Featured
-
-
Article |
 All-optical multilevel physical unclonable functions
All-optical multilevel physical unclonable functions
Employing light-transformable polymers, multiple physical unclonable functions are demonstrated within a single device with all-optical reversible reconfigurability. Such devices may enable quantum secure authentication and nonlinear cryptographic key generation applications.
- Sara Nocentini
- , Ulrich Rührmair
- & Francesco Riboli
-
News & Views |
 Quadrupolar excitons take the stage
Quadrupolar excitons take the stage
Hybridized electron or hole states across semiconducting van der Waals monolayers in heterotrilayer systems enable the emergence of quadrupolar excitons. Quadrupolar excitons, unlike their dipolar counterparts, have a tunable static dipole moment that responds nonlinearly under an applied electric field.
- Elyse Barré
- , Medha Dandu
- & Archana Raja
-
Article |
 Compact angle-resolved metasurface spectrometer
Compact angle-resolved metasurface spectrometer
Employing a miniaturized spectrometer that combines a metasurface-based spectrometer array and a metalens, angle-resolved spectral imaging is achieved with a wavelength accuracy of 0.17 nm, spectral resolution of 0.40 nm and angular resolution of 4.88 × 10−3 rad for a spectrometer with a 4 × 4 μm2 footprint.
- Guiyi Cai
- , Yanhao Li
- & Qinghai Song
-
News & Views |
 Designer quantum dot molecules and beyond
Designer quantum dot molecules and beyond
Quantum dots couple to form artificial molecules that allow for variable colour emission in response to an electric field.
- James Cassidy
- , Justin Ondry
- & Dmitri V. Talapin
-
Research Briefing |
 A spin-optical monolayer laser based on a photonic spin lattice
A spin-optical monolayer laser based on a photonic spin lattice
Inspired by valley pseudospins in two-dimensional materials, high-quality-factor (high-Q) spin–valley states were created through the photonic Rashba-type spin splitting of a bound state in the continuum. This approach enabled the construction of a coherent and controllable spin-optical laser using monolayer-integrated spin–valley microcavities without requiring magnetic fields or cryogenic temperatures.
-
Article |
 Broadband mid-infrared non-reciprocal absorption using magnetized gradient epsilon-near-zero thin films
Broadband mid-infrared non-reciprocal absorption using magnetized gradient epsilon-near-zero thin films
Using doped InAs multilayers under moderate external magnetic fields with gradient epsilon-near-zero frequencies, broadband non-reciprocal absorption that can be tailored within the mid-infrared spectral region has been demonstrated.
- Mengqi Liu
- , Shuang Xia
- & Cheng-Wei Qiu
-
Article |
 Electric-field-induced colour switching in colloidal quantum dot molecules at room temperature
Electric-field-induced colour switching in colloidal quantum dot molecules at room temperature
Current quantum dot emitters are limited to small-spectral-range colour tuning accompanied by intensity reduction. Electric-field-induced reversible emission colour switching without intensity loss can be achieved on a single-particle level in quantum dot molecules with two coupled emission centres.
- Yonatan Ossia
- , Adar Levi
- & Uri Banin
-
Article |
 Spin-valley Rashba monolayer laser
Spin-valley Rashba monolayer laser
The authors introduce a spin-optical laser based on a monolayer transition metal dichalcogenide coupled to a heterostructure microcavity supporting high-Q spin-valley resonances originating from photonic Rashba-type spin splitting of a bound state in the continuum.
- Kexiu Rong
- , Xiaoyang Duan
- & Erez Hasman
-
Research Briefing |
 Scalar photonic crystals with non-radiative topological surface modes
Scalar photonic crystals with non-radiative topological surface modes
A scalar scheme has been proposed to design photonic crystals that possess bulk dispersions resembling scalar waves and surface modes that support skyrmion-like textures. This approach addresses the challenges of realizing three-dimensional topological photonic crystals, which usually have complicated dispersions and leaky surface modes inside the light cone.
-
Article |
 Scalar topological photonic nested meta-crystals and skyrmion surface states in the light cone continuum
Scalar topological photonic nested meta-crystals and skyrmion surface states in the light cone continuum
Employing connected coaxial waveguides on a nested meta-crystal configuration, the authors design photonic crystals with scalar-wave-like band dispersions, facilitating the search for topological phases in three-dimensional photonic crystals.
- Biao Yang
- , Qinghua Guo
- & C. T. Chan
-
Article
| Open Access Intrinsic strong light-matter coupling with self-hybridized bound states in the continuum in van der Waals metasurfaces
Intrinsic strong light-matter coupling with self-hybridized bound states in the continuum in van der Waals metasurfaces
The authors demonstrate strong coupling in bound state in the continuum metasurfaces on nanostructured bulk WS2 and exhibiting sharp resonances with tailored linewidths and controllable light-matter coupling strength.
- Thomas Weber
- , Lucca Kühner
- & Andreas Tittl
-
News & Views |
 Writing above the bandgap
Writing above the bandgap
Above-bandgap, nanosecond laser pulses enable the localized in situ writing of spin defects in prefabricated nanophotonic cavities. The approach preserves defect and cavity mode properties, key requirements towards cavity–emitter coupling in quantum networks.
- Sridhar Majety
- & Marina Radulaski
-
Article |
 Strongly enhanced light–matter coupling of monolayer WS2 from a bound state in the continuum
Strongly enhanced light–matter coupling of monolayer WS2 from a bound state in the continuum
Combining a tungsten disulfide monolayer and a topologically protected bound state in the continuum formed by a one-dimensional photonic crystal, strong light–matter interaction enhancement and large exciton–polariton nonlinearities at room temperature are demonstrated.
- Eugenio Maggiolini
- , Laura Polimeno
- & Dario Ballarini
-
Letter |
 Ambipolar charge-transfer graphene plasmonic cavities
Ambipolar charge-transfer graphene plasmonic cavities
Employing an oxidation-activated charge transfer strategy to oxidize transition-metal dichalcogenides into transition-metal oxides, the authors imprint plasmonic cavities with laterally abrupt doping profiles and nanoscale precision demonstrating plasmonic whispering-gallery resonators.
- Brian S. Y. Kim
- , Aaron J. Sternbach
- & D. N. Basov
-
Article |
 From enhanced diffusion to ultrafast ballistic motion of hybrid light–matter excitations
From enhanced diffusion to ultrafast ballistic motion of hybrid light–matter excitations
The authors study ultrafast spatiotemporal dynamics of polaritons formed by mixing surface-bound optical waves with excitons observing a mobility transition from diffusive to ballistic transport flow at two-thirds the speed of light.
- Mukundakumar Balasubrahmaniyam
- , Arie Simkhovich
- & Tal Schwartz
-
Article |
 Topological steering of light by nematic vortices and analogy to cosmic strings
Topological steering of light by nematic vortices and analogy to cosmic strings
Liquid crystal (LC) applications typically rely on defining the non-topological spatial patterns of the optical axis. Here, the authors demonstrate the topological steering of light by LC nematic vortices, futher establishing an analogy between topological light steering by LC vortices and cosmic strings.
- Cuiling Meng
- , Jin-Sheng Wu
- & Ivan I. Smalyukh
-
Article
| Open Access Exchange controlled triplet fusion in metal–organic frameworks
Exchange controlled triplet fusion in metal–organic frameworks
Triplet-fusion-based photon upconversion is promising for photovoltaic or bioimaging applications, but its efficiency is limited by triplet fusion spin dependence. Here, the authors tailor spin dynamics by engineering the crystal structure with metal–organic frameworks to enable effective spin mixing between singlet and quintet triplet–triplet pair states.
- Dong-Gwang Ha
- , Ruomeng Wan
- & Mircea Dincă
-
News & Views |
 Metasurfaces provide the extra bling
Metasurfaces provide the extra bling
Structuring surfaces coated with nanoparticles in the subwavelength range allows almost complete control over the optical appearance of an object.
- Frank Scheffold
-
Letter |
 Scalable optical manufacture of dynamic structural colour in stretchable materials
Scalable optical manufacture of dynamic structural colour in stretchable materials
Desired for optical sensing or visual communications, structural colour-changing materials are hindered by the lack of scalable manufacturing. Here, by adapting Lippmann photography, large-area manufacturing of colour patterns in photosensitive elastomers is realized.
- Benjamin Harvey Miller
- , Helen Liu
- & Mathias Kolle
-
News & Views |
 Large excitons in light-dress
Large excitons in light-dress
Giant exciton–polaritons come to the scene from a thin Cu2O crystal sandwiched by a microcavity. Their anticipated strong interactions may facilitate the development of a promising Rydberg solid-state platform for quantum technologies.
- HeeBong Yang
- & Na Young Kim
-
Article |
 The visual appearances of disordered optical metasurfaces
The visual appearances of disordered optical metasurfaces
A multiscale modelling platform combining nanoscale resonant scattering, mesoscale multiple scattering and macroscale light transport effectively predicts the macroscopic visual effects created by optical metamaterials with disordered nanostructures.
- Kevin Vynck
- , Romain Pacanowski
- & Philippe Lalanne
-
Article |
 Single-junction organic solar cells with over 19% efficiency enabled by a refined double-fibril network morphology
Single-junction organic solar cells with over 19% efficiency enabled by a refined double-fibril network morphology
The morphology of donor–acceptor blends in organic photovoltaics dictates the efficiency of the exciton dissociation and charge diffusion, and thus the final device performance. Here, the authors show that filament assembly helps to maximize the output, further enabling a power conversion efficiency greater than 19%.
- Lei Zhu
- , Ming Zhang
- & Feng Liu
-
Article |
 Rydberg exciton–polaritons in a Cu2O microcavity
Rydberg exciton–polaritons in a Cu2O microcavity
Cu2O is a promising platform to host Rydberg exciton–polaritons, where excitons strongly couple to cavity photons, however their realization has been elusive. Here, the authors report Rydberg exciton–polaritons with principal quantum numbers up to n = 6.
- Konstantinos Orfanakis
- , Sai Kiran Rajendran
- & Hamid Ohadi
-
Article |
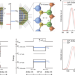 Interface polarization in heterovalent core–shell nanocrystals
Interface polarization in heterovalent core–shell nanocrystals
Controlled synthesis of heterostructured III-V–II-VI nanocrystals shows that dipole moments formed at the core–shell interface can tune the optoelectronic properties of these nanomaterials and their performance in light-emitting devices.
- Byeong Guk Jeong
- , Jun Hyuk Chang
- & Wan Ki Bae
-
News & Views |
 On-demand emission from Tamm plasmons
On-demand emission from Tamm plasmons
Tamm plasmon thermal emitters can provide efficient infrared emission, but are limited by design complexity. Now, the inverse design of Tamm modes facilitated by CdO films on aperiodic dielectric reflectors enables emission with an on-demand spectrum.
- Juerg Leuthold
- & Alexander Dorodnyy
-
Article |
 Deterministic inverse design of Tamm plasmon thermal emitters with multi-resonant control
Deterministic inverse design of Tamm plasmon thermal emitters with multi-resonant control
Tamm plasmon thermal emitters can provide low-cost, efficient mid to long infrared emission, but have been limited by a challenging design. Here the authors apply an inverse design protocol to demonstrate tailorable multi-band emission on CdO films.
- Mingze He
- , J. Ryan Nolen
- & Joshua D. Caldwell
-
Article |
 Confining isolated chromophores for highly efficient blue phosphorescence
Confining isolated chromophores for highly efficient blue phosphorescence
A strategy to confine phosphorescent organic chromophores within ionic crystals proves effective in suppressing non-radiative recombination channels and increasing the phosphorescence efficiency of blue-emitting heavy-atom-free emitters.
- Wenpeng Ye
- , Huili Ma
- & Wei Huang
-
Review Article |
 Single organic molecules for photonic quantum technologies
Single organic molecules for photonic quantum technologies
This Review discusses the photophysical properties and nonlinear behaviour of single molecules, and their use as single-photon sources and in single-molecule sensing and quantum-sensing applications.
- C. Toninelli
- , I. Gerhardt
- & M. Orrit
-
Article |
 Mechano-tunable chiral metasurfaces via colloidal assembly
Mechano-tunable chiral metasurfaces via colloidal assembly
Stacked elastomeric arrays containing plasmonic nanoparticles show efficient chiral responses that can be fully controlled by mechanical compression and stack rotation. These simple layered materials may be useful modulators for photonic applications.
- Patrick T. Probst
- , Martin Mayer
- & Andreas Fery
-
Article |
 Mid-infrared radiative emission from bright hot plasmons in graphene
Mid-infrared radiative emission from bright hot plasmons in graphene
The optical emission of graphene under pumping with femtosecond laser pulses contains a strong component linked to plasmon emission from the hot electrons in the system.
- Laura Kim
- , Seyoon Kim
- & Harry A. Atwater
-
Article |
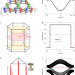 Higher-order topological semimetal in acoustic crystals
Higher-order topological semimetal in acoustic crystals
A second-order topological Weyl semimetal based on a 3D-printed acoustic crystal, exhibiting Weyl points, Fermi arc surface states, and hinge states, has been experimentally demonstrated.
- Qiang Wei
- , Xuewei Zhang
- & Suotang Jia
-
Article |
 Creation of moiré bands in a monolayer semiconductor by spatially periodic dielectric screening
Creation of moiré bands in a monolayer semiconductor by spatially periodic dielectric screening
The moiré pattern that is formed between well-aligned graphene and hexagonal boron nitride can modify the properties of WSe2 (placed close by without intentional angle alignment), leading to the formation of a mini Brillouin zone and the folding of the bands in WSe2.
- Yang Xu
- , Connor Horn
- & Kin Fai Mak
-
News & Views |
 Flatland, lineland and dotland
Flatland, lineland and dotland
Correlated real-space imaging and optical measurements of twisted MoSe2/WSe2 bilayers reveal strain-induced modulations of the moiré potential landscape, tuning arrays of 0D traps into 1D stripes and leading to substantial changes in the optical response of the heterostructures.
- Long Zhang
- & Hui Deng
-
News & Views |
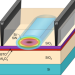 Optical switches and modulators in deep freeze
Optical switches and modulators in deep freeze
The integration of silicon-based waveguides with barium titanate thin films enables the realization of efficient electro-optic switches and modulators operating at cryogenic temperatures, offering promising opportunities for quantum technologies.
- Goran Z. Mashanovich
-
Letter |
 An integrated optical modulator operating at cryogenic temperatures
An integrated optical modulator operating at cryogenic temperatures
The integration of barium titanate thin films with silicon-based waveguides enables the operation of efficient electro-optic switches and modulators at temperatures as low as 4 K, with potential applications in quantum computing and cryogenic computing technologies.
- Felix Eltes
- , Gerardo E. Villarreal-Garcia
- & Stefan Abel
-
Article |
 Dipolar interactions between localized interlayer excitons in van der Waals heterostructures
Dipolar interactions between localized interlayer excitons in van der Waals heterostructures
Repulsive dipole–dipole interactions between localized interlayer excitons are shown to modify the optical response of van der Waals heterobilayers, forming the basis to obtain strong optical nonlinearity and excitonic many-body states in two-dimensional materials.
- Weijie Li
- , Xin Lu
- & Ajit Srivastava
-
Article |
 Design of van der Waals interfaces for broad-spectrum optoelectronics
Design of van der Waals interfaces for broad-spectrum optoelectronics
Type-II van der Waals interfaces formed by different two-dimensional materials enable robust interlayer optical transitions, regardless of common issues such as lattice constant mismatch, layer misalignment or whether the constituent compounds are direct or indirect band semiconductors.
- Nicolas Ubrig
- , Evgeniy Ponomarev
- & Alberto F. Morpurgo
-
Article |
 Dimensionally and environmentally ultra-stable polymer composites reinforced with carbon fibres
Dimensionally and environmentally ultra-stable polymer composites reinforced with carbon fibres
Multiple layers of diamond-like carbon films are shown to act as moisture barriers when conformally deposited on carbon fibre reinforced polymers used in space applications.
- J. V. Anguita
- , C. T. G. Smith
- & S. R. P. Silva
-
News & Views |
 Electroshock tuning of photonic crystals
Electroshock tuning of photonic crystals
Photonic crystals with optical bandgaps across the entire visible spectrum are generated by reconfiguring three-dimensional blue phase liquid crystalline lattices into long-lived metastable non-cubic structures using sequences of electric pulses.
- Slobodan Žumer
-
Article |
 Reconfiguration of three-dimensional liquid-crystalline photonic crystals by electrostriction
Reconfiguration of three-dimensional liquid-crystalline photonic crystals by electrostriction
Repetitive electrical pulse stimulation of blue-phase liquid crystals promotes their reconfiguration into stable non-cubic structures with promising electro-optical responses for display technologies.
- Duan-Yi Guo
- , Chun-Wei Chen
- & Tsung-Hsien Lin
-
Article |
 Scalable in operando strain tuning in nanophotonic waveguides enabling three-quantum-dot superradiance
Scalable in operando strain tuning in nanophotonic waveguides enabling three-quantum-dot superradiance
Local tuning of quantum dots embedded in a photonic waveguide can be achieved through the strain produced by laser heating of a thin layer of HfO2 deposited around the waveguide. The method is exploited to tune three quantum dots in resonance.
- Joel Q. Grim
- , Allan S. Bracker
- & Daniel Gammon
-
Review Article |
 Nanophotonic engineering of far-field thermal emitters
Nanophotonic engineering of far-field thermal emitters
This Review covers the basic physics of thermal emission, ways to engineer the thermal field radiated by hot objects in the far field and applications, such as thermophotovoltaics, radiative cooling, camouflage and privacy.
- Denis G. Baranov
- , Yuzhe Xiao
- & Mikhail A. Kats
-
Review Article |
 Droplet epitaxy of semiconductor nanostructures for quantum photonic devices
Droplet epitaxy of semiconductor nanostructures for quantum photonic devices
The droplet epitaxy technique has emerged as an alternative to the most commonly used Stranski–Krastanov for fabricating semiconductor nanostructures. This Review discusses the important aspects of droplet epitaxy quantum dots, from the growth mechanism to device application.
- Massimo Gurioli
- , Zhiming Wang
- & Stefano Sanguinetti
-
Article |
 Site-selective CO disproportionation mediated by localized surface plasmon resonance excited by electron beam
Site-selective CO disproportionation mediated by localized surface plasmon resonance excited by electron beam
Plasmonic catalysis is believed to be mediated by energy transfer from nanoparticles to adsorbed molecules. Localized surface plasmon resonance on gold nanoparticles excited by electron beam is shown to drive site-selective CO disproportionation at room temperature.
- Wei-Chang D. Yang
- , Canhui Wang
- & Renu Sharma
-
Article |
 Double-lattice photonic-crystal resonators enabling high-brightness semiconductor lasers with symmetric narrow-divergence beams
Double-lattice photonic-crystal resonators enabling high-brightness semiconductor lasers with symmetric narrow-divergence beams
An optimized design for a broad-area surface-emitting photonic-crystal laser leads to high brightness of over 300 MW cm–2 sr–1 and an output power of 10 W under pulsed excitation.
- Masahiro Yoshida
- , Menaka De Zoysa
- & Susumu Noda
-
News & Views |
 Strong Pockels materials
Strong Pockels materials
Electro-optic modulators based on epitaxial barium titanate integrated on silicon can reach speeds up to 50 Gbit s–1.
- Mo Li
- & Hong X. Tang
-
Article |
 Thermal meta-device in analogue of zero-index photonics
Thermal meta-device in analogue of zero-index photonics
In this type of thermal cloak, when a fluid circulates around the object of interest, the temperature perturbation is minimized as the effective thermal conductivity of the fluid becomes very high due to convective effects.
- Ying Li
- , Ke-Jia Zhu
- & C.-W. Qiu
-
Article |
 Large Pockels effect in micro- and nanostructured barium titanate integrated on silicon
Large Pockels effect in micro- and nanostructured barium titanate integrated on silicon
Electro-optic modulators based on epitaxial barium titanate (BTO) integrated on silicon exhibit speeds up to 50 Gbit s–1 while the Pockels coefficient of the BTO film is found to be approaching the bulk value.
- Stefan Abel
- , Felix Eltes
- & Jean Fompeyrine
-
Article |
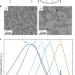 Impacts of surface depletion on the plasmonic properties of doped semiconductor nanocrystals
Impacts of surface depletion on the plasmonic properties of doped semiconductor nanocrystals
Degenerately doped semiconductor nanocrystals exhibit localized surface plasmon resonance in the infrared. Semiconducting properties such as band structure modification due to doping and surface states are now shown to strongly affect plasmonic modulation.
- Omid Zandi
- , Ankit Agrawal
- & Delia J. Milliron

 Phase patterning of liquid crystal elastomers by laser-induced dynamic crosslinking
Phase patterning of liquid crystal elastomers by laser-induced dynamic crosslinking