Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Boundaries can steer active Janus spheres
Boundaries can steer active Janus spheres
Self-propelled colloidal particles can be potentially used to transport cargoes at the microscale, but it is challenging to prevent randomization of their motion by Brownian rotations. Here, Das et al.quench these rotations by solid walls, which guide in-plane swimming without the need for external fields.
- Sambeeta Das
- , Astha Garg
- & Stephen J. Ebbens
-
Article
| Open Access Extremely stretchable and conductive water-repellent coatings for low-cost ultra-flexible electronics
Extremely stretchable and conductive water-repellent coatings for low-cost ultra-flexible electronics
The development of modern flexible electronics calls for new materials with extreme stretchability and high conductivity. Here, Mates et al. show a printable material made of commercially-available elastomers and carbon nanofibres, which exhibits low resistance and water-repellency at strain up to 500%.
- Joseph E. Mates
- , Ilker S. Bayer
- & Constantine M. Megaridis
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional membrane as elastic shell with proof on the folds revealed by three-dimensional atomic mapping
Two-dimensional membrane as elastic shell with proof on the folds revealed by three-dimensional atomic mapping
The out-of-plane bending of 2D materials is an important factor to consider for applications, but is challenging to probe experimentally. Here, the authors map the out-of-plane bending in graphene and other 2D materials using high resolution electron microscopy.
- Jiong Zhao
- , Qingming Deng
- & Mark H Rümmeli
-
Article
| Open Access Topology-generating interfacial pattern formation during liquid metal dealloying
Topology-generating interfacial pattern formation during liquid metal dealloying
Liquid metal dealloying produces topologically complex nanoporous structures, however little is known about how they form. Here, the authors use mesoscale phase-field modeling and experiments to show that structure formation is governed by both interfacial spinodal decomposition and diffusion-coupled growth.
- Pierre-Antoine Geslin
- , Ian McCue
- & Alain Karma
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic and vibrational origins of mechanical toughness in bioactive cement during setting
Atomic and vibrational origins of mechanical toughness in bioactive cement during setting
Bioactive cements are widely used in dentistry and medicine. Here, using a variety of novel experimental techniques, the authors uncover the atomic and vibrational contributions to the mechanical toughness of bioactive cement during the setting process.
- Kun V. Tian
- , Bin Yang
- & G. Neville Greaves
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanical instability of monocrystalline and polycrystalline methane hydrates
Mechanical instability of monocrystalline and polycrystalline methane hydrates
Sediment-hosted gas hydrates may release vast quantities of methane upon failure, but destabilizing mechanisms at the molecular level are poorly understood. Here, the authors study the deformation using simulations and find that failure differs between single crystals and polycrystalline hydrates.
- Jianyang Wu
- , Fulong Ning
- & Zhiliang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Influence of chemical disorder on energy dissipation and defect evolution in concentrated solid solution alloys
Influence of chemical disorder on energy dissipation and defect evolution in concentrated solid solution alloys
The understanding of complex electronic correlation and non-equilibrium atomic interactions is a grand challenge. Here, the authors show that chemical disorder in single-phase concentrated solid solution alloys can lead to reduction in electron mean free path and electrical and thermal conductivity.
- Yanwen Zhang
- , G. Malcolm Stocks
- & William J. Weber
-
Article
| Open Access Multimaterial magnetically assisted 3D printing of composite materials
Multimaterial magnetically assisted 3D printing of composite materials
Endowing composite materials with spatially discrete mechanical behaviours is possible by varying the internal concentration and arrangement of particles. Here, the authors demonstrate a 3D magnetic printing technique which enables the fabrication of materials with intricate internal designs.
- Dimitri Kokkinis
- , Manuel Schaffner
- & André R. Studart
-
Article
| Open Access Selective hydrogenation of 1,3-butadiene on platinum–copper alloys at the single-atom limit
Selective hydrogenation of 1,3-butadiene on platinum–copper alloys at the single-atom limit
Reducing the platinum content of industrial catalysts is an important research target. Here, the authors present a nanocatalyst containing less than 1% platinum, where the isolated platinum atoms contribute to both the catalyst activity and selectivity for butadiene hydrogenation.
- Felicia R. Lucci
- , Jilei Liu
- & E. Charles H. Sykes
-
Article
| Open Access Fermi states and anisotropy of Brillouin zone scattering in the decagonal Al–Ni–Co quasicrystal
Fermi states and anisotropy of Brillouin zone scattering in the decagonal Al–Ni–Co quasicrystal
Quasicrystals show long-range order but lack the symmetry of conventional crystals. Here, the authors study the bulk electronic structure of quasicrystals and their three-dimensional Fermi surface topology, providing links to the structural stability of these materials.
- V. A. Rogalev
- , O. Gröning
- & V. N. Strocov
-
Article
| Open Access Entropy-stabilized oxides
Entropy-stabilized oxides
The composition of oxide compounds controls many of their properties and electronic phases. Here, the authors show that entropy and configurational disorder can stabilize new phases of oxides, potentially enabling a better engineering of their properties.
- Christina M. Rost
- , Edward Sachet
- & Jon-Paul Maria
-
Article
| Open Access The structural origin of the hard-sphere glass transition in granular packing
The structural origin of the hard-sphere glass transition in granular packing
Glass transition shows dramatic dynamic slowdown, but its origin remains unclear. Here, Xia et al. observe in granular systems the rapid growth of a geometrically frustrated polytetrahedral order with packing fraction, which is spatially correlated with the slow dynamics.
- Chengjie Xia
- , Jindong Li
- & Yujie Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Femtosecond structural transformation of phase-change materials far from equilibrium monitored by coherent phonons
Femtosecond structural transformation of phase-change materials far from equilibrium monitored by coherent phonons
Chalcogenide-based phase-change materials such as Ge2Sb2Te5could be useful for optical data storage, but the mechanism that ultimately limits their switching speed is unclear. Here, the authors use coherent phonon spectroscopy to better understand the non-thermal pathways between the two different phases.
- Muneaki Hase
- , Paul Fons
- & Junji Tominaga
-
Article
| Open Access High damage tolerance of electrochemically lithiated silicon
High damage tolerance of electrochemically lithiated silicon
Mechanical degradation is an undesired behaviour for battery electrode materials such as lithiated silicon. Here, the authors performin situnanomechanical experiments and atomistic modelling to reveal the damage tolerance of electrochemically lithiated silicon.
- Xueju Wang
- , Feifei Fan
- & Shuman Xia
-
Article
| Open Access A predictive structural model for bulk metallic glasses
A predictive structural model for bulk metallic glasses
The atomic structure of metallic glasses is related to their properties such as the ability of materials to form glasses. Here, the authors develop a new approach to model the atomic structure of metallic glasses, to enable a better connection between atomic structure and glass properties.
- K. J. Laws
- , D. B. Miracle
- & M. Ferry
-
Article
| Open Access Transgranular liquation cracking of grains in the semi-solid state
Transgranular liquation cracking of grains in the semi-solid state
To obtain superior mechanical properties of cast components, grain refinement via semi-solid deformation is desirable. Here, the authors use in situ X-ray tomography to study the response of an alloy to indentation, and present a new mechanism of transgranular liquation cracking.
- S. Karagadde
- , P. D. Lee
- & R. C. Atwood
-
Article
| Open Access Quadruple-junction lattice coherency and phase separation in a binary-phase system
Quadruple-junction lattice coherency and phase separation in a binary-phase system
The overall physical properties of binary-phase systems ranging from metallic alloys to soft polymers are affected by phase-separation morphologies. Here, Chung et al.use atomic-resolution electron microscopy to demonstrate the influence of quadruple junctions on the morphology evolution during phase separation.
- Sung-Yoon Chung
- , Si-Young Choi
- & Young-Min Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Fractal dendrite-based electrically conductive composites for laser-scribed flexible circuits
Fractal dendrite-based electrically conductive composites for laser-scribed flexible circuits
Electrically conductive composites are increasingly being studied for their favourable mechanical and electrical properties. Here, the authors employ a new synthetic strategy to attain fractal silver micro-dendrites which can be laser-scribed for implementation in flexible printed microelectronics.
- Cheng Yang
- , Xiaoya Cui
- & Ching-Ping Wong
-
Article
| Open Access Realizing high figure of merit in heavy-band p-type half-Heusler thermoelectric materials
Realizing high figure of merit in heavy-band p-type half-Heusler thermoelectric materials
Thermoelectric materials could be used to convert waste heat into useful electricity, but the ideal substance needs to both optimize the electrical power factor and suppress thermal conductivity. Here, the authors report a high figure of merit of 1.5 at 1,200 K in the p-type half-Heusler alloy FeNbSb.
- Chenguang Fu
- , Shengqiang Bai
- & Tiejun Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale size effects in crystallization of metallic glass nanorods
Nanoscale size effects in crystallization of metallic glass nanorods
It is crucial to avoid crystallization in metallic glasses, which show appealing mechanical properties associated with their amorphous structures. Sohnet al. identify unusual nucleation kinetics in metallic glass nanorods, which exhibits a crystallization temperature minimum at a certain diameter.
- Sungwoo Sohn
- , Yeonwoong Jung
- & Judy J. Cha
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid glasses from strong and fragile metal-organic framework liquids
Hybrid glasses from strong and fragile metal-organic framework liquids
The fine interface between crystallinity and amorphicity in synthetic hybrid materials has to-date been relatively under-explored. Here, the authors probe the relationship between amorphisation and melting behaviour in zeolitic metal-organic frameworks as a route towards functional glasses.
- Thomas D. Bennett
- , Jin-Chong Tan
- & G. Neville Greaves
-
Article
| Open Access Controllable synthesis of molybdenum tungsten disulfide alloy for vertically composition-controlled multilayer
Controllable synthesis of molybdenum tungsten disulfide alloy for vertically composition-controlled multilayer
The band gap modulation of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide alloy is essential for successful applications. Here, we show a controllable synthesis of Mo1−xWxS2 alloy and vertically composition-controlled Mo1−xWxS2multilayer, which is promising as a photoactive material.
- Jeong-Gyu Song
- , Gyeong Hee Ryu
- & Hyungjun Kim
-
Article
| Open Access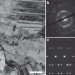 Transition of dislocation nucleation induced by local stress concentration in nanotwinned copper
Transition of dislocation nucleation induced by local stress concentration in nanotwinned copper
Metallic materials with a nanometre-scaled lamella structure can have properties that are very different from their coarser-grained counterparts. Here, the authors demonstrate how dislocations in such a material—nanotwinned copper—can nucleate in two distinctly different mechanisms depending on local stress
- N. Lu
- , K. Du
- & H. Q. Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrastrong ductile and stable high-entropy alloys at small scales
Ultrastrong ductile and stable high-entropy alloys at small scales
Refractory high-entropy alloys show promising mechanical properties at elevated temperatures, but are generally brittle at room temperature. Here, the authors observe an improved ductility and yield strength in high-entropy alloy micropillars consisting of nanometre-sized grains that also exhibit excellent thermal stability.
- Yu Zou
- , Huan Ma
- & Ralph Spolenak
-
Article
| Open Access Carbon-doped BN nanosheets for metal-free photoredox catalysis
Carbon-doped BN nanosheets for metal-free photoredox catalysis
Metal-free semiconductors with appropriate bandgaps create photocatalytic routes to water splitting and CO2reduction. Here the authors dope hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets with carbon via a simple method to synthesize a ternary B–C–N alloy capable of performing just this function.
- Caijin Huang
- , Cheng Chen
- & Xinchen Wang
-
Article
| Open Access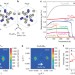 A new class of chiral materials hosting magnetic skyrmions beyond room temperature
A new class of chiral materials hosting magnetic skyrmions beyond room temperature
Magnetic skyrmions are circulating topologically-protected spin textures which can arise in chiral magnets and potentially be applied in information processing. Here, the authors demonstrate the appearance of skyrmions at and above room temperature in a β-Mn-type Co-Zn-Mn alloy.
- Y. Tokunaga
- , X. Z. Yu
- & Y. Tokura
-
Article
| Open Access Phase stability and dynamics of entangled polymer–nanoparticle composites
Phase stability and dynamics of entangled polymer–nanoparticle composites
The lowering of polymer viscosity upon addition of small amounts of nanoparticles is counter-intuitive and has puzzled researchers. Here, Mangal et al. explain this intriguing phenomenon using a model polymer–nanocomposite system comprised of well-dispersed nanoparticles in an entangled polymer melt.
- Rahul Mangal
- , Samanvaya Srivastava
- & Lynden A. Archer
-
Article
| Open Access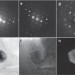 Scanning precession electron tomography for three-dimensional nanoscale orientation imaging and crystallographic analysis
Scanning precession electron tomography for three-dimensional nanoscale orientation imaging and crystallographic analysis
High-resolution microscopy allows imaging of information on the atomic scale. Here, by combining precession electron diffraction with scanning transmission electron microscopy, the authors demonstrate an efficient, alternative technique to determine the three-dimensional orientation of materials.
- Alexander S. Eggeman
- , Robert Krakow
- & Paul A. Midgley
-
Article |
 Predictive modelling-based design and experiments for synthesis and spinning of bioinspired silk fibres
Predictive modelling-based design and experiments for synthesis and spinning of bioinspired silk fibres
Reproducing many naturally occurring silk fibres—such as spider silk—remains a challenge. Here, the authors develop a predictive modelling approach to understand and design the artificial synthesis and fibre-spinning processes, which are tested in the laboratory to create de novobioinspired silk fibres.
- Shangchao Lin
- , Seunghwa Ryu
- & Markus J. Buehler
-
Article
| Open Access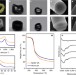 Carbonization of a stable β-sheet-rich silk protein into a pseudographitic pyroprotein
Carbonization of a stable β-sheet-rich silk protein into a pseudographitic pyroprotein
The strength and stability of silk proteins is thought to be related to the high content of β-sheets within their structures. Here, the authors show that when heated at high temperature, and above that of thermal degradation, these β-sheets are transformed into an ordered hexagonal graphitic structure.
- Se Youn Cho
- , Young Soo Yun
- & Hyoung-Joon Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Structural optimization of 3D-printed synthetic spider webs for high strength
Structural optimization of 3D-printed synthetic spider webs for high strength
Spider webs have some intriguing mechanical properties, but understanding of the properties is limited to individual silk fibres. Here, the authors create mimics of spider web using 3D techniques, which enables them to acquire knowledge of mechanical strength of the entire synthetic web.
- Zhao Qin
- , Brett G. Compton
- & Markus J. Buehler
-
Article
| Open Access External stimulation-controllable heat-storage ceramics
External stimulation-controllable heat-storage ceramics
Materials that can store and release heat on demand are of use for energy storage applications. Here, the authors discover a ceramic material that can reversibly store energy from heat, light or electricity and release this energy as heat through the application of pressure.
- Hiroko Tokoro
- , Marie Yoshikiyo
- & Shin-ichi Ohkoshi
-
Article
| Open Access Investigation of exotic stable calcium carbides using theory and experiment
Investigation of exotic stable calcium carbides using theory and experiment
Pressure causes profound changes in the properties of atoms and chemical bonding leading to unusual materials. Here, the authors investigate the Ca-C system and find that it becomes increasingly complex and develops a multitude of phases with various compositions and new structures at higher pressures.
- Yan-Ling Li
- , Sheng-Nan Wang
- & Timothy A. Strobel
-
Article
| Open Access Damage-tolerant nanotwinned metals with nanovoids under radiation environments
Damage-tolerant nanotwinned metals with nanovoids under radiation environments
Materials that are tolerant to radiation damage are important for use in nuclear reactors or the storage of nuclear materials. Here, the authors show that pre-introduced nanovoids in nanotwinned copper improve self-healing of the material and therefore enhance its radiation tolerance.
- Y. Chen
- , K Y. Yu
- & X. Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Metallic glass nanostructures of tunable shape and composition
Metallic glass nanostructures of tunable shape and composition
The nanoscale manipulation of the shape and composition of metallic glasses is challenging. Here, the authors employ a multitarget carousel oblique angle deposition strategy to synthesize metallic glass nanoarchitectures, and demonstrate applicability to a range of glass-forming alloys.
- Yanhui Liu
- , Jingbei Liu
- & Jan Schroers
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerated sintering in phase-separating nanostructured alloys
Accelerated sintering in phase-separating nanostructured alloys
In sintering, powders of small grains are packed together to form shapes or grain structures that cannot be achieved by melt casting. Here, the authors demonstrate the fast sintering of a nanostructured alloy at low temperatures, preserving its nanoscale grain structure.
- Mansoo Park
- & Christopher A. Schuh
-
Article
| Open Access Three-fold rotational defects in two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides
Three-fold rotational defects in two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides
Defects in a crystalline solid can have a dramatic effect on the material’s properties. Here, the authors demonstrate a class of defects in two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides mediated by chalcogen vacancies and inherently related to the crystal symmetry
- Yung-Chang Lin
- , Torbjörn Björkman
- & Kazu Suenaga
-
Article
| Open Access Pseudocapacitance of MXene nanosheets for high-power sodium-ion hybrid capacitors
Pseudocapacitance of MXene nanosheets for high-power sodium-ion hybrid capacitors
Conventional sodium ion batteries have low energy and power densities. Here, the authors report the use of MXene Ti2C as a negative electrode for sodium ion energy storage, and show that the pseudocapacitance of the electrode allows the hybrid capacitors to achieve high electrochemical performance.
- Xianfen Wang
- , Satoshi Kajiyama
- & Atsuo Yamada
-
Article
| Open Access Strain-induced metal–semiconductor transition observed in atomic carbon chains
Strain-induced metal–semiconductor transition observed in atomic carbon chains
Previous studies have predicted that carbyne (a single chain of sp1carbon atoms) goes from being metallic to semiconducting under strain. Here, the authors measure the electronic properties of carbyne, confirming the prediction and showing that the conductivity is determined by strain and by the contacts.
- A. La Torre
- , A. Botello-Mendez
- & F. Banhart
-
Article
| Open Access Ternary metal fluorides as high-energy cathodes with low cycling hysteresis
Ternary metal fluorides as high-energy cathodes with low cycling hysteresis
Transition metal fluorides have high theoretical specific capacities as cathodes for lithium ion batteries, but low working potentials and poor energy efficiency limit their practical applications. Here, the authors report a group of ternary metal fluorides, which may overcome these problems.
- Feng Wang
- , Sung-Wook Kim
- & Jason Graetz
-
Article |
 Formation of nickel cobalt sulfide ball-in-ball hollow spheres with enhanced electrochemical pseudocapacitive properties
Formation of nickel cobalt sulfide ball-in-ball hollow spheres with enhanced electrochemical pseudocapacitive properties
While the synthesis of hollow structures of transition metal oxides is well established, the related sulfide chemistry remains challenging. Here, the authors report the synthesis of nickel cobalt sulfide ball-in-ball hollow spheres, via anion exchange, and evaluate their pseudocapacitive behaviour.
- Laifa Shen
- , Le Yu
- & Xiong Wen (David) Lou
-
Article
| Open Access Soft network composite materials with deterministic and bio-inspired designs
Soft network composite materials with deterministic and bio-inspired designs
Soft biological composites have great potential in areas such as artificial tissue constructs and bio-integrated devices, but receive little attention. Here, the authors design soft biomimetic materials that can precisely reproduce the non-linear mechanics of relevant biological materials.
- Kyung-In Jang
- , Ha Uk Chung
- & John A. Rogers
-
Article
| Open Access High performing and stable supported nano-alloys for the catalytic hydrogenation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone
High performing and stable supported nano-alloys for the catalytic hydrogenation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone
The hydrogenation of leuvinic acid to γ-valerolactone is an important step in the conversion of lignocellulose to high value chemicals. Here, the authors report that bimetallic alloys are active and stable catalysts for this reaction, and attribute this to geometric and electronic effects.
- Wenhao Luo
- , Meenakshisundaram Sankar
- & Bert M. Weckhuysen
-
Article |
 Universal composition–structure–property maps for natural and biomimetic platelet–matrix composites and stacked heterostructures
Universal composition–structure–property maps for natural and biomimetic platelet–matrix composites and stacked heterostructures
Many layered composites exhibit a remarkable balance of strength, toughness and stiffness. Here, the authors construct a model to explain the synergy of key mechanical properties of layered composites by considering the elastic/plastic properties of the matrix and use 3D-printed samples to validate their predictions.
- Navid Sakhavand
- & Rouzbeh Shahsavari
-
Article
| Open Access Highly porous non-precious bimetallic electrocatalysts for efficient hydrogen evolution
Highly porous non-precious bimetallic electrocatalysts for efficient hydrogen evolution
Investigations into non-precious metal catalysts for hydrogen evolution are ongoing. Here, the authors report a hierarchical, nanoporous copper-titanium electrocatalyst, and demonstrate that it catalyses hydrogen production at twice the over-all rate of commercial platinum-based catalysts.
- Qi Lu
- , Gregory S. Hutchings
- & Jingguang G. Chen
-
Article |
 Topological crystalline metal in orthorhombic perovskite iridates
Topological crystalline metal in orthorhombic perovskite iridates
Topological insulators are insulators in the bulk, but can support conducting states on their surface. Here, Chen et al. predict orthorhombic perovskite iridates to be topological crystalline metals, exhibiting bulk metallic behaviour and surface states protected by certain crystal symmetries.
- Yige Chen
- , Yuan-Ming Lu
- & Hae-Young Kee
-
Article |
 Origin of pressure-induced crystallization of Ce75Al25 metallic glass
Origin of pressure-induced crystallization of Ce75Al25 metallic glass
It is commonly believed that pressure-induced crystallization in Ce-Al amorphous alloy is caused by Ce 4f orbital delocalization. Here, Wu et al. propose an alternative mechanism, whereby the crystallization is driven by a steric effect of dominant packing of cerium atoms at high pressure.
- Min Wu
- , John S. Tse
- & J.Z. Jiang
-
Article |
 Densified network glasses and liquids with thermodynamically reversible and structurally adaptive behaviour
Densified network glasses and liquids with thermodynamically reversible and structurally adaptive behaviour
Degrees of freedom can be frozen in glassy material, which results in a hysteresis in heat capacity under cooling or heating. Here, the authors show that the hysteresis can be minimized at selected thermodynamic conditions, leading to thermally reversible glasses that are isostatically rigid.
- M. Bauchy
- & M. Micoulaut
-
Article |
 Thermal conductance of metal–diamond interfaces at high pressure
Thermal conductance of metal–diamond interfaces at high pressure
The thermal conductance of interfaces between metal and diamond at high pressure is often greater than can be accounted for by two-phonon processes. Here, the authors present a new experimental system, suggesting that the ‘extra’ thermal conductance seen is controlled by Raman-like three-phonon processes.
- Gregory T. Hohensee
- , R.B. Wilson
- & David G. Cahill

 Ultralight shape-recovering plate mechanical metamaterials
Ultralight shape-recovering plate mechanical metamaterials