Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Highly parallel and ultra-low-power probabilistic reasoning with programmable gaussian-like memory transistors
Highly parallel and ultra-low-power probabilistic reasoning with programmable gaussian-like memory transistors
Probabilistic inference hardware prevents overconfidence. Lee et al. report a Gaussian-like memory transistor using p-n junction coupled with separate floating gate, offering precise control of the Gaussian outputs, simplified circuit design, and low power consumption for inference computing.
- Changhyeon Lee
- , Leila Rahimifard
- & Sung Gap Im
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled formation of three-dimensional cavities during lateral epitaxial growth
Controlled formation of three-dimensional cavities during lateral epitaxial growth
Substrate patterning offers additional degrees of freedom to engineer the structure and function of a semiconductor device. Here, fully-enclosed germanium cavities, with size and position tunable through the initial mask pattern, can be created through an unexpected self-assembly process.
- Yiwen Zhang
- , Baoming Wang
- & Rui-Tao Wen
-
Article
| Open Access Ultracompact mirror device for forming 20-nm achromatic soft-X-ray focus toward multimodal and multicolor nanoanalyses
Ultracompact mirror device for forming 20-nm achromatic soft-X-ray focus toward multimodal and multicolor nanoanalyses
Optics used for X-ray focusing suffer from wavelength dependent effects like chromatic aberration. Here the authors demonstrate fabrication of a ultracompact Kirkpatrick-Baez mirror and use it for achromatic focusing to 20 nm spot for the soft X-ray at 2-keV photon energy.
- Takenori Shimamura
- , Yoko Takeo
- & Hidekazu Mimura
-
Article
| Open Access Noise learning of instruments for high-contrast, high-resolution and fast hyperspectral microscopy and nanoscopy
Noise learning of instruments for high-contrast, high-resolution and fast hyperspectral microscopy and nanoscopy
Improving signal to noise ratio of Raman spectra is vital for the application. Here, authors show a noise learning method that learns the noise feature of a spectrometer. This improves the signal to noise ratio and makes deep learning to be instrument dependent instead of sample dependent.
- Hao He
- , Maofeng Cao
- & Bin Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Differential perovskite hemispherical photodetector for intelligent imaging and location tracking
Differential perovskite hemispherical photodetector for intelligent imaging and location tracking
Differential spectrometers recognise different wavelength via their differential photodetector responsivity. The authors combine an 8-pixel hemispherical perovskite photodetector with neural network algorithms to realise 3D trajectory tracking and 2D location tacking with colour classification.
- Xiaopeng Feng
- , Chenglong Li
- & Haotong Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Overcoming the permeability-selectivity challenge in water purification using two-dimensional cobalt-functionalized vermiculite membrane
Overcoming the permeability-selectivity challenge in water purification using two-dimensional cobalt-functionalized vermiculite membrane
Clean water and sanitation are major global challenges. Here, Prof. Zhang’s group developed a two-dimensional cobalt-functionalized vermiculite membrane, which overcame the persistent membrane permeability-selectivity trade-off in water purification.
- Mengtao Tian
- , Yi Liu
- & Zhenghua Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring gas discharge in contact electrification
Measuring gas discharge in contact electrification
Contact electrification triggers gas breakdown. Using Coulomb force to estimate voltage, this work provides experimental evidence for the Paschen curves that govern such discharge.
- Hongcheng Tao
- & James Gibert
-
Article
| Open Access Diatomic iron nanozyme with lipoxidase-like activity for efficient inactivation of enveloped virus
Diatomic iron nanozyme with lipoxidase-like activity for efficient inactivation of enveloped virus
Enveloped viruses encased within a lipid bilayer membrane are highly contagious and cause diseases like influenza and COVID-19, so strategies for their prevention and inactivation are needed. Here, the authors develop a diatomic iron nanozyme with lipoxidase-like activity for the inactivation of enveloped viruses, where the diatomic iron sites destroy the viral envelope via lipid peroxidation.
- Beibei Li
- , Ruonan Ma
- & Yadong Li
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient optimization with higher-order Ising machines
Efficient optimization with higher-order Ising machines
Combinatorial optimization problems can be solved on parallel hardware called Ising machines. Most studies have focused on the use of second-order Ising machines. Compared to second-order Ising machines, the authors show that higher-order Ising machines realized with coupled-oscillator networks can be more resource-efficient and provide superior solutions for constraint satisfaction problems.
- Connor Bybee
- , Denis Kleyko
- & Friedrich T. Sommer
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrodynamic tearing of bacteria on nanotips for sustainable water disinfection
Hydrodynamic tearing of bacteria on nanotips for sustainable water disinfection
Common methods for water disinfection involve oxidation or irradiation, and are often associated with a high carbon footprint and formation of toxic byproducts. Here, the authors describe a nano-structured material that is highly effective at killing bacteria in water through a hydrodynamic mechanism driven by mild water flow, in the absence of additional energy supply.
- Lu Peng
- , Haojie Zhu
- & Hong-Ying Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Fano resonant optical coatings platform for full gamut and high purity structural colors
Fano resonant optical coatings platform for full gamut and high purity structural colors
Fano resonant optical coatings (FROCs) present an ideal platform for structural coloring from thin-film metamaterials. This platform provides full-color gamut coverage at greater than 61% of the CIE gamut, with exceptionally high purity (up to 99%) and high brightness. FROCs exhibit tunable iridescence, cost-effective and scalable manufacturing, and significant advantages over existing structural coloring schemes.
- Mohamed ElKabbash
- , Nathaniel Hoffman
- & Chunlei Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Brownian reservoir computing realized using geometrically confined skyrmion dynamics
Brownian reservoir computing realized using geometrically confined skyrmion dynamics
Magnetic skyrmions, due to their strongly nonlinearity and multiscale dynamics, are promising for implementing reservoir computing. Here, the authors experimentally demonstrate skyrmion-based spatially multiplexed reservoir computing able to perform Boolean Logic operations, using thermal and current driven dynamics of spin structures.
- Klaus Raab
- , Maarten A. Brems
- & Mathias Kläui
-
Article
| Open Access Diamagnetically levitated nanopositioners with large-range and multiple degrees of freedom
Diamagnetically levitated nanopositioners with large-range and multiple degrees of freedom
Precision positioning stages are often central to science and technology at the micrometer and nanometer length scales. Here, the authors report compact, diamagnetically levitated positioning stages that achieve large-range, six degrees-of-freedom positioning with nanometer-scale precision.
- K. S. Vikrant
- & G. R. Jayanth
-
Article
| Open Access Simulating a chemically fueled molecular motor with nonequilibrium molecular dynamics
Simulating a chemically fueled molecular motor with nonequilibrium molecular dynamics
Molecular motors move in response to an imbalance between concentrations of fuel and waste molecules. Here, the authors simulate such non-equilibrium conditions to characterize a model motor’s performance and mechanism of operation.
- Alex Albaugh
- & Todd R. Gingrich
-
Article
| Open Access Near-field thermophotovoltaics for efficient heat to electricity conversion at high power density
Near-field thermophotovoltaics for efficient heat to electricity conversion at high power density
Near-field thermophotovoltaic holds the potential for achieving high-power density and energy conversion efficiency by utilizing evanescent modes of heat transfer, yet the performance still lags behind the far-field counterpart. Here, the authors combine thermally robust planar emitter with InGaAs PV to push the limit of near-field device further.
- Rohith Mittapally
- , Byungjun Lee
- & Edgar Meyhofer
-
Article
| Open Access Avalanches and edge-of-chaos learning in neuromorphic nanowire networks
Avalanches and edge-of-chaos learning in neuromorphic nanowire networks
Neuromorphic nanowire networks are found to exhibit neural-like dynamics, including phase transitions and avalanche criticality. Hochstetter and Kuncic et al. show that the dynamical state at the edge-of-chaos is optimal for learning and favours computationally complex information processing tasks.
- Joel Hochstetter
- , Ruomin Zhu
- & Zdenka Kuncic
-
Article
| Open Access Optical force mapping at the single-nanometre scale
Optical force mapping at the single-nanometre scale
Direct visualisation of 3D vector distributions of photoinduced fields can shed light on the optical and mechanical behaviour of different materials. Here, the authors demonstrate such visualisation using photoinduced force microscopy by observing the optical gradient force at the nanometer scale.
- Junsuke Yamanishi
- , Hidemasa Yamane
- & Yasuhiro Sugawara
-
Article
| Open Access An in-memory computing architecture based on two-dimensional semiconductors for multiply-accumulate operations
An in-memory computing architecture based on two-dimensional semiconductors for multiply-accumulate operations
In standard computing architectures, memory and logic circuits are separated, a feature that slows matrix operations vital to deep learning algorithms. Here, the authors present an alternate in-memory architecture and demonstrate a feasible approach for analog matrix multiplication.
- Yin Wang
- , Hongwei Tang
- & Wenzhong Bao
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic memristor-based reservoir computing for high-efficiency temporal signal processing
Dynamic memristor-based reservoir computing for high-efficiency temporal signal processing
Designing efficient neuromorphic systems for complex temporal tasks remains a challenge. Zhong et al. develop a parallel memristor-based reservoir computing system capable of tuning critical parameters, achieving classification accuracy of 99.6% in spoken-digit recognition and time-series prediction error of 0.046 in the Hénon map.
- Yanan Zhong
- , Jianshi Tang
- & Huaqiang Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Intelligent non-colorimetric indicators for the perishable supply chain by non-wovens with photo-programmed thermal response
Intelligent non-colorimetric indicators for the perishable supply chain by non-wovens with photo-programmed thermal response
High-performance and low-cost indicators are important in food and cosmetics industry but market uptake is low due to several challenges such as toxicity, cost and unclear reading. Here, the authors report on optically-programmed, non-colorimetric indicators based on nanotextured organic non-wovens, encoded by controlling their cross-linking degree.
- Luigi Romano
- , Alberto Portone
- & Luana Persano
-
Article
| Open Access Heterogeneously integrated flexible microwave amplifiers on a cellulose nanofibril substrate
Heterogeneously integrated flexible microwave amplifiers on a cellulose nanofibril substrate
Though flexible microwave integrated circuits (MICs) are desirable for the construction of functional microwave amplifier circuits, realizing low cost III-V-based MMICs remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a heterogeneous integration strategy for the fabrication of flexible low-cost MICs.
- Huilong Zhang
- , Jinghao Li
- & Zhenqiang Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Intercellular communication between artificial cells by allosteric amplification of a molecular signal
Intercellular communication between artificial cells by allosteric amplification of a molecular signal
The principles of intercellular communication in multicellular organisms can be explored using artificial cells. Here, the authors report on giant vesicles which can recognize diffused chemical signals and amplify the signal by synthetic enzymatic cascades to allow signal propagation over long distances.
- Bastiaan C. Buddingh’
- , Janneke Elzinga
- & Jan C. M. van Hest
-
Article
| Open Access Gap-enhanced Raman tags for physically unclonable anticounterfeiting labels
Gap-enhanced Raman tags for physically unclonable anticounterfeiting labels
Physical unclonable functions with inherent randomness are promising candidates for secure labeling systems. Here the authors demonstrate such a function using gap-enhanced Raman tags to create high-capacity and high-security labels for anticounterfeiting.
- Yuqing Gu
- , Chang He
- & Jian Ye
-
Article
| Open Access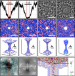 Measurements of the size and correlations between ions using an electrolytic point contact
Measurements of the size and correlations between ions using an electrolytic point contact
The size of an ion affects everything from the structure of water to life itself. Here, a sub-nanometer diameter pore sputtered through a thin silicon nitride membrane is used to systematically test ion permeability by measuring the electrolytic current and current noise and show that the ions move with a grossly distorted hydration shell in a correlated way.
- Eveline Rigo
- , Zhuxin Dong
- & Gregory Timp
-
Article
| Open Access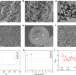 Distinguishing the sources of silica nanoparticles by dual isotopic fingerprinting and machine learning
Distinguishing the sources of silica nanoparticles by dual isotopic fingerprinting and machine learning
Determining the source of nanoparticles is critical for nanotechnology risk assessment. Here, the authors develop an approach that, by taking into account the isotopic signatures of both Si and O, may be able to distinguish between natural and engineered SiO2 nanoparticles, and even those synthesized by different manufacturers.
- Xuezhi Yang
- , Xian Liu
- & Guibin Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Emergence of winner-takes-all connectivity paths in random nanowire networks
Emergence of winner-takes-all connectivity paths in random nanowire networks
Nanowire networks with memristive properties are promising for neuromorphic applications. Here, the authors observe the formation of a preferred conduction pathway which uses the lowest possible energy to get through the network and could be exploited for the design of optimal brain-inspired devices.
- Hugh G. Manning
- , Fabio Niosi
- & John J. Boland
-
Article
| Open Access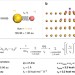 Insight into induced charges at metal surfaces and biointerfaces using a polarizable Lennard–Jones potential
Insight into induced charges at metal surfaces and biointerfaces using a polarizable Lennard–Jones potential
Molecular dynamics models for predicting the behavior of metallic nanostructures typically do not take into account polarization effects in metals. Here, the authors introduce a polarizable Lennard–Jones potential that provides quantitative insight into the role of induced charges at metal surfaces and related complex material interfaces.
- Isidro Lorenzo Geada
- , Hadi Ramezani-Dakhel
- & Hendrik Heinz
-
Article
| Open Access Integrated nano-opto-electro-mechanical sensor for spectrometry and nanometrology
Integrated nano-opto-electro-mechanical sensor for spectrometry and nanometrology
Fully integratable spectrometers have trade-offs between size and resolution. Here, the authors present a nano-opto-electro-mechanical system where the functionalities of transduction, actuation and detection are fully integrated, resulting in an ultra-compact high-resolution spectrometer with a micrometer-scale footprint.
- Žarko Zobenica
- , Rob W. van der Heijden
- & Andrea Fiore
-
Article
| Open Access A Co3O4-CDots-C3N4 three component electrocatalyst design concept for efficient and tunable CO2 reduction to syngas
A Co3O4-CDots-C3N4 three component electrocatalyst design concept for efficient and tunable CO2 reduction to syngas
Simultaneous electrochemical reduction of CO2 and H+/H2O is an attractive renewable route to produce syngas mixtures. Here, the authors introduce a ternary Co3O4-CDots-C3N4 electrocatalyst that couples hydrogen evolution and CO2 reduction catalysts and achieves cheap, stable and tunable production of syngas.
- Sijie Guo
- , Siqi Zhao
- & Zhenhui Kang
-
Article
| Open Access Shaping micro-clusters via inverse jamming and topographic close-packing of microbombs
Shaping micro-clusters via inverse jamming and topographic close-packing of microbombs
Self-assembled systems are normally composed of incompressible building blocks, which constrain their space filling efficiency. Yu et al. show programmable, densely packed clusters using thermally expandable soft microparticles, whereby the self-assembling process is realized via a jamming transition.
- Seunggun Yu
- , Hyesung Cho
- & Chong Min Koo
-
Article
| Open Access Immobilization of single argon atoms in nano-cages of two-dimensional zeolite model systems
Immobilization of single argon atoms in nano-cages of two-dimensional zeolite model systems
While noble gases can be trapped in 3D porous structures, immobilizing them on 2D surfaces represents a formidable challenge. Here, the authors cage individual argon atoms in 2D model zeolite frameworks at room temperature, providing exciting opportunities for the fundamental study of isolated noble gas atoms using surface science methods.
- Jian-Qiang Zhong
- , Mengen Wang
- & J. Anibal Boscoboinik
-
Article
| Open Access Wafer-scale single-crystal perovskite patterned thin films based on geometrically-confined lateral crystal growth
Wafer-scale single-crystal perovskite patterned thin films based on geometrically-confined lateral crystal growth
Wafer-scale deposition of uniform metal halide perovskite single-crystals is a step towards commercialisation. Using geometrically-confined lateral crystal growth, Leeet al., report patterned thin films of highly-aligned single-crystals and achieve lateral solar cells with efficiencies up to 4.83%.
- Lynn Lee
- , Jangmi Baek
- & Myung M. Sung
-
Article
| Open Access Giant heat transfer in the crossover regime between conduction and radiation
Giant heat transfer in the crossover regime between conduction and radiation
Kloppstechet al. report experimental observations of the heat transfer between a gold tip and an atomically flat gold sample in the 0.2–7 nm regime. The observed flux rates are four orders of magnitude larger than expected from theory, suggesting the possibility of additional heat transfer mechanisms.
- Konstantin Kloppstech
- , Nils Könne
- & Achim Kittel
-
Article
| Open Access Study of radiative heat transfer in Ångström- and nanometre-sized gaps
Study of radiative heat transfer in Ångström- and nanometre-sized gaps
Here, Cuiet al. report radiative heat transfer in few Ångström to 5 nm gap sizes, between a gold-coated probe and a heated planar gold substrate subjected to various surface cleaning procedures. They found that insufficiently cleaned probes and substrates led to unexpectedly large radiative thermal conductances.
- Longji Cui
- , Wonho Jeong
- & Pramod Reddy
-
Article
| Open Access Approaching the standard quantum limit of mechanical torque sensing
Approaching the standard quantum limit of mechanical torque sensing
Cavity optomechanics enables measurement of torque at levels unattainable by previous techniques, but the main obstacle to improved sensitivity is thermal noise. Here the authors present cryogenic measurement of a cavity-optomechanical torsional resonator with unprecedented torque sensitivity of 2.9 yNm/√Hz.
- P. H. Kim
- , B. D. Hauer
- & J. P. Davis
-
Article
| Open Access Chiral optical response of planar and symmetric nanotrimers enabled by heteromaterial selection
Chiral optical response of planar and symmetric nanotrimers enabled by heteromaterial selection
Alternative ways to fabricate chiral media which give rise to interesting optical phenomena are sought. Here, Banzeret al. demonstrate a two-dimensional geometrically achiral nanoparticle assembly, which exhibits a chiral optical response due to its heterogeneous composition.
- Peter Banzer
- , Paweł Woźniak
- & Robert W. Boyd
-
Article
| Open Access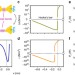 Generating giant and tunable nonlinearity in a macroscopic mechanical resonator from a single chemical bond
Generating giant and tunable nonlinearity in a macroscopic mechanical resonator from a single chemical bond
Macroscopic mechanical systems typically respond linearly to external force, and generating nonlinearity is challenging. Here, the authors generate nonlinearity in a macroscopic mechanical resonator by linking it to a gold contact and exploiting the anharmonicity in the chemical bonding interactions.
- Pu Huang
- , Jingwei Zhou
- & Jiangfeng Du
-
Article
| Open Access Single-shot read-out of a superconducting qubit using a Josephson parametric oscillator
Single-shot read-out of a superconducting qubit using a Josephson parametric oscillator
Efficient qubit readout is essential for quantum information technology, which requires sufficient recognition of signal from noise. Here, Krantz et al. propose a simplified technique using a Josephson parametric oscillator, demonstrating single-shot readout performance of a superconducting qubit.
- Philip Krantz
- , Andreas Bengtsson
- & Jonas Bylander
-
Article
| Open Access Lattice-free prediction of three-dimensional structure of programmed DNA assemblies
Lattice-free prediction of three-dimensional structure of programmed DNA assemblies
DNA may be used to fabricate functional nanostructures with various possible geometries, but first being able to predict these structures is a challenging task. Here, the authors use coarse-grained modelling to predict the shape of artificial DNA nanostructures in solution.
- Keyao Pan
- , Do-Nyun Kim
- & Mark Bathe
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of an anomalous decoherence effect in a quantum bath at room temperature
Observation of an anomalous decoherence effect in a quantum bath at room temperature
Quantum objects are subject to decoherence effects due to the surrounding environment. This study demonstrates experimentally a counterintuitive example of anomalous decoherence, in which electron spins residing at nitrogen vacancy centres in diamond display longer coherence times under stronger noises.
- Pu Huang
- , Xi Kong
- & Jiangfeng Du

 Ultrafast photoluminescence and multiscale light amplification in nanoplasmonic cavity glass
Ultrafast photoluminescence and multiscale light amplification in nanoplasmonic cavity glass