Featured
-
-
Perspective |
 Carbon nanotubes as emerging quantum-light sources
Carbon nanotubes as emerging quantum-light sources
This Perspective describes the recent advances in understanding and controlling the properties of single-wall carbon nanotubes as well as the progress towards the fabrication of new electrically driven single-photon sources.
- X. He
- , H. Htoon
- & C. Voisin
-
News & Views |
 Virtues of defects
Virtues of defects
Defects in mercury telluride quantum dots can be exploited to achieve amplified spontaneous emission under continuous-wave optical pumping at ultralow power levels.
- Frank Wise
-
News & Views |
 Electrifying quantum dots for lasers
Electrifying quantum dots for lasers
Compositional grading of colloidal quantum dots enables electrically driven amplification of light, bringing electrically driven lasers from these materials very close.
- Ifor Samuel
-
Article |
 Charge-transfer dynamics and nonlocal dielectric permittivity tuned with metamaterial structures as solvent analogues
Charge-transfer dynamics and nonlocal dielectric permittivity tuned with metamaterial structures as solvent analogues
Charge-transfer dynamics in organic semiconductors are shown to be altered by multi-layered hyperbolic metamaterial substrates, an effect linked to the number of metal–dielectric pairs used.
- Kwang Jin Lee
- , Yiming Xiao
- & Pascal André
-
News & Views |
 Harmony with superatoms
Harmony with superatoms
The thermal conductivities of superatom crystals have significant contributions from extended phonon states and show a remarkable temperature dependence due to orientational ordering.
- Longji Cui
- , Edgar Meyhofer
- & Pramod Reddy
-
News & Views |
 Shrinking the camera size
Shrinking the camera size
A miniaturized camera has been developed by integrating a planar metasurface lens doublet with a CMOS image sensor. The metasurface lens doublet corrects the monochromatic aberration and thus delivers nearly diffraction-limited image quality over a wide field of view.
- Cheng Sun
-
Article |
 Solution-based electrical doping of semiconducting polymer films over a limited depth
Solution-based electrical doping of semiconducting polymer films over a limited depth
A solution process for the diffusion of dopants in organic semiconducting films over a limited depth has been developed. The method is applied to single polymers and donor–acceptor mixtures, and for the realization of single-layer solar cells.
- Vladimir A. Kolesov
- , Canek Fuentes-Hernandez
- & Bernard Kippelen
-
Letter |
 Valley photonic crystals for control of spin and topology
Valley photonic crystals for control of spin and topology
A theoretically proposed photonic crystal design with valley-dependent spin-split bulk bands allows for the independent control of valley and topology in a single system.
- Jian-Wen Dong
- , Xiao-Dong Chen
- & Xiang Zhang
-
News & Views |
 Prime time
Prime time
In the past decade, artificial materials with unusual wave interactions have significantly evolved and matured. In honour of the tenth anniversary of the premiere metamaterials conference, we look at the directions in which this field is evolving, and its impact on technology.
- Andrea Alù
-
Article |
 Linear topology in amorphous metal oxide electrochromic networks obtained via low-temperature solution processing
Linear topology in amorphous metal oxide electrochromic networks obtained via low-temperature solution processing
Electrochromic films based on tin-doped indium oxide nanocrystals dispersed in a niobium oxide glass are now realized from solution at room temperature. The chain-like topology of niobium oxide improves the electrochemical properties of these films.
- Anna Llordés
- , Yang Wang
- & Delia J. Milliron
-
Article |
 Exploring the origin of high optical absorption in conjugated polymers
Exploring the origin of high optical absorption in conjugated polymers
The photocurrent generated in organic photodetectors and solar cells can be enhanced by increasing light absorption in the active layer. It is now shown that an extended persistence length can increase the oscillator strength of conjugated polymers.
- Michelle S. Vezie
- , Sheridan Few
- & Jenny Nelson
-
-
News & Views |
 Flexible yet robust
Flexible yet robust
Researchers have experimentally demonstrated a new type of pathway for electromagnetic waves, which allows an easy reconfiguration into various shapes while significantly suppressing backscattering.
- Bo Zhen
- & Marin Soljačić
-
Article |
 Extreme sensitivity biosensing platform based on hyperbolic metamaterials
Extreme sensitivity biosensing platform based on hyperbolic metamaterials
A highly sensitive plasmonic biosensor, based on hyperbolic metamaterials, can detect biomolecules of ultralow molecular weight at picomolar concentrations.
- Kandammathe Valiyaveedu Sreekanth
- , Yunus Alapan
- & Giuseppe Strangi
-
News & Views |
 Hand-twisting light
Hand-twisting light
Macroscopic deformation can induce chirality in initially achiral nanoparticle composites, and reversibly modulate their chiroptical properties.
- Daeyeon Lee
- & Sang Eon Han
-
Progress Article |
 Electromagnetic toroidal excitations in matter and free space
Electromagnetic toroidal excitations in matter and free space
A review on toroidal excitations, from static toroidal moments in condensed matter, to dynamic toroidal multipoles demonstrated experimentally with metamaterials.
- N. Papasimakis
- , V. A. Fedotov
- & N. I. Zheludev
-
Article |
 Robust reconfigurable electromagnetic pathways within a photonic topological insulator
Robust reconfigurable electromagnetic pathways within a photonic topological insulator
Topologically protected states at the interface of magnetic domain walls in a parallel plate waveguide with adjustable rods, are shown to be directed along different paths, as the waveguide geometry changes.
- Xiaojun Cheng
- , Camille Jouvaud
- & Alexander B. Khanikaev
-
Article |
 Structured light enables biomimetic swimming and versatile locomotion of photoresponsive soft microrobots
Structured light enables biomimetic swimming and versatile locomotion of photoresponsive soft microrobots
Soft biomimetic microswimmers and microrobots made of photoactive liquid-crystal elastomers and whose body shape is controlled by structured light are able to self-propel and perform complex motion patterns on demand.
- Stefano Palagi
- , Andrew G. Mark
- & Peer Fischer
-
Article |
 A small-molecule dye for NIR-II imaging
A small-molecule dye for NIR-II imaging
A renally cleared, water-soluble dye emitting in the near-infrared-imaging (NIR)-II window outperforms a clinically approved NIR-I dye in the in vivo imaging of tumours and their nearby blood and lymphatic vasculatures.
- Alexander L. Antaris
- , Hao Chen
- & Hongjie Dai
-
-
Review Article |
 Programmable and adaptive mechanics with liquid crystal polymer networks and elastomers
Programmable and adaptive mechanics with liquid crystal polymer networks and elastomers
This Review discusses stimuli-responsive liquid crystalline polymer networks and elastomers as materials with programmable mechanics for use in functional devices.
- Timothy J. White
- & Dirk J. Broer
-
-
Article |
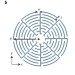 Ultra-sparse metasurface for high reflection of low-frequency sound based on artificial Mie resonances
Ultra-sparse metasurface for high reflection of low-frequency sound based on artificial Mie resonances
An ultraslow-fluid-like unit cell composed of acoustic channels, arranged in a zigzag shape, exhibits various tunable Mie resonances. It is used for the construction of a highly reflective metasurface that can efficiently block low-frequency sound.
- Y. Cheng
- , C. Zhou
- & X. J. Liu
-
News & Views |
 Large-scale dielectric metasurfaces
Large-scale dielectric metasurfaces
Researchers develop a simple and low-cost fabrication method for the production of large-scale all-dielectric metasurfaces, which exhibit near-perfect reflectivity in the telecommunications spectral window.
- Nicolas Bonod
-
Article |
 Backward phase-matching for nonlinear optical generation in negative-index materials
Backward phase-matching for nonlinear optical generation in negative-index materials
Phase matching in the backward direction—the so-called nonlinear mirror effect—is demonstrated experimentally between the fundamental and second harmonic, using two distinct modes in a metal–dielectric–metal waveguide.
- Shoufeng Lan
- , Lei Kang
- & Wenshan Cai
-
-
Letter |
 Spectroscopic evidence for negative electronic compressibility in a quasi-three-dimensional spin–orbit correlated metal
Spectroscopic evidence for negative electronic compressibility in a quasi-three-dimensional spin–orbit correlated metal
Electron filling causes a reduction of the chemical potential in (Sr1−x Lax)3Ir2O7, which suggests negative electronic compressibility. Studying the concomitant change of the bandgap provides insight into the physical mechanism behind this effect.
- Junfeng He
- , T. Hogan
- & Rui-Hua He
-
-
Article |
 Continuous control of the nonlinearity phase for harmonic generations
Continuous control of the nonlinearity phase for harmonic generations
A concept for the phase control of the nonlinear susceptibility using the left- and right-circular polarization basis for fundamental and harmonic generated light is introduced and tested using metasurfaces containing plasmonic antennas.
- Guixin Li
- , Shumei Chen
- & Shuang Zhang
-
-
Letter |
 Picosecond energy transfer and multiexciton transfer outpaces Auger recombination in binary CdSe nanoplatelet solids
Picosecond energy transfer and multiexciton transfer outpaces Auger recombination in binary CdSe nanoplatelet solids
Fast fluorescence resonance energy transfer between CdSe nanoplatelets on a picosecond timescale is measured. This process is faster than Auger recombination and leads to the observation of multiexcitonic energy transfer in these materials.
- Clare E. Rowland
- , Igor Fedin
- & Richard D. Schaller
-
Article |
 A photoreversible protein-patterning approach for guiding stem cell fate in three-dimensional gels
A photoreversible protein-patterning approach for guiding stem cell fate in three-dimensional gels
An approach that exploits two bioorthogonal photochemistries to achieve reversible immobilization of full-length proteins in synthetic hydrogels allows for the reversible differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells to osteoblasts.
- Cole A. DeForest
- & David A. Tirrell
-
-
-
Article |
 Multimodal plasmonics in fused colloidal networks
Multimodal plasmonics in fused colloidal networks
Harnessing the optical properties of noble metals down to the nanoscale is crucial for fast information processing. Lateral confinement and delocalization of surface plasmons is now observed in self-assembled network chains of fused gold nanoparticles.
- Alexandre Teulle
- , Michel Bosman
- & Erik Dujardin
-
-
Article |
 Digital metamaterials
Digital metamaterials
Inspired by Boolean binary algebra, an approach to design electromagnetic metamaterials with desired permittivity by using just two elemental building blocks is demonstrated analytically and numerically.
- Cristian Della Giovampaola
- & Nader Engheta
-
Letter |
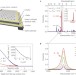 Realization of dynamic thermal emission control
Realization of dynamic thermal emission control
The dynamic control of thermal emission via the control of emissivity through intersubband absorption in n-type quantum wells, at a speed four orders of magnitude faster than is currently possible, is now demonstrated.
- Takuya Inoue
- , Menaka De Zoysa
- & Susumu Noda
-
Letter |
 Reconfigurable 3D plasmonic metamolecules
Reconfigurable 3D plasmonic metamolecules
Until now, it has not been possible to switch chirality in plasmonic nanostructures at will and repeatedly. Now, thanks to DNA-regulated conformational changes, reconfigurable 3D plasmonic metamolecules with switchable chirality have been created.
- Anton Kuzyk
- , Robert Schreiber
- & Na Liu
-
Letter |
 Stretchable liquid-crystal blue-phase gels
Stretchable liquid-crystal blue-phase gels
Liquid-crystalline elastomers combine rubber-like elasticity with the optical properties of liquid crystals, yet some of their properties depend on the particular liquid-crystal phase. Now, stretchable gels of the liquid-crystalline blue-phase I are reported. The blue-phase gels are electro-optically switchable under a moderate applied voltage, and their optical properties can be manipulated by an applied strain.
- F. Castles
- , S. M. Morris
- & H. J. Coles
-
Article |
 Engineering of light confinement in strongly scattering disordered media
Engineering of light confinement in strongly scattering disordered media
Disordered photonic materials have the ability to control the flow of light through random multiple scattering. This has the drawback of randomizing both the direction and phase of the propagating light. Now, confined and interacting light modes are demonstrated for a two-dimensional disordered photonic structure.
- Francesco Riboli
- , Niccolò Caselli
- & Diederik S. Wiersma
-
News & Views |
 Going soft
Going soft
The experimental observation of polariton condensates at room temperature in soft organic materials makes the study of quantum condensed phases easily accessible and opens inroads to optoelectronic devices based on macroscopic quantum phenomena.
- Pavlos Lagoudakis
-
Review Article |
 Flat optics with designer metasurfaces
Flat optics with designer metasurfaces
Metamaterials are artificially fabricated materials that allow for the control of light and acoustic waves in a manner that is not possible in nature. This Review covers the recent developments in the study of so-called metasurfaces, which offer the possibility of controlling light with ultrathin, planar optical components.
- Nanfang Yu
- & Federico Capasso
-
Letter |
 Observing bulk diamond spin coherence in high-purity nanodiamonds
Observing bulk diamond spin coherence in high-purity nanodiamonds
The photoluminescent properties of electron spins at nitrogen–vacancy (NV) centres are promising for use in quantum information and magnetometry. It is now shown that the coherence times of NV centres in nanodiamonds can be engineered to be comparable to those of bulk diamond.
- Helena S. Knowles
- , Dhiren M. Kara
- & Mete Atatüre
-
News & Views |
 A little twist with big consequences
A little twist with big consequences
A study on the subtle interplay between electronic structure and structural defects now explains why the suppression of conduction in the insulating state of bilayer graphene is not as strong as might be expected. It also reveals the possibility of creating graphene-based nanoscale systems with unique electronic properties.
- Philip Hofmann
-
News & Views |
 A source of energetic electrons
A source of energetic electrons
Photoexcited diamond can inject highly energetic electrons in solution and promote the catalysis of a broad range of chemical reactions.
- Christoph E. Nebel
-
Article |
 Photo-illuminated diamond as a solid-state source of solvated electrons in water for nitrogen reduction
Photo-illuminated diamond as a solid-state source of solvated electrons in water for nitrogen reduction
Solid-state catalysts do not participate efficiently in the reduction of N2 to NH3 because they tend not to form strong bonds with nitrogen molecules. It is now shown that, under ultraviolet radiation, hydrogen-terminated diamond can eject electrons directly in a liquid solution, thus allowing nitrogen reduction without requiring its preliminary adsorption on a solid surface.
- Di Zhu
- , Linghong Zhang
- & Robert J. Hamers
-
-
Article |
 Photonic topological insulators
Photonic topological insulators
Non-trivial topological phases can allow for one-way spin-polarized transport along the interfaces of topological insulators but they are relatively uncommon in the condensed state of matter. By arranging judiciously designed metamaterials into two-dimensional superlattices, a photonic topological insulator has now been demonstrated theoretically, enabling unidirectional spin-polarized photon propagation without the application of external magnetic fields or breaking of time-reversal symmetry.
- Alexander B. Khanikaev
- , S. Hossein Mousavi
- & Gennady Shvets

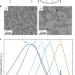 Impacts of surface depletion on the plasmonic properties of doped semiconductor nanocrystals
Impacts of surface depletion on the plasmonic properties of doped semiconductor nanocrystals None more black
None more black Ultrafast responses
Ultrafast responses Diamonds in waveguides
Diamonds in waveguides Silicon qubits
Silicon qubits