Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Resolving the cause of recurrent Plasmodium vivax malaria probabilistically
Resolving the cause of recurrent Plasmodium vivax malaria probabilistically
Relapse, reinfection and recrudescence can all cause recurrent infection after treatment of Plasmodium vivax malaria in endemic areas, but are difficult to distinguish. Here the authors show that they can be differentiated probabilistically and thereby demonstrate the high efficacy of primaquine treatment in preventing relapse.
- Aimee R. Taylor
- , James A. Watson
- & Nicholas J. White
-
Article
| Open Access GraphTyper2 enables population-scale genotyping of structural variation using pangenome graphs
GraphTyper2 enables population-scale genotyping of structural variation using pangenome graphs
Structural variants may be omitted in sequence analysis despite their importance in genome variation and phenotypic impact. Here the authors present GraphTyper2, which uses pangenome graphs to genotype structural variants using short-reads and can be applied in large-scale sequencing studies.
- Hannes P. Eggertsson
- , Snaedis Kristmundsdottir
- & Pall Melsted
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide analysis of Cushion willow provides insights into alpine plant divergence in a biodiversity hotspot
Genome-wide analysis of Cushion willow provides insights into alpine plant divergence in a biodiversity hotspot
Exceptional alpine plant diversity exists in the Hengduan Mountains. Here, through genome assembly and population genomics studies, the authors find notable intraspecific divergence among Cushion willow populations isolated by the sky island-like habitats and consider it contributes to speciation and biodiversity.
- Jia-hui Chen
- , Yuan Huang
- & Hang Sun
-
Article
| Open Access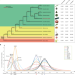 The wax gourd genomes offer insights into the genetic diversity and ancestral cucurbit karyotype
The wax gourd genomes offer insights into the genetic diversity and ancestral cucurbit karyotype
Cucurbits fruits have diverse shapes and sizes, but their genomes evolution and genetic basis of diversity are unclear. Here, the authors show that the wax gourd genome has the most ancestral karyotype among cucurbits and identify candidate genes which contribute to large fruit size by comparative and population genomics analyses.
- Dasen Xie
- , Yuanchao Xu
- & Zhonghua Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Adaptation is maintained by the parliament of genes
Adaptation is maintained by the parliament of genes
The ‘parliament of genes’ hypothesis suggests that selfish genetic elements will be counteracted by suppressors that maintain equal transmission of the rest of the genome. Here, the authors find support for this hypothesis using mathematical models to explore a range of different scenarios.
- Thomas W. Scott
- & Stuart A. West
-
Article
| Open Access Improved polygenic prediction by Bayesian multiple regression on summary statistics
Improved polygenic prediction by Bayesian multiple regression on summary statistics
Various approaches are being used for polygenic prediction including Bayesian multiple regression methods that require access to individual-level genotype data. Here, the authors extend BayesR to utilise GWAS summary statistics (SBayesR) and show that it outperforms other summary statistic-based methods.
- Luke R. Lloyd-Jones
- , Jian Zeng
- & Peter M. Visscher
-
Article
| Open Access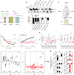 Quantitating the epigenetic transformation contributing to cholesterol homeostasis using Gaussian process
Quantitating the epigenetic transformation contributing to cholesterol homeostasis using Gaussian process
How epigenetics coordinate with genetics to impact protein fitness is unknown. Here, using a Variation Spatial Profiling strategy and machine learning, the authors map HDAC impact on a full set of Niemann pick C1 disease variants to quantitate an unanticipated plasticity in central dogma.
- Chao Wang
- , Samantha M. Scott
- & William E. Balch
-
Article
| Open Access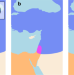 Disease transmission and introgression can explain the long-lasting contact zone of modern humans and Neanderthals
Disease transmission and introgression can explain the long-lasting contact zone of modern humans and Neanderthals
Modern humans and Neanderthals coexisted in the Levant for tens of thousands of years before modern humans spread and replaced Neanderthals. Here, Greenbaum et al. develop a model showing that transmission of disease and genes can explain the maintenance and then collapse of this contact zone.
- Gili Greenbaum
- , Wayne M. Getz
- & Oren Kolodny
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying the polygenic contribution to variable expressivity in eleven rare genetic disorders
Quantifying the polygenic contribution to variable expressivity in eleven rare genetic disorders
Rare genetic disorders (RGDs) often exhibit significant clinical variability among affected individuals. Here, Oetjens et al. systematically study the contribution of common genetic variation to variable expressivity of RGDs and find it is frequently influenced by polygenic factors identified in genome-wide association studies of relevant traits.
- M. T. Oetjens
- , M. A. Kelly
- & D. H. Ledbetter
-
Article
| Open Access The global diversity of Haemonchus contortus is shaped by human intervention and climate
The global diversity of Haemonchus contortus is shaped by human intervention and climate
Based on single worm whole genome sequencing, the authors here characterise the global evolution of the gastrointestinal parasite Haemonchus contortus and identify genes that play a role in drug resistance as well as climate-driven adaptations involving an epigenetic regulator.
- G. Sallé
- , S. R. Doyle
- & J. A. Cotton
-
Article
| Open Access Puma genomes from North and South America provide insights into the genomic consequences of inbreeding
Puma genomes from North and South America provide insights into the genomic consequences of inbreeding
Pumas are experiencing increased isolation as human persecution and habitat loss fragment the populations of this once widespread species. Here, the authors estimate the genomic consequences of this isolation by analyzing the genomes of ten pumas from across North and South America.
- Nedda F. Saremi
- , Megan A. Supple
- & Beth Shapiro
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association mapping of date palm fruit traits
Genome-wide association mapping of date palm fruit traits
Date palm is an important fruit crop in the Middle East and North Africa. Here, the authors report an improved genome assembly of this species and perform GWAS mapping of sex determining region and 21 fruit traits using high density SNP data generated from re-sequencing of the mapping population.
- Khaled M. Hazzouri
- , Muriel Gros-Balthazard
- & Michael D. Purugganan
-
Article
| Open Access Contribution of retrotransposition to developmental disorders
Contribution of retrotransposition to developmental disorders
Retrotransposition events have been linked to some human disorders. Here, Gardner et al. systematically search for mobile genetic elements (ME) in trio whole exome-sequencing datasets and ascertain 9 de novo MEs and further estimate genome-wide germline ME burden and constraint.
- Eugene J. Gardner
- , Elena Prigmore
- & Matthew E. Hurles
-
Article
| Open Access Longshot enables accurate variant calling in diploid genomes from single-molecule long read sequencing
Longshot enables accurate variant calling in diploid genomes from single-molecule long read sequencing
Single-molecule sequencing (SMS) such as Pacific Biosciences and Oxford Nanopore generate long reads with high error rate. Here, the authors develop Longshot, a computational method that detects and phases single nucleotide variants (SNV) in diploid genomes using SMS data.
- Peter Edge
- & Vikas Bansal
-
Article
| Open Access Rare mutations in the complement regulatory gene CSMD1 are associated with male and female infertility
Rare mutations in the complement regulatory gene CSMD1 are associated with male and female infertility
Many molecular and physiological mechanisms in the regulation of fertility are shared between female and male mammals. Here, Lee et al. report an association of CNVs in CSMD1 with early idiopathic menopause in women and show that loss of Csmd1 leads to gonadal dysfunction in both male and female mice.
- Arthur S. Lee
- , Jannette Rusch
- & Donald F. Conrad
-
Article
| Open Access Characterizing rare and low-frequency height-associated variants in the Japanese population
Characterizing rare and low-frequency height-associated variants in the Japanese population
Thousands of genetic loci are known to associate with human height, but these are mainly based on studies in European ancestry populations. Here, Akiyama et al. construct a genotype reference panel for the Japanese population followed by GWAS and report 573 height associated variants in 191,787 Japanese.
- Masato Akiyama
- , Kazuyoshi Ishigaki
- & Yoichiro Kamatani
-
Article
| Open Access The transferability of lipid loci across African, Asian and European cohorts
The transferability of lipid loci across African, Asian and European cohorts
The majority of published GWAS was performed in European ancestry populations. Here, Kuchenbaecker et al., test to which extent lipid loci are shared and find that the major lipid loci are mostly transferrable between Europeans and Asians while there are notable exceptions for African populations.
- Karoline Kuchenbaecker
- , Nikita Telkar
- & Dieter Wolke
-
Article
| Open Access Admixture between old lineages facilitated contemporary ecological speciation in Lake Constance stickleback
Admixture between old lineages facilitated contemporary ecological speciation in Lake Constance stickleback
Ecological speciation can proceed rapidly, but the origin of genetic variation facilitating it has remained elusive. Here, the authors show that secondary contact and introgression between deeply diverged lineages of stickleback fish facilitated rapid ecological speciation into lake and stream ecotypes in Lake Constance.
- David A. Marques
- , Kay Lucek
- & Ole Seehausen
-
Article
| Open Access Evolutionary and functional impact of common polymorphic inversions in the human genome
Evolutionary and functional impact of common polymorphic inversions in the human genome
Inversions are a little-studied type of genomic variation that could contribute to phenotypic traits. Here the authors characterize 45 common polymorphic inversions in human populations and investigate their evolutionary and functional impact.
- Carla Giner-Delgado
- , Sergi Villatoro
- & Mario Cáceres
-
Article
| Open Access Resequencing 545 ginkgo genomes across the world reveals the evolutionary history of the living fossil
Resequencing 545 ginkgo genomes across the world reveals the evolutionary history of the living fossil
Ginkgo is one of the living fossils from the plant kingdom. Here, authors conduct population genomics analyses to reveal its refugia and demographic history, and provide evidence of multiple anthropogenic introductions of ginkgo from eastern China into different continents.
- Yun-Peng Zhao
- , Guangyi Fan
- & Song Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Extensive disruption of protein interactions by genetic variants across the allele frequency spectrum in human populations
Extensive disruption of protein interactions by genetic variants across the allele frequency spectrum in human populations
Low frequency coding single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) are predicted to disproportionately affect protein function. Here, the authors evaluate 2,009 missense SNVs across 2,185 protein-protein interactions using yeast two-hybrid and protein complementation assays and find that disruptive SNVs often occur in disease-associated genes.
- Robert Fragoza
- , Jishnu Das
- & Haiyuan Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Components of genetic associations across 2,138 phenotypes in the UK Biobank highlight adipocyte biology
Components of genetic associations across 2,138 phenotypes in the UK Biobank highlight adipocyte biology
While many pleiotropic genetic loci have been identified, how they contribute to phenotypes across traits and diseases is unclear. Here, the authors propose decomposition of genetic associations (DeGAs), which uses singular value decomposition, to characterize the underlying latent structure of genetic associations of 2,138 phenotypes.
- Yosuke Tanigawa
- , Jiehan Li
- & Manuel A. Rivas
-
Article
| Open Access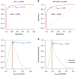 Extreme inbreeding in a European ancestry sample from the contemporary UK population
Extreme inbreeding in a European ancestry sample from the contemporary UK population
Mating between first or second-degree relatives is prohibited in most countries, yet it occurs and is under-studied. Here, Yengo et al. use large runs of homozygosity from the UK Biobank resource to provide DNA-based quantification of extreme inbreeding and its consequence for health and other complex traits.
- Loic Yengo
- , Naomi R. Wray
- & Peter M. Visscher
-
Article
| Open Access Meiotic sex in Chagas disease parasite Trypanosoma cruzi
Meiotic sex in Chagas disease parasite Trypanosoma cruzi
Here, Llewellyn and colleagues present evidence of meiotic sex in Trypanosoma cruzi, the causative agent of Chagas disease. These findings have implications for the epidemiology of the disease in endemic regions and challenge existing ideas that the parasites are strictly clonal.
- Philipp Schwabl
- , Hideo Imamura
- & Martin S. Llewellyn
-
Article
| Open Access A high-resolution map of non-crossover events reveals impacts of genetic diversity on mammalian meiotic recombination
A high-resolution map of non-crossover events reveals impacts of genetic diversity on mammalian meiotic recombination
During meiotic recombination, genetic information is transferred or exchanged between parental chromosome copies. Using a large hybrid mouse pedigree, the authors generated high-resolution maps of these transfer/exchange events and discovered new properties governing their processing and resolution.
- Ran Li
- , Emmanuelle Bitoun
- & Simon R. Myers
-
Article
| Open Access Ancient DNA from the skeletons of Roopkund Lake reveals Mediterranean migrants in India
Ancient DNA from the skeletons of Roopkund Lake reveals Mediterranean migrants in India
Remains of several hundred humans are scattered around Roopkund Lake, situated over 5,000 meters above sea level in the Himalayan Mountains. Here the authors analyze genome-wide data from 38 skeletons and find 3 clusters with different ancestries and dates, showing the people were desposited in multiple catastrophic events.
- Éadaoin Harney
- , Ayushi Nayak
- & Niraj Rai
-
Article
| Open Access Incomplete influenza A virus genomes occur frequently but are readily complemented during localized viral spread
Incomplete influenza A virus genomes occur frequently but are readily complemented during localized viral spread
The genome of influenza is often incomplete in infected cells, but the implications for infection remain unclear. Here, Jacobs et al. show that an average of 3.6 particles is necessary for productive infection and that coinfection supports efficient complementation within a host but not upon transmission to a new host.
- Nathan T. Jacobs
- , Nina O. Onuoha
- & Anice C. Lowen
-
Article
| Open Access The determinants of genetic diversity in butterflies
The determinants of genetic diversity in butterflies
Theory suggests that neutral genetic diversity is determined by census population size, but this is not observed empirically. Here, the authors show that in butterflies, neutral genetic diversity correlates with both body size and chromosome number, suggesting that linked selection is also an important factor.
- Alexander Mackintosh
- , Dominik R. Laetsch
- & Konrad Lohse
-
Article
| Open Access Sequencing of Chinese castor lines reveals genetic signatures of selection and yield-associated loci
Sequencing of Chinese castor lines reveals genetic signatures of selection and yield-associated loci
Castor is an important industrial oil crop, but knowledge on its genetic diversity is limited. Here, Fan et al. show geographic pattern of Chinese castors that have developed during domestication by population genetic analyses, and reveal candidate genes associated with agronomically important traits.
- Wei Fan
- , Jianjun Lu
- & Peng Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Lack of long-term acclimation in Antarctic encrusting species suggests vulnerability to warming
Lack of long-term acclimation in Antarctic encrusting species suggests vulnerability to warming
Genetic adaptation and physiological acclimation can potentially buffer species against climate change. Here, the authors perform a long-term warming experiment of Antarctic encrusting communities and show that focal animal species failed to acclimate and lacked genetic variation in tolerance to warming.
- Melody S. Clark
- , Leyre Villota Nieva
- & Lloyd S. Peck
-
Article
| Open Access Analysis of polygenic risk score usage and performance in diverse human populations
Analysis of polygenic risk score usage and performance in diverse human populations
Predominant participation of European-ancestry individuals in genetic studies has hindered the better understanding of genetic risk in non-European ancestry individuals. Here, Duncan et al. quantify polygenic risk score use and performance in worldwide populations.
- L. Duncan
- , H. Shen
- & B. Domingue
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping the drivers of within-host pathogen evolution using massive data sets
Mapping the drivers of within-host pathogen evolution using massive data sets
Various host factors may impact within-host pathogen evolution. Here, the authors develop a Bayesian approach for identifying host-pathogen interactions using large data sets of pathogen diversity, and apply it to investigate HLA-induced selection in the HIV-1 genome.
- Duncan S. Palmer
- , Isaac Turner
- & Gil McVean
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic signatures and correlates of widespread population declines in salmon
Genomic signatures and correlates of widespread population declines in salmon
The Atlantic salmon has suffered widespread population declines over the last century. Here, Lehnert et al. reconstruct changes in effective population size of 172 populations based on genomic linkage information revealing mostly temperature-associated population declines with over 60% of populations in decline since 1975.
- S. J. Lehnert
- , T. Kess
- & I. R. Bradbury
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic structure and diversity of Plasmodium falciparum in Southeast Asia reveal recent parasite migration patterns
Genomic structure and diversity of Plasmodium falciparum in Southeast Asia reveal recent parasite migration patterns
Understanding genomic variation in Plasmodium falciparum parasites and inferring migration patterns can guide malaria elimination strategies. Using genome-wide data for 1722 parasites collected from 54 districts, the authors use identity-by-descent approaches to estimate regional parasite migration and spread of artemisinin drug resistance.
- Amol C. Shetty
- , Christopher G. Jacob
- & Marie A. Onyamboko
-
Article
| Open Access Survival of the simplest in microbial evolution
Survival of the simplest in microbial evolution
In asexual populations selection at different genomic loci can interfere with each other. Here, using a biophysical model of molecular evolution the authors show that interference results in long-term degradation of molecular function, an effect that strongly depends on genome size.
- Torsten Held
- , Daniel Klemmer
- & Michael Lässig
-
Article
| Open Access Bivariate causal mixture model quantifies polygenic overlap between complex traits beyond genetic correlation
Bivariate causal mixture model quantifies polygenic overlap between complex traits beyond genetic correlation
To better understand the phenotypic relationships of complex traits it is also important to understand their genetic overlap. Here, Frei et al. develop MiXeR which uses GWAS summary statistics to evaluate the polygenic overlap between two traits irrespective of their genetic correlation.
- Oleksandr Frei
- , Dominic Holland
- & Anders M. Dale
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic analysis on pygmy hog reveals extensive interbreeding during wild boar expansion
Genomic analysis on pygmy hog reveals extensive interbreeding during wild boar expansion
The pygmy hog (Porcula salvania), now highly endangered and restricted in a small region at the southern foothills of the Himalaya, is the only suid species in mainland Eurasia that outlived the expansion of wild boar (Sus scrofa). Here, the authors analyze genomes of pygmy hog and related suid species, and identify signals of introgression among these species.
- Langqing Liu
- , Mirte Bosse
- & Ole Madsen
-
Article
| Open Access Genetics and evidence for balancing selection of a sex-linked colour polymorphism in a songbird
Genetics and evidence for balancing selection of a sex-linked colour polymorphism in a songbird
Gouldian finches have a head colour polymorphism that is also associated with physiological and behavioural differentiation. Here, the authors map this colour polymorphism to a putative regulatory region for follistatin on the Z chromosome and suggest it is maintained by balancing selection.
- Kang-Wook Kim
- , Benjamin C. Jackson
- & Terry Burke
-
Article
| Open Access Defining the genetic and evolutionary architecture of alternative splicing in response to infection
Defining the genetic and evolutionary architecture of alternative splicing in response to infection
Genetic ancestry might influence immunological response to infection at different regulatory levels. Here, the authors use RNA-Seq to investigate the variability of alternative splicing patterns in resting and stimulated monocytes of African- and European-descent.
- Maxime Rotival
- , Hélène Quach
- & Lluis Quintana-Murci
-
Article
| Open Access Whole genome sequencing of canids reveals genomic regions under selection and variants influencing morphology
Whole genome sequencing of canids reveals genomic regions under selection and variants influencing morphology
Being man’s best friend, dogs have been bred and selected for certain morphologic traits and breed-associated behaviours. Here, Plassais et al. analyse 722 canine whole genome sequences including modern breeds, wild canids and village dogs by GWAS and search for signatures of selection.
- Jocelyn Plassais
- , Jaemin Kim
- & Elaine A. Ostrander
-
Article
| Open Access Sequence variation at ANAPC1 accounts for 24% of the variability in corneal endothelial cell density
Sequence variation at ANAPC1 accounts for 24% of the variability in corneal endothelial cell density
The corneal endothelium is crucial for proper vision. Here, Ivarsdottir et al. perform genome-wide association studies for various corneal endothelial cell measurements and find that an intergenic variant near ANAPC1 explains 24% of the variance of endothelial cell density and associates with corneal hysteresis.
- Erna V. Ivarsdottir
- , Stefania Benonisdottir
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access Late Pleistocene human genome suggests a local origin for the first farmers of central Anatolia
Late Pleistocene human genome suggests a local origin for the first farmers of central Anatolia
Central Anatolia harbored some of the earliest farming societies outside the Fertile Crescent of the Near East. Here, the authors report and analyze genome-wide data from a 15,000-year-old Anatolian hunter-gatherer and from seven Anatolian and Levantine early farmers, and suggest high genetic continuity between the hunter-gatherers and early farmers of Anatolia.
- Michal Feldman
- , Eva Fernández-Domínguez
- & Johannes Krause
-
Article
| Open Access Low genetic variation is associated with low mutation rate in the giant duckweed
Low genetic variation is associated with low mutation rate in the giant duckweed
While the role of effective population size (Ne) in explaining variation in genetic diversity has received much attention, the role of spontaneous mutation rate is largely ignored. Here, Xu et al. show that giant duckweed has a high Ne yet low genetic diversity, likely due to its low mutation rate.
- Shuqing Xu
- , Jessica Stapley
- & Meret Huber
-
Article
| Open Access Whole-genome resequencing of 472 Vitis accessions for grapevine diversity and demographic history analyses
Whole-genome resequencing of 472 Vitis accessions for grapevine diversity and demographic history analyses
Despite the importance of grapevine cultivation in human history and the economic values of cultivar improvement, large-scale genomic variation data are lacking. Here the authors resequence 472 Vitis accessions and use the identified genetic variations for domestication history, demography, and GWAS analyses.
- Zhenchang Liang
- , Shengchang Duan
- & Yang Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Genome maps across 26 human populations reveal population-specific patterns of structural variation
Genome maps across 26 human populations reveal population-specific patterns of structural variation
Large structural variants (SV) are understudied in human genetics research because of the difficulty to detect them in the routinely generated short-read sequencing data. Here, the authors generate optical genome maps of 154 individuals from 26 populations that allow comprehensive examination of large SVs.
- Michal Levy-Sakin
- , Steven Pastor
- & Pui-Yan Kwok
-
Article
| Open Access The indirect health effects of malaria estimated from health advantages of the sickle cell trait
The indirect health effects of malaria estimated from health advantages of the sickle cell trait
Estimates of the burden of malaria often don't take wider, indirect effects on overall health into consideration. Here, Uyoga et al. estimate the indirect impact of malaria on children’s health in a case-control study, using the sickle cell trait as a proxy indicator for an effective intervention.
- Sophie Uyoga
- , Alex W. Macharia
- & Thomas N. Williams
-
Article
| Open Access Association study in African-admixed populations across the Americas recapitulates asthma risk loci in non-African populations
Association study in African-admixed populations across the Americas recapitulates asthma risk loci in non-African populations
The burden of asthma varies between ancestries, but GWAS have so far focused on mainly European ancestry populations. Here, Daya et al. perform GWAS for asthma in 14,654 individuals of African ancestry and, besides confirming previously known loci, identify two potentially African ancestry-specific loci.
- Michelle Daya
- , Nicholas Rafaels
- & Maria Yazdanbakhsh
-
Article
| Open Access Quantification of frequency-dependent genetic architectures in 25 UK Biobank traits reveals action of negative selection
Quantification of frequency-dependent genetic architectures in 25 UK Biobank traits reveals action of negative selection
Negative selection removes deleterious genetic variation, and can influence genetic architectures and evolution of complex traits. Here, the authors analyze data from 25 UK Biobank diseases and complex traits, and quantify frequency-dependent genetic architectures which suggests actions of negative selection.
- Armin P. Schoech
- , Daniel M. Jordan
- & Alkes L. Price
-
Article
| Open Access Ancient human genome-wide data from a 3000-year interval in the Caucasus corresponds with eco-geographic regions
Ancient human genome-wide data from a 3000-year interval in the Caucasus corresponds with eco-geographic regions
The Caucasus mountain range has impacted on the culture and genetics of the wider region. Here, the authors generate genome-wide SNP data for 45 Eneolithic and Bronze Age individuals across the Caucasus, and find distinct genetic clusters between mountain and steppe zones as well as occasional gene-flow.
- Chuan-Chao Wang
- , Sabine Reinhold
- & Wolfgang Haak

 A 5700 year-old human genome and oral microbiome from chewed birch pitch
A 5700 year-old human genome and oral microbiome from chewed birch pitch