Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Probing single electrons across 300-mm spin qubit wafers
Probing single electrons across 300-mm spin qubit wafers
Using a cryogenic 300-mm wafer prober, a new approach for the testing of hundreds of industry-manufactured spin qubit devices at 1.6 K provides high-volume data on performance, allowing optimization of the complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS)-compatible fabrication process.
- Samuel Neyens
- , Otto K. Zietz
- & James S. Clarke
-
Article
| Open Access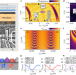 High-fidelity spin qubit operation and algorithmic initialization above 1 K
High-fidelity spin qubit operation and algorithmic initialization above 1 K
Initialization and operation of spin qubits in silicon above 1 K reach fidelities sufficient for fault-tolerant operations at these temperatures.
- Jonathan Y. Huang
- , Rocky Y. Su
- & Chih Hwan Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Single-photon superradiance in individual caesium lead halide quantum dots
Single-photon superradiance in individual caesium lead halide quantum dots
Excitonic single-photon superradiance is reported in individual perovskite quantum dots with a sub-100 ps radiative decay time, almost as short as the reported exciton coherence time.
- Chenglian Zhu
- , Simon C. Boehme
- & Gabriele Rainò
-
Article
| Open Access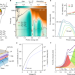 Electrically driven amplified spontaneous emission from colloidal quantum dots
Electrically driven amplified spontaneous emission from colloidal quantum dots
Colloidal quantum dot devices demonstrating electrically pumped amplified spontaneous emission are described, showing strong, broadband optical gain and bright edge emission, opening the path to solution-processable laser diodes.
- Namyoung Ahn
- , Clément Livache
- & Victor I. Klimov
-
Article |
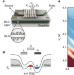 Particle–hole symmetry protects spin-valley blockade in graphene quantum dots
Particle–hole symmetry protects spin-valley blockade in graphene quantum dots
Bilayer graphene allows the realization of electron–hole double-quantum dots that exhibit near-perfect particle–hole symmetry, in which transport occurs via the creation and annihilation of single electron–hole pairs with opposite quantum numbers.
- L. Banszerus
- , S. Möller
- & C. Stampfer
-
Article |
 Realization of a minimal Kitaev chain in coupled quantum dots
Realization of a minimal Kitaev chain in coupled quantum dots
A minimal artificial Kitaev chain can be realized by using two spin-polarized quantum dots in an InSb nanowire strongly coupled by both elastic co-tunnelling and crossed Andreev reflection.
- Tom Dvir
- , Guanzhong Wang
- & Leo P. Kouwenhoven
-
Article |
 Synthesis-on-substrate of quantum dot solids
Synthesis-on-substrate of quantum dot solids
Ultrasmall monodisperse perovskite quantum dots are synthesized in situ on a substrate via ligand structure regulation, yielding the highest external quantum efficiency blue perovskite LEDs reported so far.
- Yuanzhi Jiang
- , Changjiu Sun
- & Mingjian Yuan
-
Article |
 Singlet and triplet Cooper pair splitting in hybrid superconducting nanowires
Singlet and triplet Cooper pair splitting in hybrid superconducting nanowires
Controllable detection of singlet and triplet Cooper pair splitting via crossed Andreev reflection is demonstrated in spin-polarized quantum dots on a superconducting nanowire platform with strong spin–orbit coupling.
- Guanzhong Wang
- , Tom Dvir
- & Leo P. Kouwenhoven
-
Article |
 Spin cross-correlation experiments in an electron entangler
Spin cross-correlation experiments in an electron entangler
Spin correlation experiments are demonstrated in an electron entangler device based on the ‘splitting’ of Cooper pairs from a superconductor, which can potentially be used to investigate many fundamental phases and processes related to the electron spin.
- Arunav Bordoloi
- , Valentina Zannier
- & Andreas Baumgartner
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum error correction with silicon spin qubits
Quantum error correction with silicon spin qubits
By using three silicon spin qubits to construct a phase-correcting code, quantum error correction is implemented and protection of the three-qubit state against any phase-flip error on one of the three qubits is demonstrated.
- Kenta Takeda
- , Akito Noiri
- & Seigo Tarucha
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering topological states in atom-based semiconductor quantum dots
Engineering topological states in atom-based semiconductor quantum dots
Precision-engineered devices consisting of a linear array of ten quantum dots are used to realize both the trivial and topological phases of the many-body Su–Schrieffer–Heeger model.
- M. Kiczynski
- , S. K. Gorman
- & M. Y. Simmons
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale imaging of phonon dynamics by electron microscopy
Nanoscale imaging of phonon dynamics by electron microscopy
A method for mapping phonon momenta reveals non-equilibrium phonon dynamics at nanoscale interfaces enabling study of actual nanodevices and aiding understanding of heat dissipation near nanoscale hotspots.
- Chaitanya A. Gadre
- , Xingxu Yan
- & Xiaoqing Pan
-
Article |
 Fast universal quantum gate above the fault-tolerance threshold in silicon
Fast universal quantum gate above the fault-tolerance threshold in silicon
Single- and two-qubit gate fidelities above the fault-tolerance threshold for quantum computation are demonstrated in silicon quantum dots by fast electrical control using a micromagnet-induced gradient field and tunable coupling.
- Akito Noiri
- , Kenta Takeda
- & Seigo Tarucha
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum logic with spin qubits crossing the surface code threshold
Quantum logic with spin qubits crossing the surface code threshold
A spin-based quantum processor in silicon achieves single-qubit and two-qubit gate fidelities above 99.5% using gate-set tomography, exceeding the theoretical threshold required for fault-tolerant quantum computing.
- Xiao Xue
- , Maximilian Russ
- & Lieven M. K. Vandersypen
-
-
Article |
 Perovskite-type superlattices from lead halide perovskite nanocubes
Perovskite-type superlattices from lead halide perovskite nanocubes
Through precise structural engineering, perovskite nanocrystals are co-assembled with other nanocrystal materials to form a range of binary and ternary perovskite-type superlattices that exhibit superfluorescence.
- Ihor Cherniukh
- , Gabriele Rainò
- & Maksym V. Kovalenko
-
Article |
 A four-qubit germanium quantum processor
A four-qubit germanium quantum processor
Using germanium quantum dots, a four-qubit processor capable of single-, two-, three-, and four-qubit gates, demonstrated by the creation of four-qubit Greenberger−Horne−Zeilinger states, is the largest yet realized with solid-state electron spins.
- Nico W. Hendrickx
- , William I. L. Lawrie
- & Menno Veldhorst
-
Article |
 Van der Waals heterostructure polaritons with moiré-induced nonlinearity
Van der Waals heterostructure polaritons with moiré-induced nonlinearity
Polaritons formed by moiré excitons in heterobilayers of transition metal dichalcogenides exhibit strong nonlinearity owing to quantum confinement by the tunable moiré lattice potential.
- Long Zhang
- , Fengcheng Wu
- & Hui Deng
-
Article |
 Ligand-engineered bandgap stability in mixed-halide perovskite LEDs
Ligand-engineered bandgap stability in mixed-halide perovskite LEDs
The binding of multidentate ligands to the surface of lead halide perovskite nanocrystals suppresses the formation of surface defects that result in halide segregation, yielding materials with efficient and colour-stable red emission.
- Yasser Hassan
- , Jong Hyun Park
- & Henry J. Snaith
-
Article |
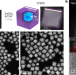 Efficient and stable blue quantum dot light-emitting diode
Efficient and stable blue quantum dot light-emitting diode
Cadmium-free blue quantum dot light-emitting diodes are constructed with a quantum yield of unity, an efficiency at the theoretical limit, high brightness and long operational lifetime.
- Taehyung Kim
- , Kwang-Hee Kim
- & Eunjoo Jang
-
Article |
 Universal quantum logic in hot silicon qubits
Universal quantum logic in hot silicon qubits
Lithographically defined qubits are shown to support full two-qubit logic at temperatures above one kelvin by using electron spin states in silicon quantum dots.
- L. Petit
- , H. G. J. Eenink
- & M. Veldhorst
-
Article |
 Operation of a silicon quantum processor unit cell above one kelvin
Operation of a silicon quantum processor unit cell above one kelvin
A scalable silicon quantum processor unit cell made of two qubits confined to quantum dots operates at about 1.5 K, achieving 98.6% single-qubit gate fidelities and a 2 μs coherence time.
- C. H. Yang
- , R. C. C. Leon
- & A. S. Dzurak
-
Article |
 Fast two-qubit logic with holes in germanium
Fast two-qubit logic with holes in germanium
Spin qubits based on hole states in strained germanium could offer the most scalable platform for quantum computation.
- N. W. Hendrickx
- , D. P. Franke
- & M. Veldhorst
-
Article |
 Highly efficient and stable InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dot light-emitting diodes
Highly efficient and stable InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dot light-emitting diodes
A method of engineering efficient and stable InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dot light-emitting diodes (QD-LEDs) has improved their performance to the level of state-of-the-art cadmium-containing QD-LEDs, removing the problem of the toxicity of cadmium in large-panel displays.
- Yu-Ho Won
- , Oul Cho
- & Eunjoo Jang
-
Article |
 A gated quantum dot strongly coupled to an optical microcavity
A gated quantum dot strongly coupled to an optical microcavity
Strong coupling between a gated semiconductor quantum dot and an optical microcavity is observed in an ultralow-loss frequency-tunable microcavity device.
- Daniel Najer
- , Immo Söllner
- & Richard J. Warburton
-
Letter |
 Coherent spin-state transfer via Heisenberg exchange
Coherent spin-state transfer via Heisenberg exchange
Transmission of single-spin and entangled quantum states without the physical displacement of electrons is demonstrated in a quadruple quantum dot array using the Heisenberg exchange interaction and coherent SWAP gates.
- Yadav P. Kandel
- , Haifeng Qiao
- & John M. Nichol
-
Letter |
 A two-qubit gate between phosphorus donor electrons in silicon
A two-qubit gate between phosphorus donor electrons in silicon
A fast, high-fidelity two-qubit exchange gate between phosphorus donor electron spin qubits in silicon is demonstrated by creating a tunable exchange interaction between two electrons bound to phosphorus atom qubits.
- Y. He
- , S. K. Gorman
- & M. Y. Simmons
-
Letter |
 Fidelity benchmarks for two-qubit gates in silicon
Fidelity benchmarks for two-qubit gates in silicon
Two-qubit logic gates in a silicon-based system are shown (using randomized benchmarking) to have high gate fidelities of operation and are used to generate Bell states, a step towards solid-state quantum computation.
- W. Huang
- , C. H. Yang
- & A. S. Dzurak
-
Letter |
 Superfluorescence from lead halide perovskite quantum dot superlattices
Superfluorescence from lead halide perovskite quantum dot superlattices
Cooperative quantum effects in superlattices of quantum dots made of caesium lead halide perovskite give rise to superfluorescence, with the individual emitters interacting coherently to give intense bursts of light.
- Gabriele Rainò
- , Michael A. Becker
- & Thilo Stöferle
-
Letter |
 Superstructures generated from truncated tetrahedral quantum dots
Superstructures generated from truncated tetrahedral quantum dots
Truncated tetrahedral nanocrystals can self-assemble into one-, two- and three-dimensional superstructures.
- Yasutaka Nagaoka
- , Rui Tan
- & Ou Chen
-
Letter |
 All-inorganic perovskite nanocrystal scintillators
All-inorganic perovskite nanocrystal scintillators
All-inorganic perovskite nanocrystals containing caesium and lead provide low-cost, flexible and solution-processable scintillators that are highly sensitive to X-ray irradiation and emit radioluminescence that is colour-tunable across the visible spectrum.
- Qiushui Chen
- , Jing Wu
- & Xiaogang Liu
-
Letter |
 A programmable two-qubit quantum processor in silicon
A programmable two-qubit quantum processor in silicon
A two-qubit quantum processor in a silicon device is demonstrated, which can perform the Deutsch–Josza algorithm and the Grover search algorithm.
- T. F. Watson
- , S. G. J. Philips
- & L. M. K. Vandersypen
-
Letter |
 Bright triplet excitons in caesium lead halide perovskites
Bright triplet excitons in caesium lead halide perovskites
The lowest-energy exciton state in caesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals is shown to be a bright triplet state, contrary to expectations that lowest-energy excitons should always be dark.
- Michael A. Becker
- , Roman Vaxenburg
- & Alexander L. Efros
-
Letter |
 Continuous-wave lasing in colloidal quantum dot solids enabled by facet-selective epitaxy
Continuous-wave lasing in colloidal quantum dot solids enabled by facet-selective epitaxy
By switching shell growth on and off on the (0001) facet of wurtzite CdSe cores to produce a built-in biaxial strain that lowers the optical gain threshold, we achieve continuous-wave lasing in colloidal quantum dot films.
- Fengjia Fan
- , Oleksandr Voznyy
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Letter |
 Universal Fermi liquid crossover and quantum criticality in a mesoscopic system
Universal Fermi liquid crossover and quantum criticality in a mesoscopic system
Zero-temperature quantum phase transitions and their associated quantum critical points are believed to underpin the exotic finite-temperature behaviours of many strongly correlated electronic systems, but identifying the microscopic origins of these transitions can be challenging and controversial; Keller et al. (see also the related paper by Iftikhar et al.) show how such behaviours can be engineered into nanoelectronic quantum dots, which permit both precise experimental control of the quantum critical behaviour and its exact theoretical characterization.
- A. J. Keller
- , L. Peeters
- & D. Goldhaber-Gordon
-
Letter |
 Two-channel Kondo effect and renormalization flow with macroscopic quantum charge states
Two-channel Kondo effect and renormalization flow with macroscopic quantum charge states
Zero-temperature quantum phase transitions and their associated quantum critical points are believed to underpin the exotic finite-temperature behaviours of many strongly correlated electronic systems, but identifying the microscopic origins of these transitions can be challenging and controversial; Iftikhar et al. (see also the related paper by Keller et al.) show how such behaviours can be engineered into nanoelectronic quantum dots, which permit both precise experimental control of the quantum critical behaviour and its exact theoretical characterization.
- Z. Iftikhar
- , S. Jezouin
- & F. Pierre
-
Letter |
 A two-qubit logic gate in silicon
A two-qubit logic gate in silicon
A high-fidelity two-qubit CNOT logic gate is presented, which is realized by combining single- and two-qubit operations with controlled phase operations in a quantum dot system using the exchange interaction.
- M. Veldhorst
- , C. H. Yang
- & A. S. Dzurak
-
Letter |
 Quantum-dot-in-perovskite solids
Quantum-dot-in-perovskite solids
Organohalide perovskites and preformed colloidal quantum dots are combined in the solution phase to produce epitaxially aligned ‘dots-in-a-matrix’ crystals that have both the excellent electrical transport properties of the perovskite matrix and the high radiative efficiency of the quantum dots.
- Zhijun Ning
- , Xiwen Gong
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Letter |
 A colloidal quantum dot spectrometer
A colloidal quantum dot spectrometer
An efficient, cost effective microspectrometer that consists of a two-dimensional absorptive filter array of 195 different colloidal quantum dots is presented, and its performance demonstrated by measuring shifts in spectral peak positions as small as one nanometre.
- Jie Bao
- & Moungi G. Bawendi
-
Letter |
 Solution-processed, high-performance light-emitting diodes based on quantum dots
Solution-processed, high-performance light-emitting diodes based on quantum dots
The insertion of an insulating layer into a multilayer light-emitting diode (LED) based on quantum dots and produced by depositing the layers from solution increases the performance of the LEDs to levels comparable to those of state-of-the-art organic LEDs produced by vacuum deposition, while retaining the advantages of solution processing.
- Xingliang Dai
- , Zhenxing Zhang
- & Xiaogang Peng
-
Letter |
 Stabilizing the magnetic moment of single holmium atoms by symmetry
Stabilizing the magnetic moment of single holmium atoms by symmetry
Single magnetic atoms on non-magnetic surfaces have magnetic moments that are usually destabilized within a microsecond, too speedily to be useful, but here the magnetic moments of single holmium atoms on a highly conductive metallic substrate can reach lifetimes of the order of minutes.
- Toshio Miyamachi
- , Tobias Schuh
- & Wulf Wulfhekel
-
News & Views |
Putting a spin on photon entanglement
Entanglement between a photon and a stationary particle is a key resource for quantum communication. The effect has now been observed for a photon and a single electron spin in a semiconductor nanostructure. See Letters p.421 & p.426
- Sophia E. Economou
-
Letter |
 Observation of entanglement between a quantum dot spin and a single photon
Observation of entanglement between a quantum dot spin and a single photon
Fast, single-photon detection enables the observation of entanglement between a stationary quantum bit (a single quantum dot spin) and a propagating quantum bit (a single photon), marking a first step towards the implementation of a quantum network with nodes consisting of semiconductor spin quantum bits.
- W. B. Gao
- , P. Fallahi
- & A. Imamoglu
-
Letter |
 Quantum-dot spin–photon entanglement via frequency downconversion to telecom wavelength
Quantum-dot spin–photon entanglement via frequency downconversion to telecom wavelength
Entanglement of the spin of an electron in a semiconductor quantum dot with a single photon is reported, and verified by means of time-resolved frequency downconversion to a telecommunications wavelength; this process is an essential requirement for future quantum networks.
- Kristiaan De Greve
- , Leo Yu
- & Yoshihisa Yamamoto
-
Letter |
 Coherent singlet-triplet oscillations in a silicon-based double quantum dot
Coherent singlet-triplet oscillations in a silicon-based double quantum dot
Exploiting the weak interactions between electron spins and nuclear spins in silicon-based quantum dots leads to a dephasing time two orders of magnitude greater than in analogous gallium-arsenide-based devices, demonstrating the potential of silicon as a host material for quantum information processing.
- B. M. Maune
- , M. G. Borselli
- & A. T. Hunter
-
Letter |
 Two types of luminescence blinking revealed by spectroelectrochemistry of single quantum dots
Two types of luminescence blinking revealed by spectroelectrochemistry of single quantum dots
- Christophe Galland
- , Yagnaseni Ghosh
- & Han Htoon
-
Letter |
 On-demand single-electron transfer between distant quantum dots
On-demand single-electron transfer between distant quantum dots
- R. P. G. McNeil
- , M. Kataoka
- & D. A. Ritchie
-
Letter |
 Electrons surfing on a sound wave as a platform for quantum optics with flying electrons
Electrons surfing on a sound wave as a platform for quantum optics with flying electrons
- Sylvain Hermelin
- , Shintaro Takada
- & Tristan Meunier
-
Letter |
 Quantum quench of Kondo correlations in optical absorption
Quantum quench of Kondo correlations in optical absorption
- C. Latta
- , F. Haupt
- & A. Imamoglu

 Long-range order enabled stability in quantum dot light-emitting diodes
Long-range order enabled stability in quantum dot light-emitting diodes Perovskite decomposition and missing crystal planes in HRTEM
Perovskite decomposition and missing crystal planes in HRTEM