Research Highlight |
Featured
-
-
Review Article |
 Moving towards personalized treatments of immune-related adverse events
Moving towards personalized treatments of immune-related adverse events
The treatment of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) in patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors has mostly been based on adapting therapeutic approaches used in the management of primary autoimmune diseases. The authors of this Review provide an overview of the different cellular and soluble immune factors involved in the pathogenesis of irAEs in order to help clinicians deliver personalized immunopathologically guided treatment to manage these adverse events.
- Khashayar Esfahani
- , Arielle Elkrief
- & Leonard Calabrese
-
Review Article |
 Tumour-associated neutrophils in patients with cancer
Tumour-associated neutrophils in patients with cancer
Neutrophils accumulate in the circulation of patients with cancer, and the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a widely used biomarker. However, the effects of neutrophils on tumour development and progression, and the efficacy of therapies, remain relatively unknown. In this Review, the authors draw on data from animal models and patients with cancer to provide an overview of the effects of neutrophils in cancer.
- Merav E. Shaul
- & Zvi G. Fridlender
-
Review Article |
 Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer
Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer
The interleukin-6 (IL-6)/Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) pathway is aberrantly hyperactivated in many types of cancer, and such hyperactivation is generally associated with a poor clinical prognosis. In this Review, the authors describe the clinical potential of agents designed to inhibit the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling pathway, either alone or in combination with other agents, in patients with cancer.
- Daniel E. Johnson
- , Rachel A. O'Keefe
- & Jennifer R. Grandis
-
Review Article |
 Perioperative events influence cancer recurrence risk after surgery
Perioperative events influence cancer recurrence risk after surgery
Despite the achievement of locoregional control, a third of patients undergoing surgery for cancer will have disease recurrence. In this Review, the authors describe the potential to optimize the outcomes of patients with cancer by minimizing inflammation and activation of the sympathetic nervous system in the perioperative period, which is often achievable with simple and cost-effective changes in patient-management strategies.
- Jonathan G. Hiller
- , Nicholas J. Perry
- & Erica K. Sloan
-
Review Article |
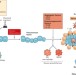 The immune contexture in cancer prognosis and treatment
The immune contexture in cancer prognosis and treatment
Virtually all successful treatments of cancer either create, restore or enhance the antitumour immune response. Therefore, the specific features of the immune microenvironment, both before and after treatment, are important determinants of patients' outcomes. In this Review, the authors describe the influence of the immunological characteristics of the tumour microenvironment on responses to treatment in patients with a variety of cancers.
- Wolf H. Fridman
- , Laurence Zitvogel
- & Guido Kroemer
-
-
Review Article |
 Inflammation and cancer: advances and new agents
Inflammation and cancer: advances and new agents
Tumour-promoting inflammation is an enabling characteristic of many cancers. Conversely, many cancers can cause inflammation. Inflammation in the tumour microenvironment arises from the interplay of many different inflammatory cells and mediators, many of which are potential treatment targets. Herein, the authors review our current knowledge of the interplay between inflammation and tumorigenesis and discuss the potential of treatments that target cancer-related inflammation.
- Shanthini M. Crusz
- & Frances R. Balkwill
-

 Intravesical therapy goes viral
Intravesical therapy goes viral