Review Article |
Featured
-
-
Review Article |
 Cholangiocarcinoma — novel biological insights and therapeutic strategies
Cholangiocarcinoma — novel biological insights and therapeutic strategies
Cholangiocarcinoma is a malignancy that continues to be associated with a dismal prognosis, and a better understanding of the disease biology is required to improve early detection and treatment strategies. In this Review, the authors describe key scientific and clinical advances made in this area over the past 5 years, encompassing novel insights into the tumour stroma and immune microenvironment, promising progress in developing liquid biopsy approaches for diagnosis and monitoring, clinical translation of molecularly targeted therapies, emerging immunotherapies and reassessment of the potential role of liver transplantation.
- Sumera I. Ilyas
- , Silvia Affo
- & Gregory J. Gores
-
Review Article |
 New treatment strategies for advanced-stage gastrointestinal stromal tumours
New treatment strategies for advanced-stage gastrointestinal stromal tumours
Gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST) is the most common form of sarcoma and has become a paradigm of precision medicine owing to the fact that almost all patients harbour one of several known molecule drivers, most of which can be targeted therapeutically. Nevertheless, novel therapeutic strategies are required to overcome the intrinsic resistance of certain subtypes of GIST to existing treatments as well as the acquired resistance that eventually arises in initially sensitive subtypes. This Review describes the biology of GIST, the evolution of the current treatments for this cancer, and the emerging therapeutic agents and approaches that might overcome the remaining clinical challenges.
- Lillian R. Klug
- , Homma M. Khosroyani
- & Michael C. Heinrich
-
Review Article |
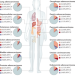 The MYC oncogene — the grand orchestrator of cancer growth and immune evasion
The MYC oncogene — the grand orchestrator of cancer growth and immune evasion
The MYC proto-oncogenes are among the most commonly activated proteins in human cancer, yet the clinical efficacy of MYC-targeted agents remains to be demonstrated. The authors of this Review describe how activation of the MYC pathway affects cancer cells as well as the tumour microenvironment and propose strategies for the therapeutic targeting of MYC-driven cancers.
- Renumathy Dhanasekaran
- , Anja Deutzmann
- & Dean W. Felsher
-
Review Article |
 Clinical and therapeutic relevance of cancer-associated fibroblasts
Clinical and therapeutic relevance of cancer-associated fibroblasts
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are inherently linked with cancers and have long been considered attractive therapeutic targets. However, the existence of several CAF subpopulations with substantial phenotypic and functional heterogeneity and plasticity is increasingly recognized. This Review provides an overview of the heterogeneity of CAFs and its implications with regard to the tumour-promoting and tumour-restraining roles of these cells as well as their clinical relevance in terms of prognostic value and therapeutic potential. The authors also provide insights and perspectives on future research and clinical studies involving CAFs.
- Yang Chen
- , Kathleen M. McAndrews
- & Raghu Kalluri
-
Review Article |
 Therapeutic targeting of the hypoxic tumour microenvironment
Therapeutic targeting of the hypoxic tumour microenvironment
Hypoxia is a common feature of tumours, contributes to many of the hallmarks of cancer and influences responses to anticancer therapies. Thus, strategies to eliminate and/or exploit tumour hypoxia have long been explored, although with limited success to date. Herein, the authors describe new insights into hypoxia biology, discuss the implications of these advances for novel hypoxia-directed therapeutic strategies, and review the progress made with longstanding methods for targeting hypoxic tumours.
- Dean C. Singleton
- , Andrew Macann
- & William R. Wilson
-
Review Article |
 Targeting cancer-promoting inflammation — have anti-inflammatory therapies come of age?
Targeting cancer-promoting inflammation — have anti-inflammatory therapies come of age?
Chronic inflammation can promote the development of various cancers. In this Review, the current clinical advances in ameliorating inflammation for the prevention or treatment of cancer are highlighted, and the experimental insights into the biological mechanisms supporting current and potential novel anti-inflammatory approaches to the management of cancer are discussed.
- Jiajie Hou
- , Michael Karin
- & Beicheng Sun
-
Review Article |
 Tumour budding in solid cancers
Tumour budding in solid cancers
Tumour budding is hypothesized to reflect the invasive and metastatic capacities of cancers and is accordingly associated with unfavourable patient outcomes. Herein, Lugli and colleagues describe the pathobiological characteristics of this phenomenon, including its associations with epithelial–mesenchymal transition and features of the tumour microenvironment, and review the evidence demonstrating the value of tumour budding as a prognostic biomarker across various solid cancers.
- Alessandro Lugli
- , Inti Zlobec
- & Iris D. Nagtegaal
-
Review Article |
 NTRK fusion-positive cancers and TRK inhibitor therapy
NTRK fusion-positive cancers and TRK inhibitor therapy
TRK fusion proteins are pathognomonic in certain rare tumour types and present in a small subset of diverse cancer types, including some common cancers; TRK inhibitors have promising efficacy in the treatment of these cancers, in a histology-agnostic manner. In this Review, the biology of TRK signalling and TRK fusions, strategies to target these drivers, the unique safety profile of TRK inhibitors and mechanisms of and strategies to overcome acquired resistance to these agents are discussed.
- Emiliano Cocco
- , Maurizio Scaltriti
- & Alexander Drilon
-
News & Views |
How to eliminate gastric cancer-related death worldwide?
Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy is effective in preventing gastric cancer, even in patients with advanced pre-neoplastic lesions (gastric atrophy and/or intestinal metaplasia). We must now focus on how to accomplish the goal of eliminating gastric cancer-related death worldwide; strategies for screening and treatment of gastric neoplasia (primary prevention) and post-treatment surveillance (secondary prevention) are discussed herein.
- Yoshio Yamaoka
-
Review Article |
 Targeting the PI3K pathway in cancer: are we making headway?
Targeting the PI3K pathway in cancer: are we making headway?
The PI3K–AKT–mTOR pathway has key roles in tumorigenesis and is dysregulated in most cancers. Consequently, numerous drugs that target key nodes of this pathway have been developed, although few of these agents have been approved for the treatment of cancer. Herein, the authors review the current experience with anticancer therapies that target the PI3K–AKT–mTOR pathway, discuss the challenges that have limited the clinical translation of these agents, and provide perspectives for the future development of these drugs.
- Filip Janku
- , Timothy A. Yap
- & Funda Meric-Bernstam
-
Review Article |
 EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: the mechanistic link and clinical implications
EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: the mechanistic link and clinical implications
According to the cancer stem cell (CSC) paradigm, a minor subpopulation of cancer cells with stem-cell properties predominantly underlies tumour progression, therapy resistance, and disease recurrence. Notably, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is implicated in these processes, and CSCs typically show markers of EMT-programme activation. Herein, the authors outline our current understanding of the links between the EMT programme, the CSC phenotype, metastasis, and drug resistance, and discuss the potential for therapeutic targeting of these facets of tumour biology.
- Tsukasa Shibue
- & Robert A. Weinberg
-
News & Views |
 Are circRNAs involved in cancer pathogenesis?
Are circRNAs involved in cancer pathogenesis?
In a paper published recently in Cell, Guarnerio et al. suggest that circular RNAs derived from cancer-associated chromosomal translocations have an oncogenic role; however, the experimental approach that the authors used was inadequate to generate sufficient evidence to prove this role, calling their study into question.
- Carlo M. Croce
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Cancer metabolism: a therapeutic perspective
Cancer metabolism: a therapeutic perspective
Metabolic reprogramming to support tumour growth is a near universal characteristic of cancer, and thus targeting cancer metabolism has been, and continues to be, a focus for drug-development efforts. In this Review, the authors describe the various metabolic alterations and vulnerabilities of tumours that are potentially important targets for anticancer agents, highlighting both the challenges and opportunities.
- Ubaldo E. Martinez-Outschoorn
- , Maria Peiris-Pagés
- & Michael P. Lisanti
-
-
Review Article |
 Diet, nutrition, and cancer: past, present and future
Diet, nutrition, and cancer: past, present and future
Diet has long been linked with the development and progression of cancer, and indeed obesity is a clear risk factor for many cancers; however, teasing out the relationships between nutritional factors and cancer aetiology has proved difficult, complicating the development of dietary recommendations for cancer prevention. In this Review, the issues and challenges in diet–cancer research are discussed, including those relating to the design of epidemiological studies, dietary data collection methods, and factors that affect the outcome of intervention trials.
- Susan T. Mayne
- , Mary C. Playdon
- & Cheryl L. Rock
-
-
-
News & Views |
 What do breast and CRC cancers and MS have in common?
What do breast and CRC cancers and MS have in common?
Dairy cattle meat and milk factors are proposed as risks for colon and breast cancers. Several novel small circular DNAs that are genetically active in human cells have been isolated from bovine sera and milk. Such agents have also been detected in two lesions of multiple sclerosis. A unifying concept is presented putatively explaining the risks for these diseases that are associated with these factors.
- Harald zur Hausen
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Can oncology recapitulate paleontology? Lessons from species extinctions
Can oncology recapitulate paleontology? Lessons from species extinctions
The evolutionary biology of cancers and organismal species are similar: in both cases, a genetically diverse population mutates and evolves through natural selection. In addition, driving both species and cancers to extinction is extremely difficult. Nevertheless, greater than 99.9% of species that have lived on Earth are now extinct, and the parallels between tumours and organismal evolution suggest that understanding species extinction through paleontology could teach us much about how to eradicate cancers. In this Review, the selective pressures that have driven species extinct and the characteristics of species that make them resistant to extinction are described, and how these factors can be translated to cancers in order to develop improved approaches to therapy and prognosis is discussed.
- Viola Walther
- , Crispin T. Hiley
- & Carlo C. Maley
-
Review Article |
 Using tumour phylogenetics to identify the roots of metastasis in humans
Using tumour phylogenetics to identify the roots of metastasis in humans
The routes and timing of metastatic dissemination during cancer progression remain shrouded in mystery. However, phylogenetic studies are beginning to shed new light on this process and various models have been proposed. In this Review, Kamila Naxerova and Rakesh Jain discuss the hypothesized trajectories of metastasis, and examine the extent to which the current phylogenetic evidence support these models. In addition, the experimental techniques of lineage tracing, their strengths and weaknesses, and future directions for studies using such methods are discussed.
- Kamila Naxerova
- & Rakesh K. Jain
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Sinonasal carcinoma: clinical, pathological, genetic and therapeutic advances
Sinonasal carcinoma: clinical, pathological, genetic and therapeutic advances
The sinonasal cavities are affected by a range of tumour types, the most common of which are sinonasal squamous-cell carcinoma (SNSCC) and intestinal-type adenocarcinoma (ITAC). Compared with the main types of head and neck cancer, these sinonasal cancers have distinct epidemiological, clinical, aetiological, pathological and genetic characteristics, and require specialized treatment, bearing in mind their important anatomical location. All these aspects of ITAC and SNSCC are reviewed in this article.
- José Luis Llorente
- , Fernando López
- & Mario A. Hermsen
-
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Paradoxical oncogenesis—the long-term effects of BRAF inhibition in melanoma
Paradoxical oncogenesis—the long-term effects of BRAF inhibition in melanoma
Although patients with melanoma generally benefit from BRAF or MEK targeted therapies, adverse events can occur on treatment, including the emergence of second malignancies. Evidence suggests unintended or paradoxical activation of MAPK signalling might underlie the majority of these second malignancies. The authors discuss the basis for this paradoxical MAPK activation, and the rationale for novel therapeutic strategies for the management of BRAF-inhibitor-induced neoplasia.
- Geoffrey T. Gibney
- , Jane L. Messina
- & Keiran S. M. Smalley
-
Review Article |
 Clinical opportunities and challenges in targeting tumour dormancy
Clinical opportunities and challenges in targeting tumour dormancy
Tumour dormancy is when cancer sleeps undetected for periods that can last up to decades. The therapeutic potential of inducing or maintaining this dormant period is clear. This Review describes the mechanisms of dormancy and uses genitourinary cancers as models to demonstrate how dormancy principles could be exploited clinically.
- Jonathan A. Hensel
- , Thomas W. Flaig
- & Dan Theodorescu
-

 The roles and implications of RNA m6A modification in cancer
The roles and implications of RNA m6A modification in cancer Study deciphers enigmatic mechanism of PD-L1 overexpression
Study deciphers enigmatic mechanism of PD-L1 overexpression A problem quartered — new subtypes, new solutions?
A problem quartered — new subtypes, new solutions? Intratumour heterogeneity — a game of snakes and ladders
Intratumour heterogeneity — a game of snakes and ladders