Abstract
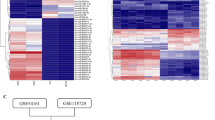
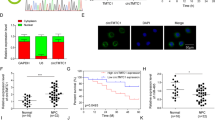
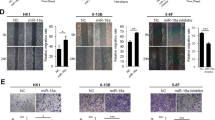
The epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is crucial to cancer progression and metastasis. Although multiple cellular miRNAs have been identified to regulate the EMT and metastasis in cancers, the role of viral miRNAs in cancer progression remains largely unknown. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated malignancy typically characterized by its early metastasis. In the present study, we have discovered the involvement of a viral miRNA, EBV-miR-BART7-3p, in the EMT and metastasis of NPC cells. Initially, we observed that EBV-miR-BART7-3p was highly expressed in NPC and positively correlated with lymph node metastasis and clinical stage of NPC. Subsequently, we demonstrated that EBV-miR-BART7-3p enhanced cell migration/invasion in vitro, cancer metastasis in vivo, and particularly the EMT characterized by loss of epithelial markers and gain of mesenchymal features in NPC cells. Furthermore, mechanistic studies disclosed that EBV-miR-BART7-3p targeted a major human tumor suppressor PTEN, modulating PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling and eventually leading to the high expression and nuclear accumulation of Snail and β-catenin, which favor EMT. Knockdown of PTEN could phenocopy the effect of EBV-miR-BART7-3p, whereas re-expression of PTEN resulted in a phenotypic reversion. Moreover, these findings were supported by an observation of an EBV-positive cell model in which silencing of endogenous EBV-miR-BART7-3p partially attenuated cell migration/invasion and altered EMT protein expression pattern via reverting PI3K/Akt, Snail and β-catenin expression. Thus, this study suggests a novel mechanism by which EBV-miR-BART7-3p modulates the EMT and metastasis of NPC cells, and a clinical implication of EBV-miR-BART7-3p as a potential biomarker or therapeutic target.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA . Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 2009; 139: 871–890.
Brabletz T . EMT and MET in metastasis: where are the cancer stem cells? Cancer Cell 2012; 22: 699–701.
Lamouille S, Xu J, Derynck R . Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2014; 15: 178–196.
Talbot LJ, Bhattacharya SD, Kuo PC . Epithelial-mesenchymal transition, the tumor microenvironment, and metastatic behavior of epithelial malignancies. Int J Biochem Mol Biol 2012; 3: 117–136.
Villarejo A, Cortes-Cabrera A, Molina-Ortiz P, Portillo F, Cano A . Differential role of Snail1 and Snail2 zinc fingers in E-cadherin repression and epithelial to mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem 2013; 289: 930–941.
Lim SO, Gu JM, Kim MS, Kim HS, Park YN, Park CK et al. Epigenetic changes induced by reactive oxygen species in hepatocellular carcinoma: methylation of the E-cadherin promoter. Gastroenterology 2008; 135: 2128–2140, 2140–2141.
Zhang J, Ma L . MicroRNA control of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2012; 31: 653–662.
Zhang JP, Zeng C, Xu L, Gong J, Fang JH, Zhuang SM . MicroRNA-148a suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of hepatoma cells by targeting Met/Snail signaling. Oncogene 2013; 33: 4069–4076.
Johansson J, Berg T, Kurzejamska E, Pang MF, Tabor V, Jansson M et al. MiR-155-mediated loss of C/EBPbeta shifts the TGF-beta response from growth inhibition to epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and metastasis in breast cancer. Oncogene 2013; 32: 5614–5624.
Formosa A, Markert EK, Lena AM, Italiano D, Finazzi-Agro' E, Levine AJ et al. MicroRNAs, miR-154, miR-299-5p, miR-376a, miR-376c, miR-377, miR-381, miR-487b, miR-485-3p, miR-495 and miR-654-3p, mapped to the 14q32.31 locus, regulate proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion in metastatic prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 2014; 33: 5173–5182.
Zhang G, Zhou H, Xiao H, Liu Z, Tian H, Zhou T . MicroRNA-92a functions as an oncogene in colorectal cancer by targeting PTEN. Dig Dis Sci 2014; 59: 98–107.
Chen D, Zhang Y, Wang J, Chen J, Yang C, Cai K et al. MicroRNA-200c overexpression inhibits tumorigenicity and metastasis of CD117+CD44+ ovarian cancer stem cells by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Ovarian Res 2013; 6: 50.
Cao M, Seike M, Soeno C, Mizutani H, Kitamura K, Minegishi Y et al. MiR-23a regulates TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting E-cadherin in lung cancer cells. Int J Oncol 2012; 41: 869–875.
Colangelo T, Fucci A, Votino C, Sabatino L, Pancione M, Laudanna C et al. MicroRNA-130b promotes tumor development and is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Neoplasia 2013; 15: 1218–1231.
Kumarswamy R, Mudduluru G, Ceppi P, Muppala S, Kozlowski M, Niklinski J et al. MicroRNA-30a inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by targeting Snai1 and is downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer 2012; 130: 2044–2053.
Ke Y, Zhao W, Xiong J, Cao R . miR-149 inhibits non-small-cell lung cancer cells EMT by targeting FOXM1. Biochem Res Int 2013; 2013: 506731.
Lyu X, Fang W, Cai L, Zheng H, Ye Y, Zhang L et al. TGFbetaR2 is a major target of miR-93 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma aggressiveness. Mol Cancer 2014; 13: 51.
Luo Z, Zhang L, Li Z, Jiang C, Dai Y, Liu X et al. miR-149 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2011; 36: 604–609.
Luo Z, Dai Y, Zhang L, Jiang C, Li Z, Yang J et al. miR-18a promotes malignant progression by impairing microRNA biogenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2013; 34: 415–425.
Zur HH . Viruses in human cancers. Science 1991; 254: 1167–1173.
McLaughlin-Drubin ME, Munger K . Viruses associated with human cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 2008; 1782: 127–150.
Parkin DM . The global health burden of infection-associated cancers in the year 2002. Int J Cancer 2006; 118: 3030–3044.
Kim DN, Chae HS, Oh ST, Kang JH, Park CH, Park WS et al. Expression of viral microRNAs in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma. J Virol 2007; 81: 1033–1036.
Ramakrishnan R, Donahue H, Garcia D, Tan J, Shimizu N, Rice AP et al. Epstein-Barr virus BART9 miRNA modulates LMP1 levels and affects growth rate of nasal NK T cell lymphomas. PLoS One 2011; 6: e27271.
Yang HJ, Huang TJ, Yang CF, Peng LX, Liu RY, Yang GD et al. Comprehensive profiling of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded miRNA species associated with specific latency types in tumor cells. Virol J 2013; 10: 314.
Lei T, Yuen KS, Xu R, Tsao SW, Chen H, Li M et al. Targeting of DICE1 tumor suppressor by Epstein-Barr virus-encoded miR-BART3* microRNA in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer 2013; 133: 79–87.
Lo AK, Dawson CW, Jin DY, Lo KW . The pathological roles of BART miRNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Pathol 2012; 227: 392–403.
Barth S, Pfuhl T, Mamiani A, Ehses C, Roemer K, Kremmer E et al. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA miR-BART2 down-regulates the viral DNA polymerase BALF5. Nucleic Acids Res 2008; 36: 666–675.
Lo AK, To KF, Lo KW, Lung RW, Hui JW, Liao G et al. Modulation of LMP1 protein expression by EBV-encoded microRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 16164–16169.
Lung RW, Tong JH, Sung YM, Leung PS, Ng DC, Chau SL et al. Modulation of LMP2A expression by a newly identified Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA miR-BART22. Neoplasia 2009; 11: 1174–1184.
Choy EY, Siu KL, Kok KH, Lung RW, Tsang CM, To KF et al. An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA targets PUMA to promote host cell survival. J Exp Med 2008; 205: 2551–2560.
Nachmani D, Stern-Ginossar N, Sarid R, Mandelboim O . Diverse herpesvirus microRNAs target the stress-induced immune ligand MICB to escape recognition by natural killer cells. Cell Host Microbe 2009; 5: 376–385.
Chan JY, Gao W, Ho WK, Wei WI, Wong TS . Overexpression of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA-BART7 in undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Anticancer Res 2012; 32: 3201–3210.
Choi H, Lee H, Kim SR, Gho YS, Lee SK . Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA BART15-3p promotes cell apoptosis partially by targeting BRUCE. J Virol 2013; 87: 8135–8144.
Ye Y, Zhou Y, Zhang L, Chen Y, Lyu X, Cai L et al. EBV-miR-BART1 is involved in regulating metabolism-associated genes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2013; 436: 19–24.
Wong AM, Kong KL, Tsang JW, Kwong DL, Guan XY . Profiling of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma reveals potential biomarkers and oncomirs. Cancer 2012; 118: 698–710.
Zheng H, Li W, Wang Y, Liu Z, Cai Y, Xie T et al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta regulates Snail and beta-catenin expression during Fas-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastrointestinal cancer. Eur J Cancer 2013; 49: 2734–2746.
Qiu J, Cosmopoulos K, Pegtel M, Hopmans E, Murray P, Middeldorp J et al. A novel persistence associated EBV miRNA expression profile is disrupted in neoplasia. PLoS Pathog 2011; 7: e1002193.
Cai X, Schafer A, Lu S, Bilello JP, Desrosiers RC, Edwards R et al. Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs are evolutionarily conserved and differentially expressed. PLoS Pathog 2006; 2: e23.
Dawson CW, Tramountanis G, Eliopoulos AG, Young LS . Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) activates the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway to promote cell survival and induce actin filament remodeling. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 3694–3704.
Portis T, Longnecker R . Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) LMP2A mediates B-lymphocyte survival through constitutive activation of the Ras/PI3K/Akt pathway. Oncogene 2004; 23: 8619–8628.
Pan YR, Vatsyayan J, Chang YS, Chang HY . Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A upregulates UDP-glucose dehydrogenase gene expression via ERK and PI3K/Akt pathway. Cell Microbiol 2008; 10: 2447–2460.
Iwakiri D, Sheen TS, Chen JY, Huang DP, Takada K . Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNA induces insulin-like growth factor 1 and supports growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma-derived cell lines. Oncogene 2005; 24: 1767–1773.
Ikeda A, Caldwell RG, Longnecker R, Ikeda M . Itchy, a Nedd4 ubiquitin ligase, downregulates latent membrane protein 2A activity in B-cell signaling. J Virol 2003; 77: 5529–5534.
Song LB, Li J, Liao WT, Feng Y, Yu CP, Hu LJ et al. The polycomb group protein Bmi-1 represses the tumor suppressor PTEN and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. J Clin Invest 2009; 119: 3626–3636.
Pagano JS . Epstein-Barr virus: the first human tumor virus and its role in cancer. Proc Assoc Am Physicians 1999; 111: 573–580.
Chen SJ, Chen GH, Chen YH, Liu CY, Chang KP, Chang YS et al. Characterization of Epstein-Barr virus miRNAome in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by deep sequencing. PLoS ONE 2010; 5: e12745.
Hsu CY, Yi YH, Chang KP, Chang YS, Chen SJ, Chen HC. The Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA MiR-BART9 promotes tumor metastasis by targeting E-cadherin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS Pathog 2014; 10: e1003974.
Qu C, Liang Z, Huang J, Zhao R, Su C, Wang S et al. MiR-205 determines the radioresistance of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma by directly targeting PTEN. Cell Cycle 2012; 11: 785–796.
Chen P, Guo X, Zhou H, Zhang W, Zeng Z, Liao Q et al. SPLUNC1 regulates cell progression and apoptosis through the miR-141-PTEN/p27 pathway, but is hindered by LMP1. PLoS ONE 2013; 8: e56929.
Zhang LY, Ho-Fun LV, Wong AM, Kwong DL, Zhu YH, Dong SS et al. MicroRNA-144 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through repression of PTEN. Carcinogenesis 2013; 34: 454–463.
Wang X, Jiang X . Post-translational regulation of PTEN. Oncogene 2008; 27: 5454–5463.
Song MS, Salmena L, Pandolfi PP . The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2012; 13: 283–296.
Ho FC, Tham IW, Earnest A, Lee KM, Lu JJ . Patterns of regional lymph node metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a meta-analysis of clinical evidence. Bmc Cancer 2012; 12: 98.
Larue L, Bellacosa A . Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in development and cancer: role of phosphatidylinositol 3' kinase/AKT pathways. Oncogene 2005; 24: 7443–7454.
Ding VW, Chen RH, McCormick F . Differential regulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta by insulin and Wnt signaling. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 32475–32481.
Ho MY, Tang SJ, Chuang MJ, Cha TL, Li JY, Sun GH et al. TNF-alpha induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal cell carcinoma cells via a GSK3beta-dependent mechanism. Mol Cancer Res 2012; 10: 1109–1119.
Mishra P, Senthivinayagam S, Rana A, Rana B . Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3beta regulates Snail and beta-catenin during gastrin-induced migration of gastric cancer cells. J Mol Signal 2010; 5: 9.
Liu H, Xu L, He H, Zhu Y, Liu J, Wang S et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes hepatoma cell invasion and metastasis by stabilizing Snail protein. Cancer Sci 2012; 103: 2072–2081.
Rosano L, Spinella F, Di Castro V, Nicotra MR, Dedhar S, de Herreros AG et al. Endothelin-1 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 11649–11657.
Jorda M, Olmeda D, Vinyals A, Valero E, Cubillo E, Llorens A et al. Upregulation of MMP-9 in MDCK epithelial cell line in response to expression of the Snail transcription factor. J Cell Sci 2005; 118: 3371–3385.
Dave N, Guaita-Esteruelas S, Gutarra S, Frias A, Beltran M, Peiro S et al. Functional cooperation between Snail1 and twist in the regulation of ZEB1 expression during epithelial to mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 12024–12032.
Min H, Hong M, Ma J, Zhang E, Zheng Q, Zhang J et al. A new staging system for nasopharyngeal carcinoma in China. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1994; 30: 1037–1042.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81372895, 81172586), Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (No. 20134433110013), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. S2011010004157) and Guangzhou Science and Technology research project (No. 2014J4100149).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, LM., Lyu, XM., Luo, WR. et al. EBV-miR-BART7-3p promotes the EMT and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by suppressing the tumor suppressor PTEN. Oncogene 34, 2156–2166 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.341
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.341
This article is cited by
-
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: current views on the tumor microenvironment's impact on drug resistance and clinical outcomes
Molecular Cancer (2024)
-
Quantitative analysis of Epstein–Barr virus DNA in plasma and stomach biopsies of patients with gastric cancer
Virus Genes (2023)
-
Epstein–Barr virus-encoded microRNA BART22 serves as novel biomarkers and drives malignant transformation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI predicts PTEN protein expression which can function as a prognostic measure of progression-free survival in NPC patients
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2022)
-
Exosomal HMGA2 protein from EBV-positive NPC cells destroys vascular endothelial barriers and induces endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition to promote metastasis
Cancer Gene Therapy (2022)