Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Reconfigurable exciton-plasmon interconversion for nanophotonic circuits
Reconfigurable exciton-plasmon interconversion for nanophotonic circuits
Here the authors demonstrate functionality for on-chip optical communications via reconfigurable exciton-plasmon interconversion in 200 nm-diameter silver nanowires overlapping onto two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide transistors.
- Hyun Seok Lee
- , Dinh Hoa Luong
- & Young Hee Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Topological magnetoplasmon
Topological magnetoplasmon
The two dimensional magnetoplasmon edge state has been observed for a long time, but its nature is yet to be uncovered. Here, Jin et al. report that such a state is actually topological protected, analogous to the chiral Majorana edge state in a p-wave topological superconductor.
- Dafei Jin
- , Ling Lu
- & Nicholas X. Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Demonstration of a chip-based optical isolator with parametric amplification
Demonstration of a chip-based optical isolator with parametric amplification
Non-reciprocal optical elements usually require the presence of magnetic fields, which makes chip integration difficult. Here, Hua et al. demonstrate a non-magnetic optical isolator with bidirectional injection on a silicon platform utilizing parametric amplification in four-wave mixing.
- Shiyue Hua
- , Jianming Wen
- & Min Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Simultaneous Faraday filtering of the Mollow triplet sidebands with the Cs-D1 clock transition
Simultaneous Faraday filtering of the Mollow triplet sidebands with the Cs-D1 clock transition
Hybrid quantum systems combine efficient high-quality quantum dot sources with atomic vapours that can serve as precise frequency standards or quantum memories. Here, Portalupi et al. demonstrate an optimized atomic Cs-Faraday filter working with single photons emitted from a semiconductor quantum dot.
- Simone Luca Portalupi
- , Matthias Widmann
- & Ilja Gerhardt
-
Article
| Open Access Generation of single photons with highly tunable wave shape from a cold atomic ensemble
Generation of single photons with highly tunable wave shape from a cold atomic ensemble
Generation of narrowband pure and storable single photons is an enabling step towards hybrid quantum networks interconnecting different systems. Here the authors report on a heralded single photon source based on a cold ensemble of atoms with controllable emission time and high photon shape tunability.
- Pau Farrera
- , Georg Heinze
- & Hugues de Riedmatten
-
Article
| Open Access Electromagnon dispersion probed by inelastic X-ray scattering in LiCrO2
Electromagnon dispersion probed by inelastic X-ray scattering in LiCrO2
Whilst terahertz optical spectroscopy allows for the study of coupled spin and lattice excitations, it is limited in momentum space. Here, the authors use inelastic x-ray scattering to demonstrate strong magnon-phonon coupling and electromagnon excitations across the Brillouin zone of LiCrO2.
- Sándor Tóth
- , Björn Wehinger
- & Christian Rüegg
-
Article
| Open Access Nanomechanical electro-optical modulator based on atomic heterostructures
Nanomechanical electro-optical modulator based on atomic heterostructures
Van der Waals heterostructures can be combined with metallic nanostructures to enable enhanced light–matter interaction. Here, the authors fabricate a broadband mechanical electro-optical modulator using a graphene/hexagonal boron nitride vertical heterojunction, suspended over a gold nanostripe array.
- P. A. Thomas
- , O. P. Marshall
- & A. N. Grigorenko
-
Article
| Open Access Mid-infrared ultra-high-Q resonators based on fluoride crystalline materials
Mid-infrared ultra-high-Q resonators based on fluoride crystalline materials
Highly sensitive trace-gas detection is possible in the mid-infrared range with transparent microresonators. Here, the authors directly measure the necessary ultra-high quality factors of microresonators made from fluoride crystal materials using a tapered chalcogenide fibre.
- C. Lecaplain
- , C. Javerzac-Galy
- & T. J. Kippenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Quantum memory with strong and controllable Rydberg-level interactions
Quantum memory with strong and controllable Rydberg-level interactions
Quantum information processing requires long-storage time of quantum states, but this typically comes at the expense of their addressability. Here the authors developed a method that exploits interaction between Rydberg and ground states of an atom reporting fast state generation and long-term storage.
- Lin Li
- & A Kuzmich
-
Article
| Open Access Phase retrieval by coherent modulation imaging
Phase retrieval by coherent modulation imaging
Robust coherent diffractive imaging generally requires many exposures that may damage samples. Here, the authors develop a single-shot X-ray imaging method applicable to general samples for materials and biological sciences, also enabling imaging of dynamic processes, using a pulsed X-ray laser.
- Fucai Zhang
- , Bo Chen
- & Ian K. Robinson
-
Article
| Open Access Selectively tunable optical Stark effect of anisotropic excitons in atomically thin ReS2
Selectively tunable optical Stark effect of anisotropic excitons in atomically thin ReS2
The optical Stark effect is a light-matter interaction phenomenon that can be used to address and control exciton states in semiconductors. Here, the authors achieve optical tuning of the Stark effect of an individual exciton state in few-layer ReS2with varying light polarization.
- Sangwan Sim
- , Doeon Lee
- & Hyunyong Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Proposal and proof-of-principle demonstration of non-destructive detection of photonic qubits using a Tm:LiNbO3 waveguide
Proposal and proof-of-principle demonstration of non-destructive detection of photonic qubits using a Tm:LiNbO3 waveguide
Rare-earth doped crystals are a promising platform for developing quantum devices. Here, Sinclair et al. propose and demonstrate a concept for non-destructive detection of photonic qubits using solid-state waveguides, which could help reduce signal losses in quantum information processing.
- N. Sinclair
- , K. Heshami
- & W. Tittel
-
Article
| Open Access Jahn-Teller-induced femtosecond electronic depolarization dynamics of the nitrogen-vacancy defect in diamond
Jahn-Teller-induced femtosecond electronic depolarization dynamics of the nitrogen-vacancy defect in diamond
Understanding ultrafast dynamics of excited states of nitrogen-vacancy helps its manipulation for technological applications. Here the authors use polarization anisotropy spectroscopy and molecular dynamics to investigate sub-picosecond dephasing dynamics, identifying the origin of orbital averaging effects.
- Ronald Ulbricht
- , Shuo Dong
- & Zhi-Heng Loh
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetofermionic condensate in two dimensions
Magnetofermionic condensate in two dimensions
The motion of particles in a quantum condensate state are described by a single macroscopic wave function, leading to a host of unusual properties. Here, the authors generate such a condensation of magnetically induced excitons, known as cyclotron magnetoexcitons, in a high-mobility quantum well.
- L. V. Kulik
- , A. S. Zhuravlev
- & S. Schmult
-
Article
| Open Access High spatial dynamics-photoluminescence imaging reveals the metallurgy of the earliest lost-wax cast object
High spatial dynamics-photoluminescence imaging reveals the metallurgy of the earliest lost-wax cast object
Photoluminescence is a powerful probe of chemical composition and structure, but it is challenging to image heterogeneous materials over large scale. Thoury et al. develop a full-field imaging approach to map two cuprous oxide phases in the earliest known lost-wax cast artefact manufactured 6,000 years ago.
- M. Thoury
- , B. Mille
- & L. Bertrand
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast all-optical coherent control of single silicon vacancy colour centres in diamond
Ultrafast all-optical coherent control of single silicon vacancy colour centres in diamond
All-optical coherent control schemes offer well-localized and ultrafast control of individual qubits in many-qubit systems. Here the authors report on all-optical resonant and Raman-based control of single silicon vacancies using picosecond pulses, much faster than the ground state coherence time.
- Jonas Nils Becker
- , Johannes Görlitz
- & Christoph Becher
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous time delays and quantum weak measurements in optical micro-resonators
Anomalous time delays and quantum weak measurements in optical micro-resonators
Interference of linear plane waves produces non-trivial phenomena in both classical and quantum wave systems. Here, the authors describe and observe anomalously large time delays and frequency shifts in the resonant inelastic scattering of a 1D wave packet near a zero of the scattering coefficient.
- M. Asano
- , K. Y. Bliokh
- & F. Nori
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasensitive plasmonic sensing in air using optical fibre spectral combs
Ultrasensitive plasmonic sensing in air using optical fibre spectral combs
Fibre sensors are key to many minimally-invasive detection techniques but, owing to an index mismatch, they are often limited to aqueous environments. Here, Caucheteur et al. develop a high-resolution fibre gas sensor with a tilted in-fibre grating that allows coupling to higher-order plasmon modes.
- Christophe Caucheteur
- , Tuan Guo
- & Jacques Albert
-
Article
| Open Access Continuous injection synthesis of indium arsenide quantum dots emissive in the short-wavelength infrared
Continuous injection synthesis of indium arsenide quantum dots emissive in the short-wavelength infrared
Indium arsenide quantum dots are promising materials for short-wavelength infrared emissive applications. Here, the authors investigate the kinetics of indium arsenide nanocrystal growth and design large quantum dots with narrow emission wavelengths which can be used for through-skull fluorescence imaging.
- Daniel Franke
- , Daniel K. Harris
- & Moungi G. Bawendi
-
Article
| Open Access Cascaded emission of single photons from the biexciton in monolayered WSe2
Cascaded emission of single photons from the biexciton in monolayered WSe2
Atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides constitute an ideal platform to investigate solid state excitonic effects. Here, the authors provide experimental evidence of a localized biexciton in a monolayer of WSe2, which induces an emission cascade of single photons.
- Yu-Ming He
- , Oliver Iff
- & Christian Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access Photomotility of polymers
Photomotility of polymers
The demand for soft robots urges the development of new light-responsive materials for remotely powered actuation. Here, Wie et al. show directional motion over centimeter scales using azobenzene-functionalized liquid crystalline polymer films upon continuous radiation from ultraviolet to visible light.
- Jeong Jae Wie
- , M. Ravi Shankar
- & Timothy J. White
-
Article
| Open Access High-energy electron emission from metallic nano-tips driven by intense single-cycle terahertz pulses
High-energy electron emission from metallic nano-tips driven by intense single-cycle terahertz pulses
High-energy electron sources are powerful tools for investigating dynamics at atomic and subatomic scales. Here, Li and Jones demonstrate the terahertz-driven emission of electrons with energies exceeding five kiloelectronvolts from nano-tips and study its dependence on the tip radius.
- Sha Li
- & R. R. Jones
-
Article
| Open Access Increasing the density of passive photonic-integrated circuits via nanophotonic cloaking
Increasing the density of passive photonic-integrated circuits via nanophotonic cloaking
Photonic-integrated devices need to be spaced apart to prevent signal crosstalk, which limits their packing density. Here, Shen et al. report the use of nanophotonic cloaking to render neighbouring devices invisible to one another, which allows them to be placed closer together than is otherwise achievable.
- Bing Shen
- , Randy Polson
- & Rajesh Menon
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental verification of multipartite entanglement in quantum networks
Experimental verification of multipartite entanglement in quantum networks
Multipartite entangled states are a fundamental resource for quantum information processing tasks; it is thus important to verify their presence. Here the authors present and demonstrate a protocol that allows any party in a network to verify if an untrusted source is distributing multipartite entangled states.
- W. McCutcheon
- , A. Pappa
- & M. S. Tame
-
Article
| Open Access Excitonic linewidth and coherence lifetime in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides
Excitonic linewidth and coherence lifetime in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides
The interplay between dark and bright excitons has a significant impact on the optical properties of semiconducting transition metal dichalcogenides. Here, the authors perform computational and experimental studies which unveil the microscopic origin of the excitonic coherence lifetime in WS2 and MoSe2.
- Malte Selig
- , Gunnar Berghäuser
- & Andreas Knorr
-
Article
| Open Access Photoemission-based microelectronic devices
Photoemission-based microelectronic devices
Most microelectronic devices today exploit the electronic properties of semiconductors. Here, the authors demonstrate a microelectronic device for free-space electrons by using the enhanced fields in a microstructured metal surface to induce effective photoemission.
- Ebrahim Forati
- , Tyler J. Dill
- & Dan Sievenpiper
-
Article
| Open Access Exploiting the speckle-correlation scattering matrix for a compact reference-free holographic image sensor
Exploiting the speckle-correlation scattering matrix for a compact reference-free holographic image sensor
Holographic techniques store and retrieve complete optical information, but the requirement of a reference beam can make the process complicated and sensitive to noise. Here, the authors develop a reference-free method that harnesses self-interference in a diffusive scattering medium.
- KyeoReh Lee
- & YongKeun Park
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature Tamm-plasmon exciton-polaritons with a WSe2 monolayer
Room-temperature Tamm-plasmon exciton-polaritons with a WSe2 monolayer
Thanks to their strong light-matter interaction, atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenides are ideal active materials for cavity quantum electrodynamics. Here, the authors embed a WSe2monolayer within a Tamm-plasmon-polariton cavity, and observe exciton-polariton formation at room temperature.
- Nils Lundt
- , Sebastian Klembt
- & Christian Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access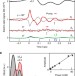 Ultrafast photocurrents at the surface of the three-dimensional topological insulator Bi2Se3
Ultrafast photocurrents at the surface of the three-dimensional topological insulator Bi2Se3
Surface currents in topological insulators can be controlled by light, but the underlying mechanisms are not well understood. Here, Braun et al. report an ultrafast shift photocurrent at the surface of Ca-doped Bi2Se3, whereas injection currents are much smaller than expected from asymmetric depopulation of the Dirac cone.
- Lukas Braun
- , Gregor Mussler
- & Tobias Kampfrath
-
Article
| Open Access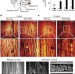 Monitoring peripheral nerve degeneration in ALS by label-free stimulated Raman scattering imaging
Monitoring peripheral nerve degeneration in ALS by label-free stimulated Raman scattering imaging
Sensitive and label-free imaging methods to visualize nerve degeneration are currently lacking. Here authors show that stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) microscopy can be used to monitor peripheral nerve degeneration in mouse models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and in postmortem tissue from ALS patients.
- Feng Tian
- , Wenlong Yang
- & Kevin Eggan
-
Article
| Open Access Hybrid metamaterials for electrically triggered multifunctional control
Hybrid metamaterials for electrically triggered multifunctional control
Despite their exotic properties active metamaterials, where active materials are introduced to advance tunability, switchability and nonlinearity, are seldom reported. Here, Liu et al. demonstrate a vanadium dioxide integrated photonic metamaterial as a transformative platform for multifunctional control.
- Liu Liu
- , Lei Kang
- & Douglas H. Werner
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution from the plasmon to exciton state in ligand-protected atomically precise gold nanoparticles
Evolution from the plasmon to exciton state in ligand-protected atomically precise gold nanoparticles
Little is known about the transition of a metal nanoparticle from the plasmonic to excitonic state. Here, the authors map this evolution in atomically precise gold nanoparticles, a critical step for understanding the origins of surface plasmon resonance, metallic bonding, and catalytic behaviour.
- Meng Zhou
- , Chenjie Zeng
- & Rongchao Jin
-
Article
| Open Access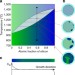 Laser recrystallization and inscription of compositional microstructures in crystalline SiGe-core fibres
Laser recrystallization and inscription of compositional microstructures in crystalline SiGe-core fibres
Using SiGe in the core of optical fibres extends the wavelength range and potential optical functionality, but fabrication challenges exist. Here, Coucheronet al. report the fabrication and tailoring of SiGe-core optical fibres using CO2laser irradiation to heat the glass cladding and recrystallize the core.
- David A. Coucheron
- , Michael Fokine
- & Ursula J. Gibson
-
Article
| Open Access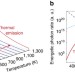 Thermally enhanced photoluminescence for heat harvesting in photovoltaics
Thermally enhanced photoluminescence for heat harvesting in photovoltaics
In photovoltaics, sub-band gap energy photons can be harvested using up-conversion strategies. Here, the authors show that the thermally enhanced up-converted photoluminescence results in enhanced energy conversion, for an accessible temperature range and with a broad range of incident photon energy.
- Assaf Manor
- , Nimrod Kruger
- & Carmel Rotschild
-
Article
| Open Access Scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy with low-repetition-rate pulsed light source through phase-domain sampling
Scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy with low-repetition-rate pulsed light source through phase-domain sampling
Low repetition rate lasers are suitable for studying nonlinear optical phenomena, while near-field microscopy allows high spatial resolution for nanomaterial characterisation. Here, Wang et al. enable scattering-type near-field microscopy with low repetition rate lasers through phase-domain sampling.
- Haomin Wang
- , Le Wang
- & Xiaoji G. Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Chiral optical response of planar and symmetric nanotrimers enabled by heteromaterial selection
Chiral optical response of planar and symmetric nanotrimers enabled by heteromaterial selection
Alternative ways to fabricate chiral media which give rise to interesting optical phenomena are sought. Here, Banzeret al. demonstrate a two-dimensional geometrically achiral nanoparticle assembly, which exhibits a chiral optical response due to its heterogeneous composition.
- Peter Banzer
- , Paweł Woźniak
- & Robert W. Boyd
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging and controlling plasmonic interference fields at buried interfaces
Imaging and controlling plasmonic interference fields at buried interfaces
Visualizing surface plasmon polaritons at buried interfaces has remained elusive. Here, the authors develop a methodology to study the spatiotemporal evolution of buried near-fields within complex heterostructures, enabling the characterization of the next generation of plasmonic devices.
- Tom T. A. Lummen
- , Raymond J. Lamb
- & F. Carbone
-
Article
| Open Access High-harmonic generation by field enhanced femtosecond pulses in metal-sapphire nanostructure
High-harmonic generation by field enhanced femtosecond pulses in metal-sapphire nanostructure
It has been suggested that strong field enhancement for high harmonic generation may be achievable with nano-antennas. Here, the authors show relevant field enhancement using a metal-sapphire nanostructure that provides a solid tip as the high harmonic emitter, replacing commonly used gaseous atoms.
- Seunghwoi Han
- , Hyunwoong Kim
- & Seung-Woo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Giant Kerr response of ultrathin gold films from quantum size effect
Giant Kerr response of ultrathin gold films from quantum size effect
When plasmonic structures reach the nanoscale, quantum size effects become important for their optical properties. Here, Qian et al. find a giant third-order nonlinear Kerr response from nanometre thick gold quantum wells, which they attribute to quantum size effects.
- Haoliang Qian
- , Yuzhe Xiao
- & Zhaowei Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Near-infrared exciton-polaritons in strongly coupled single-walled carbon nanotube microcavities
Near-infrared exciton-polaritons in strongly coupled single-walled carbon nanotube microcavities
The formation of exciton-polaritons in organic semiconductors by strong coupling to a cavity is a promising route towards electrically pumped organic lasers. Here, Graf et al. demonstrate strong coupling from semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes in the near infrared frequency range.
- Arko Graf
- , Laura Tropf
- & Malte C. Gather
-
Article
| Open Access Single-shot observation of optical rogue waves in integrable turbulence using time microscopy
Single-shot observation of optical rogue waves in integrable turbulence using time microscopy
A rogue wave is an unexpected oscillation of large amplitude and is an example of the spontaneous formation of a coherent structure out of disorder. Here, the authors develop an experimental strategy that can provide snapshots in time and thus record the real shape of optical rogue waves emerging from random noise.
- Pierre Suret
- , Rebecca El Koussaifi
- & Serge Bielawski
-
Article
| Open Access Interplay between evanescence and disorder in deep subwavelength photonic structures
Interplay between evanescence and disorder in deep subwavelength photonic structures
Features much smaller than the wavelength are not expected to have a significant impact on the transport of a wave. Here, the authors show that Anderson localization can dominate light transport in a one-dimensional disordered system, even when the disordered features are a thousand times smaller than the wavelength.
- Hanan Herzig Sheinfux
- , Ido Kaminer
- & Mordechai Segev
-
Article
| Open Access Thermopile detector of light ellipticity
Thermopile detector of light ellipticity
Differences in the intensity of the left- and right-circularly polarized components of light can provide useful information about the chirality of electromagnetic radiation. Here, the authors demonstrate a monolithic photodetector that translates this difference in incident radiation directly into a voltage
- Feng Lu
- , Jongwon Lee
- & Mikhail A. Belkin
-
Article
| Open Access Photonic crystals possessing multiple Weyl points and the experimental observation of robust surface states
Photonic crystals possessing multiple Weyl points and the experimental observation of robust surface states
To realize Weyl points carrying topological charges higher than one is challenging. Here, Chen et al. report a photonic crystal possessing single and multiple Weyl points with topological charges of two and three using planar fabrication technology.
- Wen-Jie Chen
- , Meng Xiao
- & C. T. Chan
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental determination of excitonic band structures of single-walled carbon nanotubes using circular dichroism spectra
Experimental determination of excitonic band structures of single-walled carbon nanotubes using circular dichroism spectra
The experimental determination of band structure of single wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) is a challenging task, and often must be theoretically predicted. Here, the authors separate SWCNTs in high purity and experimentally determine their excitonic band structures using circular dichroism spectra.
- Xiaojun Wei
- , Takeshi Tanaka
- & Hiromichi Kataura
-
Article
| Open Access Self-assembled fibre optoelectronics with discrete translational symmetry
Self-assembled fibre optoelectronics with discrete translational symmetry
The thermal-draw technique offers fibre devices with a multiplicity of geometries, but these are constrainted to being translationally symmetric. Here, the authors disrupt this symmetry by applying selective capillary instability, resulting in electrically connected spherical photodetecting elements.
- Michael Rein
- , Etgar Levy
- & Yoel Fink
-
Article
| Open Access Self-amplified photo-induced gap quenching in a correlated electron material
Self-amplified photo-induced gap quenching in a correlated electron material
The non-equilibrium dynamics of correlated electron materials are still poorly understood. Here, the authors use time- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy to show that carrier multiplication is important in initial non-equilibrium dynamics of 1T-TiSe2and depends on the size of the energy gap.
- S. Mathias
- , S. Eich
- & M. Aeschlimann
-
Article
| Open Access The optical frequency comb fibre spectrometer
The optical frequency comb fibre spectrometer
An ideal optical frequency-comb system should combine both single-line spectral resolution and a bandwidth broad enough to cover as many lines as possible. Here, the authors incorporate a fibre spectrometer to detect approximately 500 comb-lines with an instrument resolution of 120 megahertz.
- Nicola Coluccelli
- , Marco Cassinerio
- & Gianluca Galzerano
-
Article
| Open Access Projection-type see-through holographic three-dimensional display
Projection-type see-through holographic three-dimensional display
The design of holographic displays usually involves a trade-off between size and viewing angle. Here, the authors combine holographic projection with a digitally designed holographic optical element so that display size and the visual angle can be designed independently.
- Koki Wakunami
- , Po-Yuan Hsieh
- & Kenji Yamamoto

 Miniature optical planar camera based on a wide-angle metasurface doublet corrected for monochromatic aberrations
Miniature optical planar camera based on a wide-angle metasurface doublet corrected for monochromatic aberrations