has demonstrated that pistil-biased orthologous pairs evolve more quickly than stem-, leaf-, and root-biased genes19. However, these results were inconsistent with our finding that somatic tissue-specific genes evolved more rapidly than sex-specific genes. This discrepancy may be explained by our use of tissue-specific genes, while this previous study used tissue-biased genes. The evolutionary rates and gene expression levels of tissue-specific and tissue-biased genes may of course differ. We have demonstrated that the expression levels of tissue-specific genes were lower than those of common genes in this study. Recently, Cheng and Kirkpatrick20 demonstrated that sex-biased expression is consistent with ongoing sex-specific selection in humans and files. Similarly, the evolutionary patterns and expression levels of these genes may have recently changed. In addition, amino acid sequence length has likely affected the evolutionary rate. Previous studies have shown that amino acid sequence length was negatively correlated with evolutionary rate21, 22. In the present study, amino acid sequences of sex-specific genes were longer than those of somatic tissue-specific genes.
Overall, somatic tissue-specific genes exhibited higher codon usage bias than sex-specific genes. We found that natural selection acted on codon usage bias of orthologous pairs between A. duranensis and A. ipaënsis (unpublished data). These previous results indicate that somatic tissue-specific genes were more highly expressed than sex-specific genes. However, sex-specific genes were expressed at a higher level than somatic-specific genes in the present study. This discrepancy in conclusions between the two studies may be explained by differences in the abundances of tRNAs in different tissues23. Thus, selection on codon bias may differ based on how tRNA abundance affects the efficiency and accuracy of translation processes in various tissues and cell types24.
Materials and Methods
Sequence data and gene ontology
The data used in the present study include A. duranensis and A. ipaënsis genomic CDSs and RNA-seq data from various tissues in cultivated peanut, which are available from PeanutBase (http://peanutbase.org/download)10, 11. The 22 RNA-seq datasets were generated from leaf, shoot, peg, fruit, pericarp, seed, stamen, and pistil tissues. All details of the sequencing, de novo transcriptome assembly, and generation of expression values were previously described by Clevenger, et al.10. Briefly, first, cultivated peanuts (‘Tifrunner’) were grown in a greenhouse (maintained at 24–30 °C). All tissues were harvested at 14:00 except for flower samples, which were collected at 8:30. Three biological replicates of each tissue were sampled from three different plants. The total RNA of each pooled tissue sample was extracted. TruSeq RNA Sample Preparation v2 kits were used for library construction and paired-end 2 × 100 bp sequencing was conducted using an Illumina HiSeq. 2500 instrument with a total of 209 cycles of TruSeq Rapid SBS Kit v1 (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) chemistry. Second, an in silico amphidiploid genome was created by simply disregarding scaffolds and concatenating the A. duranensis genome assembly with the A. ipaënsis genome assembly and labeling each simply the “A” and “B” genomes, respectively. Once the reads were mapped, the SAM file was run through the genome-guided pipeline. Third, total reads were mapped to the transcript assembly from 58 libraries (consisting of samples from 22 distinct tissue types and developmental stages including vegetative and seed stages) using Bowtie, allowing 2 mismatches within a particular 25 bp seed. Fragments per kilobase per million reads mapped (FPKM) were estimated using RSEM25 for each library. When reads map to multiple transcripts, RSEM fractionates the read count among the transcripts so read counts are not integers. Transcripts that had less than 1 FPKM for all 58 libraries were filtered out using the Trinity package, because they were deemed to lack sufficient minimum read coverage. The FPKM values for each gene were distinguished for both the A (A. duranensis) and B (A. ipaënsis) genomes from cultivated peanut. In this study, the log2-transformed FPKM values were considered as normalised gene expression levels in these various tissues. The tissue-specific gene was considered as a gene with a FPKM value in a given tissue but not found in other tissues. Common genes were considered to be genes expressed in all 22 tissues.
GO analysis was conducted using Blast2Go26, and the presented figures describing this GO analysis were conducted in WEGO27 and using R scripts.
Measurement of synonymous and nonsynonymous substitution rates
We used CDSs as queries to themselves in a comparison using local BLAST. The following evaluation criteria were used as thresholds to identify gene duplicates10: (1) length of aligned sequences > 80% of the longer sequence’s length, (2) identity > 80%, and (3) E-value ≤ 10−10. To avoid matches to partial sequences, all query sequences contained full-length coding frames. If a duplicate gene pair was expressed in a single tissue, it was classified as a homogeneous gene pair. In turn, duplicate gene pairs expressed only in different tissues were labeled heterogeneous gene pairs.
MAFFT28 was then used to obtain alignments of duplicate gene pairs. PAL2NAL29 was used for conversion of protein sequences into their corresponding nucleotide sequences. PAML 4.030 was used to calculate the K a/K s, ratio of nonsynonymous to synonymous per site substitution rates. The duplicate gene pairs for which K s values were less than 0.01 and greater than 0.30 were excluded because low sequence divergence can result in unreliable estimates and high K s values indicate potential sequence saturation, respectively30. Generally, K a/K s equal to 1, greater than 1, and less than 1 indicated neutral, positive, and purifying selection, respectively.
Codon usage bias and amino acid length
Codon usage bias, measured as the frequency of optimal codons (Fop) and amino acid length were estimated by Codon W (version 1.4, http://codonw.sourceforge.net). Fop values can range from 0 to 1. Fop values approaching 1 indicate a given gene has extreme codon usage bias31. To avoid partial sequences, the following evaluation criteria were adopted: (1) CDSs must start in ATG and end in TAA, TAG, or TGA and (2) CDSs must lack premature termination or ambiguous codons.
Statistical analysis
The Mann–Whitney U and Kruskal–Wallis tests were conducted in JMP 9.0 (SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA). P-values less than 0.05 were considered significant.
References
Grath, S. & Parsch, J. Sex-biased gene expression. Annu Rev Genet 50, 29–44 (2016).
Ellegren, H. & Parsch, J. The evolution of sex-biased genes and sex-biased gene expression. Nat Rev Genet 8, 689–698 (2007).
Gossmann, T. I., Schmid, M. W., Grossniklaus, U. & Schmid, K. J. Selection-driven evolution of sex-biased genes is consistent with sexual selection in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Bio Evol 31, 574–583 (2013).
Arunkumar, R., Josephs, E. B., Williamson, R. J. & Wright, S. I. Pollen-specific, but not sperm-specific, genes show stronger purifying selection and higher rates of positive selection than sporophytic genes in Capsella grandiflora. Mol Bio Evol 30, 2475–2486 (2013).
Hersh, E. et al. Sexual antagonism in the pistil varies among populations of a hermaphroditic mixed-mating plant. J Evolution Biol 28, 1321–1334 (2015).
Lipinska, A. et al. Sexual dimorphism and the evolution of sex-biased gene expression in the brown alga. Ectocarpus. Mol Bio Evol 32, 1581–1597 (2015).
Zemp, N. et al. Evolution of sex-biased gene expression in a dioecious plant. Nature Plants 2, 16168 (2016).
Lipinska, A. P., Damme, E. J. M. V. & De Clerck, O. Molecular evolution of candidate male reproductive genes in the brown algal model Ectocarpus. BMC Evol Biol 16, 5 (2016).
Whittle, C. A., Malik, M. R. & Krochko, J. E. Gender-specific selection on codon usage in plant genomes. BMC Genomics 8, 169 (2007).
Clevenger, J., Chu, Y., Scheffler, B. & Ozias-Akins, P. A developmental transcriptome map for allotetraploid Arachis hypogaea. Front Plant Sci 7, 1446 (2016).
Bertioli, D. J. et al. The genome sequences of Arachis duranensis and Arachis ipaensis, the diploid ancestors of cultivated peanut. Nat Genet 48, 438–446 (2016).
Zhang, Y. et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis of basal and zygote-located tip regions of peanut ovaries provides insight into the mechanism of light regulation in peanut embryo and pod development. BMC Genomics 17, 606 (2016).
Zhu, W. et al. Comparative proteomics analysis of developing peanut aerial and subterranean pods identifies pod swelling related proteins. J Proteomics 91, 172–187 (2013).
Zhu, W. et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis of aerial and subterranean pods development provides insights into seed abortion in peanut. Plant Mol Biol 85, 395–409 (2014).
Wang, H. et al. Comparative transcript profiling of resistant and susceptible peanut post-harvest seeds in response to aflatoxin production by Aspergillus flavus. BMC Plant Biol 16, 54 (2016).
Drummond, D. A., Bloom, J. D., Adami, C., Wilke, C. O. & Arnold, F. H. Why highly expressed proteins evolve slowly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102, 14338–14343 (2005).
Geiler-Samerotte, K. A. et al. Misfolded proteins impose a dosage-dependent fitness cost and trigger a cytosolic unfolded protein response in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 680–685 (2011).
Gossmann, T. I., Saleh, D., Schmid, M. W., Spence, M. A. & Schmid, K. J. Transcriptomes of plant gametophytes have a higher proportion of rapidly evolving and young genes than sporophytes. Mol Bio Evol 33, 1669–1678 (2016).
Shi, T. et al. Accelerated rates of protein evolution in barley grain and pistil biased genes mignt be legacy of domestication. Plant Mol Biol 89, 253–261 (2015).
Cheng, C. & Kirkpatrick, M. Sex-specific selection and sex-biased gene expression in humans and flies. PLoS Genet 12, e1006170 (2016).
Mugal, C. F., Wolf, J. B. W. & Kaj, I. Why time matters: codon evolution and the temporal dynamics of dN/dS. Mol Bio Evol 31, 212–231 (2014).
Yang, L. & Gaut, B. S. Factors that contribute to variation in evolutionary rate among Arabidopsis genes. Mol Bio Evol 28, 2359–2369 (2011).
Camiolo, S., Farina, L. & Porceddu, A. The relation of codon bias to tissue-specific gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 192, 641–649 (2012).
Novoa, E. M. & de Pouplana, L. R. Speeding with control: codon usage, tRNAs, and ribosomes. Trends Genet 28, 574–581 (2012).
Li, B. & Dewey, C. N. RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics 12, 323 (2011).
Conesa, A. et al. Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 21, 3674–3676 (2005).
Ye, J. et al. WEGO: a web tool for plotting GO annotations. Nucleic Acids Res 34, 293–297 (2006).
Katoh, K. & Standley, D. M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol Bio Evol 30, 772–780 (2013).
Suyama, M., Torrents, D. & Bork, P. PAL2NAL: robust conversion of protein sequence alignments into the corresponding codon alignments. Nucleic Acids Res 34, 609–612 (2006).
Yang, Z. PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol Bio Evol 24, 1586–1591 (2007).
Sharp, P. M. & Li, W. H. The codon adaption index-a measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res 15, 1281–1295 (1987).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2014CB138702), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31502001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.S. and Z.N. conceived and designed research. H.S. analyzed data and wrote the manuscript. Q.Z. executed the statistical analyses. P.T. participated in the discussion of the results. Z.N. contributed to the evaluation and discussion of the results and manuscript revision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, H., Zhang, Q., Tian, P. et al. Differential evolutionary patterns and expression levels between sex-specific and somatic tissue-specific genes in peanut. Sci Rep 7, 9016 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09905-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09905-8
This article is cited by
-
Deciphering evolutionary dynamics of WRKY genes in Arachis species
BMC Genomics (2023)
-
Comprehensive analysis of coding sequence architecture features and gene expression in Arachis duranensis
Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants (2021)
-
Old and young duplicate genes reveal different responses to environmental changes in Arachis duranensis
Molecular Genetics and Genomics (2019)
-
WRKY transcription factors in legumes
BMC Plant Biology (2018)
-
Comparative analysis of selection mode reveals different evolutionary rate and expression pattern in Arachis duranensis and Arachis ipaënsis duplicated genes
Plant Molecular Biology (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.