Matters Arising
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Allopolyploid origin and diversification of the Hawaiian endemic mints
Allopolyploid origin and diversification of the Hawaiian endemic mints
Hawaiian endemic mints represent the second largest plant radiation in the archipelago. Here, the authors present a reference genome and numerous resequenced individuals to uncover evidence for polyploidy, geographic speciation and localized hybridization underlying diversification in this lineage
- Crystal M. Tomlin
- , Sitaram Rajaraman
- & Charlotte Lindqvist
-
Article
| Open Access Exome-wide analysis implicates rare protein-altering variants in human handedness
Exome-wide analysis implicates rare protein-altering variants in human handedness
Left-handedness is a common and partly heritable trait. Here, the authors perform a genome-wide screen for rare, protein-altering genetic variants associated with handedness in over 350,000 people, and implicate the tubulin gene TUBB4B.
- Dick Schijven
- , Sourena Soheili-Nezhad
- & Clyde Francks
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamics of extrachromosomal circular DNA in rice
Dynamics of extrachromosomal circular DNA in rice
Comparing to other biological systems, our understanding of plant extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA) is limited. Here, the authors profile eccDNA from six rice tissues and investigate eccDNA characteristics, formation mechanisms, distribution, and functional implications.
- Jundong Zhuang
- , Yaoxin Zhang
- & Tingting Lu
-
Article
| Open Access A genomic toolkit for winged bean Psophocarpus tetragonolobus
A genomic toolkit for winged bean Psophocarpus tetragonolobus
Winged bean is a tropical legume that can produce similar level of seed protein to soybean. Here, the authors report the genome assembly, population genetics, QTL mapping of the plant architecture, protein content and phytonutrients for this species.
- Wai Kuan Ho
- , Alberto Stefano Tanzi
- & Sean Mayes
-
Article
| Open Access Dipterocarpoidae genomics reveal their demography and adaptations to Asian rainforests
Dipterocarpoidae genomics reveal their demography and adaptations to Asian rainforests
Dipterocarp trees are iconic but severely threatened species in Asian rainforests. This study assembles high-quality genomes of seven dipterocarp species to reveal the molecular basis of key adaptations and identifies a recent sharp population decline coinciding with local human activity.
- Rong Wang
- , Chao-Nan Liu
- & Xiao-Yong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Porous borders at the wild-crop interface promote weed adaptation in Southeast Asia
Porous borders at the wild-crop interface promote weed adaptation in Southeast Asia
Genome-wide evidence to support that wild rice can contribute to weedy rice evolution by hybridization and adaptive introgression is very limited. Here, the authors sequence the weedy rice genomes and show reproductively compatible wild rice can contribute to weedy rice evolution.
- Lin-Feng Li
- , Tonapha Pusadee
- & Kenneth M. Olsen
-
Article
| Open Access Cepharanthine analogs mining and genomes of Stephania accelerate anti-coronavirus drug discovery
Cepharanthine analogs mining and genomes of Stephania accelerate anti-coronavirus drug discovery
Cepharanthine is a secondary metabolite isolated from Stephania with a variety of medicinal properties. Here, the authors assembled three Stephania genomes, propose cepharanthine biosynthetic pathway, and assess the antiviral potential of cepharanthine-related metabolites.
- Liang Leng
- , Zhichao Xu
- & Shilin Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Natural selection and genetic diversity maintenance in a parasitic wasp during continuous biological control application
Natural selection and genetic diversity maintenance in a parasitic wasp during continuous biological control application
Parasitoid wasps are reared and released as biocontrol agents to manage aphids and protect crops. Here, the authors use genomes from 542 wasps to show that, in spite of wide scale release of low-diversity captive individuals, diversity in wild populations is maintained.
- Bingyan Li
- , Yuange Duan
- & Hu Li
-
Article
| Open Access A method to estimate the contribution of rare coding variants to complex trait heritability
A method to estimate the contribution of rare coding variants to complex trait heritability
The contribution of rare variants to complex traits has not been well studied. Here, the authors present RARity, a method to assess rare variant heritability without assuming a particular genetic architecture and enabling both gene-level and exome-wide heritability estimation of continuous traits.
- Nazia Pathan
- , Wei Q. Deng
- & Guillaume Paré
-
Article
| Open Access Large-scale genomic rearrangements boost SCRaMbLE in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Large-scale genomic rearrangements boost SCRaMbLE in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Synthetic Chromosome Rearrangement and Modification by LoxP-mediated Evolution (SCRaMbLE) is a promising tool to study genomic rearrangements. Here the authors present an engineered yeast strain with 83 sparsely distributed loxPsym sites across the genome can genrerate large-scale genomic rearrangements, which benefits cell fitness under stress and boosts the SCRaMbLE system when combined with synthetic chromosomes.
- Li Cheng
- , Shijun Zhao
- & Junbiao Dai
-
Article
| Open Access A chromosome-scale assembly reveals chromosomal aberrations and exchanges generating genetic diversity in Coffea arabica germplasm
A chromosome-scale assembly reveals chromosomal aberrations and exchanges generating genetic diversity in Coffea arabica germplasm
Coffea arabica is an allotetraploid hybrid of C. eugenioides and C. canephora and contributes to approximately 60% of world coffee production. Here, the authors report its chromosome-level genome assembly and identify that chromosomal abnormalities and introgression from C. canephora may contribute to diversity and pathogen resistance.
- Simone Scalabrin
- , Gabriele Magris
- & Michele Morgante
-
Editorial
| Open AccessEfficient genetic improvement of orphan crops cannot follow the old path
Orphan crops hold the potential to diversify our food systems. Considering their unique characteristics, our deep understanding of major crops, and the availability of modern genomic tools, taking a different research path from what major crops have gone through could accelerate the genetic improvement of orphan crops.
-
Comment
| Open Access Integrative and inclusive genomics to promote the use of underutilised crops
Integrative and inclusive genomics to promote the use of underutilised crops
Underutilised crops or orphan crops are important for diversifying our food systems towards food and nutrition security. Here, the authors discuss how the development of underutilised crop genomic resource should align with their breeding and capacity building strategies, and leverage advances made in major crops.
- Oluwaseyi Shorinola
- , Rose Marks
- & Mark A. Chapman
-
Article
| Open Access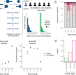 Quantifying negative selection in human 3ʹ UTRs uncovers constrained targets of RNA-binding proteins
Quantifying negative selection in human 3ʹ UTRs uncovers constrained targets of RNA-binding proteins
Identifying functional genetic variants in non-coding regions of the human genome is challenging. Here the authors apply their iMAPS approach to 3ʹ untranslated regions, identifying thousands of variants that disrupt post-transcriptional gene regulation.
- Scott D. Findlay
- , Lindsay Romo
- & Christopher B. Burge
-
Article
| Open Access Tandem gene duplications contributed to high-level azole resistance in a rapidly expanding Candida tropicalis population
Tandem gene duplications contributed to high-level azole resistance in a rapidly expanding Candida tropicalis population
Candida tropicalis is a cause of invasive candidiasis infection in humans that has been increasingly associated with azole drug resistance. In this study, the authors investigate the genetic basis for azole resistance through analysis of whole-genome sequencing and multilocus sequence typing data.
- Xin Fan
- , Rong-Chen Dai
- & Meng Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Mosaic chromosomal alterations in peripheral blood leukocytes of children in sub-Saharan Africa
Mosaic chromosomal alterations in peripheral blood leukocytes of children in sub-Saharan Africa
Mosaic chromosomal alterations (mCAs) in peripheral blood leukocytes are associated with an increased risk of malignancy. Here, the authors use genome-wide genotyping array data to investigate the prevalence of mCAs in sub-Saharan African children with versus those without Burkitt lymphoma.
- Weiyin Zhou
- , Anja Fischer
- & Sam M. Mbulaiteye
-
Article
| Open Access Whole genomes from Angola and Mozambique inform about the origins and dispersals of major African migrations
Whole genomes from Angola and Mozambique inform about the origins and dispersals of major African migrations
African human genome variation remains under-sampled. Here, the authors present a collection of 350 whole genome sequences from Angola and Mozambique and model the timing and extent of significant demographic events in African history.
- Sam Tallman
- , Maria das Dores Sungo
- & Sandra Beleza
-
Article
| Open Access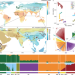 Global genetic diversity, introgression, and evolutionary adaptation of indicine cattle revealed by whole genome sequencing
Global genetic diversity, introgression, and evolutionary adaptation of indicine cattle revealed by whole genome sequencing
Indicine cattle make up half of all cattle populations worldwide. Using a large genomic dataset, this study finds historic migrations and extensive introgression with domestic and wild bovine species has facilitated this species physiological adaptation to extreme environments.
- Ningbo Chen
- , Xiaoting Xia
- & Chuzhao Lei
-
Article
| Open Access Ancient diversity in host-parasite interaction genes in a model parasitic nematode
Ancient diversity in host-parasite interaction genes in a model parasitic nematode
Host-parasite interactions can lead to negative frequency-dependent selection. Here, the authors sequence the genomes of H. bakeri and H. polygyrus, parasites of house and wood mice, respectively, and find that proteins that interact with the host immune response are often highly diverse.
- Lewis Stevens
- , Isaac Martínez-Ugalde
- & Mark Blaxter
-
Article
| Open Access Pan-genome analysis of 13 Malus accessions reveals structural and sequence variations associated with fruit traits
Pan-genome analysis of 13 Malus accessions reveals structural and sequence variations associated with fruit traits
A pan-genome can reduce bias in genetic diversity analysis inherent in using a single reference genome. Here, the authors assemble genomes of 10 diverse apple accessions, conduct pan-genome analysis together with three existing genomes, and reveal the role of mitogen-activated protein kinase homolog MMK2 in fruit coloration.
- Ting Wang
- , Shiyao Duan
- & Ting Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Candidate genes under selection in song sparrows co-vary with climate and body mass in support of Bergmann’s Rule
Candidate genes under selection in song sparrows co-vary with climate and body mass in support of Bergmann’s Rule
Ecogeographic rules link spatial patterns in phenotype and environment, potentially reflecting adaptation. This study identifies nine genes associated with body mass variation in song sparrow populations, supporting Bergmann’s Rule and highlighting the role of natural selection in local adaptation.
- Katherine Carbeck
- , Peter Arcese
- & Jennifer Walsh
-
Article
| Open Access Ancestry-specific polygenic risk scores are risk enhancers for clinical cardiovascular disease assessments
Ancestry-specific polygenic risk scores are risk enhancers for clinical cardiovascular disease assessments
Polygenic risk scores have been proposed as useful to refine cardiovascular risk assessments. Here, the authors validate polygenic risk scores in multiple ancestries and demonstrate their utility to more accurately assess 10 year risk.
- George B. Busby
- , Scott Kulm
- & Giordano Bottà
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic analysis of paralogous regions in 41,755 exomes uncovers clinically relevant variation
Systematic analysis of paralogous regions in 41,755 exomes uncovers clinically relevant variation
Chameleolyser enables the accurate identification of genetic variants hidden within complex regions of the genome. Its application uncovers the disease-explanatory variant in 25 previously undiagnosed patients.
- Wouter Steyaert
- , Lonneke Haer-Wigman
- & Christian Gilissen
-
Article
| Open Access Clinical utility of polygenic scores for cardiometabolic disease in Arabs
Clinical utility of polygenic scores for cardiometabolic disease in Arabs
Arabs account for 5% of the world population and have a high burden of cardiometabolic disease. Here, the authors optimize polygenic scores for 10 cardiometabolic traits in 5399 Arabs, achieving a performance on par with that among European-ancestry individuals.
- Injeong Shim
- , Hiroyuki Kuwahara
- & Akl C. Fahed
-
Article
| Open Access The pan-genome and local adaptation of Arabidopsis thaliana
The pan-genome and local adaptation of Arabidopsis thaliana
Single reference genomes and short-read sequencing data are not enough to harness the full genetic variation of a species. Here, the authors report pan-genome of Arabidopsis thaliana based on chromosomal-level genomes of 32 accessions and identify variations associated with local adaptation.
- Minghui Kang
- , Haolin Wu
- & Jianquan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Targetable NOTCH1 rearrangements in reninoma
Targetable NOTCH1 rearrangements in reninoma
Reninomas are very rare kidney tumours of juxtaglomerular cells. Here, the authors analyse reninomas using whole-genome and transcriptome sequencing, and reveal the presence and functional effects of NOTCH1 rearrangements.
- Taryn D. Treger
- , John E. G. Lawrence
- & Tanzina Chowdhury
-
Article
| Open Access Evolutionary origin of genomic structural variations in domestic yaks
Evolutionary origin of genomic structural variations in domestic yaks
Yaks have been subject to natural selection, human domestication and interspecific introgression during their evolution. Here, the authors have identified genomic structural variations and the linked genes involved in these processes in domestic yaks, to reveal new insight into genetic basis of phenotypic diversity.
- Xinfeng Liu
- , Wenyu Liu
- & Jianquan Liu
-
Article
| Open Access The genomic footprint of whaling and isolation in fin whale populations
The genomic footprint of whaling and isolation in fin whale populations
Industrial whaling drove several species to near extinction. From an analysis of 50 whole-genomes from fin whale populations, this study shows that the fin whale population in the Eastern North Pacific was reduced 99% during whaling but has maintained genomic diversity, whereas the Gulf of California population remained small and isolated, resulting in increased genetic load.
- Sergio F. Nigenda-Morales
- , Meixi Lin
- & Robert K. Wayne
-
Article
| Open Access Genomes of cultivated and wild Capsicum species provide insights into pepper domestication and population differentiation
Genomes of cultivated and wild Capsicum species provide insights into pepper domestication and population differentiation
Existing genetics and genomics studies of peppers mainly focus on single species. Here, the authors report a pepper graph pan-genome and a genome variation map of 500 accessions from five domesticated species and close wild relatives to reveal their domestication, introgression and population differentiation.
- Feng Liu
- , Jiantao Zhao
- & Xuexiao Zou
-
Article
| Open Access Global determinants of insect mitochondrial genetic diversity
Global determinants of insect mitochondrial genetic diversity
This study presents a global map of predicted insect mitochondrial genetic diversity from cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 sequences. From over 2 million mtDNA sequences, they find a negative quadratic latitudinal gradient in genetic diversity evenness, peaking in the subtropics and correlating with hot, stable environments.
- Connor M. French
- , Laura D. Bertola
- & Michael J. Hickerson
-
Article
| Open Access Hepatic SREBP signaling requires SPRING to govern systemic lipid metabolism in mice and humans
Hepatic SREBP signaling requires SPRING to govern systemic lipid metabolism in mice and humans
Hendrix et al show that absence of hepatic Spring dramatically lowers levels of lipids in the liver and plasma in mice, and protects from development of diet-induced steatosis. In line, genetic variation in SPRING is associated with lipid levels in humans.
- Sebastian Hendrix
- , Jenina Kingma
- & Noam Zelcer
-
Article
| Open Access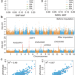 Accurate haplotype construction and detection of selection signatures enabled by high quality pig genome sequences
Accurate haplotype construction and detection of selection signatures enabled by high quality pig genome sequences
Accurate haplotypes with abundant genomic variations benefit genetic research. Here, the authors accurately construct 1,874 pig haplotypes and demonstrate their applications in genome-wide association studies, prediction of breeding values and analyses of evolutionary selection.
- Xinkai Tong
- , Dong Chen
- & Lusheng Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Subtelomeric 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase copy number variation confers glyphosate resistance in Eleusine indica
Subtelomeric 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase copy number variation confers glyphosate resistance in Eleusine indica
Resistance to herbicide glyphosate can be evolved trough copy number variation (CNV) of its target gene EPSPS in goosegrass. Here, the authors assemble the genomes of glyphosate susceptible and resistance lines and provide evidence of sub-telomeric-repeat driven CNV of EPSPS could lead to glyphosate resistance.
- Chun Zhang
- , Nicholas A. Johnson
- & Eric L. Patterson
-
Article
| Open Access Genomic insight into domestication of rubber tree
Genomic insight into domestication of rubber tree
Understanding the genetic basis of rubber tree domestication is critical for improving natural rubber production. Here, the authors assemble the genome of the rubber tree clone CATAS8-79 and conduct population and genetic association analyses to reveal the function of phytosulfokine in regulating number of laticifer rings.
- Jinquan Chao
- , Shaohua Wu
- & Wei-Min Tian
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid gene content turnover on the germline-restricted chromosome in songbirds
Rapid gene content turnover on the germline-restricted chromosome in songbirds
Songbirds have an extra chromosome with unknown function found only in their germline. This study assembles and compares this chromosome in two closely related nightingale species, finding large differences in genetic content and only one conserved gene with probable essential function.
- Stephen A. Schlebusch
- , Jakub Rídl
- & Radka Reifová
-
Article
| Open Access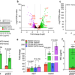 Decoding a cryptic mechanism of metronidazole resistance among globally disseminated fluoroquinolone-resistant Clostridioides difficile
Decoding a cryptic mechanism of metronidazole resistance among globally disseminated fluoroquinolone-resistant Clostridioides difficile
Detection of resistance to the antibiotic metronidazole in C. difficile often requires the presence of heme in the media, for unclear reasons. Here, the authors show that most metronidazole-resistant strains carry a mutation that promotes expression of a heme-dependent enzyme that degrades nitroimidazoles, and the mutation often co-occurs with an amino-acid substitution in DNA gyrase that confers resistance to another class of antibiotics, fluoroquinolones.
- Abiola O. Olaitan
- , Chetna Dureja
- & Julian G. Hurdle
-
Article
| Open Access Optimal strategies for learning multi-ancestry polygenic scores vary across traits
Optimal strategies for learning multi-ancestry polygenic scores vary across traits
There are challenges with transferring genetic risk scores from ancestry in which they were generated to another. Here, the authors investigate the use of multi-ancestry versus single-ancestry training sets to construct polygenic scores and find that the optimal strategy varies across traits.
- Brieuc Lehmann
- , Maxine Mackintosh
- & Chris Holmes
-
Article
| Open Access Characterizing the evolution and phenotypic impact of ampliconic Y chromosome regions
Characterizing the evolution and phenotypic impact of ampliconic Y chromosome regions
A major part of the human Y chromosome consists of palindromes with multiple copies of genes primarily expressed in testis. Here, the authors investigate copy number variation in these palindromes based on whole genome sequence data from 11,527 Icelandic men.
- Elise A. Lucotte
- , Valdís Björt Guðmundsdóttir
- & Kari Stefansson
-
Article
| Open Access Oncogenic structural aberration landscape in gastric cancer genomes
Oncogenic structural aberration landscape in gastric cancer genomes
Gastric cancers (GC) are driven by genomic alterations, but the underlying molecular mechanisms remain unclear. Here, the authors analyse the structural rearrangement landscape of 170 GCs using whole-genome sequencing, identify recurrent structural variant hotspots and find oncogene amplicons driven by extrachromosomal DNA.
- Mihoko Saito-Adachi
- , Natsuko Hama
- & Tatsuhiro Shibata
-
Article
| Open Access Genome analyses reveal population structure and a purple stigma color gene candidate in finger millet
Genome analyses reveal population structure and a purple stigma color gene candidate in finger millet
Finger millet is an orphan crop key to food security of people living in eastern Africa, India and Nepal. Here, the authors assemble its genome, conduct population genetics analyses to infer the diversification history, and reveal a candidate gene for purple coloration of anthers and stigma.
- Katrien M. Devos
- , Peng Qi
- & Damaris A. Odeny
-
Comment
| Open Access Unravelling the genetic architecture of human complex traits through whole genome sequencing
Unravelling the genetic architecture of human complex traits through whole genome sequencing
Whole genome sequencing has enabled new insights into the genetic architecture of complex traits, especially through access to low-frequency and rare variation. This Comment highlights the key contributions from this technology and discusses considerations for its use and future perspectives.
- Ozvan Bocher
- , Cristen J. Willer
- & Eleftheria Zeggini
-
Article
| Open Access Breakdown of self-incompatibility due to genetic interaction between a specific S-allele and an unlinked modifier
Breakdown of self-incompatibility due to genetic interaction between a specific S-allele and an unlinked modifier
Breakdown of self-incompatibility in plants is often attributed to S-locus mutations. Here, by crossing between populations of Arabidopsis lyrate that differ in their breeding system, the authors propose that a modifier unlinked to the S-locus causes self-compatibility by disrupting S-locus function.
- Yan Li
- , Ekaterina Mamonova
- & Marc Stift
-
Article
| Open Access South Asian medical cohorts reveal strong founder effects and high rates of homozygosity
South Asian medical cohorts reveal strong founder effects and high rates of homozygosity
South Asia is home to almost 2 billion people but is extremely underrepresented in human genetics. This study uses genomes from ~5,000 South Asians to characterize genetic variation and help facilitate future South Asian genetic studies.
- Jeffrey D. Wall
- , J. Fah Sathirapongsasuti
- & Andrew S. Peterson
-
Article
| Open Access INSurVeyor: improving insertion calling from short read sequencing data
INSurVeyor: improving insertion calling from short read sequencing data
Current methods for detecting insertions from short read sequencing data generally have low sensitivity. Here, the authors develop a new tool that runs quickly and detects significantly more true positive insertions compared to any combination of existing methods.
- Ramesh Rajaby
- , Dong-Xu Liu
- & Wing-Kin Sung
-
Article
| Open Access Epidemiological inference for emerging viruses using segregating sites
Epidemiological inference for emerging viruses using segregating sites
Epidemiological models are commonly fit to case and pathogen sequence data to estimate parameters and to reconstruct disease dynamics. Here, the authors present an inference approach based on sequence data that is well suited for model fitting early on during the expansion of a viral lineage.
- Yeongseon Park
- , Michael A. Martin
- & Katia Koelle
-
Article
| Open Access Direct haplotype-resolved 5-base HiFi sequencing for genome-wide profiling of hypermethylation outliers in a rare disease cohort
Direct haplotype-resolved 5-base HiFi sequencing for genome-wide profiling of hypermethylation outliers in a rare disease cohort
HiFi genome sequencing accesses DNA methylation and nucleotide variation in long sequence reads. Here, the authors apply this approach in a rare disease cohort to identify DNA hypermethylation linked to genetic variants including rare disease alleles.
- Warren A. Cheung
- , Adam F. Johnson
- & Tomi Pastinen
-
Article
| Open Access Selection-driven trait loss in independently evolved cavefish populations
Selection-driven trait loss in independently evolved cavefish populations
Repeated evolution provides valuable insight into adaptation. In this study, the authors found that repeated evolution of cave-adapted phenotypes of a fish (Astyanax mexicanus) was driven by selection on standing genetic variation and novel mutations and genes repeatedly under selection are longer compared to the rest of the genome.
- Rachel L. Moran
- , Emilie J. Richards
- & Suzanne E. McGaugh
-
Article
| Open Access Chromosome-level genome assembly and population genomic resource to accelerate orphan crop lablab breeding
Chromosome-level genome assembly and population genomic resource to accelerate orphan crop lablab breeding
Lablab is a legume native to Africa and cultivated throughout the tropics for food and forage; however, as an orphan crop, limited genomic resources hampers its genetic improvement. Here, an African-led South-North plant genome collaboration produces an improved genome assembly and population genomic resource to accelerate its breeding.
- Isaac Njaci
- , Bernice Waweru
- & Chris S. Jones
-
Article
| Open Access Characterization of genome-wide STR variation in 6487 human genomes
Characterization of genome-wide STR variation in 6487 human genomes
Short tandem repeat studies in humans have often focused on European populations. Here, the authors report a comprehensive map of 366,013 polymorphic short tandem repeats in Chinese individuals and their mutational patterns, functional properties, gene regulatory effects and population characteristics.
- Yirong Shi
- , Yiwei Niu
- & Shunmin He

 Population genetic considerations regarding the interpretation of within-patient SARS-CoV-2 polymorphism data
Population genetic considerations regarding the interpretation of within-patient SARS-CoV-2 polymorphism data