Featured
-
-
News & Views |
 Moving beyond passive separations
Moving beyond passive separations
A composite membrane that contains porous organic cages is shown to be dynamic, with pore aperture diameter controlled by solvent allowing for graded molecular sieving.
- Jeffrey R. McCutcheon
- , Mayur Ostwal
- & Mi Zhang
-
Editorial |
 Weaving tangled webs
Weaving tangled webs
From the realization of their true nature one hundred years ago to the latest approaches for structuring materials using molecular weaving, high-molecular-weight polymers still have much to offer society.
-
Perspective |
 Molecular weaving
Molecular weaving
Molecular weaving is the entanglement of one-dimensional flexible molecules into higher-dimensional networks. This Perspective provides an overview of the progress so far, and discusses the future challenges and potentials of this field.
- Zhi-Hui Zhang
- , Björn J. Andreassen
- & Liang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access A smart and responsive crystalline porous organic cage membrane with switchable pore apertures for graded molecular sieving
A smart and responsive crystalline porous organic cage membrane with switchable pore apertures for graded molecular sieving
The separation of multicomponent mixtures is performed by distillation, as multiple-membrane cascades are too complex. Here, a porous organic cage composite undergoes solid-state transformation in solvent; this alters pore size, enabling graded separation of three dyes with a single membrane.
- Ai He
- , Zhiwei Jiang
- & Andrew I. Cooper
-
Article |
 Highly compressible glass-like supramolecular polymer networks
Highly compressible glass-like supramolecular polymer networks
Glass-like supramolecular polymer networks with high compressibility and fast self-recovery are fabricated using host–guest crosslinkers with slow dissociation kinetics.
- Zehuan Huang
- , Xiaoyi Chen
- & Oren A. Scherman
-
Article |
 Solvent-free autocatalytic supramolecular polymerization
Solvent-free autocatalytic supramolecular polymerization
The solvent-free conversion of phthalonitrile derivatives into phthalocyanines in the bulk is described, involving a reductive cyclotetramerization step and the formation of one-dimensional single-crystalline fibres. This solvent-free autocatalytic supramolecular polymerization may enable for a sustainable fabrication of multi-block supramolecular copolymers.
- Zhen Chen
- , Yukinaga Suzuki
- & Takuzo Aida
-
Review Article |
 Porous materials for carbon dioxide separations
Porous materials for carbon dioxide separations
Porous materials can selectively and reversibly adsorb large quantities of gas. This Review highlights progress made in using this class of materials for CO2 capture processes and discusses key gaps that the materials community can address to accelerate greater adoption of adsorptive carbon capture technologies.
- Rebecca L. Siegelman
- , Eugene J. Kim
- & Jeffrey R. Long
-
Article |
 Cofactor-free oxidase-mimetic nanomaterials from self-assembled histidine-rich peptides
Cofactor-free oxidase-mimetic nanomaterials from self-assembled histidine-rich peptides
Self-assembling, histidine-rich peptides with similar catalytic functions as those of haem-dependent peroxidases are reported. These findings may have implications for the design of cofactor-free catalytic nanomaterials.
- Qing Liu
- , Kaiwei Wan
- & Baoquan Ding
-
Article |
 A poly(thymine)–melamine duplex for the assembly of DNA nanomaterials
A poly(thymine)–melamine duplex for the assembly of DNA nanomaterials
Melamine is shown to associate with two poly(thymine) strands, forming antiparallel duplexes that can be used for the dynamic assembly of DNA-based nanostructures.
- Qian Li
- , Jiemin Zhao
- & Chengde Mao
-
Comment |
 Complex assemblies and crystals guided by DNA
Complex assemblies and crystals guided by DNA
The complexity of DNA-programmed nanoparticle assemblies has reached an unprecedented level owing to recent advances that enable delicate and comprehensive control over the formation of DNA bonds.
- Shuoxing Jiang
- , Fei Zhang
- & Hao Yan
-
Article |
 Supramolecular–covalent hybrid polymers for light-activated mechanical actuation
Supramolecular–covalent hybrid polymers for light-activated mechanical actuation
Peptide amphiphile supramolecular polymers with a crosslinked spiropyran network respond to light by expelling water, enabling the fabrication of soft actuators or light-driven crawlers.
- Chuang Li
- , Aysenur Iscen
- & Samuel I. Stupp
-
Letter |
 Electric-field-driven dual-functional molecular switches in tunnel junctions
Electric-field-driven dual-functional molecular switches in tunnel junctions
A multifunctional molecule acting both as diode and variable resistor is used to fabricate compact molecular switches with a thickness of 2 nm, good current rectification and resistive on/off ratio, and requiring a drive voltage as low as 0.89 V.
- Yingmei Han
- , Cameron Nickle
- & Christian A. Nijhuis
-
Article |
 Quantum dynamics of a single molecule magnet on superconducting Pb(111)
Quantum dynamics of a single molecule magnet on superconducting Pb(111)
A superconducting transition is used to switch a single molecule magnet from a blocked magnetization state to a resonant quantum tunnelling regime
- Giulia Serrano
- , Lorenzo Poggini
- & Roberta Sessoli
-
News & Views |
 Proteins tailor pore geometry
Proteins tailor pore geometry
Using organic solvent shortens formation time of membrane nanosheets comprising proteins and copolymers, while tuning protein structure tailors the pore geometry, resulting in superior water permeation.
- Andrew G. Livingston
- & Zhiwei Jiang
-
Article |
 Rapid fabrication of precise high-throughput filters from membrane protein nanosheets
Rapid fabrication of precise high-throughput filters from membrane protein nanosheets
Protein channels are highly selective, but application in membranes is limited due to low protein content. Here, protein channels are embedded into block copolymers to form nanosheets using rapid solvent casting, with better water permeability and similar molecular exclusions relative to other membrane systems.
- Yu-Ming Tu
- , Woochul Song
- & Manish Kumar
-
Article |
 Synthesis of orthogonally assembled 3D cross-stacked metal oxide semiconducting nanowires
Synthesis of orthogonally assembled 3D cross-stacked metal oxide semiconducting nanowires
Orthogonal self-assembly of amphiphilic diblock copolymers and polyoxometallates followed by calcination allows the formation of cross-stacked multilayer 3D arrays of tungsten oxide nanowires.
- Yuan Ren
- , Yidong Zou
- & Yonghui Deng
-
Article |
 Chiral crystal-like droplets displaying unidirectional rotational sliding
Chiral crystal-like droplets displaying unidirectional rotational sliding
A chiral discotic triphenylene derivative spontaneously forms millimetre-sized assemblies with high structural order and fluid-like behaviour.
- Takashi Kajitani
- , Kyuri Motokawa
- & Takanori Fukushima
-
Perspective |
 Carbon nanotubes as emerging quantum-light sources
Carbon nanotubes as emerging quantum-light sources
This Perspective describes the recent advances in understanding and controlling the properties of single-wall carbon nanotubes as well as the progress towards the fabrication of new electrically driven single-photon sources.
- X. He
- , H. Htoon
- & C. Voisin
-
Letter |
 Homochiral porous nanosheets for enantiomer sieving
Homochiral porous nanosheets for enantiomer sieving
By using stacked macrocycle dimers, a 2D nanosheet self-assembles that exclusively captures a single enantiomer, and can release it by external stimulus via salt addition.
- Bo Sun
- , Yongju Kim
- & Myongsoo Lee
-
Article |
 Quantitative self-assembly prediction yields targeted nanomedicines
Quantitative self-assembly prediction yields targeted nanomedicines
Molecular simulations reveal the self-assembly of small molecules into nanoparticle drug carriers. Targeting of colon and liver cancer cells by the nanoparticles via kinase inhibitors is employed in anti-tumour therapy in vivo.
- Yosi Shamay
- , Janki Shah
- & Daniel A. Heller
-
News & Views |
 Broad-spectrum antivirals
Broad-spectrum antivirals
Nanoparticle mimics of heparan sulfate proteoglycans offer a new strategy for the inhibition of a range of viral infections.
- Benson J. Edagwa
- & Howard E. Gendelman
-
Article |
 Broad-spectrum non-toxic antiviral nanoparticles with a virucidal inhibition mechanism
Broad-spectrum non-toxic antiviral nanoparticles with a virucidal inhibition mechanism
Antiviral nanoparticle-formulated mimics of heparan sulfate proteoglycans were developed and shown to permit strong viral association as well as inhibition of a range of viruses on in vitro and in vivo models of infection.
- Valeria Cagno
- , Patrizia Andreozzi
- & Francesco Stellacci
-
Article |
 Molecular engineering of chiral colloidal liquid crystals using DNA origami
Molecular engineering of chiral colloidal liquid crystals using DNA origami
DNA origami allows the design of rod-shaped particles with specific geometrical features. This is exploited to examine how particle-level characteristics affect properties of the bulk phase and the superstructures such colloids assemble into.
- Mahsa Siavashpouri
- , Christian H. Wachauf
- & Zvonimir Dogic
-
Editorial |
 Suprapowered nanomachines
Suprapowered nanomachines
The 2016 Nobel Prize in Chemistry celebrates the development of molecular machinery and highlights the importance of fundamental and curiosity-driven research for furthering science.
-
News & Views |
 Creative tension in layered crystals
Creative tension in layered crystals
New findings suggest that the mechanical stretching of layered crystals can transform them from a polar to a nonpolar state. This could spur the design of multifunctional materials controlled by an electric field.
- Venkatraman Gopalan
- & Roman Engel-Herbert
-
Article |
 Topological defects in liquid crystals as templates for molecular self-assembly
Topological defects in liquid crystals as templates for molecular self-assembly
Nanoscale environments created by topological defects in liquid crystals can template the self-assembly of molecular amphiphiles within the defects.
- Xiaoguang Wang
- , Daniel S. Miller
- & Nicholas L. Abbott
-
Article |
 Fast and long-range triplet exciton diffusion in metal–organic frameworks for photon upconversion at ultralow excitation power
Fast and long-range triplet exciton diffusion in metal–organic frameworks for photon upconversion at ultralow excitation power
Controlled overlap of molecular orbitals in metal–organic frameworks enhances triplet exciton diffusion in these structures, which are now used in solid-state photon upconverters operating under excitation power comparable to solar irradiance.
- Prasenjit Mahato
- , Angelo Monguzzi
- & Nobuo Kimizuka
-
-
Article |
 Gradated assembly of multiple proteins into supramolecular nanomaterials
Gradated assembly of multiple proteins into supramolecular nanomaterials
Peptide-based nanofibres with bioactive proteins attached can now be made such that the protein ligands are introduced in a controlled manner. This tailoring of the nanofibre’s composition enables the ratio of multiple different proteins to be highly tuned within the assemblies. By changing the protein content of the nanofibres, it is possible to adjust the antibody responses in mice to the different nanofibres.
- Gregory A. Hudalla
- , Tao Sun
- & Joel H. Collier
-
News & Views |
 Printing with magnets
Printing with magnets
Planar patterns of colloidal microparticles have been manufactured with high yield over square centimetre areas by using magnetic-field microgradients in a paramagnetic fluid. This approach could evolve into technology capable of printing three-dimensional objects through programmable and reconfigurable 'magnetic pixels'.
- Changqian Yu
- , Jie Zhang
- & Steve Granick
-
-
Article |
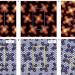 Tuning the catalytic activity of Ag(110)-supported Fe phthalocyanine in the oxygen reduction reaction
Tuning the catalytic activity of Ag(110)-supported Fe phthalocyanine in the oxygen reduction reaction
A major obstacle to fully understanding the catalytic mechanisms of oxygen reduction reactions and to designing more efficient catalysts is the lack of detailed information about the active site structure. Molecular local chemisorption sites and the long-range supramolecular arrangement of metallophthalocyanine molecules on a metal surface can now be controlled by the fine tuning of the overlayer coverage.
- F. Sedona
- , M. Di Marino
- & M. Sambi
-
News & Views |
 Surface attraction
Surface attraction
A new route to layer-by-layer assembly of metal–organic framework thin films affords highly ordered and controllable surfaces with potential in chemical sensing and catalyst applications.
- Mark A. Green

 Self-assembled soft alloy with Frank–Kasper phases beyond metals
Self-assembled soft alloy with Frank–Kasper phases beyond metals