Featured
-
-
Article |
 Synergistic geometric and electronic effects for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide using gold–copper bimetallic nanoparticles
Synergistic geometric and electronic effects for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide using gold–copper bimetallic nanoparticles
The efficient and selective reduction of carbon dioxide is a major challenge in artificial photosynthesis. Here, the authors study gold–copper bimetallic nanoparticles and attempt to resolve the electronic and geometric factors that lead to high activity carbon dioxide reduction catalysis.
- Dohyung Kim
- , Joaquin Resasco
- & Peidong Yang
-
Article |
 Self-assembly of two-dimensional DNA origami lattices using cation-controlled surface diffusion
Self-assembly of two-dimensional DNA origami lattices using cation-controlled surface diffusion
DNA origami is useful for organizing nanoscale objects, and linear arrays of DNA origami have previously been assembled via programmable bonds based on DNA base-stacking. Here, such ‘stacking bonds’ are used to assemble large 2D lattices of DNA origami by a novel cation-controlled surface diffusion mechanism.
- Sungwook Woo
- & Paul W. K. Rothemund
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetic antibody-linked nanomatchmakers for therapeutic cell targeting
Magnetic antibody-linked nanomatchmakers for therapeutic cell targeting
Cell therapy requires sufficient amounts of therapeutic cells to be delivered to the injured tissue. Here the authors use magnetic iron nanoparticles conjugated with antibodies that bind therapeutic cells and cardiomyocytes to treat myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats and show that targeting to the heart is enhanced upon local application of a magnetic field.
- Ke Cheng
- , Deliang Shen
- & Eduardo Marbán
-
Article
| Open Access Uncovering many-body correlations in nanoscale nuclear spin baths by central spin decoherence
Uncovering many-body correlations in nanoscale nuclear spin baths by central spin decoherence
Detecting many-body correlations is a long-standing challenge in many-body physics. By studying their effects on the decoherence of the central spin under dynamical decoupling, Ma et al.provide an experimental demonstration of detection of many-body correlations in nanoscale nuclear spin bath.
- Wen-Long Ma
- , Gary Wolfowicz
- & Ren-Bao Liu
-
Article |
 Electrophoretic and field-effect graphene for all-electrical DNA array technology
Electrophoretic and field-effect graphene for all-electrical DNA array technology
Field-effect transistor biomolecule sensors have numerous advantages including sensitivity and label-free operation. Here, the authors fabricate field-effect transistor arrays from graphene, which represent steps towards multiplexed DNA arrays, where graphene acts as both a sensor and electrophoretic electrode.
- Guangyu Xu
- , Jeffrey Abbott
- & Donhee Ham
-
Article |
 Hotspot-mediated ultrafast nonlinear control of multifrequency plasmonic nanoantennas
Hotspot-mediated ultrafast nonlinear control of multifrequency plasmonic nanoantennas
The subwavelength scale of plasmonics is attractive for optical nanodevices, if greater control over such systems can be achieved. Here, the authors show the independent control of hotspot-mediated Kerr nonlinearities in a nanoantenna array, enabling individual tuning of optical pathways in the medium.
- Martina Abb
- , Yudong Wang
- & Otto L. Muskens
-
Article |
 Selective metal deposition at graphene line defects by atomic layer deposition
Selective metal deposition at graphene line defects by atomic layer deposition
Defects in graphene strongly influence the material's physical properties, leading to the suggestion that defects might be tuned to improve performance. Here, via atomic layer deposition, the authors selectively deposit Pt at graphene line defects and yield a superior platform for sensing applications.
- Kwanpyo Kim
- , Han-Bo-Ram Lee
- & Zhenan Bao
-
Article |
 Hierarchical synthesis of non-centrosymmetric hybrid nanostructures and enabled plasmon-driven photocatalysis
Hierarchical synthesis of non-centrosymmetric hybrid nanostructures and enabled plasmon-driven photocatalysis
The continued development of hybrid nanostructures is important for a range of applications. Here, the authors fabricate non-centrosymmetric hybrid nanostructures of programmable composition, and demonstrate that they are capable of plasmon enhanced photocatalysis.
- Lin Weng
- , Hui Zhang
- & Min Ouyang
-
Article |
 One-dimensional surface phonon polaritons in boron nitride nanotubes
One-dimensional surface phonon polaritons in boron nitride nanotubes
Surface plasmon and phonon polaritons are useful for sub-diffraction limit waveguiding of light, but phonon polaritons are advantageous in the mid-infrared. Xu et al.show that one-dimensional boron nitride nanotubes can support propagating phonon polaritons, making them a suitable platform for further study.
- Xiaoji G. Xu
- , Behnood G. Ghamsari
- & Gilbert C. Walker
-
Article |
 A smart and versatile theranostic nanomedicine platform based on nanoporphyrin
A smart and versatile theranostic nanomedicine platform based on nanoporphyrin
Nanoparticles can be used for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. Here, the authors report that nanoparticles made of a single chemical building block, called nanoporphyrins, incorporate eight different functionalities, including various types of imaging, drug delivery and cancer therapy.
- Yuanpei Li
- , Tzu-yin Lin
- & Kit S. Lam
-
Article |
 Nanoscale nickel oxide/nickel heterostructures for active hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis
Nanoscale nickel oxide/nickel heterostructures for active hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis
There is ongoing research into new electrocatalysts for hydrogen production from water splitting. Here, the authors report the electrocatalytic performance of nickel/nickel oxide heterostructures on carbon nanotubes, and are able to assemble a water electrolyzer operated by a single-cell 1.5 V battery.
- Ming Gong
- , Wu Zhou
- & Hongjie Dai
-
Article
| Open Access Thermoelectric Seebeck effect in oxide-based resistive switching memory
Thermoelectric Seebeck effect in oxide-based resistive switching memory
Oxide-based resistive switching memory is known to depend on the formation and rupture of a conducting filament, although the mechanism behind this remains debated. Here, the authors measure the Seebeck effect to understand the intrinsic electronic transport mechanism in the conducting filament.
- Ming Wang
- , Chong Bi
- & Ming Liu
-
Article |
 Multimode laser cooling and ultra-high sensitivity force sensing with nanowires
Multimode laser cooling and ultra-high sensitivity force sensing with nanowires
Light can cool and control the motion of nanoscale resonators to the point that they oscillate with only a single quantum of vibrational energy. Hosseini et al. now demonstrate a technique for optically cooling four mechanical modes of a nanowire that enables highly sensitive force measurements.
- Mahdi Hosseini
- , Giovanni Guccione
- & Ping Koy Lam
-
Article |
 Controlled stripes of ultrafine ferroelectric domains
Controlled stripes of ultrafine ferroelectric domains
In magnets and ferroelectrics, domains of regions with different ferroic orientation play an important role for the performance of devices based on these materials. Here, the authors create and control ultrafine domains in a ferroelectric that are only 10 nm wide and extend for tens of micrometres.
- Ludwig Feigl
- , Petr Yudin
- & Nava Setter
-
Article |
 Copper nanoparticle heterogeneous catalytic ‘click’ cycloaddition confirmed by single-molecule spectroscopy
Copper nanoparticle heterogeneous catalytic ‘click’ cycloaddition confirmed by single-molecule spectroscopy
Metal nanoparticles are widely used as heterogeneous catalysis, but the possibility of simultaneous homogeneous pathway via metal ion leaching also exists. Here, the authors use single-molecule spectroscopy to observe catalytic events directly on the surface of the nanoparticles, supporting a purely heterogeneous pathway.
- Matthew R. Decan
- , Stefania Impellizzeri
- & Juan C. Scaiano
-
Article
| Open Access A graphene quantum dot photodynamic therapy agent with high singlet oxygen generation
A graphene quantum dot photodynamic therapy agent with high singlet oxygen generation
Photosensitisers are used in cancer therapy to promote the formation of reactive oxygen species on irradiation with light. Here, the authors present a graphene quantum dot photosensitiser with a singlet oxygen quantum yield of approximately 1.3, and investigate its in vitro and in vivoapplications
- Jiechao Ge
- , Minhuan Lan
- & Xiaodong Han
-
Article |
 Holey graphene frameworks for highly efficient capacitive energy storage
Holey graphene frameworks for highly efficient capacitive energy storage
Carbon-based materials are promising supercapacitor electrodes, but suffer from limited energy densities. Here, the authors report a holey graphene framework with hierarchical porous structures and fully accessible surface areas, leading to high energy densities comparable to lead-acid batteries.
- Yuxi Xu
- , Zhaoyang Lin
- & Xiangfeng Duan
-
Article |
 Atomically precise interfaces from non-stoichiometric deposition
Atomically precise interfaces from non-stoichiometric deposition
Molecular-beam epitaxy is famous for creating heterostructures with atomic-layer precision. Here, the authors show that rather than following the stoichiometry suggested by the crystal structure of a layered oxide, the desired layering is obtained utilizing deliberate non-stoichiometric growth conditions.
- Y. F. Nie
- , Y. Zhu
- & D. G. Schlom
-
Article |
 Self-adaptive strain-relaxation optimization for high-energy lithium storage material through crumpling of graphene
Self-adaptive strain-relaxation optimization for high-energy lithium storage material through crumpling of graphene
Crumpled graphene structures are promising for electrochemical energy storage. Here, the authors synthesize deeply crumpled pinecone-like graphene sheets, which show self-adaptive folding-unfolding behaviours in cycling leading to robust battery performances.
- Yunlong Zhao
- , Jiangang Feng
- & Liqiang Mai
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping the spatial distribution of charge carriers in quantum-confined heterostructures
Mapping the spatial distribution of charge carriers in quantum-confined heterostructures
The confinement of electrical charges in quantum dots makes them of interest for applications in imaging and photovoltaics. Here, the authors demonstrate that based on optical absorption measurements and theoretical modelling it is possible to derive the charge carrier distribution in quantum dots.
- Andrew M. Smith
- , Lucas A. Lane
- & Shuming Nie
-
Article |
 Vertical atomic manipulation with dynamic atomic-force microscopy without tip change via a multi-step mechanism
Vertical atomic manipulation with dynamic atomic-force microscopy without tip change via a multi-step mechanism
Understanding vertical manipulation mechanisms in atomic-force microscopy applications is a serious challenge. Here, the authors report vertical extraction and deposition processes of copper atoms at an oxidized copper surface, and rationalize the processes with a multi-step manipulation mechanism.
- J. Bamidele
- , S.H. Lee
- & L. Kantorovich
-
Article |
 Strain-engineered manufacturing of freeform carbon nanotube microstructures
Strain-engineered manufacturing of freeform carbon nanotube microstructures
Reproducing complex surface geometries for high-performance composite materials is very desirable, although current synthesis methods are limited. Here, the authors present a technique to produce large-area freeform microstructures via strain-engineered growth of patterned vertically aligned carbon nanotubes.
- M. De Volder
- , S. Park
- & A. J. Hart
-
Article
| Open Access Giant dielectric and magnetoelectric responses in insulating nanogranular films at room temperature
Giant dielectric and magnetoelectric responses in insulating nanogranular films at room temperature
The electric and magnetic responses of matter are of interest for their use in electronic applications. Here, the authors find a large dielectric and magnetoelectric response in FeCo-MgF nanogranular films, caused by quantum mechanical tunnelling oscillation between magnetic granules.
- Nobukiyo Kobayashi
- , Hiroshi Masumoto
- & Sadamichi Maekawa
-
Article |
 Solar steam generation by heat localization
Solar steam generation by heat localization
Steam generation from solar energy is currently inefficient because of costly high optical concentration and large heat losses involved. Ghasemi et al. develop an efficient approach with internal efficiency up to 85% at low water temperature using a carbon-based material with a double-layer structure.
- Hadi Ghasemi
- , George Ni
- & Gang Chen
-
Article |
 A one-dimensional optomechanical crystal with a complete phononic band gap
A one-dimensional optomechanical crystal with a complete phononic band gap
Cavity optomechanics connects light to the mechanical degrees of freedom of a resonator and has great potential for sensing applications. Here, the authors realize a one-dimensional optomechanical crystal with a complete phononic bandgap containing high Q-factor modes and limited clamping losses.
- J. Gomis-Bresco
- , D. Navarro-Urrios
- & C.M. Sotomayor Torres
-
Article
| Open Access High-mobility transport anisotropy and linear dichroism in few-layer black phosphorus
High-mobility transport anisotropy and linear dichroism in few-layer black phosphorus
Two-dimensional (2D) materials with a large electronic bandgap in addition to high carrier mobility are required for future nanoelectronics. Here, the authors present a theoretical investigation of black phosphorous, a new category of 2D semiconductor with high potential for nanoelectronic applications.
- Jingsi Qiao
- , Xianghua Kong
- & Wei Ji
-
Article |
 Water-induced correlation between single ions imaged at the solid–liquid interface
Water-induced correlation between single ions imaged at the solid–liquid interface
The organization of ions at solid–liquid interfaces is of interest in many fields, but little information at the nanoscale is available. Here, the authors report atomic-level observations of ordering of ions at surfaces in solutions, which is driven by water instead of the conventional electrostatic correlations.
- Maria Ricci
- , Peter Spijker
- & Kislon Voïtchovsky
-
Article |
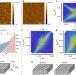 Super switching and control of in-plane ferroelectric nanodomains in strained thin films
Super switching and control of in-plane ferroelectric nanodomains in strained thin films
In ferroelectrics, domains of different polarization determine the switching behaviour and are therefore crucial to their practical use. Here, Matzen et al. observe the formation and control of superdomain arrangements of nanoscale domains in thin films that mimic the single-domain ground state.
- S. Matzen
- , O. Nesterov
- & B. Noheda
-
Article |
 Reconfigurable nanoantennas using electron-beam manipulation
Reconfigurable nanoantennas using electron-beam manipulation
Raising plasmonic nanoantennas on pillars enhances their performance for sensor devices. Here, the authors show that the proximity of such pillar structures can be dynamically tuned by electron beams, offering an additional mechanical degree of freedom to alter their optical properties.
- Brian J. Roxworthy
- , Abdul M. Bhuiya
- & Kimani C. Toussaint Jr
-
Article
| Open Access A critical analysis of calcium carbonate mesocrystals
A critical analysis of calcium carbonate mesocrystals
The term mesocrystal describes three-dimensional crystals formed by oriented assembly and that exhibit nanoparticle substructures. Here, the authors perform detailed structural analyses on synthetic calcium carbonate/polymer crystals, and show that common signatures used to assign mesocrystals may be unreliable.
- Yi-Yeoun Kim
- , Anna S. Schenk
- & Fiona C. Meldrum
-
Article
| Open Access Trapping atoms using nanoscale quantum vacuum forces
Trapping atoms using nanoscale quantum vacuum forces
Atoms experience large and typically undesirable forces near dielectric surfaces due to quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic vacuum. The work of Chang et al.proposes a scheme in which these forces can be exploited to create strong atomic traps at nanoscale distances from surfaces.
- D. E. Chang
- , K. Sinha
- & H. J. Kimble
-
Article |
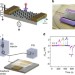 Graphene nanoelectronic heterodyne sensor for rapid and sensitive vapour detection
Graphene nanoelectronic heterodyne sensor for rapid and sensitive vapour detection
Nanoelectronic gas sensors allow highly sensitive detection, but are often limited by slow response times due to the dynamics of the charge detection mechanism. Here, the authors show a graphene nanoelectronic heterodyne-sensing mechanism based on the detection of molecular dipoles, allowing rapid and highly sensitive detection of vapours.
- Girish S. Kulkarni
- , Karthik Reddy
- & Xudong Fan
-
Article |
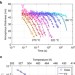 Crystal growth within a phase change memory cell
Crystal growth within a phase change memory cell
Phase change materials play a key role in information technology. Here, the authors measure the crystal growth velocity in doped Ge2Sb2Te5up to the melting temperature, exploiting the nanoscale dimensions and the fast thermal dynamics of a phase change memory cell.
- Abu Sebastian
- , Manuel Le Gallo
- & Daniel Krebs
-
Article |
 High-sensitivity linear piezoresistive transduction for nanomechanical beam resonators
High-sensitivity linear piezoresistive transduction for nanomechanical beam resonators
Obtaining efficient transduction in nanomechanical beam resonators is challenging. Here, the authors describe a mechanism for enhanced piezoresistive transduction in silicon beams, based on asymmetry in the beam shape, removing the need for large piezoresistive coefficients.
- Marc Sansa
- , Marta Fernández-Regúlez
- & Francesc Pérez-Murano
-
Article |
 Quantifying thiol–gold interactions towards the efficient strength control
Quantifying thiol–gold interactions towards the efficient strength control
The thiol–gold interaction is a fundamental one for the functionalization of nanoparticles and surfaces. Here, the authors use AFM to study individual thiol–gold contacts, showing that oxidized gold surfaces enhance the stability, in addition to monitoring shifts from coordinated to covalent bonding.
- Yurui Xue
- , Xun Li
- & Wenke Zhang
-
Article |
 Self-assembly of free-standing RNA membranes
Self-assembly of free-standing RNA membranes
Nucleic acids possess a number of properties that can be beneficial for the fabrication of nanomaterials. Here, the authors present an enzymatically synthesised RNA membrane, and show how its physical properties can be controlled by changes to base-pairing.
- Daehoon Han
- , Yongkuk Park
- & Jong Bum Lee
-
Article |
 Direct experimental determination of onset of electron–electron interactions in gap opening of zigzag graphene nanoribbons
Direct experimental determination of onset of electron–electron interactions in gap opening of zigzag graphene nanoribbons
It has been predicted that nanoribbon width can be used as a parameter for changing bandgap in zig-zag edged graphene nanoribbons. The authors provide an experimental demonstration of this here, observing that nanoribbons with a width less than 3 nm display larger band gaps than in wider nanoribbons.
- Y. Y. Li
- , M. X. Chen
- & L. Li
-
Article |
 Approaching the limits of transparency and conductivity in graphitic materials through lithium intercalation
Approaching the limits of transparency and conductivity in graphitic materials through lithium intercalation
Graphene-based materials have potential as transparent electrodes, but still fall short of desired performance goals. Here, Bao et al.report that upon intercalation of lithium into few-layer graphene, desired sheet resistance and optical transmittance may be achieved.
- Wenzhong Bao
- , Jiayu Wan
- & Liangbing Hu
-
Article |
 Wigner and Kondo physics in quantum point contacts revealed by scanning gate microscopy
Wigner and Kondo physics in quantum point contacts revealed by scanning gate microscopy
The electrical conductance across quantum point contacts shows quantum steps that are well understood except for some anomalies. Here, the authors are able to explain their origin in terms of spontaneously localized electron states by tuning the potential landscape of the contact with a scanning gate microscope.
- B. Brun
- , F. Martins
- & H. Sellier
-
Article |
 Ultra-high aspect ratio high-resolution nanofabrication for hard X-ray diffractive optics
Ultra-high aspect ratio high-resolution nanofabrication for hard X-ray diffractive optics
The increasing use of hard X-ray sources for scientific and biomedical imaging applications requires the development of suitable optical devices to focus and shape these high-energy beams. Here, Chang and Sakdinawat have fabricated ultra-high aspect ratio nanostructures for hard X-ray focusing.
- Chieh Chang
- & Anne Sakdinawat
-
Article |
 Anomalous piezoelectricity in two-dimensional graphene nitride nanosheets
Anomalous piezoelectricity in two-dimensional graphene nitride nanosheets
In piezoelectric materials, mechanical strain and electrical polarization are interlinked. Here, the authors find piezoelectricity in carbon nitride nanosheets, arising from the presence of holes in the two-dimensional sheets.
- Matthew Zelisko
- , Yuranan Hanlumyuang
- & Pradeep Sharma
-
Article |
 Engineering interlocking DNA rings with weak physical interactions
Engineering interlocking DNA rings with weak physical interactions
Catenanes are structures composed of interlocked supramolecular rings, and they have possible applications as molecular switches and nanomotors. Here, the authors present a catenane formed of interlocked DNA rings, and show how each ring can display independent functionalities.
- Zai-Sheng Wu
- , Zhifa Shen
- & Yingfu Li
-
Article |
 Time-bin entangled photons from a quantum dot
Time-bin entangled photons from a quantum dot
Future quantum technologies will need to be integrated with existing fibre networks, so compatible sources of photons are needed. Towards this aim, Jayakumar et al. present a source of time-bin entangled photons using biexciton–exciton cascade in quantum dots.
- Harishankar Jayakumar
- , Ana Predojević
- & Gregor Weihs
-
Article |
 Self-assembled nanoscale coordination polymers with trigger release properties for effective anticancer therapy
Self-assembled nanoscale coordination polymers with trigger release properties for effective anticancer therapy
Nanoscale coordination polymers are promising materials for use as drug delivery nanoparticles, as their structural properties can be easily and precisely controlled to influence drug loading and release. Here, the authors present such a structure for effective in vivoanticancer therapy.
- Demin Liu
- , Christopher Poon
- & Wenbin Lin
-
Article |
 π–π interaction of aromatic groups in amphiphilic molecules directing for single-crystalline mesostructured zeolite nanosheets
π–π interaction of aromatic groups in amphiphilic molecules directing for single-crystalline mesostructured zeolite nanosheets
The preparation of mesoporous zeolites is important for their incorporation into industrially relevant applications. Here, the authors design a single quaternary ammonium head amphiphilic template, which directs the formation of mesostructured crystalline zeolites due to π-stacking supramolecular interactions.
- Dongdong Xu
- , Yanhang Ma
- & Shunai Che
-
Article |
 Supersensitive fingerprinting of explosives by chemically modified nanosensors arrays
Supersensitive fingerprinting of explosives by chemically modified nanosensors arrays
Reliable detection and identification of explosives is difficult due to the large numbers of compounds and the trace amount of material with which to work. Here, the authors show a nanosensor array capable of fingerprinting individual explosives and detecting them down to the parts-per-quadrillion concentration range.
- Amir Lichtenstein
- , Ehud Havivi
- & Fernando Patolsky
-
Article |
 Electrochemical dynamics of nanoscale metallic inclusions in dielectrics
Electrochemical dynamics of nanoscale metallic inclusions in dielectrics
Nanoscale metal inclusions play an important role in solid-state dielectric devices. Here, the authors demonstrate that these inclusions can change their shape, size and position in response to an applied electric field, and that electrochemical processes can lead to metal cluster nucleation and growth.
- Yuchao Yang
- , Peng Gao
- & Wei D. Lu
-
Article |
 Fully-printed high-performance organic thin-film transistors and circuitry on one-micron-thick polymer films
Fully-printed high-performance organic thin-film transistors and circuitry on one-micron-thick polymer films
Organic electronics with good electrical performance and high mechanical stability are of great potential because of their low cost and scalability. Here, Fukuda et al.report the large-area fabrication of fully printable organic thin-film transistors that are only 1 μm thick.
- Kenjiro Fukuda
- , Yasunori Takeda
- & Shizuo Tokito
-
Article |
 Template-mediated nano-crystallite networks in semiconducting polymers
Template-mediated nano-crystallite networks in semiconducting polymers
The formation of a nano-crystalline pathway between the crystalline domains of conjugated polymers is crucial for their charge transport properties. Kwon et al. report a template-mediated crystallization approach at room temperature to improve charge mobility for printable electronics applications.
- Sooncheol Kwon
- , Kilho Yu
- & Kwanghee Lee

 Principle of direct van der Waals epitaxy of single-crystalline films on epitaxial graphene
Principle of direct van der Waals epitaxy of single-crystalline films on epitaxial graphene