Abstract
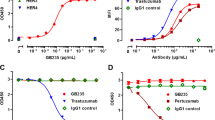
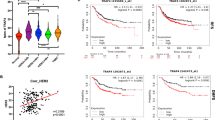
The transmembrane tyrosine kinase HER2 (ErbB2, neu) is a prototypical biomarker for breast cancers and a therapeutic target. Although anti-HER2 therapies are remarkably effective, HER2-positive tumors are heterogeneous and some subtypes do not respond or develop resistance to these therapies. Here we show that H2NTF, a novel N-terminal fragment of HER2, is expressed at variable levels in 60% of the breast cancer samples analyzed. Characterization of H2NTF shows that it is devoid of the tyrosine kinase domain but it readily interacts with full-length HER2 and other HER receptors. As a consequence, H2NTF acts as a dominant-negative, attenuating the signaling triggered by full-length HER receptors. Expression of H2NTF results in resistance to the treatment with low concentrations of trastuzumab in vitro. However, cells expressing H2NTF and non-expressing cells have similar sensitivity to trastuzumab in vivo, indicating that H2NTF/trastuzumab complexes trigger antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baselga J, Swain SM . Novel anticancer targets: revisiting ERBB2 and discovering ERBB3. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 463–475.
Sibilia M, Kroismayr R, Lichtenberger BM, Natarajan A, Hecking M, Holcmann M . The epidermal growth factor receptor: from development to tumorigenesis. Differentiation 2007; 75: 770–787.
Citri A, Yarden Y . EGF-ERBB signalling: towards the systems level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2006; 7: 505–516.
Abramson V, Arteaga CL . New strategies in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer: many combinations of targeted drugs available. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 952–958.
Spector NL, Blackwell KL . Understanding the mechanisms behind trastuzumab therapy for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 5838–5847.
Arribas J, Baselga J, Pedersen K, Parra-Palau JL . p95HER2 and breast cancer. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 1515–1519.
Scaltriti M, Rojo F, Ocana A, Anido J, Guzman M, Cortes J et alExpression of p95HER2, a truncated form of the HER2 receptor, and response to anti-HER2 therapies in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 2007; 99: 628–638.
Pedersen K, Angelini PD, Laos S, Bach-Faig A, Cunningham MP, Ferrer-Ramon C et alA naturally occurring HER2 carboxy-terminal fragment promotes mammary tumor growth and metastasis. Mol Cell Biol 2009; 29: 3319–3331.
Sperinde J, Jin X, Banerjee J, Penuel E, Saha A, Diedrich G et alQuantitation of p95HER2 in paraffin sections by using a p95-specific antibody and correlation with outcome in a cohort of trastuzumab-treated breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16: 4226–4235.
Parra-Palau JL, Pedersen K, Peg V, Scaltriti M, Angelini PD, Escorihuela M et alA major role of p95/611-CTF, a carboxy-terminal fragment of HER2, in the down-modulation of the estrogen receptor in HER2-positive breast cancers. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 8537–8546.
Benoit V, Chariot A, Delacroix L, Deregowski V, Jacobs N, Merville MP et alCaspase-8-dependent HER-2 cleavage in response to tumor necrosis factor alpha stimulation is counteracted by nuclear factor kappaB through c-FLIP-L expression. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 2684–2691.
Kulkarni S, Reddy KB, Esteva FJ, Moore HC, Budd GT, Tubbs RR . Calpain regulates sensitivity to trastuzumab and survival in HER2-positive breast cancer. Oncogene 2010; 29: 1339–1350.
Strohecker AM, Yehiely F, Chen F, Cryns VL . Caspase cleavage of HER-2 releases a Bad-like cell death effector. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 18269–18282.
Tikhomirov O, Carpenter G . Geldanamycin induces ErbB-2 degradation by proteolytic fragmentation. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 26625–26631.
Tikhomirov O, Carpenter G . Caspase-dependent cleavage of ErbB-2 by geldanamycin and staurosporin. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 33675–33680.
Tikhomirov O, Carpenter G . Identification of ErbB-2 kinase domain motifs required for geldanamycin-induced degradation. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 39–43.
Tikhomirov O, Dikov M, Carpenter G . Identification of proteolytic fragments from ErbB-2 that induce apoptosis. Oncogene 2005; 24: 3906–3913.
Tompa P, Buzder-Lantos P, Tantos A, Farkas A, Szilagyi A, Banoczi Z et alOn the sequential determinants of calpain cleavage. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 20775–20785.
Anelli T, Sitia R . Protein quality control in the early secretory pathway. Embo J 2008; 27: 315–327.
Ryan Q, Ibrahim A, Cohen MH, Johnson J, Ko CW, Sridhara R et alFDA drug approval summary: lapatinib in combination with capecitabine for previously treated metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER-2. Oncologist 2008; 13: 1114–1119.
Hasui M, Saikawa Y, Miura M, Takano N, Ueno Y, Yachie A et alEffector and precursor phenotypes of lymphokine-activated killer cells in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency (scid) and athymic (nude) mice. Cell Immunol 1989; 120: 230–239.
Doherty JK, Bond C, Jardim A, Adelman JP, Clinton GM . The HER-2/neu receptor tyrosine kinase gene encodes a secreted autoinhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 10869–10874.
Sanchez-Martin M, Pandiella A . Differential action of small molecule HER kinase inhibitors on receptor heterodimerization: Therapeutic implications. Int J Cancer 2012; 131: 244–252.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Instituto de Salud Carlos III (Intrasalud PI081154, PI11/02496 and the network of cooperative cancer research (RTICC-RD06/0020/0022 and RTICC-RD06/0020/0041)), GlaxoSmithKline and the Breast Cancer Research Foundation (BCRF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morancho, B., Parra-Palau, J., Ibrahim, Y. et al. A dominant-negative N-terminal fragment of HER2 frequently expressed in breast cancers. Oncogene 32, 1452–1459 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.152
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.152