Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access RETRACTED ARTICLE: High-rate aluminium yolk-shell nanoparticle anode for Li-ion battery with long cycle life and ultrahigh capacity
RETRACTED ARTICLE: High-rate aluminium yolk-shell nanoparticle anode for Li-ion battery with long cycle life and ultrahigh capacity
Aluminium offers an attractive alternative anode for lithium-ion batteries, but its practical performance falls far short of the theoretical promise. Here, the authors present a yolk-shell structured nanocomposite anode of aluminium core and titanium oxide shell which displays outstanding electrochemical properties.
- Sa Li
- , Junjie Niu
- & Ju Li
-
Article
| Open Access Design of aqueous redox-enhanced electrochemical capacitors with high specific energies and slow self-discharge
Design of aqueous redox-enhanced electrochemical capacitors with high specific energies and slow self-discharge
The energy density of electrochemical capacitors can be increased by using a redox-active electrolyte, but such capacitors often suffer from significant self-discharge and low operating voltage. Here, the authors report a new redox-active aqueous electrolyte to effectively tackle the problems.
- Sang-Eun Chun
- , Brian Evanko
- & Shannon W. Boettcher
-
Article |
 Understanding complete oxidation of methane on spinel oxides at a molecular level
Understanding complete oxidation of methane on spinel oxides at a molecular level
The development of methane oxidation catalysts made of earth-abundant elements is an important challenge. Here, the authors report a cost-effective nickel-cobalt oxide which outperforms precious-metal-based alternatives, due to the combination of transition metal cations and surface oxygen vacancies.
- Franklin Feng Tao
- , Jun-jun Shan
- & P. Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Flexible lithium–oxygen battery based on a recoverable cathode
Flexible lithium–oxygen battery based on a recoverable cathode
Flexible energy storage systems usually have limited energy densities. Here the authors report a flexible lithium–oxygen battery with the cathode consisting of titanium dioxide nanowire arrays grown on carbon textiles, which displays high mechanical strength as well as promising electrochemical performance.
- Qing-Chao Liu
- , Ji-Jing Xu
- & Xin-Bo Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Unlocking the energy capabilities of micron-sized LiFePO4
Unlocking the energy capabilities of micron-sized LiFePO4
Nanonization of battery electrode particles is a usual way to enhance their conductivity, but the decreased tap density is detrimental to battery performance. Here, the authors coat micron-sized lithium iron phosphate with a conducting polymer layer and demonstrate some excellent electrochemical properties.
- Limin Guo
- , Yelong Zhang
- & Zhangquan Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Direct observation of multistep energy transfer in LHCII with fifth-order 3D electronic spectroscopy
Direct observation of multistep energy transfer in LHCII with fifth-order 3D electronic spectroscopy
Photosynthesis is a complex process, involving the transfer of sunlight driven excitation energy to a reaction centre. Here, the authors directly observe the multistep excitation energy transitions in a light-harvesting complex using ultrafast fifth-order three-dimensional electronic spectroscopy.
- Zhengyang Zhang
- , Petar H. Lambrev
- & Howe-Siang Tan
-
Article
| Open Access The geometric phase controls ultracold chemistry
The geometric phase controls ultracold chemistry
Ultracold reactions can give insights into reactions dynamics in the quantum regime. Here, the authors show that the geometric phase can have a dramatic effect on ultracold reactions, enhancing or suppressing rates by nearly two orders of magnitude in the reaction studied.
- B. K. Kendrick
- , Jisha Hazra
- & N. Balakrishnan
-
Article
| Open Access A molecular propeller effect for chiral separation and analysis
A molecular propeller effect for chiral separation and analysis
Separation and analysis of enantiomers is a difficult task due to the normally identical physical properties they display. Here, the authors show how chiral molecules with non-zero dipoles can be propelled in opposite directions under the influence of a rotating electric field.
- Jonathon B. Clemens
- , Osman Kibar
- & Mirianas Chachisvilis
-
Article
| Open Access The water catalysis at oxygen cathodes of lithium–oxygen cells
The water catalysis at oxygen cathodes of lithium–oxygen cells
The main challenges in lithium-oxygen batteries are the low round-trip efficiency and decaying cycle life. Here, the authors present that a trace amount of water in electrolytes facilitates oxygen cathode reactions, enabling the batteries to be operated with small overpotential and good cycling stability.
- Fujun Li
- , Shichao Wu
- & Haoshen Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Controllable synthesis of molybdenum tungsten disulfide alloy for vertically composition-controlled multilayer
Controllable synthesis of molybdenum tungsten disulfide alloy for vertically composition-controlled multilayer
The band gap modulation of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide alloy is essential for successful applications. Here, we show a controllable synthesis of Mo1−xWxS2 alloy and vertically composition-controlled Mo1−xWxS2multilayer, which is promising as a photoactive material.
- Jeong-Gyu Song
- , Gyeong Hee Ryu
- & Hyungjun Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of vibrational overtones by single-molecule resonant photodissociation
Observation of vibrational overtones by single-molecule resonant photodissociation
Studying the spectra of molecules typically requires large samples, which can be difficult to achieve for hard-to-generate ions. Here, the authors obtain spectra from single CaH+molecules in a three-ion Columbic crystal, observing new molecular transitions.
- Ncamiso B. Khanyile
- , Gang Shu
- & Kenneth R. Brown
-
Article
| Open Access Combined crystal structure prediction and high-pressure crystallization in rational pharmaceutical polymorph screening
Combined crystal structure prediction and high-pressure crystallization in rational pharmaceutical polymorph screening
Crystal polymorphism can lead to substances with vastly differing physicochemical properties, which has serious implications in the pharmaceutical industry. Here, the authors use in silicopolymorph screening to accurately predict the resulting structures under set crystallisation environments.
- M. A. Neumann
- , J. van de Streek
- & O. Grassmann
-
Article
| Open Access Noble metal-comparable SERS enhancement from semiconducting metal oxides by making oxygen vacancies
Noble metal-comparable SERS enhancement from semiconducting metal oxides by making oxygen vacancies
Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy is widely used for rapid and sensitive molecular detection in chemistry and biology, but typically relies on noble metals. Here the authors report a non-stoichiometric semiconducting material with defect-rich surface that displays excellent detection limits and enhancement factors.
- Shan Cong
- , Yinyin Yuan
- & Zhigang Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Long-life Li/polysulphide batteries with high sulphur loading enabled by lightweight three-dimensional nitrogen/sulphur-codoped graphene sponge
Long-life Li/polysulphide batteries with high sulphur loading enabled by lightweight three-dimensional nitrogen/sulphur-codoped graphene sponge
There is intensive research underway into the cathode development of lithium–sulphur batteries. Here, the authors report a lithium–sulphur battery using nitrogen/sulphur codoped graphene structure which displays excellent electrochemical performance with high sulphur loading.
- Guangmin Zhou
- , Eunsu Paek
- & Arumugam Manthiram
-
Article |
 Hot photocarrier dynamics in organic solar cells
Hot photocarrier dynamics in organic solar cells
An optically excited electrical current flows through an organic solar cell by charge transfer between electron donors and acceptors. Here, the authors use terahertz photoconductivity measurements to show that any energy in excess of that needed to create these carriers can influence charge mobility
- P. A. Lane
- , P. D. Cunningham
- & E. J. Heilweil
-
Article
| Open Access Uphill diffusion and overshooting in the adsorption of binary mixtures in nanoporous solids
Uphill diffusion and overshooting in the adsorption of binary mixtures in nanoporous solids
During the transient adsorption of a binary mixture in a nanoporous host, the concentration of one component may temporarily exceed its equilibrium value, with molecules diffusing in the direction of increasing concentration. Here, the authors use microimaging to examine this process in a real system.
- Alexander Lauerer
- , Tomas Binder
- & Jörg Kärger
-
Article
| Open Access Thermodynamic picture of ultrafast charge transport in graphene
Thermodynamic picture of ultrafast charge transport in graphene
A linear energy–momentum relation of graphene results in a high direct-current electron mobility, but this is not necessarily true at terahertz frequencies. Here, the authors show that its ultrafast conductivity is dependent on a highly nonlinear interplay between heating and cooling of the electron gas.
- Zoltán Mics
- , Klaas-Jan Tielrooij
- & Dmitry Turchinovich
-
Article |
 Self-assembled two-dimensional nanofluidic proton channels with high thermal stability
Self-assembled two-dimensional nanofluidic proton channels with high thermal stability
Two-dimensional materials can be used to construct nanofluidic channels to study molecular transport. Here the authors report a lamellar membrane constructed from exfoliated layers of a clay mineral, which exhibits high proton conductivity and extraordinary thermal stability.
- Jiao-Jing Shao
- , Kalyan Raidongia
- & Jiaxing Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic structural evolution of supported palladium–ceria core–shell catalysts revealed by in situ electron microscopy
Dynamic structural evolution of supported palladium–ceria core–shell catalysts revealed by in situ electron microscopy
There is currently renewed interest in the use of core–shell catalysts for methane combustion. Here, the authors perform anex situ and in situelectron microscopy study to probe the structural evolution of palladium–cerium dioxide catalytic core–shell subunits over a wide temperature range.
- Shuyi Zhang
- , Chen Chen
- & Xiaoqing Pan
-
Article
| Open Access Collisional dynamics in a gas of molecular super-rotors
Collisional dynamics in a gas of molecular super-rotors
Super-rotors are fast rotating molecules whose rotational–translational energy transfer is suppressed. Here the authors study the equilibration of super-rotor gases through molecular dynamics simulations, showing the emergence and explosive termination of an anisotropy in the molecular angular distribution.
- Yuri Khodorkovsky
- , Uri Steinitz
- & Ilya Sh. Averbukh
-
Article
| Open Access Carbon-doped BN nanosheets for metal-free photoredox catalysis
Carbon-doped BN nanosheets for metal-free photoredox catalysis
Metal-free semiconductors with appropriate bandgaps create photocatalytic routes to water splitting and CO2reduction. Here the authors dope hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets with carbon via a simple method to synthesize a ternary B–C–N alloy capable of performing just this function.
- Caijin Huang
- , Cheng Chen
- & Xinchen Wang
-
Article
| Open Access The minimal work cost of information processing
The minimal work cost of information processing
Irreversible computation cannot be performed without a work cost, and energy dissipation imposes limitations on devices' performances. Here the authors show that the minimal work requirement of logical operations is given by the amount of discarded information, measured by entropy.
- Philippe Faist
- , Frédéric Dupuis
- & Renato Renner
-
Article
| Open Access Heat capacity peak at the quantum critical point of the transverse Ising magnet CoNb2O6
Heat capacity peak at the quantum critical point of the transverse Ising magnet CoNb2O6
The archetypal transverse Ising magnet CoNb2O6possesses a set of collective spin modes near its quantum critical point. Here, the authors use heat capacity measurements to evidence the existence of Fermionic gapless spin excitations at the critical point.
- Tian Liang
- , S. M. Koohpayeh
- & N. P. Ong
-
Article
| Open Access Conductance of a single flexible molecular wire composed of alternating donor and acceptor units
Conductance of a single flexible molecular wire composed of alternating donor and acceptor units
Molecular wires with high conductivity and conformable flexibility are desirable in nanoelectronics. Here, Nacci et al.grow flexible molecular wires, composed of alternating donor and acceptor units, on a metal surface, and show that high conductance can be achieved without electronic delocalization.
- Christophe Nacci
- , Francisco Ample
- & Leonhard Grill
-
Article
| Open Access Creation and manipulation of topological states in chiral nematic microspheres
Creation and manipulation of topological states in chiral nematic microspheres
Controlling the topology of matter offers an alternative way to make functional materials, among which liquid crystals hold promise due to their spontaneously occurring defects. Here Orlova et al. demonstrate the formation and remote control of topological structures in frustrated cholesteric droplets.
- Tetiana Orlova
- , Sarah Jane Aßhoff
- & Etienne Brasselet
-
Article
| Open Access Low-temperature thermodynamics with quantum coherence
Low-temperature thermodynamics with quantum coherence
Thermal operations, a model of thermodynamic processes for small quantum systems out of equilibrium, are well-understood in absence of coherence. Here the authors introduce cooling processes, a generalization of thermal operations and find necessary and sufficient conditions for coherent state transitions via cooling processes.
- Varun Narasimhachar
- & Gilad Gour
-
Article
| Open Access Determining the location and nearest neighbours of aluminium in zeolites with atom probe tomography
Determining the location and nearest neighbours of aluminium in zeolites with atom probe tomography
Substitution of framework silicon for aluminium in zeolites affects Brønsted acidity and subsequently catalytic activity. Here, the authors use atom probe tomography to obtain quantitative insights into the spatial distribution of individual aluminium atoms, including their distribution and segregation.
- Daniel E. Perea
- , Ilke Arslan
- & Bert M. Weckhuysen
-
Article
| Open Access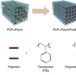 Mixing of immiscible polymers using nanoporous coordination templates
Mixing of immiscible polymers using nanoporous coordination templates
The intimate mixing of immiscible polymers is desirable both to aid understanding of the fundamental science and for the development of new materials. Here, the authors successfully compatibilize polystyrene and poly(methyl methacrylate) using a porous coordination polymer as a removable template.
- Takashi Uemura
- , Tetsuya Kaseda
- & Susumu Kitagawa
-
Article
| Open Access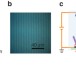 Vibrational spectroscopy at electrolyte/electrode interfaces with graphene gratings
Vibrational spectroscopy at electrolyte/electrode interfaces with graphene gratings
Understanding of electrolyte-electrode interfaces is limited due to the lack of suitable probing techniques. Here, the authors present a vibrational spectroscopy based on graphene gratings, which enables sensitive and interface-specific detection of molecular vibrations at electrolyte-electrode interfaces.
- Ya-Qing Bie
- , Jason Horng
- & Feng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Kinetics and fracture resistance of lithiated silicon nanostructure pairs controlled by their mechanical interaction
Kinetics and fracture resistance of lithiated silicon nanostructure pairs controlled by their mechanical interaction
It is imperative to understand how individual Si nanostructures interact in battery operations. Here, the authors design well-defined crystalline Si nanopillars and show how mechanical interactions of neighbouring Si structures affect their reaction kinetics and fracture resistance during electrochemical lithiation.
- Seok Woo Lee
- , Hyun-Wook Lee
- & Yi Cui
-
Article
| Open Access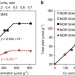 Single-site trinuclear copper oxygen clusters in mordenite for selective conversion of methane to methanol
Single-site trinuclear copper oxygen clusters in mordenite for selective conversion of methane to methanol
Copper-exchanged zeolites with mordenite structure can mimic the active sites in particulate methane monooxygenase. Here, the authors show that mordenite micropores can stabilize trinuclear copper-oxo clusters that exhibit a high reactivity towards activation of carbon–hydrogen bonds in methane.
- Sebastian Grundner
- , Monica A.C. Markovits
- & Johannes A. Lercher
-
Article
| Open Access Enantiomer-specific analysis of multi-component mixtures by correlated electron imaging–ion mass spectrometry
Enantiomer-specific analysis of multi-component mixtures by correlated electron imaging–ion mass spectrometry
Detecting enantiomers in dilute mixtures of volatile organic compounds is a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate a method to identify enantiomers and enantiomeric excess in a multi-component mixture containing two chiral species using laser mass spectrometry and photoelectron circular dichroism.
- Mohammad M Rafiee Fanood
- , N. Bhargava Ram
- & Maurice H. M. Janssen
-
Article
| Open Access Ionic transport in hybrid lead iodide perovskite solar cells
Ionic transport in hybrid lead iodide perovskite solar cells
Understanding the mechanism of ionic transport in organic–inorganic halide perovskites is crucial for the design of future solar cells. Here, Eames et al.undertake a combined experimental and computational study to elucidate the ion conducting species and help rationalize the unusual behaviour observed in these perovskite-based devices.
- Christopher Eames
- , Jarvist M. Frost
- & M. Saiful Islam
-
Article
| Open Access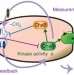 Maxwell’s demon in biochemical signal transduction with feedback loop
Maxwell’s demon in biochemical signal transduction with feedback loop
The connection between information and thermodynamics is embodied in the figure of Maxwell’s demon, a feedback controller. Here, the authors apply thermodynamics of information to signal transduction in chemotaxis of E. coli, predicting that its robustness is quantified by transfer entropy.
- Sosuke Ito
- & Takahiro Sagawa
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing the planar chemistry of two-dimensional heterostructures at the atomic level
Revealing the planar chemistry of two-dimensional heterostructures at the atomic level
The properties of 2D materials such as graphene can vary according to the quality and, for vertical devices, the interfaces between materials. Here, the authors report a method using TOF-SIMS, micro-Raman spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy to give high levels of detail of vertical 2D heterostructures.
- Harry Chou
- , Ariel Ismach
- & Andrei Dolocan
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling dispersion forces between small particles with artificially created random light fields
Controlling dispersion forces between small particles with artificially created random light fields
Natural dispersion forces acting between molecules and particles arise from electromagnetic fields generated by quantum and thermal fluctuations. Here, Brügger et al.show that isotropic dispersion forces between colloidal particles can be induced, controlled and tuned with artificial, fluctuating laser light fields.
- Georges Brügger
- , Luis S. Froufe-Pérez
- & Juan José Sáenz
-
Article
| Open Access The solvation of electrons by an atmospheric-pressure plasma
The solvation of electrons by an atmospheric-pressure plasma
Free, or solvated, electrons in a solution are known to form at the interface between a liquid and a gas. Here, the authors use absorption spectroscopy in a total internal reflection geometry to probe solvated electrons generated at a plasma in contact with the surface of an aqueous solution
- Paul Rumbach
- , David M. Bartels
- & David B. Go
-
Article
| Open Access Role of redox centre in charge transport investigated by novel self-assembled conjugated polymer molecular junctions
Role of redox centre in charge transport investigated by novel self-assembled conjugated polymer molecular junctions
To date, conjugated polymers have not yet been used in molecular junctions despite the fact that they transport charge more efficiently than small-molecular systems. Here, Wang et al.showcase the self-assembly of conjugated polymers into ultrathin films in a planar manner for device construction.
- Zongrui Wang
- , Huanli Dong
- & Wenping Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Conjugated polyelectrolyte hole transport layer for inverted-type perovskite solar cells
Conjugated polyelectrolyte hole transport layer for inverted-type perovskite solar cells
There is intensive research underway into the development of hole transport layers for perovskite solar cells. Here, the authors report an inverted-type perovskite solar cell with low-temperature solution-processable conjugated polyelectrolyte as the hole transport layer, which exhibits an efficiency of over 12%.
- Hyosung Choi
- , Cheng-Kang Mai
- & Alan J. Heeger
-
Article
| Open Access Photonic sensing of organic solvents through geometric study of dynamic reflection spectrum
Photonic sensing of organic solvents through geometric study of dynamic reflection spectrum
Photonic sensing is a method for detecting individual chemical species, but can fail when they are sufficiently similar in physical properties. Here, the authors report a method that can distinguish even very closely related species, such as homologues and chemical isomers.
- Yuqi Zhang
- , Qianqian Fu
- & Jianping Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamics enhanced by HCl doping triggers 60% Pauling entropy release at the ice XII–XIV transition
Dynamics enhanced by HCl doping triggers 60% Pauling entropy release at the ice XII–XIV transition
The preparation of fully proton-ordered ice phases remains challenging and residual entropy usually remains even at the absolute zero. Here, the authors achieve a transition from disordered ice XII to fully ordered ice XIV triggered by HCl doping, which enhances proton transfer dynamics by five orders of magnitude.
- K. W. Köster
- , V. Fuentes-Landete
- & R. Böhmer
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum ferroelectricity in charge-transfer complex crystals
Quantum ferroelectricity in charge-transfer complex crystals
Quantum critical behaviour emerges when quantum fluctuations perturb the balance between electronic states of a material having the same energy, and can lead to novel phenomena. Here, the authors discover quantum criticality in the ferroelectric behaviour of organic molecular solids.
- Sachio Horiuchi
- , Kensuke Kobayashi
- & Yoshinori Tokura
-
Article
| Open Access Facile synthesis of ultrahigh-surface-area hollow carbon nanospheres for enhanced adsorption and energy storage
Facile synthesis of ultrahigh-surface-area hollow carbon nanospheres for enhanced adsorption and energy storage
Well-defined, large surface area nanostructures are promising functional materials but can be difficult to fabricate. Here the authors show how to prepare ultrahigh-surface-area hollow carbon nanospheres, via a controlled carbonization route, and assess their organic vapour adsorption and electrochemical performance.
- Fei Xu
- , Zhiwei Tang
- & Dingcai Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Photogated humidity-driven motility
Photogated humidity-driven motility
Hygroinduced motion is fundamental for applications that require actuation in response to changes in atmospheric humidity. Here, the authors report an actuating material that is capable of fast and perpetual motion driven by humidity gradient incorporating a photoactive dopant that can be controlled by light.
- Lidong Zhang
- , Haoran Liang
- & Panče Naumov
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical reaction mechanisms in solution from brute force computational Arrhenius plots
Chemical reaction mechanisms in solution from brute force computational Arrhenius plots
Obtaining activation entropies and enthalpies of a reaction is important for distinguishing between alternative reaction mechanisms. Here the authors use computational methods to accurately obtain the enthalpic/entropic components of the activation free energy for hydrolytic deamination reactions.
- Masoud Kazemi
- & Johan Åqvist
-
Article
| Open Access Carbonization of a stable β-sheet-rich silk protein into a pseudographitic pyroprotein
Carbonization of a stable β-sheet-rich silk protein into a pseudographitic pyroprotein
The strength and stability of silk proteins is thought to be related to the high content of β-sheets within their structures. Here, the authors show that when heated at high temperature, and above that of thermal degradation, these β-sheets are transformed into an ordered hexagonal graphitic structure.
- Se Youn Cho
- , Young Soo Yun
- & Hyoung-Joon Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Strain induced fragility transition in metallic glass
Strain induced fragility transition in metallic glass
The equivalency of stress and temperature as driving force for the relaxation in metallic glasses is widely accepted. Here, Yu et al.examine this assumption in simulations and find that stress induces a fragile-to-strong transition in addition to accelerated relaxation dynamics as temperature does.
- Hai-Bin Yu
- , Ranko Richert
- & Konrad Samwer
-
Article
| Open Access External stimulation-controllable heat-storage ceramics
External stimulation-controllable heat-storage ceramics
Materials that can store and release heat on demand are of use for energy storage applications. Here, the authors discover a ceramic material that can reversibly store energy from heat, light or electricity and release this energy as heat through the application of pressure.
- Hiroko Tokoro
- , Marie Yoshikiyo
- & Shin-ichi Ohkoshi
-
Article
| Open Access Chirality transfer from gold nanocluster to adsorbate evidenced by vibrational circular dichroism
Chirality transfer from gold nanocluster to adsorbate evidenced by vibrational circular dichroism
The transfer of chirality from surfaces to molecular species may have implications in areas from the origin of homochirality to heterogeneous catalysis. Here, the authors show that a chiral gold cluster can transfer its inherent chirality to adsorbed, achiral molecules, causing them to adopt chiral conformations.
- Igor Dolamic
- , Birte Varnholt
- & Thomas Bürgi

 Mode-selective vibrational modulation of charge transport in organic electronic devices
Mode-selective vibrational modulation of charge transport in organic electronic devices