Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Direct mechanochemical cleavage of functional groups from graphene
Direct mechanochemical cleavage of functional groups from graphene
Breaking chemical bonds with mechanical force can be a useful route to modify chemical species, but studying the process in detail can be challenging. Here, the authors use atomic force microscopy to apply pressure and monitor bond cleavage on chemically modified graphene.
- Jonathan R. Felts
- , Andrew J. Oyer
- & Paul E. Sheehan
-
Article
| Open Access Origin and consequences of silicate glass passivation by surface layers
Origin and consequences of silicate glass passivation by surface layers
The long term durability of silicate glasses is of significant importance, not least due to applications in nuclear waste repositories. Here, the authors study glass corrosion and show that its rate drops as a passivating layer forms via a self-healing mechanism.
- Stéphane Gin
- , Patrick Jollivet
- & Thibault Charpentier
-
Article |
 Hierarchical structural design for fracture resistance in the shell of the pteropod Clio pyramidata
Hierarchical structural design for fracture resistance in the shell of the pteropod Clio pyramidata
The hierarchical structural motifs of biomaterials can lead to advantageous mechanical properties. Here, the authors reveal that a fibre-like helical structure across the shell of a planktonic pteropod suppresses crack propagation and is responsible for a high fracture resistance.
- Ling Li
- , James C. Weaver
- & Christine Ortiz
-
Article |
 The dual role of coherent twin boundaries in hydrogen embrittlement
The dual role of coherent twin boundaries in hydrogen embrittlement
When exposed to hydrogen, alloys may lose their ductility and fracture unexpectedly, a phenomenon known as hydrogen embrittlement. Here, the authors investigate hydrogen embrittlement in a Ni-based superalloy and find that coherent twin boundaries are susceptible to crack initiation.
- Matteo Seita
- , John P. Hanson
- & Michael J. Demkowicz
-
Article
| Open Access Emerging magnetic order in platinum atomic contacts and chains
Emerging magnetic order in platinum atomic contacts and chains
The development of magnetism in metallic atomic chains is a widely debated phenomenon, of relevance to atomic-scale spintronics. Here, Strigl et al. measure the magneto-conductance of platinum break junctions stretched over sub-atomic distances, evidencing the evolution of distinct magnetic order.
- Florian Strigl
- , Christopher Espy
- & Torsten Pietsch
-
Article |
 Nanoarchitectured materials composed of fullerene-like spheroids and disordered graphene layers with tunable mechanical properties
Nanoarchitectured materials composed of fullerene-like spheroids and disordered graphene layers with tunable mechanical properties
Type-II glass-like carbon is a widely used material with desirable physical properties for industrial applications. Here, the authors investigate its structure-property performance under compression, and propose a model to explain its unusual, and pressure-tunable, elastic and mechanical properties.
- Zhisheng Zhao
- , Erik F. Wang
- & Guoyin Shen
-
Article |
 A dendrite-suppressing composite ion conductor from aramid nanofibres
A dendrite-suppressing composite ion conductor from aramid nanofibres
Lithium dendrite growth is a serious hazard in battery operations. Here, the authors report an ion-conducting membrane based on aramid nanofibers, and demonstrate effective suppression of copper and lithium dendrites.
- Siu-On Tung
- , Szushen Ho
- & Nicholas A. Kotov
-
Article
| Open Access Mutual information reveals multiple structural relaxation mechanisms in a model glass former
Mutual information reveals multiple structural relaxation mechanisms in a model glass former
One mystery of glass transition from supercooled liquid is the lack of apparent change in structure, which is in contrast to a large change in dynamics. Here Dunleavy et al. provide a possible solution to this discrepancy by simulating dynamic correlation using a mutual information approach.
- Andrew J. Dunleavy
- , Karoline Wiesner
- & C. Patrick Royall
-
Article |
 Synthesis of large single-crystal hexagonal boron nitride grains on Cu–Ni alloy
Synthesis of large single-crystal hexagonal boron nitride grains on Cu–Ni alloy
High nucleation density has thus far limited the quality and grain size of CVD-grown hexagonal boron nitride. Here, by optimizing the Ni ratio in Cu–Ni substrates, the authors successfully reduce nucleation density and report single-crystal hexagonal boron nitride grains up to 7500 μm2.
- Guangyuan Lu
- , Tianru Wu
- & Mianheng Jiang
-
Article |
 Deviation from high-entropy configurations in the atomic distributions of a multi-principal-element alloy
Deviation from high-entropy configurations in the atomic distributions of a multi-principal-element alloy
Alloys containing multiple elements of equal distributions are known to show enhanced properties as they tend to form single phases. Here, the authors demonstrate that even in cases of elemental segregation and chemical ordering, these alloys can still maintain enhanced properties.
- Louis J. Santodonato
- , Yang Zhang
- & Peter K Liaw
-
Article
| Open Access Recoverable plasticity in penta-twinned metallic nanowires governed by dislocation nucleation and retraction
Recoverable plasticity in penta-twinned metallic nanowires governed by dislocation nucleation and retraction
1D nanostructures are widely regarded as important building blocks for a broad range of applications. Here, the authors study dislocation-mediated plastic deformation in penta-twinned silver nanowires, finding that in situdeformation at small to moderate strains can be entirely reversible.
- Qingquan Qin
- , Sheng Yin
- & Huajian Gao
-
Article |
 Hidden topological order and its correlation with glass-forming ability in metallic glasses
Hidden topological order and its correlation with glass-forming ability in metallic glasses
Metallic glasses are amorphous in the absence of long-range atomic packing orders, but their medium-range order may not be completely lost. Here, Wu et al.identify a number of crystalline units that are entangled in medium range and their influence on the glass-forming ability in binary glasses.
- Z. W. Wu
- , M. Z. Li
- & K. X. Liu
-
Article
| Open Access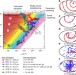 Unravelling the physics of size-dependent dislocation-mediated plasticity
Unravelling the physics of size-dependent dislocation-mediated plasticity
Size-affected dislocation-mediated plasticity is important in a wide range of materials and technologies. Here, El-Awady develops a validated generalized size-dependent dislocation-based model that can predict strength as a function of crystal/grain size and dislocation density.
- Jaafar A. El-Awady
-
Article |
 n-type chalcogenides by ion implantation
n-type chalcogenides by ion implantation
The use of chalcogenide glasses in simple electronic devices, such as a p-n junction, is hindered by the lack of n-type material. Here, Hughes et al.demonstrate n-type doping of GeTe and GaLaSO amorphous films using bismuth-ion implantation.
- Mark A. Hughes
- , Yanina Fedorenko
- & Richard J. Curry
-
Article |
 Temperature-dependent elastic anisotropy and mesoscale deformation in a nanostructured ferritic alloy
Temperature-dependent elastic anisotropy and mesoscale deformation in a nanostructured ferritic alloy
Nanostructured ferritic alloys offer many attractive properties that make them suitable for use in extreme environments. Here, the authors use neutron diffraction to determine single-crystal elastic constants of nanoscale ferrite grains, observing a large temperature-induced elastic anisotropy.
- G.M. Stoica
- , A.D. Stoica
- & D. Ma
-
Article |
 How thermally activated deformation starts in metallic glass
How thermally activated deformation starts in metallic glass
Understanding the atomic-scale processes by which deformation occurs in a metallic glass remains a challenge. Here, the authors apply atomic-scale simulations to study the mechanism by which thermally activated deformation initiates in a model binary metallic glass.
- Yue Fan
- , Takuya Iwashita
- & Takeshi Egami
-
Article
| Open Access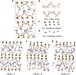 Combinatorial molecular optimization of cement hydrates
Combinatorial molecular optimization of cement hydrates
Concrete is a vital material in meeting present day construction demands. Here, the authors report a computational combinatorial approach to understand how molecular level characteristics influence the mechanical properties of cement hydrates, via screening against distinct defect types.
- M.J. Abdolhosseini Qomi
- , K.J. Krakowiak
- & R.J-.M. Pellenq
-
Article |
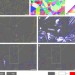 Large recovery strain in Fe-Mn-Si-based shape memory steels obtained by engineering annealing twin boundaries
Large recovery strain in Fe-Mn-Si-based shape memory steels obtained by engineering annealing twin boundaries
It has previously been shown experimentally that nanotwins in cubic boron nitride can lead to significant strengthening. Here, the authors perform simulations to understand the mechanism behind this, reporting a twin-boundary dominated indentation strain stiffening phenomena.
- Y.H. Wen
- , H.B. Peng
- & Y.Y. Du
-
Article |
 Low-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation catalysed by regenerable atomically dispersed palladium on alumina
Low-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation catalysed by regenerable atomically dispersed palladium on alumina
There has been a great deal of interest in single-atom heterogeneous catalysis recently. Here, the authors show that industrially relevant lanthanum oxide-doped alumina supports are capable of stabilizing atomically dispersed palladium species, which are evaluated for low-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation.
- Eric J. Peterson
- , Andrew T. DeLaRiva
- & Abhaya K. Datye
-
Article |
 Classification of stable three-dimensional Dirac semimetals with nontrivial topology
Classification of stable three-dimensional Dirac semimetals with nontrivial topology
Three-dimensional Dirac semimetals are a recently discovered state of condensed matter considered as the 3D analogue of graphene. Here, Yang et al. propose a general framework to classify stable 3D Dirac semimetals in systems with time-reversal, inversion and uniaxial rotational symmetries.
- Bohm-Jung Yang
- & Naoto Nagaosa
-
Article |
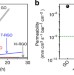 Impermeable barrier films and protective coatings based on reduced graphene oxide
Impermeable barrier films and protective coatings based on reduced graphene oxide
Although defect-free graphene is a promising membrane that is impermeable to all gases and liquids, it is difficult to produce large area films for practical applications. Su et al.show that multilayer graphitic films based on reduced graphene oxide can achieve the same goal but on larger scales.
- Y. Su
- , V. G. Kravets
- & R. R. Nair
-
Article |
 In situ nanoindentation study on plasticity and work hardening in aluminium with incoherent twin boundaries
In situ nanoindentation study on plasticity and work hardening in aluminium with incoherent twin boundaries
Nanotwinned metals containing a high density of coherent twin boundaries have the potential to exhibit high strength and ductility. Here, the authors study the effect that incoherent twin boundaries have on mechanical properties of nanotwinned aluminium with high stacking-fault energy, observing substantial work hardening and plasticity.
- D. Bufford
- , Y. Liu
- & X. Zhang
-
Article |
 Negative poisson’s ratio in single-layer black phosphorus
Negative poisson’s ratio in single-layer black phosphorus
Auxetic materials display a negative Poisson’s ratio and are usually observed in engineered structures. Here, the authors observe intrinsic auxetic behaviour in unmodified two-dimensional black phosphorous by first-principles calculations, with the auxetic behaviour resulting from its puckered structure.
- Jin-Wu Jiang
- & Harold S. Park
-
Article |
 Quantum-to-continuum prediction of ductility loss in aluminium–magnesium alloys due to dynamic strain aging
Quantum-to-continuum prediction of ductility loss in aluminium–magnesium alloys due to dynamic strain aging
Aluminum-Magnesium alloys exhibit negative strain-rate sensitivity due to dynamic strain aging, causing reduced ductility at room temperature. Here, the authors develop an atomistically informed multiscale model that can predict the rate sensitivity and ductility as a function of the alloy chemistry.
- S. M. Keralavarma
- , A. F. Bower
- & W. A. Curtin
-
Article |
 Liquid-metal electrode to enable ultra-low temperature sodium–beta alumina batteries for renewable energy storage
Liquid-metal electrode to enable ultra-low temperature sodium–beta alumina batteries for renewable energy storage
Sodium–beta alumina batteries often need high operating temperatures, and one of the reasons is poor wettability of liquid sodium on the surface of beta alumina. Here, Lu et al. report an alloying strategy that improves the wettability, allowing the batteries to be operated at much lower temperatures.
- Xiaochuan Lu
- , Guosheng Li
- & Jun Liu
-
Article |
 Low-density three-dimensional foam using self-reinforced hybrid two-dimensional atomic layers
Low-density three-dimensional foam using self-reinforced hybrid two-dimensional atomic layers
Low-density foams offer a number of attractive properties as compared to bulk materials. Here, the authors report a three-dimensional foam structure composed of stacked graphene oxide layers reinforced by hexagonal boron nitride, causing enhanced mechanical integrity.
- Soumya Vinod
- , Chandra Sekhar Tiwary
- & Pulickel M. Ajayan
-
Article |
 Strain-engineered manufacturing of freeform carbon nanotube microstructures
Strain-engineered manufacturing of freeform carbon nanotube microstructures
Reproducing complex surface geometries for high-performance composite materials is very desirable, although current synthesis methods are limited. Here, the authors present a technique to produce large-area freeform microstructures via strain-engineered growth of patterned vertically aligned carbon nanotubes.
- M. De Volder
- , S. Park
- & A. J. Hart
-
Article |
 Multiple reentrant glass transitions in confined hard-sphere glasses
Multiple reentrant glass transitions in confined hard-sphere glasses
Wall–fluid interactions are known to have a large influence on the physics of confined glasses. Here, the authors observe a multiple re-entrant glass transition for a polydisperse hard-sphere system confined between two surfaces, when the wall separation distance is of the order of a few particle diameters.
- Suvendu Mandal
- , Simon Lang
- & Fathollah Varnik
-
Article |
 High-strength carbon nanotube fibre-like ribbon with high ductility and high electrical conductivity
High-strength carbon nanotube fibre-like ribbon with high ductility and high electrical conductivity
There is strong interest in carbon nanotube assemblies for a variety of applications, many of which require combined high mechanical and electrical properties. Here, the authors demonstrate a rolling technique for performance improvement, reporting tensile strength of 4.34 GPa, ductility of 10% and electrical conductivity of 2.0 × 104 S cm−1.
- J. N. Wang
- , X. G. Luo
- & Y. Chen
-
Article |
 Oxidation-assisted ductility of aluminium nanowires
Oxidation-assisted ductility of aluminium nanowires
The mechanical properties of small volumes are often studied but rarely are the effects of surface oxidation considered. Here, the authors perform a simulation of an aluminium nanowire with an oxide shell deforming in oxygen, finding that the oxide demonstrates superplastic deformation under load.
- Fatih G. Sen
- , Ahmet T. Alpas
- & Yue Qi
-
Article
| Open Access Multiscale structural gradients enhance the biomechanical functionality of the spider fang
Multiscale structural gradients enhance the biomechanical functionality of the spider fang
Fangs are segments of the spider mouthparts, which are used to inject venom into prey and are required to sustain large mechanical loads. Here, the authors perform experiment-driven simulations, so to understand the correlation between the multiscale structural gradients and the biomechanical function of the fang.
- Benny Bar-On
- , Friedrich G. Barth
- & Yael Politi
-
Article |
 Revealing the fast atomic motion of network glasses
Revealing the fast atomic motion of network glasses
Studying relaxation in network-forming glasses on the atomic scale is experimentally challenging. Here, the authors perform X-ray photon correlation spectroscopy to study relaxation in sodium silicate at 297–762 K and show that fast atomic rearrangements occur even in the deep glassy state.
- B. Ruta
- , G. Baldi
- & F. Nazzani
-
Article |
 Fracture toughness of graphene
Fracture toughness of graphene
While the intrinsic strength of graphene has previously been demonstrated to be high, the fracture toughness remains unknown. Here, the authors perform in situtesting of graphene in a scanning electron microscope and report a critical stress intensity factor of ~4.0 MPa√m.
- Peng Zhang
- , Lulu Ma
- & Jun Lou
-
Article |
 Fractal free energy landscapes in structural glasses
Fractal free energy landscapes in structural glasses
Potential energy landscape models are often used to describe transitions in the glassy state. Here, the authors report that the landscape is much rougher than usually assumed, and demonstrate that it undergoes a transition to fractal basins before the jamming point is reached.
- Patrick Charbonneau
- , Jorge Kurchan
- & Francesco Zamponi
-
Article |
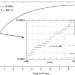 Crossover from random three-dimensional avalanches to correlated nano shear bands in metallic glasses
Crossover from random three-dimensional avalanches to correlated nano shear bands in metallic glasses
Understanding the activation of the units that control plastic deformation in metallic glasses is important. Here, the authors use dynamic mechanical analysis to analyse the statistics of the activation of these units, observing a crossover from three-dimensional random activity to two-dimensional shear banding.
- Jon-Olaf Krisponeit
- , Sebastian Pitikaris
- & Konrad Samwer
-
Article
| Open Access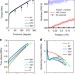 Evading the strength–ductility trade-off dilemma in steel through gradient hierarchical nanotwins
Evading the strength–ductility trade-off dilemma in steel through gradient hierarchical nanotwins
It is a long-standing goal in metallurgy to enhance the strength of materials without sacrificing ductility. Here, the authors demonstrate that applying pre-torsion to a twinning-induced plasticity steel generates a hierarchical nanotwin structure, improving strength whilst retaining ductility.
- Yujie Wei
- , Yongqiang Li
- & Huajian Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Deformation-induced structural transition in body-centred cubic molybdenum
Deformation-induced structural transition in body-centred cubic molybdenum
Structural phase transitions are known to accommodate plastic deformation in some metals and ceramics. Here, the authors observe the in situtransformation of body-centred cubic molybdenum to face-centred cubic, and finally to body-centred cubic, allowing for 15.4% tensile strain accommodation.
- S. J. Wang
- , H. Wang
- & S. X. Mao
-
Article
| Open Access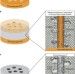 Enantioselective recognition at mesoporous chiral metal surfaces
Enantioselective recognition at mesoporous chiral metal surfaces
Chemical synthesis of chiral materials with enantioselective properties is an ongoing challenge. Here, the authors fabricate a chirally imprinted mesoporous metal from the electrochemical reduction of platinum salts in the presence of a liquid crystal phase and chiral templating molecules.
- Chularat Wattanakit
- , Yémima Bon Saint Côme
- & Alexander Kuhn
-
Article |
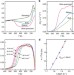 Structural origins of Johari-Goldstein relaxation in a metallic glass
Structural origins of Johari-Goldstein relaxation in a metallic glass
The mechanisms by which Johari-Goldstein relaxation is accommodated in metallic glasses are difficult to clarify. Here, the authors elucidate the mechanism in an ultra-quenched metallic glass with a cooling rate of ~1010 K s−1, by extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy.
- Y. H. Liu
- , T. Fujita
- & M. W. Chen
-
Article |
 Textured fluorapatite bonded to calcium sulphate strengthen stomatopod raptorial appendages
Textured fluorapatite bonded to calcium sulphate strengthen stomatopod raptorial appendages
The raptorial appendages of stomatopods are known to inflict large impact forces at high speeds, while exhibiting large damage tolerance. Here, the authors study the structure, distribution and nanomechanical properties of mineral phases in stomatopod's clubs, finding that calcium sulphate is co-localized with crystalline fluorapatite.
- Shahrouz Amini
- , Admir Masic
- & Ali Miserez
-
Article |
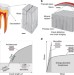 Overcoming the brittleness of glass through bio-inspiration and micro-architecture
Overcoming the brittleness of glass through bio-inspiration and micro-architecture
Glass is well known to be a brittle material, with fracture occurring soon after crack nucleation. Here, inspired by natural architectures, the authors report the laser patterning of features within an oxide glass, leading to a two order of magnitude improvement in fracture toughness.
- M. Mirkhalaf
- , A. Khayer Dastjerdi
- & F. Barthelat
-
Article |
 Reversible cyclic deformation mechanism of gold nanowires by twinning–detwinning transition evidenced from in situ TEM
Reversible cyclic deformation mechanism of gold nanowires by twinning–detwinning transition evidenced from in situ TEM
In situstudies of deformation in metal nanowires have yielded interesting results. Here, the authors perform cyclic loading on gold nanowires and observe twinning and detwinning phenomena, respectively caused by tensile and compressive loading, and elucidate the underpinning mechanism by molecular dynamics simulations.
- Subin Lee
- , Jiseong Im
- & Sang Ho Oh
-
Article |
 Mapping the evolution of hierarchical microstructures in a Ni-based superalloy
Mapping the evolution of hierarchical microstructures in a Ni-based superalloy
Phase separation in nickel-based superalloys is known to be complex and to determine the resulting microstructure and mechanical properties. Here, the authors use atom probe tomography to study phase development, finding that nickel concentration is critical in driving the formation of the γ phase from γ′.
- Florian Vogel
- , Nelia Wanderka
- & John Banhart
-
Article |
 Forced protein unfolding leads to highly elastic and tough protein hydrogels
Forced protein unfolding leads to highly elastic and tough protein hydrogels
Protein-based hydrogels are of great interest for many biomedical applications. Here, the authors demonstrate the use of mechanical labile proteins to initiate large-scale forced unfolding in order to engineer the mechanical properties of protein-based biomaterials.
- Jie Fang
- , Alexander Mehlich
- & Hongbin Li
-
Article |
 Coal as an abundant source of graphene quantum dots
Coal as an abundant source of graphene quantum dots
Coal is widely used for energy generation, but has not been considered for possible functional materials. Here, the authors report the one-step formation of graphene quantum dots from coal at yields of up to 20%, which is advantageous when compared with their syntheses from sp2-type carbon structures.
- Ruquan Ye
- , Changsheng Xiang
- & James M. Tour
-
Article |
 Microscopic response to inhomogeneous deformations in curvilinear coordinates
Microscopic response to inhomogeneous deformations in curvilinear coordinates
The electrostatic response of materials to macroscopic deformations is crucial for the operation of sensors and actuators. Here, the author combines ideas from transformation optics and density-functional perturbation theory to achieve a general description of surface flexoelectric effects.
- Massimiliano Stengel
-
Article |
 Mechanical adaptability of the Bouligand-type structure in natural dermal armour
Mechanical adaptability of the Bouligand-type structure in natural dermal armour
The scales of Arapaima gigas, a fresh water fish found in the Amazon Basin, act as effective armour against predators. Here, Zimmermann et al. elucidate the deformation mechanisms that allow for this resistance, concluding that lamellae in the scales reorient under an applied load, preventing fracture.
- Elizabeth A. Zimmermann
- , Bernd Gludovatz
- & Robert O. Ritchie
-
Article |
 Tensile testing of ultra-thin films on water surface
Tensile testing of ultra-thin films on water surface
The mechanical testing of thin films is non-trivial, due to their very fine dimensions. Kim et al. use the inherent surface tension of water as a platform for the frictionless tensile testing of gold films, with a thickness as fine as 55 nm.
- Jae-Han Kim
- , Adeel Nizami
- & Taek-Soo Kim
-
Article |
 Atomic structure of amorphous shear bands in boron carbide
Atomic structure of amorphous shear bands in boron carbide
Boron carbide is known to deform and fail via the formation of amorphous shear bands, but the atomic-scale events by which this occurs are unknown. Reddy et al.study the atomic structure of these shear bands and find that they form via the disassembly of icosahedra.
- K. Madhav Reddy
- , P. Liu
- & M.W. Chen

 Accelerated exploration of multi-principal element alloys with solid solution phases
Accelerated exploration of multi-principal element alloys with solid solution phases