Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerated single photon emission from dye molecule-driven nanoantennas assembled on DNA
Accelerated single photon emission from dye molecule-driven nanoantennas assembled on DNA
Downsizing antennas to the nanoscale is a promising way to manipulate light emission from fluorescent sources. Bussonet al. used a short DNA strand to position a lone fluorescent molecule between two gold particles with nanometre resolution, achieving enhanced decay rates and single photon emission.
- Mickaël P. Busson
- , Brice Rolly
- & Sébastien Bidault
-
Article |
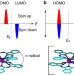 Real-space observation of spin-split molecular orbitals of adsorbed single-molecule magnets
Real-space observation of spin-split molecular orbitals of adsorbed single-molecule magnets
Controlling the behaviour of single molecules on electrode interfaces is crucial for the development of molecular spintronics. This study reports spin-polarized scanning tunnelling microscopy data of the spin-split molecular orbitals of a single-molecule magnet adsorbed on a cobalt surface.
- Jörg Schwöbel
- , Yingshuang Fu
- & Roland Wiesendanger
-
Article |
 Self-assembling subnanometer pores with unusual mass-transport properties
Self-assembling subnanometer pores with unusual mass-transport properties
Molecular systems with rigid macrocyclic backbones self-assemble into synthetic nanopores that mimic the mass-transport characteristics of biological channels. Zhouet al. produce self-assembling hydrophobic nanopores that mediate highly selective transmembrane ion transport and highly efficient transmembrane water permeability.
- Xibin Zhou
- , Guande Liu
- & Bing Gong
-
Article |
 Towards a quantum representation of the ampere using single electron pumps
Towards a quantum representation of the ampere using single electron pumps
Single electron pumps have been proposed as potential candidates for redefining the ampere. This study reports measurements of the quantized current flowing through a semiconductor electron pump with a precision that makes a substantial step towards establishing a direct metric for electrical currents.
- S.P. Giblin
- , M. Kataoka
- & D.A. Ritchie
-
Article
| Open Access Robust spin crossover and memristance across a single molecule
Robust spin crossover and memristance across a single molecule
Switches made up of single molecules form the basis for the concept of molecular electronics. Miyamachiet al.demonstrate that an iron-based spin crossover molecule can be switched between different spin states, provided it is decoupled from a metallic substrate by a thin insulating layer.
- Toshio Miyamachi
- , Manuel Gruber
- & Wulf Wulfhekel
-
Article |
 Field-directed sputter sharpening for tailored probe materials and atomic-scale lithography
Field-directed sputter sharpening for tailored probe materials and atomic-scale lithography
Scanning probe microscopy and related techniques rely on the availability of very sharp tips. Here, a sharpening technique based on field-directed sputtering is demonstrated, resulting in ultrasharp metallic tips for use in scanning tunnelling microscopy as well as atomic-scale lithographic experiments.
- S.W. Schmucker
- , N. Kumar
- & J.W. Lyding
-
Article |
 Three-dimensional nanonetworks for giant stretchability in dielectrics and conductors
Three-dimensional nanonetworks for giant stretchability in dielectrics and conductors
Stretchable electronics based on conducting polymers offer new opportunities for designing flexible technologies. Parket al. build three-dimensional nanostructures from elastomers soaked with liquid metal to produce stretchable conductors with greatly improved strain properties over solid films.
- Junyong Park
- , Shuodao Wang
- & Seokwoo Jeon
-
Article
| Open Access Lifetime blinking in nonblinking nanocrystal quantum dots
Lifetime blinking in nonblinking nanocrystal quantum dots
Nanocrystal quantum dots can exhibit photoluminescence blinking, where the intensity of the emitted light fluctuates due to random charging and discharging. Gallandet al.study thick shell nanocrystals and find that the photoluminescence lifetime can also undergo blinking, without intensity changes.
- Christophe Galland
- , Yagnaseni Ghosh
- & Victor I. Klimov
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic scale dynamics of ultrasmall germanium clusters
Atomic scale dynamics of ultrasmall germanium clusters
Ultrasmall clusters of atoms form the building blocks of many nanoscale materials. Using a combination of aberration-corrected transmission electron microscopy and numerical simulations, this study uncovers the geometry of these clusters in three dimensions.
- S. Bals
- , S. Van Aert
- & G. Van Tendeloo
-
Article |
 Direct printing of nanostructures by electrostatic autofocussing of ink nanodroplets
Direct printing of nanostructures by electrostatic autofocussing of ink nanodroplets
Ink-jet printing methods are an attractive approach to nanofabrication, where electrohydrodynamic control allows for flexible and cheap fabrication. Here, a new approach is presented using electrostatic nanodroplet autofocussing to produce high aspect ratio nanoscale structures like plasmonic nanoantennas.
- P. Galliker
- , J. Schneider
- & D. Poulikakos
-
Article |
 Anomalous high capacitance in a coaxial single nanowire capacitor
Anomalous high capacitance in a coaxial single nanowire capacitor
Devices made up of nanowires offer promise for a range of electronic, photonic and energy applications. Liuet al. fabricate a miniature capacitor by employing a thin layer of Cu2O as a separator between layers of carbon and copper.
- Zheng Liu
- , Yongjie Zhan
- & Pulickel M. Ajayan
-
Article |
 Electric-field control of magnetic domain-wall velocity in ultrathin cobalt with perpendicular magnetization
Electric-field control of magnetic domain-wall velocity in ultrathin cobalt with perpendicular magnetization
The manipulation of domain walls in magnetic materials is attracting interest because of its potential use in memory devices. Chibaet al. demonstrate that the velocity of domain walls in perpendicularly magnetized films can be changed by more than an order of magnitude by applying an electric field.
- D. Chiba
- , M. Kawaguchi
- & T. Ono
-
Article |
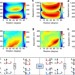 Twisted optical metamaterials for planarized ultrathin broadband circular polarizers
Twisted optical metamaterials for planarized ultrathin broadband circular polarizers
Three-dimensional optical metamaterials provide a range of exciting features, such as broadband circular dichroism, yet their fabrication is challenging. Here, a broadband optical circular polarizer is presented based on twisted stacks of metasurfaces, avoiding the issues of three-dimensional fabrication.
- Y. Zhao
- , M.A. Belkin
- & A. Alù
-
Article
| Open Access Nanotomy-based production of transferable and dispersible graphene nanostructures of controlled shape and size
Nanotomy-based production of transferable and dispersible graphene nanostructures of controlled shape and size
Current top-down and bottom-up syntheses of graphene nanostructures suffer from low yields or do not produce structures with different and controlled shapes. Here, monodisperse graphene shapes are produced by diamond-edge cutting of pyrolytic graphite followed by exfoliation.
- Nihar Mohanty
- , David Moore
- & Vikas Berry
-
Article |
 Transforming moiré blisters into geometric graphene nano-bubbles
Transforming moiré blisters into geometric graphene nano-bubbles
Strain engineering has been proposed as a promising strategy for manipulating the electronic properties of graphene. This scanning tunnelling microscopy study demonstrates the feasibility of controlling strain patterns in graphene down to the nanoscale.
- Jiong Lu
- , A.H. Castro Neto
- & Kian Ping Loh
-
Article
| Open Access Frequency stabilization in nonlinear micromechanical oscillators
Frequency stabilization in nonlinear micromechanical oscillators
Micromechanical oscillators present a route to miniaturisation of devices and may be used as frequency references or sensitive sensors, but their small size means that they often behave nonlinearly. Antonioet al. demonstrate frequency stabilisation of nonlinear resonators by coupling two vibrational modes.
- Dario Antonio
- , Damián H. Zanette
- & Daniel López
-
Article |
 Topological repulsion between domain walls in magnetic nanowires leading to the formation of bound states
Topological repulsion between domain walls in magnetic nanowires leading to the formation of bound states
The manipulation of domain walls in magnetic nanodevices is a topic of increasing technological relevance. This study examines the interactions that occur between vortex domain walls in permalloy nanowires, and finds that bound states occur between domain walls with opposite magnetic charge.
- Luc Thomas
- , Masamitsu Hayashi
- & Stuart Parkin
-
Article |
 Ultra-low carrier concentration and surface-dominant transport in antimony-doped Bi2Se3 topological insulator nanoribbons
Ultra-low carrier concentration and surface-dominant transport in antimony-doped Bi2Se3 topological insulator nanoribbons
The singular properties of topological insulators are defined by the topological nature of their metallic surface states. This study shows that by doping Bi2Se3nanoribbons with antimony, the transport properties of these surface states are measurable and can be distinguished from the contributions due to the bulk of the samples.
- Seung Sae Hong
- , Judy J. Cha
- & Yi Cui
-
Article |
 Giant spin-dependent thermoelectric effect in magnetic tunnel junctions
Giant spin-dependent thermoelectric effect in magnetic tunnel junctions
The spin-dependent thermal and electrical transport properties of nanostructures are central for future applications of spintronic devices. Here, Linet al. report an enhanced spin-dependent thermoelectric effect in an Al2O3-based magnetic tunnel junction.
- Weiwei Lin
- , Michel Hehn
- & Stéphane Mangin
-
Article
| Open Access Bright single-photon sources in bottom-up tailored nanowires
Bright single-photon sources in bottom-up tailored nanowires
Single-photon sources are important for quantum optical technologies, although achieving efficient light extraction from them with waveguides is limited in top-down approaches. Reimeret al. show a high extraction efficiency using a bottom-up method to grow quantum dots on the axis of nanowire waveguides.
- Michael E. Reimer
- , Gabriele Bulgarini
- & Val Zwiller
-
Article |
 Observation of conducting filament growth in nanoscale resistive memories
Observation of conducting filament growth in nanoscale resistive memories
Resistive switching devices are promising candidates for non-volatile memories. Usingin-situ and ex-situ transmission electron microscopy, Yang et al. present an extensive study of the dynamics of filaments forming across the electrodes of resisting switching devices known as electrochemical metallization memories.
- Yuchao Yang
- , Peng Gao
- & Wei Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Microwave cavity-enhanced transduction for plug and play nanomechanics at room temperature
Microwave cavity-enhanced transduction for plug and play nanomechanics at room temperature
Advances in nanoelectromechanical systems have brought improvements in the quality factor of nanomechanical resonators, yet few low-loss transduction schemes exist at high temperature. Using non-dissipative dielectric coupling to a microwave cavity, Faustet al. present an integrated nanomechanical transducer.
- T. Faust
- , P. Krenn
- & E.M. Weig
-
Article |
 Three-dimensional imaging of single nanotube molecule endocytosis on plasmonic substrates
Three-dimensional imaging of single nanotube molecule endocytosis on plasmonic substrates
Imaging and tracking the motion of single molecules on cell plasma membranes requires high spatial resolution in three dimensions. Honget al. develop a plasmonic ruler based on the fluorescence enhancement of carbon nanotubes on a gold plasmonic substrate, allowing the observation of nanotube endocytosis in three dimensions.
- Guosong Hong
- , Justin Z. Wu
- & Hongjie Dai
-
Article
| Open Access Precise hierarchical self-assembly of multicompartment micelles
Precise hierarchical self-assembly of multicompartment micelles
Multicompartment micelles can be assembled from block copolymers but it is difficult to manipulate their hierarchical superstructures using straightforward concepts. Here, methods are developed that involve the pre-assembly of subunits for the structurally controlled production of micelles.
- André H. Gröschel
- , Felix H. Schacher
- & Axel H.E. Müller
-
Article
| Open Access Broadband omnidirectional antireflection coating based on subwavelength surface Mie resonators
Broadband omnidirectional antireflection coating based on subwavelength surface Mie resonators
Minimising reflection from the interface between materials is an important goal for optical devices such as solar cells or photodetectors. Spinelliet al. show almost total loss of reflection over a broad spectral range from a silicon surface using periodic arrays of sub-wavelength silicon nanocylinders.
- P. Spinelli
- , M.A. Verschuuren
- & A. Polman
-
Article
| Open Access Generation and control of polarization-entangled photons from GaAs island quantum dots by an electric field
Generation and control of polarization-entangled photons from GaAs island quantum dots by an electric field
As quantum information and communication experiments grow in sophistication, the need for efficient sources of entangled photons escalates. Using exciton and biexciton emission in GaAs island quantum dots, Ghaliet al. demonstrate the electric field-induced generation of entangled photons with high fidelity.
- Mohsen Ghali
- , Keita Ohtani
- & Hideo Ohno
-
Article
| Open Access Time-resolved ultrafast photocurrents and terahertz generation in freely suspended graphene
Time-resolved ultrafast photocurrents and terahertz generation in freely suspended graphene
Graphene's broad bandwidth makes it promising as a photodetector, but common electronics cannot analyse the currents at high frequencies. Here, using photocurrent measurements, laser-induced carrier generation effects in freely suspended graphene and at graphene–metal interfaces are clarified up to 1 THz.
- Leonhard Prechtel
- , Li Song
- & Alexander W. Holleitner
-
Article
| Open Access Synergistic toughening of composite fibres by self-alignment of reduced graphene oxide and carbon nanotubes
Synergistic toughening of composite fibres by self-alignment of reduced graphene oxide and carbon nanotubes
Composite fibres made of polymers reinforced by carbon nanotubes are known for their exceptional toughness. Shinet al. make these composites even tougher, by self-aligning carbon nanotubes and reduced graphene oxide flakes within the polymer matrix.
- Min Kyoon Shin
- , Bommy Lee
- & Seon Jeong Kim
-
Article |
 Biomedical photoacoustics beyond thermal expansion using triggered nanodroplet vaporization for contrast-enhanced imaging
Biomedical photoacoustics beyond thermal expansion using triggered nanodroplet vaporization for contrast-enhanced imaging
A dual-contrast agent has been developed for combined ultrasound and photoacoustic imaging. This agent uses vaporization for ultrasound contrast enhancement and photoacoustic signal generation, providing significantly higher signals than thermal expansion, the most commonly used photoacoustic mechanism.
- Katheryne Wilson
- , Kimberly Homan
- & Stanislav Emelianov
-
Article
| Open Access Measurement of finite-frequency current statistics in a single-electron transistor
Measurement of finite-frequency current statistics in a single-electron transistor
Fluctuations of the electrical current in nanoscale devices reveal important details of the physical processes occurring inside them. Using a quantum point contact placed in its vicinity, Ubbelohde et al. measure the electrical fluctuations in a single-electron transistor, and determine the dynamical features of the transport.
- Niels Ubbelohde
- , Christian Fricke
- & Rolf J. Haug
-
Article
| Open Access Extraordinary carrier multiplication gated by a picosecond electric field pulse
Extraordinary carrier multiplication gated by a picosecond electric field pulse
Studying carrier multiplication in materials is important to understand their transport properties and interaction with light. Hiroriet al. show that intense terahertz pulses can generate electron-hole pairs in GaAs quantum wells that then emit infrared light, contrary to the effect with a DC field.
- H. Hirori
- , K. Shinokita
- & K. Tanaka
-
Article |
 Revealing the role of defects in ferroelectric switching with atomic resolution
Revealing the role of defects in ferroelectric switching with atomic resolution
Ferroelectric materials are characterized by a spontaneous polarization, which in practical applications is manipulated by an electric field. This study examines how defects affect the switching with atomic resolution, by usingin situaberration-corrected transmission electron microscopy.
- Peng Gao
- , Christopher T. Nelson
- & Xiaoqing Pan
-
Article |
 Band structure engineering in (Bi1−xSbx)2Te3 ternary topological insulators
Band structure engineering in (Bi1−xSbx)2Te3 ternary topological insulators
The unique band structure of topological insulators gives rise to insulating bulk and unusual metallic surface properties. By tuning the content of Sb in the ternary compound (Bi1–xSbx)2Te3, Wang and collaborators show it is possible to control the precise features of the band structure in a continuous fashion.
- Jinsong Zhang
- , Cui-Zu Chang
- & Yayu Wang
-
Article |
 Magnetic resonance force microscopy of paramagnetic electron spins at millikelvin temperatures
Magnetic resonance force microscopy of paramagnetic electron spins at millikelvin temperatures
Magnetic resonance force microscopy is a scanning probe technique capable of detecting and imaging electron spins. Vinanteet al.bring the operating temperature of this method into the millikelvin temperature regime, revealing spin diffusion phenomena that were hitherto inaccessible.
- A. Vinante
- , G. Wijts
- & T.H. Oosterkamp
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of an anomalous decoherence effect in a quantum bath at room temperature
Observation of an anomalous decoherence effect in a quantum bath at room temperature
Quantum objects are subject to decoherence effects due to the surrounding environment. This study demonstrates experimentally a counterintuitive example of anomalous decoherence, in which electron spins residing at nitrogen vacancy centres in diamond display longer coherence times under stronger noises.
- Pu Huang
- , Xi Kong
- & Jiangfeng Du
-
Article
| Open Access Graphene chiral liquid crystals and macroscopic assembled fibres
Graphene chiral liquid crystals and macroscopic assembled fibres
Chiral liquid crystals of two-dimensional colloids have not been extensively investigated. Xu and Gao show that graphene oxide can form chiral liquid crystals, and demonstrate that they can be spun into macroscopic fibres, and that subsequent chemical reduction provides graphene fibres with high conductivity.
- Zhen Xu
- & Chao Gao
-
Article |
 Plasmon resonance enhanced multicolour photodetection by graphene
Plasmon resonance enhanced multicolour photodetection by graphene
Among the wide range of potential applications of graphene, photodetection is believed to be among the most promising. By combining graphene with plasmonic nanostructures, Duan and colleagues observe dramatic improvements in the efficiency and spectral sensitivity of graphene-based photodetectors.
- Yuan Liu
- , Rui Cheng
- & Xiangfeng Duan
-
Article
| Open Access Gate-tuned normal and superconducting transport at the surface of a topological insulator
Gate-tuned normal and superconducting transport at the surface of a topological insulator
Topological insulators are a unique class of materials characterized by exotic metallic states at their surface, while remaining insulated in the bulk. Sacépéet al. show how to manipulate normal and superconducting electronic transport at the surface of the topological insulator Bi2Se3, by tuning a gate-voltage to vary the electronic density.
- Benjamin Sacépé
- , Jeroen B. Oostinga
- & Alberto F. Morpurgo
-
Article |
 Three-dimensional high-resolution quantitative microscopy of extended crystals
Three-dimensional high-resolution quantitative microscopy of extended crystals
X-ray ptychography has been used to extend the field of view in high-resolution quantitative imaging. Godardet al. develop Bragg-mode ptychography to reconstruct, in three dimensions, a crystalline specimen that is too large to be studied as a single object with a coherence-limited X-ray beam.
- P. Godard
- , G. Carbone
- & V. Chamard
-
Article
| Open Access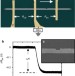 Suppression of the intrinsic stochastic pinning of domain walls in magnetic nanostripes
Suppression of the intrinsic stochastic pinning of domain walls in magnetic nanostripes
The propagation of magnetic domain walls in nanowires offers promise as the basis of future memory storage technologies. Muñoz and Prieto show that the random pinning of domain walls to structural defects in the nanowires can be suppressed at low fields, thus improving the reliability of the transmission of the domain walls substantially.
- Manuel Muñoz
- & José L. Prieto
-
Article |
 Towards hybrid superlattices in graphene
Towards hybrid superlattices in graphene
The controllable modification of graphene by chemical functionalization can modulate its optical and electronic properties. Sunet al. devise a functionalisation-based method to pattern graphane/graphene superlattices within a single sheet of graphene.
- Zhengzong Sun
- , Cary L. Pint
- & James M. Tour
-
Article |
 Charge density waves in the graphene sheets of the superconductor CaC6
Charge density waves in the graphene sheets of the superconductor CaC6
Charge density waves in the structure and electron density of layered materials are closely linked to superconductivity. Using scanning tunnelling techniques, Rahnejatet al. demonstrate the occurrence of such waves in the doped graphene sheets of the superconductor CaC6.
- K.C. Rahnejat
- , C.A. Howard
- & M. Ellerby
-
Article
| Open Access A new regime for mechanical annealing and strong sample-size strengthening in body centred cubic molybdenum
A new regime for mechanical annealing and strong sample-size strengthening in body centred cubic molybdenum
Mechanical annealing is a process through which the dislocation density in submicrometre metal crystals can be removed purely by applying a mechanical stress. This study shows that mechanical annealing occurs in body centred cubic molybdenum, and not only in face centred crystals as previously thought.
- Ling Huang
- , Qing-Jie Li
- & Evan Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Coupling artificial molecular spin states by photon-assisted tunnelling
Coupling artificial molecular spin states by photon-assisted tunnelling
Tunnelling transitions triggered by microwave irradiation between coupled quantum dots have generally been assumed to be spin-conserving. This study shows that this condition is violated in the presence of spin–orbit coupling, thus opening new possibilities for manipulating a two–spin qubit system by microwave irradiation.
- L.R. Schreiber
- , F.R. Braakman
- & L.M.K. Vandersypen
-
Article
| Open Access High-density magnetoresistive random access memory operating at ultralow voltage at room temperature
High-density magnetoresistive random access memory operating at ultralow voltage at room temperature
Magnetoresistive random access memory offers significant promise as a next-generation memory technology. Nan and colleagues present a design concept for a device that simultaneously possesses ultrahigh storage capacity, ultralow power dissipation, and high-speed operation at room temperature.
- Jia-Mian Hu
- , Zheng Li
- & Ce-Wen Nan
-
Article
| Open Access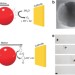 Electric field-induced chemical locomotion of conducting objects
Electric field-induced chemical locomotion of conducting objects
External electric fields have been used to control the motion of small objects through electrostatic repulsion. Here, electric fields are used to polarize conducting objects, triggering their movement by spatially separated electrochemical reactions leading to directionally controlled bubble evolution.
- Gabriel Loget
- & Alexander Kuhn
-
Article |
 Ultrafast direct modulation of a single-mode photonic crystal nanocavity light-emitting diode
Ultrafast direct modulation of a single-mode photonic crystal nanocavity light-emitting diode
Photonic alternatives to electrical circuits require low energy demand and fast modulation speed, which has proven difficult for on-chip devices. Using quantum dot photonic crystal nanocavities, Vučkovićet al. demonstrate an electrically-switchable light-emitting diode with such capabilities.
- Gary Shambat
- , Bryan Ellis
- & Jelena Vučković
-
Article |
 Functionalized arrays of Raman-enhancing nanoparticles for capture and culture-free analysis of bacteria in human blood
Functionalized arrays of Raman-enhancing nanoparticles for capture and culture-free analysis of bacteria in human blood
Detecting bacteria in clinical samples usually requires culture processes that are time consuming and impede rapid diagnoses. Now, a surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic method is reported that allows the label- and culture-free detection and analysis of bacteria.
- Ting-Yu Liu
- , Kun-Tong Tsai
- & Yuh-Lin Wang
-
Article |
 Self-assembly of DNA nanotubes with controllable diameters
Self-assembly of DNA nanotubes with controllable diameters
DNA nanotubes could be used to transport nano-cargo and incorporated into nano-devices. In this study, rolling circle amplification is used to generate DNA subunits, and their thermodynamic growth results in the formation of nanotubes with a controlled diameter.
- Ofer I. Wilner
- , Ron Orbach
- & Itamar Willner

 Ambient-stable tetragonal phase in silver nanostructures
Ambient-stable tetragonal phase in silver nanostructures