Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access A photoacoustic patch for three-dimensional imaging of hemoglobin and core temperature
A photoacoustic patch for three-dimensional imaging of hemoglobin and core temperature
The authors present a wearable photoacoustic patch, which integrates laser diodes and piezoelectric transducers for three-dimensional imaging of hemoglobin and temperature in deep tissues.
- Xiaoxiang Gao
- , Xiangjun Chen
- & Sheng Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Optical-resolution functional gastrointestinal photoacoustic endoscopy based on optical heterodyne detection of ultrasound
Optical-resolution functional gastrointestinal photoacoustic endoscopy based on optical heterodyne detection of ultrasound
The authors developed an optical-fiber-based photoacoustic endoscope for gastroenterology. It can noninvasively view the internal vascular structures and visualize the hemodynamic response in a lesion.
- Yizhi Liang
- , Wubing Fu
- & Bai-Ou Guan
-
Article
| Open Access Giant spin ensembles in waveguide magnonics
Giant spin ensembles in waveguide magnonics
‘Giant atom’ physics occurs when the size of the atomic system becomes comparable to the wavelength of the light it interacts with. For atoms, such a regime is impossible to reach, however, for artificial atomic systems such ‘giant atom’ physics can be explored. Here, Wang et al demonstrate giant spin ensembles, consisting of magnetic spheres coupled to a microwave waveguide.
- Zi-Qi Wang
- , Yi-Pu Wang
- & J. Q. You
-
Article
| Open Access The BrightEyes-TTM as an open-source time-tagging module for democratising single-photon microscopy
The BrightEyes-TTM as an open-source time-tagging module for democratising single-photon microscopy
The authors developed an open-source, low-cost, multi-channel time-tagging module for fluorescence lifetime image scanning microscopy and correlation spectroscopy that can tag in parallel multiple single-photon events with 30 ps precision.
- Alessandro Rossetta
- , Eli Slenders
- & Giuseppe Vicidomini
-
Article
| Open Access Optical cavity-mediated exciton dynamics in photosynthetic light harvesting 2 complexes
Optical cavity-mediated exciton dynamics in photosynthetic light harvesting 2 complexes
Light-matter interaction can induce changes to the properties of the system by creating hybrid collective states of light and molecular excitations, the so called polaritons. Here the authors use femtosecond pump-probe spectroscopy to explore exciton-polariton dynamics in a photosynthetic protein, light harvesting 2 complexes, and find evidence for rapid energy transfer to dark polariton states.
- Fan Wu
- , Daniel Finkelstein-Shapiro
- & Tönu Pullerits
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional Thouless pumping of light in photonic moiré lattices
Two-dimensional Thouless pumping of light in photonic moiré lattices
Extending the control over topological system will open the doors to both fundamental studies and applications. Here the authors demonstrate thouless topological transport of light in a bulk tunable moiré lattice.
- Peng Wang
- , Qidong Fu
- & Fangwei Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Topological polarization singular lasing with highly efficient radiation channel
Topological polarization singular lasing with highly efficient radiation channel
Here the authors develop topological polarization singular lasers that feature paired radiation channels carrying distinct topological properties which leads to single mode lasing with high external quantum efficiency.
- Yun-Gang Sang
- , Jing-Yu Lu
- & Ren-Min Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesized spatiotemporal mode-locking and photonic flywheel in multimode mesoresonators
Synthesized spatiotemporal mode-locking and photonic flywheel in multimode mesoresonators
Here the authors demonstrate spatiotemporal mode-locked dissipative Kerr soliton and enhanced photonic flywheel performances in both the fundamental comb linewidth and DKS timing jitter.
- Mingming Nie
- , Kunpeng Jia
- & Shu-Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Mirror-induced reflection in the frequency domain
Mirror-induced reflection in the frequency domain
We show frequency domain mirrors that provide reflections of optical mode propagation in the frequency domain. We theoretically investigated the mirror properties and experimentally demonstrate it using polarization and coupled-resonator-based coupling on thin film Lithium Niobate.
- Yaowen Hu
- , Mengjie Yu
- & Marko Lončar
-
Article
| Open Access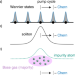 Quantized topological pumping of solitons in nonlinear photonics and ultracold atomic mixtures
Quantized topological pumping of solitons in nonlinear photonics and ultracold atomic mixtures
Synthetic lattice systems are powerful platforms for studying the influence of intrinsic nonlinearities on topological phenomena. Here the authors elucidate the topological transport of solitons in terms of Wannier functions displacement and they introduce a nonlinearity-induced topological transport effect that could be observed in ultracold quantum mixtures.
- Nader Mostaan
- , Fabian Grusdt
- & Nathan Goldman
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent terahertz radiation with 2.8-octave tunability through chip-scale photomixed microresonator optical parametric oscillation
Coherent terahertz radiation with 2.8-octave tunability through chip-scale photomixed microresonator optical parametric oscillation
High-spectral-purity frequency-agile room-temperature THz sources are foundational elements for imaging, sensing, metrology, and communications. Here a parametric oscillator-photomixer chip with coherent 2.8-octave tunable THz radiation is achieved.
- Wenting Wang
- , Ping-Keng Lu
- & Chee Wei Wong
-
Article
| Open Access Zero dispersion Kerr solitons in optical microresonators
Zero dispersion Kerr solitons in optical microresonators
Here, the authors find the missing link for soliton microcombs that exist at the boundary where the group velocity dispersion of light changes sign: zero-dispersion solitons. The resulting microresonator frequency comb, based in Si3N4, spans almost an octave.
- Miles H. Anderson
- , Wenle Weng
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Space-time wave packets localized in all dimensions
Space-time wave packets localized in all dimensions
Propagation-invariant wave packets confined in space and time can be useful for optical sensing, imaging, and nonlinear and quantum optics. Here the authors demonstrate control over the angular dispersion of optical wave packets in two-transverse dimensions to synthesize space-time wave packets localized in all dimensions.
- Murat Yessenov
- , Justin Free
- & Ayman F. Abouraddy
-
Article
| Open Access Frequency wavelength multiplexed optoacoustic tomography
Frequency wavelength multiplexed optoacoustic tomography
Optoacoustic imaging is mostly performed in the time domain. Here the authors demonstrate frequency wavelength multiplexed optoacoustic tomography that can operate at multiple wavelengths simultaneously and offers signal-to-noise ratio advantages over time domain methods.
- Antonios Stylogiannis
- , Ludwig Prade
- & Vasilis Ntziachristos
-
Article
| Open Access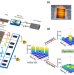 Bayesian tomography of high-dimensional on-chip biphoton frequency combs with randomized measurements
Bayesian tomography of high-dimensional on-chip biphoton frequency combs with randomized measurements
Full tomography of biphoton frequency comb states requires frequency mixing operations which are hard to scale. Here, the authors propose and demonstrate a protocol exploiting advanced Bayesian statistical methods and randomized measurements coming from complex mode mixing in electro-optic phase modulators.
- Hsuan-Hao Lu
- , Karthik V. Myilswamy
- & Joseph M. Lukens
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time precision opto-control of chemical processes in live cells
Real-time precision opto-control of chemical processes in live cells
There is a need to control molecular activities at high spatial precision. Here the authors report a real-time precision opto-control technology that detects a chemical-specific optical response from molecular targets, and precisely control photoswitchable microtubule polymerization inhibitors in cells.
- Matthew G. Clark
- , Gil A. Gonzalez
- & Chi Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access All-fibre heterogeneously-integrated frequency comb generation using silicon core fibre
All-fibre heterogeneously-integrated frequency comb generation using silicon core fibre
Silicon core fibre is a highly nonlinear waveguide that combines the benefits of both fibre and planar waveguide systems. Here, the authors demonstrate frequency comb generation using a fully-fibre integrated silicon core fibre as a nonlinear mixer.
- Ronit Sohanpal
- , Haonan Ren
- & Zhixin Liu
-
Article
| Open Access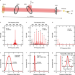 Passive mode-locking and terahertz frequency comb generation in resonant-tunneling-diode oscillator
Passive mode-locking and terahertz frequency comb generation in resonant-tunneling-diode oscillator
The authors report passive mode-locking and frequency-comb generation induced by optical feedback in the resonant-tunneling-diode terahertz oscillator, a semiconductor-based oscillator covering the frequency range of 0.1 to 2 THz.
- Tomoki Hiraoka
- , Yuta Inose
- & Koichiro Tanaka
-
Article
| Open Access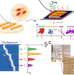 Terahertz thermal curve analysis for label-free identification of pathogens
Terahertz thermal curve analysis for label-free identification of pathogens
A label-free sensing method has been developed for identifying hazardous pathogens based on their intrinsic properties. This was possible by interrogating the temperature-dependent dielectric constant of the microbes in the far-infrared range.
- S. W. Jun
- & Y. H. Ahn
-
Article
| Open Access Creating boundaries along a synthetic frequency dimension
Creating boundaries along a synthetic frequency dimension
The exploration of topological boundary effects is one of the important aspects that could foster the development of future topological photonics devices. Here the authors propose a straightforward method to construct sharp boundaries in synthetic dimensions using a modulated ring resonator strongly coupled to an auxiliary ring.
- Avik Dutt
- , Luqi Yuan
- & Shanhui Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Optomechanical crystal with bound states in the continuum
Optomechanical crystal with bound states in the continuum
Unsuspended optomechanical systems might enable unique applications for quantum sensing and transduction. Here, the authors demonstrate a two-dimensional slab-on-substrate optomechanical crystal empowered by mechanical bound states in the continuum.
- Shengyan Liu
- , Hao Tong
- & Kejie Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Optical linewidth of soliton microcombs
Optical linewidth of soliton microcombs
Understanding noise dynamics in frequency combs is crucial for applications. Here, the authors study the phase noise dynamics and the linewidth of soliton microcombs, revealing that some comb lines can be more quiet than the pump laser itself.
- Fuchuan Lei
- , Zhichao Ye
- & Victor Torres-Company
-
Article
| Open Access A continuum of bright and dark-pulse states in a photonic-crystal resonator
A continuum of bright and dark-pulse states in a photonic-crystal resonator
A Kerr-nonlinear resonator with normal dispersion supports bright and dark pulse states. With photonic crystal ring resonators, this work demonstrates a continuum across these nonlinear states and explores the underlying mechanism.
- Su-Peng Yu
- , Erwan Lucas
- & Scott B. Papp
-
Article
| Open Access Diamond mirrors for high-power continuous-wave lasers
Diamond mirrors for high-power continuous-wave lasers
Mirrors that demonstrate 98% reflectivity and withstand 10 kilowatts of focused continuous-wave laser light are created by nanoscale fabrication of single-crystal diamond. The work finds applications in medicine, defence, industry, and communications.
- Haig A. Atikian
- , Neil Sinclair
- & Marko Lončar
-
Article
| Open Access Two octave supercontinuum generation in a non-silica graded-index multimode fiber
Two octave supercontinuum generation in a non-silica graded-index multimode fiber
Two-octave supercontinuum generation in the femtosecond regime from the visible to mid-infrared and self-cleaning dynamics are reported in a non-silica graded-index multimode fiber with nanostructured design and enhanced nonlinearity.
- Zahra Eslami
- , Lauri Salmela
- & Goëry Genty
-
Article
| Open Access Platicon microcomb generation using laser self-injection locking
Platicon microcomb generation using laser self-injection locking
’Here the authors provide the demonstration of platicon comb generation in an integrated photonic chip using laser self-injection locking, They take advantage of platicons generation in normal GVD resonators, which significantly relaxes the material and geometry design restrictions
- Grigory Lihachev
- , Wenle Weng
- & Tobias J. Kippenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Silicon-photonics acoustic detector for optoacoustic micro-tomography
Silicon-photonics acoustic detector for optoacoustic micro-tomography
High-resolution photoacoustic tomography is challenging due to reduced efficiency of miniaturized piezoelectric elements. Here, the authors fabricate a miniaturized silicon-photonics acoustic detector coated with a sensitivity-enhancing elastomer, and demonstrate high-resolution in vivo imaging.
- Yoav Hazan
- , Ahiad Levi
- & Amir Rosenthal
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient Kerr soliton comb generation in micro-resonator with interferometric back-coupling
Efficient Kerr soliton comb generation in micro-resonator with interferometric back-coupling
Increasing the conversion efficiency of soliton crystals will enable further application of optical frequency comb. Here the authors engineer an hybrid Mach-Zehnder micro-ring resonator to achieve 80% pump-to-comb conversion efficiency based on dissipative Kerr solitons.
- J. M. Chavez Boggio
- , D. Bodenmüller
- & T. Hansson
-
Article
| Open Access Deep tissue localization and sensing using optical microcavity probes
Deep tissue localization and sensing using optical microcavity probes
Optical microcavities are useful as probes in cells due to their narrow emission spectra and high sensitivity to environment. Here, the authors use the unique spectral features of microcavities, which are unaffected by tissue scattering, and show 3D localisation and tracking of cells deep in tissues.
- Aljaž Kavčič
- , Maja Garvas
- & Matjaž Humar
-
Article
| Open Access Fast custom wavelet analysis technique for single molecule detection and identification
Fast custom wavelet analysis technique for single molecule detection and identification
The authors introduce an accurate, fast and efficient technique to analyze sensory data. They use a continuous wavelet transform concept to look for certain patterns in noisy raw data. The superiority of this approach is demonstrated with fluorescence signals from a chip-based, optofluidic single particle sensor.
- Vahid Ganjalizadeh
- , Gopikrishnan G. Meena
- & Holger Schmidt
-
Article
| Open Access All-optical dissipative discrete time crystals
All-optical dissipative discrete time crystals
Discrete time crystals are described by a subharmonic response with respect to an external drive and have been mostly observed in closed periodically-driven systems. Here, the authors demonstrate a dissipative discrete time crystal in a Kerr-nonlinear optical microcavity pumped by two lasers.
- Hossein Taheri
- , Andrey B. Matsko
- & Krzysztof Sacha
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrastable microwave and soliton-pulse generation from fibre-photonic-stabilized microcombs
Ultrastable microwave and soliton-pulse generation from fibre-photonic-stabilized microcombs
A compact yet high-performance stabilization method has been the missing ingredient for microcombs. Here, optical fibre is used for stabilizing microcombs, enabling the generation of ultrastable soliton pulses and microwaves from palm-sized platforms
- Dohyeon Kwon
- , Dongin Jeong
- & Jungwon Kim
-
Comment
| Open Access Connecting reservoir computing with statistical forecasting and deep neural networks
Connecting reservoir computing with statistical forecasting and deep neural networks
Among the existing machine learning frameworks, reservoir computing demonstrates fast and low-cost training, and its suitability for implementation in various physical systems. This Comment reports on how aspects of reservoir computing can be applied to classical forecasting methods to accelerate the learning process, and highlights a new approach that makes the hardware implementation of traditional machine learning algorithms practicable in electronic and photonic systems.
- Lina Jaurigue
- & Kathy Lüdge
-
Article
| Open Access Comparing ultrastable lasers at 7 × 10−17 fractional frequency instability through a 2220 km optical fibre network
Comparing ultrastable lasers at 7 × 10−17 fractional frequency instability through a 2220 km optical fibre network
Precision measurement plays an important role in frequency metrology and optical communications. Here the authors compare two geographically separate ultrastable lasers at 7 × 10−17 fractional frequency instability over a 2220 km optical fibre link and these measurements can be useful for dissemination of ultrastable light to distant optical clocks.
- M. Schioppo
- , J. Kronjäger
- & G. Grosche
-
Article
| Open Access Coherent phase transfer for real-world twin-field quantum key distribution
Coherent phase transfer for real-world twin-field quantum key distribution
Exploiting technologies derived from the optical clocks community, the authors demonstrate a setup for twin-field QKD which extends the coherence times by three orders of magnitude, overcoming the main challenge towards real-world implementation.
- Cecilia Clivati
- , Alice Meda
- & Davide Calonico
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time ultrafast oscilloscope with a relativistic electron bunch train
Real-time ultrafast oscilloscope with a relativistic electron bunch train
A travelling wave inside a metal slit can reveal its own waveform by probing deflecting motions of charged particles. Here, a real-time THz oscilloscope was demonstrated by utilizing the relativistic electrons and the subwavelength slit waveguide.
- In Hyung Baek
- , Hyun Woo Kim
- & Young Uk Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access A H2O2-activatable nanoprobe for diagnosing interstitial cystitis and liver ischemia-reperfusion injury via multispectral optoacoustic tomography and NIR-II fluorescent imaging
A H2O2-activatable nanoprobe for diagnosing interstitial cystitis and liver ischemia-reperfusion injury via multispectral optoacoustic tomography and NIR-II fluorescent imaging
Fluorescent imaging in the second biological window has advantages for in vivo applications. Here, the authors synthesise a molecular nanoprobe which activates upon binding H2O2, generating both strong fluorescent NIR-II emission and ultrasound signal for multi-mode imaging of inflammatory diseases.
- Junjie Chen
- , Longqi Chen
- & Yanli Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Architecture for microcomb-based GHz-mid-infrared dual-comb spectroscopy
Architecture for microcomb-based GHz-mid-infrared dual-comb spectroscopy
Chip-based architectures for mid-infrared gas sensing could enable many applications. In this direction, the authors demonstrate a microcomb-based dual-comb spectroscopy sensor with GHz resolution in the mid-IR band, with stability completely determined by a single high-Q microresonator.
- Chengying Bao
- , Zhiquan Yuan
- & Kerry J. Vahala
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic apposition compound eye fabricated using microfluidic-assisted 3D printing
Biomimetic apposition compound eye fabricated using microfluidic-assisted 3D printing
Insect-like biomimetic compound eyes have many technological applications. Here, the authors present a facile fabrication scheme involving microfluidics assisted 3D printing that permits to completely separate design, optimization and construction of optical and sensor components.
- Bo Dai
- , Liang Zhang
- & Dawei Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Laser nano-filament explosion for enabling open-grating sensing in optical fibre
Laser nano-filament explosion for enabling open-grating sensing in optical fibre
Engineered stop bands to sense an ambient environment can enable many applications. Here, the authors demonstrate well-controlled processes to open high-aspect ratio nanoholes through optical fibre for Bragg gratings in the telecomm spectrum and to enable high-resolution refractive index sensing
- Keivan Mahmoud Aghdami
- , Abdullah Rahnama
- & Peter R. Herman
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast optical circuit switching for data centers using integrated soliton microcombs
Ultrafast optical circuit switching for data centers using integrated soliton microcombs
Optical technologies could enable fast and power-efficient networks for data centers. Here, the authors report Si3N4 microcomb based ultrafast photonic switching to provide enhanced performance for data center applications.
- Arslan Sajid Raja
- , Sophie Lange
- & Hitesh Ballani
-
Article
| Open Access Angle-based wavefront sensing enabled by the near fields of flat optics
Angle-based wavefront sensing enabled by the near fields of flat optics
Generally, wavefronts are measured using angle-based sensors like the Shack-Hartmann sensor. Here, the authors present an angle-sensitive device that uses flat optics integrated on a focal plane array for compact wavefront sensing with improved resolution.
- Soongyu Yi
- , Jin Xiang
- & Zongfu Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Aluminum nitride nanophotonics for beyond-octave soliton microcomb generation and self-referencing
Aluminum nitride nanophotonics for beyond-octave soliton microcomb generation and self-referencing
Though octave soliton microcombs are attractive for on-chip metrology and optical clocks, limitations in existing materials lead to increased chip integration complexity. Here, the authors report access to octave soliton microcombs and self-referencing using aluminium nitride nanophotonic chips.
- Xianwen Liu
- , Zheng Gong
- & Hong X. Tang
-
Article
| Open Access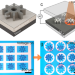 Reconfigurable multi-component micromachines driven by optoelectronic tweezers
Reconfigurable multi-component micromachines driven by optoelectronic tweezers
Light-driven micromotors can convert energy to motion in sub-millimeter dimensions. Here, the authors extend this concept and introduce reconfigurable micromachines with multiple components, driven by optoelectronic tweezers, and demonstrate new functionalities.
- Shuailong Zhang
- , Mohamed Elsayed
- & Aaron R. Wheeler
-
Article
| Open Access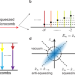 A squeezed quantum microcomb on a chip
A squeezed quantum microcomb on a chip
Microcombs operating in the deterministic quantum regime could lead to new applications. Here, the authors demonstrate a quantum microcomb consisting of 20 two-mode squeezed comb pairs, in an optical microresonator on a silicon chip.
- Zijiao Yang
- , Mandana Jahanbozorgi
- & Xu Yi
-
Article
| Open Access Visible light photonic integrated Brillouin laser
Visible light photonic integrated Brillouin laser
In this work the authors demonstrate on-chip integration of Brillouin lasing operating at visible wavelengths, with engineered design for stable output. This technical and scientific advance will help develop integrated light sources for quantum computing or atomic and molecular spectroscopy.
- Nitesh Chauhan
- , Andrei Isichenko
- & Daniel J. Blumenthal
-
Article
| Open Access Frequency comb ptychoscopy
Frequency comb ptychoscopy
Frequency-comb-based multiheterodyne spectroscopy requires that total bandwidth of the measured spectrum covers less than half the comb spacing, which is usually not the case for incoherent spectra. Here, the authors propose a technique that lifts this requirement, and demonstrate it in the microwave regime.
- David J. Benirschke
- , Ningren Han
- & David Burghoff
-
Article
| Open Access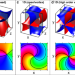 Engineering phase and polarization singularity sheets
Engineering phase and polarization singularity sheets
Metasurfaces allow for vast possibilities of light control. Here, the authors demonstrate on-demand engineering and realization of a broad family of two-dimensional phase singularity sheets and transverse polarization singularity sheets, opening up new aspects of light-matter interaction.
- Soon Wei Daniel Lim
- , Joon-Suh Park
- & Federico Capasso
-
Article
| Open Access Vectorial Doppler metrology
Vectorial Doppler metrology
The Doppler effect is a wave phenomenon that can find the magnitude of velocity of moving targets with scalar waves. Here, the authors use vectorially structured light with spatially variant polarization to fully determine both the magnitude of velocity and motion direction of a moving particle.
- Liang Fang
- , Zhenyu Wan
- & Jian Wang

 Multi-dimensional data transmission using inverse-designed silicon photonics and microcombs
Multi-dimensional data transmission using inverse-designed silicon photonics and microcombs