Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Global urban expansion offsets climate-driven increases in terrestrial net primary productivity
Global urban expansion offsets climate-driven increases in terrestrial net primary productivity
Robust estimates of either urban expansion worldwide or the effects of such phenomenon on terrestrial net primary productivity (NPP) are lacking. Here the authors used the new dataset of global land use to show that the global urban areas expanded largely between 2000 and 2010, which in turn reduced terrestrial NPP globally.
- Xiaoping Liu
- , Fengsong Pei
- & Zhu Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Game theoretical inference of human behavior in social networks
Game theoretical inference of human behavior in social networks
Based on a strategic network formation model, the authors develop game-theoretical and statistical methods to infer individuals’ incentives in complex social networks, and validate their findings in real-world, historical data sets.
- Nicolò Pagan
- & Florian Dörfler
-
Article
| Open Access Human confidence judgments reflect reliability-based hierarchical integration of contextual information
Human confidence judgments reflect reliability-based hierarchical integration of contextual information
Because our immediate observations are often ambiguous, we must use the context (prior beliefs) to guide inference, but the context may also be uncertain. Here, the authors show that humans can accurately estimate the reliability of the context and combine it with sensory uncertainty to form their decisions and estimate confidence.
- Philipp Schustek
- , Alexandre Hyafil
- & Rubén Moreno-Bote
-
Article
| Open Access Early coauthorship with top scientists predicts success in academic careers
Early coauthorship with top scientists predicts success in academic careers
By examining publication records of scientists from four disciplines, the authors show that coauthoring a paper with a top-cited scientist early in one's career predicts lasting increases in career success, especially for researchers affiliated with less prestigious institutions.
- Weihua Li
- , Tomaso Aste
- & Giacomo Livan
-
Article
| Open Access Clustering knowledge and dispersing abilities enhances collective problem solving in a network
Clustering knowledge and dispersing abilities enhances collective problem solving in a network
Using agent-based models of a problem-solving task in a network, the authors show that clustering people of similar knowledge maintains solution diversity and increases long run system collective performance. Clustering those with similar abilities, however, lowers solution diversity and performance.
- Charles J. Gomez
- & David M. J. Lazer
-
Perspective
| Open Access Economic value of protected areas via visitor mental health
Economic value of protected areas via visitor mental health
Parks have a previously unquantified economic value attributable to mental health, a health services value. Here, the authors proposed three methods to estimate this, and applied one of these methods to show that this value is at least US$6 trillion per annum worldwide.
- Ralf Buckley
- , Paula Brough
- & Neil Harris
-
Article
| Open Access Illusory sound texture reveals multi-second statistical completion in auditory scene analysis
Illusory sound texture reveals multi-second statistical completion in auditory scene analysis
Auditory textures are sounds defined by a particular statistical distribution, e.g. as is produced by rain, or a swarm of insects. Here, the authors describe a striking perceptual illusion in which sound textures are heard to continue, even though they have in fact been replaced by white noise.
- Richard McWalter
- & Josh H. McDermott
-
Article
| Open Access Acute hunger does not always undermine prosociality
Acute hunger does not always undermine prosociality
Previous studies have suggested that being hungry causes people to make more selfish and less prosocial decisions. Here, the authors carried out a series of studies to test this claim and found that the effect of acute hunger was very weak at best.
- Jan A. Häusser
- , Christina Stahlecker
- & Nadira S. Faber
-
Comment
| Open Access Motivating actions to mitigate plastic pollution
Motivating actions to mitigate plastic pollution
Plastic pollution is a purely anthropogenic problem and cannot be solved without large-scale human action. Motivating mitigation actions requires more realistic assumptions about human decision-making based on empirical evidence from the behavioural sciences enabling the design of more effective interventions.
- Lili Jia
- , Steve Evans
- & Sander van der Linden
-
Article
| Open Access Early-career setback and future career impact
Early-career setback and future career impact
Little is known about the long-term effects of early-career setback. Here, the authors compare junior scientists who were awarded a NIH grant to those with similar track records, who were not, and find that individuals with the early setback systematically performed better in the longer term.
- Yang Wang
- , Benjamin F. Jones
- & Dashun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Ideological differences in the expanse of the moral circle
Ideological differences in the expanse of the moral circle
How do liberals and conservatives differ in their expression of compassion and moral concern? The authors show that conservatives tend to express concern toward smaller, more well-defined, and less permeable social circles, while liberals express concern toward larger, less well-defined, and more permeable social circles.
- Adam Waytz
- , Ravi Iyer
- & Jesse Graham
-
Article
| Open Access A Bayesian psychophysics model of sense of agency
A Bayesian psychophysics model of sense of agency
Sense of agency (SoA) refers to the experience that one's own actions caused an external event. Here, the authors present a model of SoA in terms of optimal Bayesian cue integration taking into account reliability of action and outcome sensory signals and judging if the action caused the outcome.
- Roberto Legaspi
- & Taro Toyoizumi
-
Article
| Open Access Examining charitable giving in real-world online donations
Examining charitable giving in real-world online donations
Questions related to human altruism are often studied through self-reported behavior or by measuring behavior in laboratory experiments. Here, the authors examine real-world prosocial behavior using charitable donations made online.
- Matthew R. Sisco
- & Elke U. Weber
-
Article
| Open Access Females show more sustained performance during test-taking than males
Females show more sustained performance during test-taking than males
Females tend to perform poorer than males on math and science tests, but better on verbal reading tests. Here, by analysing performance during a cognitive test, the authors provide evidence that females are better able to sustain their performance during a test across all of these topics.
- Pau Balart
- & Matthijs Oosterveen
-
Article
| Open Access Bounded rationality in C. elegans is explained by circuit-specific normalization in chemosensory pathways
Bounded rationality in C. elegans is explained by circuit-specific normalization in chemosensory pathways
Innate odor preferences in C. elegans are controlled by the activation of a pair of olfactory sensory neurons. Here, the authors show that asymmetric activation of the AWCON and AWCOFF neurons can lead to irrational olfactory preferences that are explained by a model of normalization of sensory gain control.
- Dror Cohen
- , Guy Teichman
- & Oded Rechavi
-
Article
| Open Access Discrepancy in scientific authority and media visibility of climate change scientists and contrarians
Discrepancy in scientific authority and media visibility of climate change scientists and contrarians
The role of climate change (CC) contrarians is neglected in climate change communication studies. Here the authors used a data-driven approach to identify CC contrarians and CC scientists and found that CC scientists have much higher citation impact than those for contrarians but lower media visibility.
- Alexander Michael Petersen
- , Emmanuel M. Vincent
- & Anthony LeRoy Westerling
-
Article
| Open Access Novel data show expert wildlife agencies are important to endangered species protection
Novel data show expert wildlife agencies are important to endangered species protection
The U.S. Endangered Species Act (ESA) requires that federal agencies consult with the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS) or National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS) to ensure federal actions do not jeopardize the existence of listed species. Here, the authors analyze recorded from 2000–2017 and investigate the role of NMFS in the consultations.
- Michael J. Evans
- , Jacob W. Malcom
- & Ya-Wei Li
-
Article
| Open Access Estimating the success of re-identifications in incomplete datasets using generative models
Estimating the success of re-identifications in incomplete datasets using generative models
Anonymization has been the main means of addressing privacy concerns in sharing medical and socio-demographic data. Here, the authors estimate the likelihood that a specific person can be re-identified in heavily incomplete datasets, casting doubt on the adequacy of current anonymization practices.
- Luc Rocher
- , Julien M. Hendrickx
- & Yves-Alexandre de Montjoye
-
Article
| Open Access Mendelian randomisation analysis of the effect of educational attainment and cognitive ability on smoking behaviour
Mendelian randomisation analysis of the effect of educational attainment and cognitive ability on smoking behaviour
Higher educational attainment is positively associated with a number of health outcomes. Here, Sanderson et al. use multivariable Mendelian randomisation analysis to test whether the association of educational attainment with smoking behaviour is direct or indirectly mediated via general cognitive ability.
- Eleanor Sanderson
- , George Davey Smith
- & Marcus R. Munafò
-
Article
| Open Access Structural balance emerges and explains performance in risky decision-making
Structural balance emerges and explains performance in risky decision-making
How do socially polarized systems change and how does a change in polarization relate to performance? Using instant messaging data and performance records from day traders, the authors find that certain relations are prone to balance and that balance is associated with better trading decisions.
- Omid Askarisichani
- , Jacqueline Ng Lane
- & Brian Uzzi
-
Article
| Open Access Facial recognition from DNA using face-to-DNA classifiers
Facial recognition from DNA using face-to-DNA classifiers
Prediction of face from DNA followed by matching to facial images has been proposed for forensic applications. Here, Sero et al. present a different approach that can establish facial identity from DNA without directly predicting the face but is based on classifying given faces by individual DNA-encoded traits.
- Dzemila Sero
- , Arslan Zaidi
- & Peter Claes
-
Article
| Open Access Introducing risk inequality metrics in tuberculosis policy development
Introducing risk inequality metrics in tuberculosis policy development
Failure to account for heterogeneity in TB risk can mislead model-based evaluation of proposed interventions. Here, the authors introduce a metric to estimate the distribution of risk in populations from routinely collected data and find that variation in infection acquisition is the most impactful.
- M. Gabriela M. Gomes
- , Juliane F. Oliveira
- & Christian Lienhardt
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying and predicting success in show business
Quantifying and predicting success in show business
For most actors sustained productivity defines success. Here the authors study the careers of actors and identify a "rich-get-richer" mechanism with respect to productivity, the emergence of hot streaks and the presence of gender bias, and are able to predict whether the most productive year of an actor is yet to come.
- Oliver E. Williams
- , Lucas Lacasa
- & Vito Latora
-
Article
| Open Access Uncovering the structure of self-regulation through data-driven ontology discovery
Uncovering the structure of self-regulation through data-driven ontology discovery
Scientific progress relies on integrating and building on existing knowledge. Here, the authors propose improving cumulative science by developing data-driven ontologies, and they apply this approach to understanding the construct of self-regulation.
- Ian W. Eisenberg
- , Patrick G. Bissett
- & Russell A. Poldrack
-
Article
| Open Access The ecological drivers of variation in global language diversity
The ecological drivers of variation in global language diversity
Could similar ecological and biogeographic drivers explain the distributions of biological diversity and human cultural diversity? The authors explore ecological correlates of human language diversity, finding strong support for a role of high year-round productivity but less support for landscape features.
- Xia Hua
- , Simon J. Greenhill
- & Lindell Bromham
-
Article
| Open Access Decoding individual differences in STEM learning from functional MRI data
Decoding individual differences in STEM learning from functional MRI data
People differ in their current levels of understanding of many complex concepts. Here, the authors show using fMRI that brain activity during a task that requires concept knowledge can be used to compute a ‘neural score’ of the participant’s understanding.
- Joshua S. Cetron
- , Andrew C. Connolly
- & David J. M. Kraemer
-
Article
| Open Access Optimizing the conservation of migratory species over their full annual cycle
Optimizing the conservation of migratory species over their full annual cycle
Conservation decisions to protect land used by migratory birds rely on understanding species’ dynamic habitat associations. Here the authors identify conservation scenarios needed to maintain >30% of the abundances of 117 migratory birds across the Americas, considering spatial and temporal patterns of species abundance.
- Richard Schuster
- , Scott Wilson
- & Joseph. R. Bennett
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerating dynamics of collective attention
Accelerating dynamics of collective attention
The impacts of technological development on social sphere lack strong empirical foundation. Here the authors presented quantitative analysis of the phenomenon of social acceleration across a range of digital datasets and found that interest appears in bursts that dissipate on decreasing timescales and occur with increasing frequency.
- Philipp Lorenz-Spreen
- , Bjarke Mørch Mønsted
- & Sune Lehmann
-
Article
| Open Access Urbanity and the dynamics of language shift in Galicia
Urbanity and the dynamics of language shift in Galicia
In areas with two or more spoken languages, linguistic shift may occur as speakers of one language switch to the other. Here, the authors show that linguistic shift is faster in rural compared to urban regions of Galicia, a bilingual community in Spain, due to the competition of internal complexity and network relevance.
- Mariamo Mussa Juane
- , Luis F. Seoane
- & Jorge Mira
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying economic resilience from input–output susceptibility to improve predictions of economic growth and recovery
Quantifying economic resilience from input–output susceptibility to improve predictions of economic growth and recovery
Supply demand equilibria in modern macroeconomic theories do not hold during recessionary shocks. Here the authors developed a non-equilibrium theory for the susceptibility of industrial sectors to shocks and showed these susceptibilities vary across countries, sectors and time and full economic recovery may take six to ten years.
- Peter Klimek
- , Sebastian Poledna
- & Stefan Thurner
-
Article
| Open Access The carbon footprint of the U.S. multinationals’ foreign affiliates
The carbon footprint of the U.S. multinationals’ foreign affiliates
Multinational enterprises (MNE) play a key role in climate mitigation as the significance of the environmental impacts of MNE. Here the authors measured the carbon footprint of U.S. MNE affiliates throughout their global value chains and show their carbon footprint beyond borders at 0.5082 GtCO2 in 2009.
- Luis-Antonio López
- , María-Ángeles Cadarso
- & Guadalupe Arce
-
Article
| Open Access The fishery performance indicators for global tuna fisheries
The fishery performance indicators for global tuna fisheries
Building an economically healthy fishing industry that supports participating communities is challenging and requires consistent performance measures. Here the authors compare the performance of world’s major tuna fisheries and find large differences, primarily in post-harvest sector benefits.
- Jessica K. McCluney
- , Christopher M. Anderson
- & James L. Anderson
-
Article
| Open Access Bridge ties bind collective memories
Bridge ties bind collective memories
Social groups form collective memories, but the temporal dynamics of this process are unclear. Here, the authors show that when early conversations involve individuals that bridge across clusters of a social network, the network reaches higher mnemonic convergence compared to when early conversations occur within clusters.
- Ida Momennejad
- , Ajua Duker
- & Alin Coman
-
Article
| Open Access The neural computation of inconsistent choice behavior
The neural computation of inconsistent choice behavior
Humans are often inconsistent when choosing between alternatives, but the neural basis of deviations from economic rationality is unclear. Here, the authors show that irrational choices arise in the same brain regions responsible for value computation, implying that brain ‘noise’ may underlie inconsistency.
- Vered Kurtz-David
- , Dotan Persitz
- & Dino J. Levy
-
Article
| Open Access The computational and neural substrates of moral strategies in social decision-making
The computational and neural substrates of moral strategies in social decision-making
The authors show that individuals apply different ‘moral strategies’ in interpersonal decision-making. These strategies are linked to distinct patterns of neural activity, even when they produce the same choice outcomes, illuminating how distinct moral principles can guide social behavior.
- Jeroen M. van Baar
- , Luke J. Chang
- & Alan G. Sanfey
-
Article
| Open Access Trans-provincial health impacts of atmospheric mercury emissions in China
Trans-provincial health impacts of atmospheric mercury emissions in China
Mercury (Hg) is a global neurotoxic pollutant and has a long chain from economic activities to human health risks. Here the authors presented a map of Hg-related health risks in China and found significant impacts of interprovincial trade on health risks, such as the prevention of deaths from fatal heart attacks by the trade induced by final consumption.
- Long Chen
- , Sai Liang
- & Zhifeng Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Inferring HIV-1 transmission networks and sources of epidemic spread in Africa with deep-sequence phylogenetic analysis
Inferring HIV-1 transmission networks and sources of epidemic spread in Africa with deep-sequence phylogenetic analysis
Here, Ratmann et al. show how viral deep sequencing data can be used to reconstruct HIV-1 transmission networks and to infer the direction of transmission in these networks.
- Oliver Ratmann
- , M. Kate Grabowski
- & Jennifer Wagman
-
Article
| Open Access Assessing the Policy gaps for achieving China’s climate targets in the Paris Agreement
Assessing the Policy gaps for achieving China’s climate targets in the Paris Agreement
The extent to which China’s existing and forthcoming policies would lead to emission reductions domestically has not been well understood. Here the authors combined expert elicitation and a system dynamic model and showed that China is on track to peak its emissions well in advance of 2030.
- Kelly Sims Gallagher
- , Fang Zhang
- & Qiang Liu
-
Review Article
| Open Access Advancing environmental exposure assessment science to benefit society
Advancing environmental exposure assessment science to benefit society
How can scientists and policymakers work together to reduce the health impacts of air pollution? In this review paper, the authors discuss the interplay between advances in environmental exposure assessment and policy advances to tackle pollution in a focused way.
- Andrew Caplin
- , Masoud Ghandehari
- & George Thurston
-
Comment
| Open Access The sharing economy promotes sustainable societies
The sharing economy promotes sustainable societies
Sharing activities are under wide debate regarding the environmental impacts. Here the authors reviewed their benefits and problems and suggested that a simultaneous improvement of both ecological and economic efficiency is necessary to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Zhifu Mi
- & D’Maris Coffman
-
Article
| Open Access Social networks and risk of delayed hospital arrival after acute stroke
Social networks and risk of delayed hospital arrival after acute stroke
Rapid arrival to hospital after stroke is critical for patients to receive effective treatment. Here, the authors examine how stroke patients’ social network structure relates to stroke arrival time, and show that small and close-knit personal networks predict delayed arrival.
- Amar Dhand
- , Douglas Luke
- & Jin-Moo Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Forming global estimates of self-performance from local confidence
Forming global estimates of self-performance from local confidence
Human confidence tracks current performance, but little is known about the formation of ‘global’ self-performance estimates over longer timescales. Here, the authors show that people use local confidence to form global estimates, but tend to underestimate their performance when feedback is absent.
- Marion Rouault
- , Peter Dayan
- & Stephen M. Fleming
-
Article
| Open Access How long do floods throughout the millennium remain in the collective memory?
How long do floods throughout the millennium remain in the collective memory?
Concept of learning from history assumes that information is handed between generations to avoid negative effect of hazards. Here the authors analysed human behaviour and decision making on post-flood settlements and showed flood memory faded away in two generations, which is insufficient to protect human settlements from rare catastrophic floods.
- Václav Fanta
- , Miroslav Šálek
- & Petr Sklenicka
-
Article
| Open Access Resource sharing in technologically defined social networks
Resource sharing in technologically defined social networks
Resource sharing over peer-to-peer technological networks is emerging as economically important, yet little is known about how people choose to share in this context. Here, the authors introduce a new game to model sharing, and test how players form sharing strategies depending on technological constraints.
- Hirokazu Shirado
- , George Iosifidis
- & Nicholas A. Christakis
-
Article
| Open Access The importance of cognitive diversity for sustaining the commons
The importance of cognitive diversity for sustaining the commons
Social intelligence and general intelligence are two distinct cognitive abilities. Here, the authors show that groups of people with high competency in both social and general intelligence perform better in a resource-management task involving cooperation, and adjustment to unexpected ecological change.
- Jacopo A. Baggio
- , Jacob Freeman
- & David Pillow
-
Article
| Open Access Extortion strategies resist disciplining when higher competitiveness is rewarded with extra gain
Extortion strategies resist disciplining when higher competitiveness is rewarded with extra gain
In game theory, ‘extortionate’ tactics in two-player games are predicted to give way to ‘generous’ strategies. Here, the authors show in a human experimental sample that extortion can prevail as a strategy in games in which there is a specific reward for doing better than the other player.
- Lutz Becks
- & Manfred Milinski
-
Article
| Open Access The rise and fall of cooperation through reputation and group polarization
The rise and fall of cooperation through reputation and group polarization
Group membership can inform individuals’ decisions on whether to cooperate. Here, the authors show how cooperative groups themselves can emerge and change due to use of reputation heuristics (such as “the enemy of a friend is an enemy”), and how this destabilizes cooperation over time.
- Jörg Gross
- & Carsten K. W. De Dreu
-
Article
| Open Access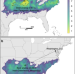 Contemporary climatic analogs for 540 North American urban areas in the late 21st century
Contemporary climatic analogs for 540 North American urban areas in the late 21st century
It is challenging to communicate abstract future climate estimates. Here the authors utilized climate-analog mapping and they identified that North American urban areas’ climate by the 2080’s will become similar to the contemporary climate of locations hundreds of kilometers away and mainly to the south, while many urban areas will have no modern equivalent analogs under the RCP8.5 scenario.
- Matthew C. Fitzpatrick
- & Robert R. Dunn
-
Article
| Open Access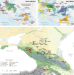 Ancient human genome-wide data from a 3000-year interval in the Caucasus corresponds with eco-geographic regions
Ancient human genome-wide data from a 3000-year interval in the Caucasus corresponds with eco-geographic regions
The Caucasus mountain range has impacted on the culture and genetics of the wider region. Here, the authors generate genome-wide SNP data for 45 Eneolithic and Bronze Age individuals across the Caucasus, and find distinct genetic clusters between mountain and steppe zones as well as occasional gene-flow.
- Chuan-Chao Wang
- , Sabine Reinhold
- & Wolfgang Haak

 The visual word form area (VWFA) is part of both language and attention circuitry
The visual word form area (VWFA) is part of both language and attention circuitry