Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access pH effects on the electrochemical reduction of CO(2) towards C2 products on stepped copper
pH effects on the electrochemical reduction of CO(2) towards C2 products on stepped copper
CO2 conversion to reduced products provides a use for greenhouse gases, but reaction complexity stymies mechanistic studies. Here, authors present a microkinetic model for CO2 and CO reduction on copper, based on ab initio simulations, to elucidate pH’s impact on competitive reaction pathways.
- Xinyan Liu
- , Philomena Schlexer
- & Karen Chan
-
Article
| Open Access Deeply subwavelength phonon-polaritonic crystal made of a van der Waals material
Deeply subwavelength phonon-polaritonic crystal made of a van der Waals material
Photonic crystals can steer, shape, and sculpture the flow of photons. Here, the author fabricate a deep-subwavelength photonic crystal slab that supports ultra-confined phonon polaritons, by patterning a nanoscale hole array in h-BN.
- F. J. Alfaro-Mozaz
- , S. G. Rodrigo
- & A. Y. Nikitin
-
Article
| Open Access Holographic colour prints for enhanced optical security by combined phase and amplitude control
Holographic colour prints for enhanced optical security by combined phase and amplitude control
Here, the authors fabricate a device that integrates multiple computer-generated holograms into a single colour print. Under white light, a colour image is seen, whereas illumination with a red, green, or blue beam from a handheld laser pointer projects three different holograms onto a distant screen.
- Kevin T. P. Lim
- , Hailong Liu
- & Joel K. W. Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasensitive detection of miRNA with an antimonene-based surface plasmon resonance sensor
Ultrasensitive detection of miRNA with an antimonene-based surface plasmon resonance sensor
Label-free molecular-level quantification of MicroRNA (miRNA) remains challenging. Here, the authors develop a new surface plasmon resonance sensor based on two-dimensional nanomaterial of antimonene for the specific label-free detection of clinically relevant biomarkers such as miRNA-21 and miRNA-155.
- Tianyu Xue
- , Weiyuan Liang
- & Qiaoliang Bao
-
Article
| Open Access Spin density encodes intramolecular singlet exciton fission in pentacene dimers
Spin density encodes intramolecular singlet exciton fission in pentacene dimers
Singlet exciton fission – the separation of photoexcited singlet states into two triplet states – holds promise for enhancing photocurrents in photovoltaic technologies. Krishnapriya et al. characterize how electron delocalization over the bridges in a series of pentacene dimers controls this process.
- K. C. Krishnapriya
- , Palas Roy
- & Satish Patil
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional monolithic integration in flexible printed organic transistors
Three-dimensional monolithic integration in flexible printed organic transistors
The scalability of printable integrated circuits is lagging far behind that of conventional silicon-based technologies. Here, Kwon et al. show a three-dimensional integration approach by stacking printeddual-gate organic transistors on plastic foils with a density of 60 transistors per centimeter square.
- Jimin Kwon
- , Yasunori Takeda
- & Sungjune Jung
-
Article
| Open Access The conformational changes coupling ATP hydrolysis and translocation in a bacterial DnaB helicase
The conformational changes coupling ATP hydrolysis and translocation in a bacterial DnaB helicase
DnaB helicases are motor proteins that couple ATP-hydrolysis to the movement of the protein along single-stranded DNA leading to a separation of double-stranded DNA at the replication fork. Here authors use solid-state NMR spectroscopy and reveal DnaB’s conformational responses to ATP hydrolysis and the resulting DNA loading and translocation.
- Thomas Wiegand
- , Riccardo Cadalbert
- & Beat H. Meier
-
Article
| Open Access Double-slit photoelectron interference in strong-field ionization of the neon dimer
Double-slit photoelectron interference in strong-field ionization of the neon dimer
The wave nature of light and particles is of interest to the fundamental quantum mechanics. Here the authors show the double-slit interference effect in the strong-field ionization of neon dimers by employing COLTRIMS method to record the momentum distribution of the photoelectrons in the molecular frame
- Maksim Kunitski
- , Nicolas Eicke
- & Reinhard Dörner
-
Article
| Open Access Strain-controlled shell morphology on quantum rods
Strain-controlled shell morphology on quantum rods
Core/shell semiconductor nanocrystals have advantageous optoelectronic properties, which depend on the shell architecture. Here the authors show that by reducing the growth rate of ZnS shells on ZnSe nanorods the shell morphology can be tuned from flat to islands-like to helical
- Botao Ji
- , Yossef E. Panfil
- & Uri Banin
-
Article
| Open Access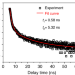 Band-like transport in small-molecule thin films toward high mobility and ultrahigh detectivity phototransistor arrays
Band-like transport in small-molecule thin films toward high mobility and ultrahigh detectivity phototransistor arrays
The potential of organic phototransistors to surpass silicon-based devices is limited by the low carrier mobility of organic photoresponsive materials. Here, Ji et al. report high performance organic phototransistors featuring vacuum-deposited small-molecule films with band-like charge transport.
- Deyang Ji
- , Tao Li
- & Harald Fuchs
-
Article
| Open Access Influence of fake news in Twitter during the 2016 US presidential election
Influence of fake news in Twitter during the 2016 US presidential election
The influence of 'fake news’, spread via social media, has been much discussed in the context of the 2016 US presidential election. Here, the authors use data on 30 million tweets to show how content classified as fake news diffused on Twitter before the election.
- Alexandre Bovet
- & Hernán A. Makse
-
Article
| Open Access Detecting topological variations of DNA at single-molecule level
Detecting topological variations of DNA at single-molecule level
Ultrathin nanopore membranes have the potential for detecting topological variation in DNA. Here the authors use barcoded DNA to characterise the translocation profiles of DNA with single strand gaps.
- Ke Liu
- , Chao Pan
- & Aleksandra Radenovic
-
Article
| Open Access Pressure-driven phase transitions and reduction of dimensionality in 2D silicon nanosheets
Pressure-driven phase transitions and reduction of dimensionality in 2D silicon nanosheets
Silicon nanostructures have important applications as functional materials. Here the authors investigate the structural transformations of 2D silicon nanosheets under compression and decompression, showing the irreversible formation of 1D silicon nanowires.
- Gil Chan Hwang
- , Douglas A. Blom
- & Yongjae Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembled membrane composed of amyloid-like proteins for efficient size-selective molecular separation and dialysis
Self-assembled membrane composed of amyloid-like proteins for efficient size-selective molecular separation and dialysis
Membrane separation is important for a range of industrial and medical applications. Here, the authors report on the formation of self-assembled protein membranes for size selective separation and demonstrate application in the separation of dyes, nanoparticles and in hemodialysis.
- Facui Yang
- , Fei Tao
- & Peng Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced oxygen reduction with single-atomic-site iron catalysts for a zinc-air battery and hydrogen-air fuel cell
Enhanced oxygen reduction with single-atomic-site iron catalysts for a zinc-air battery and hydrogen-air fuel cell
Development of fuel cells and metal-air batteries is hindered by electrocatalyst performance, which can be enhanced with uniform and atomically dispersed active sites. Here the authors report an iron-based electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction in cathodes for a zinc-air battery and a hydrogen-air fuel cell.
- Yuanjun Chen
- , Shufang Ji
- & Yadong Li
-
Article
| Open Access Gas-responsive porous magnet distinguishes the electron spin of molecular oxygen
Gas-responsive porous magnet distinguishes the electron spin of molecular oxygen
Gas-sensing materials are of increasing societal importance, but the ability to differentiate between similarly sized gases remains highly challenging. Here the authors report on a porous ferrimagnet that distinguishes diamagnetic N2 and CO2 gases from paramagnetic O2 gas.
- Wataru Kosaka
- , Zhaoyuan Liu
- & Hitoshi Miyasaka
-
Article
| Open Access Geometric quenching of orbital pair breaking in a single crystalline superconducting nanomesh network
Geometric quenching of orbital pair breaking in a single crystalline superconducting nanomesh network
It is highly desired to maintain superconductivity in presence of magnetic fields but it is by far difficult. Here, Nam et al. create a single crystalline superconducting Pb nanowire network, where critical temperatures are maintained and critical fields are enhanced in either parallel or perpendicular fields.
- Hyoungdo Nam
- , Hua Chen
- & Chih-Kang Shih
-
Article
| Open Access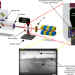 Revealing internal flow behaviour in arc welding and additive manufacturing of metals
Revealing internal flow behaviour in arc welding and additive manufacturing of metals
Understanding what happens to the liquid in melt pools during welding and metal-based additive manufacturing remains a challenge. Here, the authors directly image internal melt pool dynamics using synchrotron radiation to show surface tension affects flow speed, orientation and surface turbulence.
- Lee Aucott
- , Hongbiao Dong
- & Helen. V. Atkinson
-
Article
| Open Access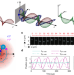 Transverse spin forces and non-equilibrium particle dynamics in a circularly polarized vacuum optical trap
Transverse spin forces and non-equilibrium particle dynamics in a circularly polarized vacuum optical trap
Here, the authors provide a vivid demonstration of the dynamic effect of transverse spin momentum in an optical beam in free space revealed by placing a dielectric bead in a counter-propagating optical beam trap in vacuum.
- V. Svak
- , O. Brzobohatý
- & S. H. Simpson
-
Article
| Open Access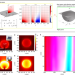 Broadband single molecule SERS detection designed by warped optical spaces
Broadband single molecule SERS detection designed by warped optical spaces
In standard SERS the probability for the molecules to reach tiny hotpot regions is low. Here, the authors introduce an approach based on warped spaces that offers a strategy to manipulate hotspots of metallic nanostructures, resulting in large broadband enhancements in both the magnitude and the volume size.
- Peng Mao
- , Changxu Liu
- & Shuang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Low-loss YIG-based magnonic crystals with large tunable bandgaps
Low-loss YIG-based magnonic crystals with large tunable bandgaps
Control of spin wave transport in magnonic crystals is vital for magnonic devices. Here the authors show low-loss spin-wave manipulation in nanometer thick magnonic crystals of discrete YIG stripes separated by air or CoFeB filled grooves exhibiting tunable bandgaps of 50–200 MHz.
- Huajun Qin
- , Gert-Jan Both
- & Sebastiaan van Dijken
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrastrong nanocrystalline steel with exceptional thermal stability and radiation tolerance
Ultrastrong nanocrystalline steel with exceptional thermal stability and radiation tolerance
Weaker ferritic/matensitic steels rather than stronger austenitic steels are usually candidates for nuclear reactors since they do not easily swell under irradiation. Here, the authors make an ultrastrong lanthanum-doped nanocrystalline austenitic steel that is thermally stable and radiation-tolerant.
- Congcong Du
- , Shenbao Jin
- & Tongde Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Cleaning interfaces in layered materials heterostructures
Cleaning interfaces in layered materials heterostructures
Atomically-clean interfaces are required in heterostructures. Here, authors report a method for fast and parallel removal of contaminants from fully-formed heterostructures, including sample intentionally exposed to polymers and solvent, achieving room temperature mobility over 180,000 cm2/Vs for graphene.
- D. G. Purdie
- , N. M. Pugno
- & A. Lombardo
-
Article
| Open Access Resonant terahertz detection using graphene plasmons
Resonant terahertz detection using graphene plasmons
Plasmons confined in field effect transistors were long envisioned for resonant detection of light at THz frequencies, however realization of such photodetectors has proven challenging. Here, the authors fabricate antenna-coupled graphene transistors which exhibit resonant photoresponse to incident radiation and use them to study plasmons in graphene and its moiré superlattices.
- Denis A. Bandurin
- , Dmitry Svintsov
- & Georgy Fedorov
-
Article
| Open Access Probing multi-spinon excitations outside of the two-spinon continuum in the antiferromagnetic spin chain cuprate Sr2CuO3
Probing multi-spinon excitations outside of the two-spinon continuum in the antiferromagnetic spin chain cuprate Sr2CuO3
Quasi-1D magnetic insulators are very attractive for searching and studying quantum many-body phenomena. Here the authors report the four-spinon excitations in quasi-1D spin-chain cuprate Sr2CuO3 by momentum resolved RIXS technique which provides a new route for the creation of magnetic excitations in 1D materials.
- J. Schlappa
- , U. Kumar
- & T. Schmitt
-
Article
| Open Access Topological one-way fiber of second Chern number
Topological one-way fiber of second Chern number
Topological one-way fibers are promising candidates for novel fiber devices. Here, Lu et al. propose that one-way fiber modes are topologically protected by the second Chern number in a four-dimensional parameter space, which develop in a helically-modulated magnetic Weyl photonic crystal.
- Ling Lu
- , Haozhe Gao
- & Zhong Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Ultimate limit in size and performance of WSe2 vertical diodes
Ultimate limit in size and performance of WSe2 vertical diodes
Vertical charge transport through homogeneous WSe2 layers can be effectively tuned by the layer number and contacting metals deposited. Here, the authors report WSe2 vertical diodes with superior device performance characteristics based on variable WSe2 thickness and gadolinium and platinum contact metals.
- Ghazanfar Nazir
- , Hakseong Kim
- & Suyong Jung
-
Article
| Open Access The propagation of active-passive interfaces in bacterial swarms
The propagation of active-passive interfaces in bacterial swarms
The study of interfaces in bacterial systems is of relevance to the spreading of bacterial colonies and pathological infections. Here the authors investigate the dynamics of active/passive interfaces in bacterial swarms and find that the boundary can be described as a propagating, diffuse elastic interface.
- Alison E. Patteson
- , Arvind Gopinath
- & Paulo E. Arratia
-
Article
| Open Access Deoxyribose and deoxysugar derivatives from photoprocessed astrophysical ice analogues and comparison to meteorites
Deoxyribose and deoxysugar derivatives from photoprocessed astrophysical ice analogues and comparison to meteorites
Sugars are known to form from the UV photoprocessing of ices under astrophysical conditions. Here, the authors report the detection of deoxyribose, the sugar of DNA, and other deoxysugars from the UV photoprocessing of H2O:CH3OH ice mixtures, which are compared with materials from carbonaceous meteorites.
- Michel Nuevo
- , George Cooper
- & Scott A. Sandford
-
Article
| Open Access Source-device-independent heterodyne-based quantum random number generator at 17 Gbps
Source-device-independent heterodyne-based quantum random number generator at 17 Gbps
For many applications, quantum random number generation should be fast and independent from assumptions on the apparatus. Here, the authors devise and implement an approach which assumes a trusted detector but not a trusted source, and allows random bit generations at ~17 Gbps using off-the-shelf components.
- Marco Avesani
- , Davide G. Marangon
- & Paolo Villoresi
-
Article
| Open Access Information-based autonomous reconfiguration in systems of interacting DNA nanostructures
Information-based autonomous reconfiguration in systems of interacting DNA nanostructures
Strand displacement is commonly used in DNA nanotechnology to program dynamic interactions between individual DNA strands. Here, the authors describe a tile displacement principle that is similar in concept but occurs on a larger structural level: the displacement reactions take place between DNA origami tiles, allowing reconfiguration of entire systems of interacting DNA structures.
- Philip Petersen
- , Grigory Tikhomirov
- & Lulu Qian
-
Matters Arising
| Open AccessReply to: “The diamine cation is not a chemical example where density functional theory fails”
- Xinxin Cheng
- , Elvar Jónsson
- & Peter M. Weber
-
Article
| Open Access Stretched and compressed exponentials in the relaxation dynamics of a metallic glass-forming melt
Stretched and compressed exponentials in the relaxation dynamics of a metallic glass-forming melt
Glasses show peculiar relaxation dynamics below glass transition temperature, yet a deeper understanding of this phenomenon is still lacking. Wu et al. show the coexistence of stretched and compressed relaxation in a metallic glass system and attribute their origins to different local cluster structures.
- Zhen Wei Wu
- , Walter Kob
- & Limei Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Overcoming efficiency and stability limits in water-processing nanoparticular organic photovoltaics by minimizing microstructure defects
Overcoming efficiency and stability limits in water-processing nanoparticular organic photovoltaics by minimizing microstructure defects
Water-based semiconducting polymer nanoparticles are eco-friendly and non-toxic but their performance suffers from the surfactants. Here Xie et al. design an approach to minimize the amount of residual surfactant in these nanoparticles and make high-efficiency and stability solar cells.
- Chen Xie
- , Thomas Heumüller
- & Christoph J. Brabec
-
Article
| Open Access Polymer morphology and interfacial charge transfer dominate over energy-dependent scattering in organic-inorganic thermoelectrics
Polymer morphology and interfacial charge transfer dominate over energy-dependent scattering in organic-inorganic thermoelectrics
To realize the potential of soft hybrid (inorganic-organic) materials for thermoelectrics, the underlying transport-related physics must be understood. Here, the authors extend the Kang-Synder framework with experimental analysis to gain insight on the thermoelectric transport in hybrid materials.
- Pawan Kumar
- , Edmond W. Zaia
- & Kedar Hippalgaonkar
-
Article
| Open Access Effective weight control via an implanted self-powered vagus nerve stimulation device
Effective weight control via an implanted self-powered vagus nerve stimulation device
Developing new technologies for the neuromodulation of the vagus nerve can enable therapeutic strategies for body weight control in obese patients. Here, the authors present a battery-free self-powered implantable vagus nerve stimulation system that electrically responds to stomach movement.
- Guang Yao
- , Lei Kang
- & Xudong Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Single crystal hybrid perovskite field-effect transistors
Single crystal hybrid perovskite field-effect transistors
The methylammonium lead halide perovskites have shown excellent optoelectronic properties but the field-effect transistors are much less studied. Here Yu et al. synthesize micrometer-thin crystals of perovskites with low surface contamination and make ambipolar transistor devices with high mobilities.
- Weili Yu
- , Feng Li
- & Aram Amassian
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum majorization and a complete set of entropic conditions for quantum thermodynamics
Quantum majorization and a complete set of entropic conditions for quantum thermodynamics
Similarly to entropy, majorization allows to quantify deviation from uniformity in a wide range of fields. In this paper, the authors use its generalization to the quantum realm to derive a complete set of necessary and sufficient conditions for thermal transformations of quantum states.
- Gilad Gour
- , David Jennings
- & Iman Marvian
-
Article
| Open Access Electron aspirator using electron–electron scattering in nanoscale silicon
Electron aspirator using electron–electron scattering in nanoscale silicon
Power dissipation is usually unavoidable in transistor channels due to the inelastic scattering of electrons. Here, Firdaus et al. propose a nanoscaled silicon electron-aspirator to remove this constraint, which shows enhanced current output by 3 times at 8 K without additional power supply.
- Himma Firdaus
- , Tokinobu Watanabe
- & Yukinori Ono
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of Mcl-1-specific inhibitor AZD5991 and preclinical activity in multiple myeloma and acute myeloid leukemia
Discovery of Mcl-1-specific inhibitor AZD5991 and preclinical activity in multiple myeloma and acute myeloid leukemia
High expression of Mcl-1 promotes tumorigenesis and resistance to anticancer therapies. Here they report a macrocyclic molecule with high selectivity and affinity for Mcl-1 that exhibits potent anti-tumor effects as single agent and in combination with bortezomib or venetoclax in preclinical models of multiple myeloma and acute myeloid leukemia.
- Adriana E. Tron
- , Matthew A. Belmonte
- & Alexander W. Hird
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Characterizing coral skeleton mineralogy with Raman spectroscopy
Characterizing coral skeleton mineralogy with Raman spectroscopy
- Thomas M. DeCarlo
-
Article
| Open Access Click chemistry enables quantitative chiroptical sensing of chiral compounds in protic media and complex mixtures
Click chemistry enables quantitative chiroptical sensing of chiral compounds in protic media and complex mixtures
Chiroptical sensing in complex mixtures remains a challenging task. Here, the authors report an efficient coumarin probe for chiroptical click chirality sensing of absolute configuration, concentration and enantiomeric excess of several compound classes. The method can be directly applied to crude asymmetric reaction mixtures.
- F. Yushra Thanzeel
- , Kaluvu Balaraman
- & Christian Wolf
-
Article
| Open Access Spike-timing-dependent plasticity learning of coincidence detection with passively integrated memristive circuits
Spike-timing-dependent plasticity learning of coincidence detection with passively integrated memristive circuits
Hardware implementation of spiking neural networks holds promise for high energy efficient brain-inspired computing. Here, Prezioso et al. realize the detection of synchrony in a demo circuit composed of 20 metal-oxide memristor synapses connected to a leaky-integrate-and-fire silicon neuron.
- M. Prezioso
- , M. R. Mahmoodi
- & D. B. Strukov
-
Article
| Open Access Constructing exact representations of quantum many-body systems with deep neural networks
Constructing exact representations of quantum many-body systems with deep neural networks
Significant improvements in numerical methods for quantum systems often come from finding new ways of representing quantum states that can be optimized and simulated more efficiently. Here the authors demonstrate a method to calculate exact neural network representations of many-body ground states.
- Giuseppe Carleo
- , Yusuke Nomura
- & Masatoshi Imada
-
Article
| Open Access Overall water splitting by graphdiyne-exfoliated and -sandwiched layered double-hydroxide nanosheet arrays
Overall water splitting by graphdiyne-exfoliated and -sandwiched layered double-hydroxide nanosheet arrays
The need for cheap water-splitting materials in order to scale-up and commercialize solar-to-fuel technologies is urgent, but there are still few candidate materials. Here, authors integrate layered double hydroxides with graphdiyne as high-performance overall water-splitting electrocatalysts.
- Lan Hui
- , Yurui Xue
- & Yuliang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Templated synthesis of cubic crystalline single networks having large open-space lattices by polymer cubosomes
Templated synthesis of cubic crystalline single networks having large open-space lattices by polymer cubosomes
Cubic crystalline single networks of large open-space lattices are ubiquitous in nature. Here the authors show that the topology of the circumferential bilayer of polymer cubosomes differentiates between two non-intersecting pore networks embedded in the cubic mesophase by sealing one channel network at the interface.
- Yunju La
- , Jeongeun Song
- & Kyoung Taek Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Blocking-cyclization technique for precise synthesis of cyclic polymers with regulated topology
Blocking-cyclization technique for precise synthesis of cyclic polymers with regulated topology
Cyclic polymers can be usually accessed by ring-expansion and ring-closure approaches. Here, the authors report an alternative blocking-cyclization technique which enables the tunable synthesis of multicyclic polymers via commercial Ru-based Grubbs catalysts and conventional ring-opening metathesis polymerisation.
- Jie Chen
- , Hongfei Li
- & Meiran Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Neuroinspired unsupervised learning and pruning with subquantum CBRAM arrays
Neuroinspired unsupervised learning and pruning with subquantum CBRAM arrays
To realize the potential of resistive RAM crossbar arrays as platforms for neuromorphic computing, reduced network-level energy consumption must be achieved. Here, the authors use a hardware/software co-design approach to realize reduced energy consumption during network training for the network.
- Yuhan Shi
- , Leon Nguyen
- & Duygu Kuzum
-
Article
| Open Access Fluorine-free water-in-ionomer electrolytes for sustainable lithium-ion batteries
Fluorine-free water-in-ionomer electrolytes for sustainable lithium-ion batteries
The flammability and toxicity of the currently used electrolytes are the concerns that must be addressed. Here the authors show a non-fluorinated and non-toxic ionomeric aqueous gel electrolyte called water-in-ionomer that allows an enlargement of electrochemical stability window and design of environmentally friendly battery cell chemistries.
- Xin He
- , Bo Yan
- & Elie Paillard

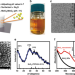 Defect engineered bioactive transition metals dichalcogenides quantum dots
Defect engineered bioactive transition metals dichalcogenides quantum dots