Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Learning grain boundary segregation energy spectra in polycrystals
Learning grain boundary segregation energy spectra in polycrystals
Predicting segregation energies of alloy systems can be challenging even for a single grain boundary. Here the authors propose a machine-learning framework, which maps the local environments on a distribution of segregation energies, to predict segregation energies of alloy elements in polycrystalline materials.
- Malik Wagih
- , Peter M. Larsen
- & Christopher A. Schuh
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrahigh strength and ductility in newly developed materials with coherent nanolamellar architectures
Ultrahigh strength and ductility in newly developed materials with coherent nanolamellar architectures
Nano-lamellar materials with ultrahigh strengths are highly desirable for technological applications. Here the authors report a nanolamellar architecturing approach by utilizing coherent L12 structures to achieve ultrahigh strength and ductility in Ni-Fe-Co-Cr-Al-Ti multicomponent alloys.
- Lei Fan
- , Tao Yang
- & Chain-Tsuan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable analog thermal material
Tunable analog thermal material
Thermal metamaterials are able to produce unconventional physical properties. Here, the authors demonstrate a thermal metamaterial with conductivity that can be continuously tuned over a very large range.
- Guoqiang Xu
- , Kaichen Dong
- & Cheng-Wei Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoparticles suppress fluid instabilities in the thermal drawing of ultralong nanowires
Nanoparticles suppress fluid instabilities in the thermal drawing of ultralong nanowires
Thermal drawing of glass-cladded metal nanowires is limited by fluid instabilities. Hwang et al. show how admixing tungsten carbide nanoparticles to the zinc core of a borosilicate-cladded wire leads to intact fibres over lengths significantly exceeding those of metals with high melting points.
- Injoo Hwang
- , Zeyi Guan
- & Xiaochun Li
-
Article
| Open Access 3D-printed cellular tips for tuning fork atomic force microscopy in shear mode
3D-printed cellular tips for tuning fork atomic force microscopy in shear mode
The authors investigate 3D-printed tips, based on controlled microstructural architectured materials, as probes for shear-mode atomic force microscopy. They demonstrate that the tailored stiffness and energy-absorbing behaviour of the material are beneficial for improving image quality.
- Liangdong Sun
- , Hongcheng Gu
- & Zhongze Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Strategies for simultaneous strengthening and toughening via nanoscopic intracrystalline defects in a biogenic ceramic
Strategies for simultaneous strengthening and toughening via nanoscopic intracrystalline defects in a biogenic ceramic
Biominerals are nanocomposites that often incorporate nanoscopic defects such as organic inclusions within the mineral matrix. Here, the authors report on an experimental and computational study into the effects of intracrystalline defects on the intrinsic mechanical behaviour of biominerals.
- Zhifei Deng
- , Hongshun Chen
- & Ling Li
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous mechanical materials squeezing three-dimensional volume compressibility into one dimension
Anomalous mechanical materials squeezing three-dimensional volume compressibility into one dimension
Anomalous mechanical behaviors provide an opportunity to regulate the functions of materials. Here the authors show that materials with coexisting negative, zero and positive compressibilities can “squeeze” volume compressibility into one direction, and thus stabilize transmission processes under pressure.
- Xingxing Jiang
- , Maxim S. Molokeev
- & Zheshuai Lin
-
Article
| Open Access An all-natural bioinspired structural material for plastic replacement
An all-natural bioinspired structural material for plastic replacement
It is desirable yet challenging to develop sustainable structural materials to replace petroleum-based plastics. Here, the authors report a facile assembly method for manufacturing high-performance structural materials with a unique combination of high strength, toughness and stiffness.
- Qing-Fang Guan
- , Huai-Bin Yang
- & Shu-Hong Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Training high-strength aluminum alloys to withstand fatigue
Training high-strength aluminum alloys to withstand fatigue
The fatigue performance of high strength aluminum alloys is notoriously poor, leading to design limitations for transportation structures. Here the authors design microstructures to exploit the mechanical energy of fatigue to dynamically heal the microstructural weak points and improve the high cycle fatigue life.
- Qi Zhang
- , Yuman Zhu
- & Christopher Hutchinson
-
Article
| Open Access Repulsion leads to coupled dislocation motion and extended work hardening in bcc metals
Repulsion leads to coupled dislocation motion and extended work hardening in bcc metals
Work hardening of tungsten in the thermally activated regime is highly orientation dependent. Here, we show that kink-pair nucleation controlled coupled motion of repulsively oriented screw dislocation pairs occurs and leads to an orientation dependent additional plastic slip on unexpected slip systems.
- K. Srivastava
- , D. Weygand
- & P. Gumbsch
-
Article
| Open Access A defect-resistant Co–Ni superalloy for 3D printing
A defect-resistant Co–Ni superalloy for 3D printing
Additive manufacturing promises a major transformation of the production of high economic value metallic materials. Here, the authors describe a new class of 3D printable superalloys that are amenable to crack-free 3D printing via electron beam melting as well as selective laser melting.
- Sean P. Murray
- , Kira M. Pusch
- & Tresa M. Pollock
-
Article
| Open Access Strain localisation and failure at twin-boundary complexions in nickel-based superalloys
Strain localisation and failure at twin-boundary complexions in nickel-based superalloys
Coherent twin boundaries in nickel-based superalloys are vulnerable sites for alloy failure in demanding environments. Here, the authors show that the abnormal γ″ precipitation mechanism at twin boundaries is responsible for pronounced strain localisation and subsequent failure.
- Zhenbo Zhang
- , Zhibiao Yang
- & Michael Preuss
-
Article
| Open Access Flexopiezoelectricity at ferroelastic domain walls in WO3 films
Flexopiezoelectricity at ferroelastic domain walls in WO3 films
Observation of a strain-gradient-induced piezoresponse at domain walls remains a challenge. Here, the authors find the piezoelectric response to be enhanced in the ferroelastic domain walls of centrosymmetric tungsten trioxide thin films due to a large strain gradient over a wide width of the wall.
- Shinhee Yun
- , Kyung Song
- & Chan-Ho Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Emergent solidity of amorphous materials as a consequence of mechanical self-organisation
Emergent solidity of amorphous materials as a consequence of mechanical self-organisation
Glass materials are solid, like crystals, but lack long-range order, whilst the origin of their solidity remains elusive. Tong et al. show that the emergent solidity of glasses is induced by self-organization of percolation of force-bearing network appeared at the non-equilibrium glass transition upon cooling.
- Hua Tong
- , Shiladitya Sengupta
- & Hajime Tanaka
-
Article
| Open Access Reinforcing materials modelling by encoding the structures of defects in crystalline solids into distortion scores
Reinforcing materials modelling by encoding the structures of defects in crystalline solids into distortion scores
The presence of defects in crystalline solids affects material properties, the precise knowledge of defect characteristics being highly desirable. Here the authors demonstrate a machine-learning outlier detection method based on distortion score as an effective tool for modelling defects in crystalline solids.
- Alexandra M. Goryaeva
- , Clovis Lapointe
- & Mihai-Cosmin Marinica
-
Article
| Open Access Connecting shear localization with the long-range correlated polarized stress fields in granular materials
Connecting shear localization with the long-range correlated polarized stress fields in granular materials
Understanding the behavior of jammed granular matter is important for a range of phenomena, from materials science to geology. Wang et al. uncover relations between stress correlations and emergence of localized shear bands due to external shear stress, which breaks the rotational symmetry.
- Yinqiao Wang
- , Yujie Wang
- & Jie Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access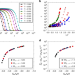 Excess-entropy scaling in supercooled binary mixtures
Excess-entropy scaling in supercooled binary mixtures
Supercooled liquids near the glass transition show remarkable non-Arrhenius transport phenomena, whose origin is yet to be clarified. Here, the authors use GPU molecular dynamics simulations for various binary mixtures in the supercooled regime to show the validity of a quasiuniversal excess-entropy scaling relation for viscosity and diffusion.
- Ian H. Bell
- , Jeppe C. Dyre
- & Trond S. Ingebrigtsen
-
Article
| Open Access Unique universal scaling in nanoindentation pop-ins
Unique universal scaling in nanoindentation pop-ins
Although power laws are observed during nanoindentation and the power-law exponents are estimated to be approximately 1.5-1.6 for face-centered cubic metals, the origin of the exponent remains unclear. In this paper, we show the power-law statistics in pop-in magnitudes and unveil the nature of the exponent.
- Yuji Sato
- , Shuhei Shinzato
- & Shigenobu Ogata
-
Article
| Open Access Stretchable hydrogels with low hysteresis and anti-fatigue fracture based on polyprotein cross-linkers
Stretchable hydrogels with low hysteresis and anti-fatigue fracture based on polyprotein cross-linkers
High stretchability, low hysteresis and anti-fatigue fracture are essential for hydrogel-based devices but it is rare to achieve. Here the authors demonstrate a hydrogel design using tandem-repeat proteins as the cross-linkers and random coiled polymers as the percolating network which results in high stretchability, low hysteresis and high fracture toughness.
- Hai Lei
- , Liang Dong
- & Wei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Proton irradiation-decelerated intergranular corrosion of Ni-Cr alloys in molten salt
Proton irradiation-decelerated intergranular corrosion of Ni-Cr alloys in molten salt
Better understanding the synergy between radiation and corrosion is necessary to deploy advanced nuclear reactors. Here, the authors contradict the misconception that radiation always results in deleterious effects and show that proton irradiation slows the corrosion of Ni-Cr alloys in 650 °C molten salt.
- Weiyue Zhou
- , Yang Yang
- & Michael P. Short
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying microscale drivers for fatigue failure via coupled synchrotron X-ray characterization and simulations
Quantifying microscale drivers for fatigue failure via coupled synchrotron X-ray characterization and simulations
Structural alloys have distinct microstructural features known as twins that are preferential sites for fatigue crack initiation and need to be better understood to mitigate catastrophic failures. Here, the authors show unusually large stress gradients near a twin boundary, using X-ray techniques and modelling.
- Sven Gustafson
- , Wolfgang Ludwig
- & Michael D. Sangid
-
Article
| Open Access Metallic nanocrystals with low angle grain boundary for controllable plastic reversibility
Metallic nanocrystals with low angle grain boundary for controllable plastic reversibility
Improving the reversible plastic deformability and damage tolerance of nanosized metals remains challenging. Here, the authors custom-design low angle grain boundaries in metallic bicrystals to achieve controllable plastic reversibility via fully conservative grain boundary migration.
- Qi Zhu
- , Qishan Huang
- & Jiangwei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access A strong and ductile medium-entropy alloy resists hydrogen embrittlement and corrosion
A strong and ductile medium-entropy alloy resists hydrogen embrittlement and corrosion
Strong and ductile materials with resistance to both corrosion and hydrogen embrittlement remain rare and yet are essential for hydrogen-propelled industries. Here, the authors show that a CoNiV medium-entropy alloy with face-centered cubic structure fulfils all the above criteria.
- Hong Luo
- , Seok Su Sohn
- & Dierk Raabe
-
Article
| Open Access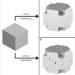 Hardening in Au-Ag nanoboxes from stacking fault-dislocation interactions
Hardening in Au-Ag nanoboxes from stacking fault-dislocation interactions
Fabricating and mechanically testing nanoarchitected materials remains a challenge. Here, the authors use colloidal synthesis to fabricate Au-Ag hollow nanoboxes and investigate the effect of either a rough or a smooth nanobox surface on the mechanical properties.
- Radhika P. Patil
- , David Doan
- & X. Wendy Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Single-atom Pt in intermetallics as an ultrastable and selective catalyst for propane dehydrogenation
Single-atom Pt in intermetallics as an ultrastable and selective catalyst for propane dehydrogenation
Propylene production via propane dehydrogenation demands a highly stable catalyst that works without deactivation even at high temperatures. Here, the authors show that single-atom Pt included in thermally stable intermetallic PtGa works as an active and selective catalyst for propane dehydrogenation even at 600 °C for 96 h without deactivation.
- Yuki Nakaya
- , Jun Hirayama
- & Shinya Furukawa
-
Article
| Open Access A powder-metallurgy-based strategy toward three-dimensional graphene-like network for reinforcing copper matrix composites
A powder-metallurgy-based strategy toward three-dimensional graphene-like network for reinforcing copper matrix composites
Graphene networks have been used to reinforce polymer and ceramic composites, but connecting graphene into a three dimensional network in a metal matrix is challenging. Here the authors use a powder-metallurgy-based strategy to construct a three-dimensional graphene network reinforced copper matrix composite.
- Xiang Zhang
- , Yixin Xu
- & Chunnian He
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrahigh high-strain-rate superplasticity in a nanostructured high-entropy alloy
Ultrahigh high-strain-rate superplasticity in a nanostructured high-entropy alloy
Superplasticity at high strain rates is challenging to achieve in high strength materials. Here, the authors show superplastic elongation in excess of 2000% in a high entropy alloy nanostructured by high-pressure torsion.
- Nhung Thi-Cam Nguyen
- , Peyman Asghari-Rad
- & Hyoung Seop Kim
-
Comment
| Open AccessBringing nuclear materials discovery and qualification into the 21st century
Time horizons for nuclear materials development and qualification must be shortened to realize future nuclear energy concepts. Inspired by the Materials Genome Initiative, we present an integrated approach to materials discovery and qualification to insert new materials into service.
- Jeffery A. Aguiar
- , Andrea M. Jokisaari
- & R. Allen Roach
-
Article
| Open Access Fracture toughness of a metal–organic framework glass
Fracture toughness of a metal–organic framework glass
Metal-organic framework glasses are gaining interest, but large samples are difficult to fabricate and mechanical properties are not well understood. Here, the authors use experiments and simulations to assess fracture toughness and flexural strength of a zeolitic imidazolate framework glass.
- Theany To
- , Søren S. Sørensen
- & Morten M. Smedskjaer
-
Article
| Open Access Unstable twin in body-centered cubic tungsten nanocrystals
Unstable twin in body-centered cubic tungsten nanocrystals
Body-centred cubic metals rarely show twinning during deformation. Here, the authors use high resolution transmission electron microscopy to show tungsten, a body-centred cubic metal, spontaneously undergoes detwinning when unloaded.
- Xiang Wang
- , Jiangwei Wang
- & Scott X. Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Yield strength and misfit volumes of NiCoCr and implications for short-range-order
Yield strength and misfit volumes of NiCoCr and implications for short-range-order
Chemical short-range order (SRO) NiCoCr has been proposed to account for its positive stacking fault energy and good mechanical properties. Here, a combination of theory and experiment shows that SRO is of negligible importance in NiCoCr processed by standard methods.
- Binglun Yin
- , Shuhei Yoshida
- & W. A. Curtin
-
Article
| Open Access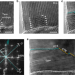 Direct observation of dual-step twinning nucleation in hexagonal close-packed crystals
Direct observation of dual-step twinning nucleation in hexagonal close-packed crystals
Aspects of twinning in hexagonal-close-packed crystals remain elusive. Here, the authors directly image twinning in rhenium nanocrystals and show the process is mediated by disconnections on Prismatic│Basal interfaces as the twin initially deviates from its ideal orientation before it is corrected.
- Yang He
- , Bin Li
- & Scott X. Mao
-
Article
| Open Access Dual heterogeneous structures lead to ultrahigh strength and uniform ductility in a Co-Cr-Ni medium-entropy alloy
Dual heterogeneous structures lead to ultrahigh strength and uniform ductility in a Co-Cr-Ni medium-entropy alloy
Improving both strength and ductility simultaneously in structural metals and alloys remains a challenge. Here, the authors design a heterogeneous structure in a Co-Cr-Ni alloy that results in ultrahigh strength and significant uniform elongation.
- X. H. Du
- , W. P. Li
- & E. W. Huang
-
Article
| Open Access In-situ observation of the initiation of plasticity by nucleation of prismatic dislocation loops
In-situ observation of the initiation of plasticity by nucleation of prismatic dislocation loops
Prismatic dislocation loops (PDLs) form during the elastic-to-plastic transition of a dislocation-free volume under nanoindentation. Here the authors observe the initial plasticity and burst-like emission of PDLs in Au nanowires by in-situ transmission electron microscopy, elucidating fundamental aspects of the formation process.
- Subin Lee
- , Aviral Vaid
- & Sang Ho Oh
-
Comment
| Open Access Metal 3D printing as a disruptive technology for superalloys
Metal 3D printing as a disruptive technology for superalloys
3D printing can allow for the efficient manufacturing of elaborate structures difficult to realise conventionally without waste, such as the hollow geometries of nickel-based superalloy aeronautic components. To fully exploit this method, we must move towards new alloys and processes.
- Chinnapat Panwisawas
- , Yuanbo T. Tang
- & Roger C. Reed
-
Article
| Open Access Machine-learning-revealed statistics of the particle-carbon/binder detachment in lithium-ion battery cathodes
Machine-learning-revealed statistics of the particle-carbon/binder detachment in lithium-ion battery cathodes
Developing understanding of degradation phenomena in nickel rich cathodes is under intense investigation. Here the authors use learning-assisted statistical analysis and experiment-informed mathematical modelling to resolve the microstructure of a Ni-rich NMC composite cathode.
- Zhisen Jiang
- , Jizhou Li
- & Yijin Liu
-
Article
| Open Access High temperature rise dominated cracking mechanisms in ultra-ductile and tough titanium alloy
High temperature rise dominated cracking mechanisms in ultra-ductile and tough titanium alloy
Specific titanium alloys combine transformation-induced plasticity and twinning-induced plasticity for improved work hardening. Here, the authors show that these alloys also have an ultra-large fracture resistance and an unexpected fracture mechanism via dynamic recrystallization and local melting in a deformation band.
- L. Choisez
- , L. Ding
- & P. J. Jacques
-
Article
| Open Access Origin of micro-scale heterogeneity in polymerisation of photo-activated resin composites
Origin of micro-scale heterogeneity in polymerisation of photo-activated resin composites
Resin-based-composites are widely used in industry and medicine but the influence of the filler particles on the reactive group conversion in photocurable resins is yet to be elucidated. Here the authors observe reduced local conversion and chemical bond strain in silica filler acrylate composite using synchrotron-based wide-field IR imaging.
- Slobodan Sirovica
- , Johanne H. Solheim
- & Owen Addison
-
Article
| Open Access Water-mediated crystallohydrate–polymer composite as a phase-change electrolyte
Water-mediated crystallohydrate–polymer composite as a phase-change electrolyte
Here the authors report composite electrolytes combining polymer chains and hydrated salts with a similar bonding structure to that of natural bones. The design breaks the trade-off between strength and ionic mobility of solid electrolytes and allows for good electrochemical performance in supercapacitors.
- Ziyang Tai
- , Junjie Wei
- & Qigang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Circumventing huge volume strain in alloy anodes of lithium batteries
Circumventing huge volume strain in alloy anodes of lithium batteries
Alloy anode materials in lithium batteries usually suffer from fatal structural degradation due to the large volume change during cycling. Here the authors report a design in which Al foil serves as both anode and current collector to circumvent the strain.
- Hongyi Li
- , Takitaro Yamaguchi
- & Tetsu Ichitsubo
-
Article
| Open Access A flexible topo-optical sensing technology with ultra-high contrast
A flexible topo-optical sensing technology with ultra-high contrast
Flexible materials with mechano-responsive luminescence has gained interest for their potential in sensing devices. Here, the authors demonstrate targeted folding under high compressive strains, which, together with the oxygen quenching of fluorophores, forms the basis for topo-optical sensing.
- Cong Wang
- , Ding Wang
- & Ben Bin Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Elastic conducting polymer composites in thermoelectric modules
Elastic conducting polymer composites in thermoelectric modules
Though deformable thermoelectric materials are desirable for integrating thermoelectric devices into wearable electronics, typical thermoelectric materials are too brittle for practical application. Here, the authors report a high-performance elastic composite for stretchable thermoelectric modules.
- Nara Kim
- , Samuel Lienemann
- & Klas Tybrandt
-
Article
| Open Access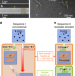 Transforming solid-state precipitates via excess vacancies
Transforming solid-state precipitates via excess vacancies
Exactly how seemingly simple solid-state precipitation occurs in alloys remains elusive. Here, the authors show that excess vacancies introduced into a nanoscale, irradiated or deformed aluminium-copper alloy enable template-directed nucleation of the known strengthening phase θʹ.
- Laure Bourgeois
- , Yong Zhang
- & Nikhil V. Medhekar
-
Article
| Open Access Simulating the mechanisms of serrated flow in interstitial alloys with atomic resolution over diffusive timescales
Simulating the mechanisms of serrated flow in interstitial alloys with atomic resolution over diffusive timescales
Understanding the plastic deformation mechanism within specific ranges of temperature and strain in metal alloys is of great technological importance. Here the authors report on dynamic simulations of dislocation–solute coevolution in tungsten crystals containing a few atomic parts per million of interstitial oxygen and their relation to unstable plastic flow.
- Yue Zhao
- , Lucile Dezerald
- & Jaime Marian
-
Article
| Open Access In situ atomic-scale observation of grain size and twin thickness effect limit in twin-structural nanocrystalline platinum
In situ atomic-scale observation of grain size and twin thickness effect limit in twin-structural nanocrystalline platinum
The deformation mechanisms of micron-sized twinned metals are well-understood, but it is not so for twinned nanocrystalline metals. Here, the authors use high resolution microscopy to image the deformation of nanocrystalline twinned platinum and show that grain boundary behaviors dominate plasticity below 6 nm.
- Lihua Wang
- , Kui Du
- & Xiaodong Han
-
Article
| Open Access Entropy and interfacial energy driven self-healable polymers
Entropy and interfacial energy driven self-healable polymers
Different self-healing materials were developed in the past but development of mechanically robust and affordable self-healing materials with high strain and stiffness is challenging. Here the authors develop mechanically robust thermoplastic polyurethane fibers and films capable of autonomous self-healing under ambient conditions.
- Chris C. Hornat
- & Marek W. Urban
-
Article
| Open Access Interpreting nanovoids in atom probe tomography data for accurate local compositional measurements
Interpreting nanovoids in atom probe tomography data for accurate local compositional measurements
Atom probe tomography can image chemical composition at the nanoscale, but our understanding of how it images voids, or empty spaces, is still lacking. Here, the authors combine atom probe tomography, scanning transmission electron microscopy, and field-evaporation theory to show how voids are imaged and subsequently measured.
- Xing Wang
- , Constantinos Hatzoglou
- & Jonathan D. Poplawsky
-
Article
| Open Access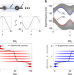 Robust temporal pumping in a magneto-mechanical topological insulator
Robust temporal pumping in a magneto-mechanical topological insulator
A robust time-controlled energy pumping in a classical metamaterial remains to be achieved. Here, Grinberg et al. demonstrate a temporal topological pump that produces on-demand, robust transport of mechanical energy using a one-dimensional magneto-mechanical metamaterial.
- Inbar Hotzen Grinberg
- , Mao Lin
- & Gaurav Bahl
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time observations of TRIP-induced ultrahigh strain hardening in a dual-phase CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy
Real-time observations of TRIP-induced ultrahigh strain hardening in a dual-phase CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy
In dual-phase Cantor-like high entropy alloys, how local chemistry affects enhanced deformation mechanisms remains unclear. Here, the authors image 3D stacking fault networks formation and show they both impede dislocations and facilitate phase transformations via local chemical composition variations.
- Sijing Chen
- , Hyun Seok Oh
- & Qian Yu

 Multi-scale characterisation of a ferroelectric polymer reveals the emergence of a morphological phase transition driven by temperature
Multi-scale characterisation of a ferroelectric polymer reveals the emergence of a morphological phase transition driven by temperature