Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Protein identification by nanopore peptide profiling
Protein identification by nanopore peptide profiling
Peptide mass fingerprinting is a traditional approach for protein identification by mass spectrometry. Here, the authors provide evidence that peptide mass fingerprinting is also feasible using FraC nanopores, demonstrating protein identification based on nanopore measurements of digested peptides.
- Florian Leonardus Rudolfus Lucas
- , Roderick Corstiaan Abraham Versloot
- & Giovanni Maglia
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable nano-reactors for stochastic sensing
Programmable nano-reactors for stochastic sensing
Monitoring single molecule chemical reactions can be difficult and nanopore based strategies which have shown promise are technically challenging. Here, the authors report on a technique which allows for the direct observation of different reactions and demonstrate the ability to distinguish clinically relevant analogues.
- Wendong Jia
- , Chengzhen Hu
- & Shuo Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Cell membrane coating integrity affects the internalization mechanism of biomimetic nanoparticles
Cell membrane coating integrity affects the internalization mechanism of biomimetic nanoparticles
Cell membrane coating of nanomaterials has become an attractive method of improving targeting, residence and biocompatibility. Here, the authors demonstrated that most nanoparticles are only partially coated by standard methods, and show the coating degree can impact the biological fate of nanoparticles.
- Lizhi Liu
- , Xuan Bai
- & Vesa-Pekka Lehto
-
Article
| Open Access A general approach to protein folding using thermostable exoshells
A general approach to protein folding using thermostable exoshells
In vitro protein folding can often result in aggregation and low yields. Here the authors use nanoscale exoshells to improve soluble yield, functional yield and specific activity of folded proteins.
- Samira Sadeghi
- , Siddharth Deshpande
- & Chester L. Drum
-
Article
| Open Access Near-infrared manipulation of multiple neuronal populations via trichromatic upconversion
Near-infrared manipulation of multiple neuronal populations via trichromatic upconversion
Conventional upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) cannot activate multiple neuron populations independently using optogenetics. Here the authors report trichromatic UCNPs with excitation-specific luminescence to allow activation of three distinct neuronal populations in the brain of awake mice.
- Xuan Liu
- , Heming Chen
- & Fan Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic hydrogel nanoparticles for sepsis therapy
Synthetic hydrogel nanoparticles for sepsis therapy
Sepsis caused by the release of inflammatory mediators into the blood is a life threatening disease. Here, the authors report on the development of hydrogel nanoparticles for the capture and neutralisation of histones, major inflammatory mediators, and demonstrate sepsis treatment in a murine model.
- Hiroyuki Koide
- , Anna Okishima
- & Kenneth J. Shea
-
Article
| Open Access One-step construction of circularized nanodiscs using SpyCatcher-SpyTag
One-step construction of circularized nanodiscs using SpyCatcher-SpyTag
Circularised nanodiscs (cNDs) are able to stabilise large lipid bilayer patches and are used for structural and functional studies. Current techniques to build cNDs have numerous steps and low yields; here the authors report a single step construction method using the SpyCatcher-SpyTag system.
- Shanwen Zhang
- , Qian Ren
- & Huan Bao
-
Article
| Open Access Digital immunoassay for biomarker concentration quantification using solid-state nanopores
Digital immunoassay for biomarker concentration quantification using solid-state nanopores
The concentration of a biomarker in solution can be determined by counting single molecules. Here the authors report a digital immunoassay scheme with solid-state nanopore readout to quantify a target protein and use this to measure thyroid-stimulating hormone from human serum.
- Liqun He
- , Daniel R. Tessier
- & Vincent Tabard-Cossa
-
Article
| Open Access Genetically encoded cell-death indicators (GEDI) to detect an early irreversible commitment to neurodegeneration
Genetically encoded cell-death indicators (GEDI) to detect an early irreversible commitment to neurodegeneration
Cell death is a critical process in health and disease, yet available markers record later stages of cell death once a cell has already begun to decompose. Here the authors show the use of a genetically encoded calcium indicator that demarcates an irreversible stage of cell death earlier than previously possible.
- Jeremy W. Linsley
- , Kevan Shah
- & Steven Finkbeiner
-
Article
| Open Access Synergistic effect of tumor chemo-immunotherapy induced by leukocyte-hitchhiking thermal-sensitive micelles
Synergistic effect of tumor chemo-immunotherapy induced by leukocyte-hitchhiking thermal-sensitive micelles
Targeting the adenosinergic pathway represents a therapeutic option to overcome tumor-induced immunosuppression. Here the authors design E-selectin-modified thermal-sensitive micelles loaded with doxorubicin and an adenosine A2 receptor antagonist to enhance chemotherapy-induced anti-tumor immune responses.
- Jing Qi
- , Feiyang Jin
- & Yongzhong Du
-
Article
| Open Access Microfluidic device with brain extracellular matrix promotes structural and functional maturation of human brain organoids
Microfluidic device with brain extracellular matrix promotes structural and functional maturation of human brain organoids
Brain organoids derived from human pluripotent stem cells can model human brain development and disease, though current culture systems fail to ensure reliable production of high-quality organoids. Here the authors combine human brain extracellular matrix and culture in a microfluidic device to promote structural and functional maturation of human brain organoids.
- Ann-Na Cho
- , Yoonhee Jin
- & Seung-Woo Cho
-
Article
| Open Access Turn-key mapping of cell receptor force orientation and magnitude using a commercial structured illumination microscope
Turn-key mapping of cell receptor force orientation and magnitude using a commercial structured illumination microscope
The authors have recently developed molecular force microscopy (MFM) which uses fluorescence polarisation to measure cell-surface receptor force orientation. Here they show that structured illumination microscopes, which inherently use fluorescence polarisation, can be used for MFM in a turn-key manner.
- Aaron Blanchard
- , J. Dale Combs
- & Khalid Salaita
-
Article
| Open Access Circulating trophoblast cell clusters for early detection of placenta accreta spectrum disorders
Circulating trophoblast cell clusters for early detection of placenta accreta spectrum disorders
Placenta accreta spectrum (PAS) is a high-risk obstetrical complication associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Here the authors discover a uniquely high prevalence of circulating trophoblasts clusters in PAS and explore their diagnostic potential to augment current diagnostic modalities for the early detection of PAS.
- Yalda Afshar
- , Jiantong Dong
- & Yazhen Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid discovery of self-assembling peptides with one-bead one-compound peptide library
Rapid discovery of self-assembling peptides with one-bead one-compound peptide library
Self-assembling peptides have a range of potential applications but developing self-assembling sequences can be challenging. Here, the authors report on a one-bead one-compound combinatorial library where fluorescence is used to detect the potential for self-assembly and identified candidates are evaluated.
- Pei-Pei Yang
- , Yi-Jing Li
- & Kit S. Lam
-
Article
| Open Access Self-rechargeable cardiac pacemaker system with triboelectric nanogenerators
Self-rechargeable cardiac pacemaker system with triboelectric nanogenerators
Self-powered implantable devices have the potential to extend device operation, though current energy harvesters are both insufficient and inconvenient. Here the authors report on a commercial coin battery-sized high-performance inertia-driven triboelectric nanogenerator based on body motion and gravity that can be used to charge a lithium-ion battery and integrated into a cardiac pacemaker.
- Hanjun Ryu
- , Hyun-moon Park
- & Sang-Woo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Integration of photocatalytic and dark-operating catalytic biomimetic transformations through DNA-based constitutional dynamic networks
Integration of photocatalytic and dark-operating catalytic biomimetic transformations through DNA-based constitutional dynamic networks
Nucleic acid-based constitutional dynamic networks (CDNs) enable control of various catalytic processes, but it is challenging to achieve intercommunication between different CDNs and by that mimic complex cell biology networks. Here, the authors report two CDNs that control the integration of photochemical and dark-operating processes, and show their intercommunication afforded by environmental components.
- Chen Wang
- , Michael P. O’Hagan
- & Itamar Willner
-
Article
| Open Access Post-capillary venules are the key locus for transcytosis-mediated brain delivery of therapeutic nanoparticles
Post-capillary venules are the key locus for transcytosis-mediated brain delivery of therapeutic nanoparticles
Limited understanding of the interactions between nanoparticle drug carriers and the blood-brain barrier underlies many translational failures in treatments of brain disorders. Here the authors use two-photon microscopy in mice to characterize the receptor-mediated transcytosis of nanoparticles at all steps of delivery from the blood to the brain in vivo.
- Krzysztof Kucharz
- , Kasper Kristensen
- & Martin Johannes Lauritzen
-
Article
| Open Access Surfactant-guided spatial assembly of nano-architectures for molecular profiling of extracellular vesicles
Surfactant-guided spatial assembly of nano-architectures for molecular profiling of extracellular vesicles
Current methods for controlled assembly of nanomaterials into desired architectures often lack the precision and versatility to develop complex architectures. Here the authors report STAR, surfactant tunable spatial architecture, to guide nanomaterial integration in metal-organic frameworks.
- Zhigang Wang
- , Haitao Zhao
- & Huilin Shao
-
Review Article
| Open Access Nanophotonic biosensors harnessing van der Waals materials
Nanophotonic biosensors harnessing van der Waals materials
This review presents an overview of scenarios where van der Waals (vdW) materials provide unique advantages for nanophotonic biosensing applications. The authors discuss basic sensing principles based on vdW materials, advantages of the reduced dimensionality as well as technological challenges.
- Sang-Hyun Oh
- , Hatice Altug
- & Michael S. Strano
-
Article
| Open Access Acoustoelectronic nanotweezers enable dynamic and large-scale control of nanomaterials
Acoustoelectronic nanotweezers enable dynamic and large-scale control of nanomaterials
Precise and dynamic manipulation of nano-objects on a large scale has been challenging. Here, the authors introduce acoustoelectronic nanotweezers, combining precision of electronic tweezers with large-field dynamic control of acoustic tweezers, demonstrating complex patterning of sub-100 nm objects.
- Peiran Zhang
- , Joseph Rufo
- & Tony Jun Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Ionic contrast across a lipid membrane for Debye length extension: towards an ultimate bioelectronic transducer
Ionic contrast across a lipid membrane for Debye length extension: towards an ultimate bioelectronic transducer
The design of bioelectronic devices that enables accurate detection of biomolecules in ionic solutions at physiologically-relevant concentrations remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a ion-impermeable supported lipid bilayer-assisted field-effect transistor platform for biomolecule detection.
- Donggeun Lee
- , Woo Hyuk Jung
- & Chulki Kim
-
Article
| Open Access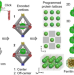 Designed and biologically active protein lattices
Designed and biologically active protein lattices
Organising proteins in 2D and 3D is needed to develop complex bimolecular materials for a range of applications. Here, the authors report the encapsulation of ferritin and apoferritin in DNA-based voxels with programmed assembly to generate both 2D and 3D protein lattices and demonstrate the retention of protein function.
- Shih-Ting Wang
- , Brian Minevich
- & Oleg Gang
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled self-assembly of plant proteins into high-performance multifunctional nanostructured films
Controlled self-assembly of plant proteins into high-performance multifunctional nanostructured films
Green use of plant derived proteins in functional materials has been limited by inefficient methods to control micro and nanoscale structure. Here, the authors use nanoscale assembly of water-insoluble plant proteins to make meter scale films with comparable properties to conventional plastics.
- Ayaka Kamada
- , Marc Rodriguez-Garcia
- & Tuomas P. J. Knowles
-
Article
| Open Access Designing zero-dimensional dimer-type all-inorganic perovskites for ultra-fast switching memory
Designing zero-dimensional dimer-type all-inorganic perovskites for ultra-fast switching memory
Halide perovskite has been applied for resistive switching memory devices, but there are challenges remained to achieve practical application. By using high-throughput screening based on first-principles calculations, the authors discover that lead-free dimer-Cs3Sb2I9 meets the requirements, which exhibits switching speed of 20 ns.
- Youngjun Park
- , Seong Hun Kim
- & Jang-Sik Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule amplification-free multiplexed detection of circulating microRNA cancer biomarkers from serum
Single-molecule amplification-free multiplexed detection of circulating microRNA cancer biomarkers from serum
miRNA profiling from patient blood can be used for cancer diagnosis. Here the authors present an electro-optical nanopore sensing platform which allows sensitive and specific miRNA detection directly in human serum and apply to monitoring of miR-141-3p and miR-375-3p in different stage of prostate cancer.
- Shenglin Cai
- , Thomas Pataillot-Meakin
- & Joshua B. Edel
-
Article
| Open Access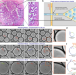 Curvature in the reproductive tract alters sperm–surface interactions
Curvature in the reproductive tract alters sperm–surface interactions
The effect of fallopian tube’s curvature on sperm motion has not been studied in detail. Here, the authors use droplet microfluidics to create soft curved interfaces, revealing a dynamic switch in sperm motility from a progressive surface-aligned mode at low curvatures, to an aggressive surface-attacking mode at high curvatures.
- Mohammad Reza Raveshi
- , Melati S. Abdul Halim
- & Reza Nosrati
-
Article
| Open Access Geometrically encoded SERS nanobarcodes for the logical detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma-related progression biomarkers
Geometrically encoded SERS nanobarcodes for the logical detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma-related progression biomarkers
SERS assays have potential for multiplexed detection of biomarkers but differentiation of SERS tags remains a challenge. Here, the authors report the creation of 14 distinct geometrically controlled metal carbonyl tags and demonstrate multiplexed detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma biomarkers from patient blood.
- Duo Lin
- , Chang-Lin Hsieh
- & Kien Voon Kong
-
Article
| Open Access Nucleoside-modified VEGFC mRNA induces organ-specific lymphatic growth and reverses experimental lymphedema
Nucleoside-modified VEGFC mRNA induces organ-specific lymphatic growth and reverses experimental lymphedema
Dysfunction of the lymphatic system leads to secondary lymphedema and results in degradation of quality of life. Here, the authors show that delivery of nucleoside-modified Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C (VEGFC) mRNA, encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles, induces organ-specific lymphatic growth and reverses experimental lymphedema.
- Dániel Szőke
- , Gábor Kovács
- & Zoltán Jakus
-
Article
| Open Access Glucose-oxidase like catalytic mechanism of noble metal nanozymes
Glucose-oxidase like catalytic mechanism of noble metal nanozymes
Gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) with enzyme-like activities are useful glucose oxidase mimics, but the insights into the mechanism of this reaction are limited. Here, the authors show that the process of glucose oxidation by Au NPs is analogous to the one catalysed by glucose oxidase, involving dehydrogenation and oxygen reduction to H2O2; and that other noble metal NPs also catalyse glucose dehydrogenation, but oxygen is preferably reduced to water.
- Jinxing Chen
- , Qian Ma
- & Shaojun Dong
-
Article
| Open Access Structural-profiling of low molecular weight RNAs by nanopore trapping/translocation using Mycobacterium smegmatis porin A
Structural-profiling of low molecular weight RNAs by nanopore trapping/translocation using Mycobacterium smegmatis porin A
Nanopores have been used for direct observation of RNA structure in native environments but have limited RNA differentiation capabilities. Here, the authors report on the use of Mycobacterium smegmatis porin A nanopores for the trapping and translocation identification of microRNA, siRNA, tRNA and ribosomal RNA.
- Yuqin Wang
- , Xiaoyu Guan
- & Shuo Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Dielectric nanohole array metasurface for high-resolution near-field sensing and imaging
Dielectric nanohole array metasurface for high-resolution near-field sensing and imaging
Dielectric metasurfaces have different Q-factor and light localisation requirements for sensing and imaging. Here, the authors present a dielectric metasurface, supporting two optical modes with sharp Fano resonances for high Q-factors and strong spatial confinement, allowing both sensing and imaging.
- Donato Conteduca
- , Isabel Barth
- & Thomas F. Krauss
-
Article
| Open Access An electronic neuromorphic system for real-time detection of high frequency oscillations (HFO) in intracranial EEG
An electronic neuromorphic system for real-time detection of high frequency oscillations (HFO) in intracranial EEG
A major challenge across a variety of fields is how to process the vast quantities of data produced by sensors without large computation resources. Here, the authors present a neuromorphic chip which can detect a relevant signature of epileptogenic tissue from intracranial recordings in patients.
- Mohammadali Sharifshazileh
- , Karla Burelo
- & Giacomo Indiveri
-
Article
| Open Access Label-free characterization of organic nanocarriers reveals persistent single molecule cores for hydrocarbon sequestration
Label-free characterization of organic nanocarriers reveals persistent single molecule cores for hydrocarbon sequestration
In-situ methods are important for investigating the local structure and function in molecular nanostructures but such investigations often involve laborious labeling methods that can disrupt behavior or are not fast enough to capture stimuli-responsive phenomena. Here, the authors use X-rays resonant with molecular bonds to demonstrate an in-situ nanoprobe that eliminates the need for labels and enables data collection times within seconds.
- Terry McAfee
- , Thomas Ferron
- & Brian A. Collins
-
Article
| Open Access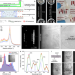 Cellular lensing and near infrared fluorescent nanosensor arrays to enable chemical efflux cytometry
Cellular lensing and near infrared fluorescent nanosensor arrays to enable chemical efflux cytometry
The authors present nanosensor chemical cytometry, based on an array of nIR fluorescent single walled carbon nanotube integrated along a microfluidic channel. The lensing effect of the flowing cells allows for extracting information, and correlating biomolecular information with physical properties.
- Soo-Yeon Cho
- , Xun Gong
- & Michael S. Strano
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular exclusion limits for diffusion across a porous capsid
Molecular exclusion limits for diffusion across a porous capsid
Molecular transport across physical barriers requires pores that connect to the environment. Here, the authors report on a solution based dynamic study into the effects of size and charge on the transport through the pores of virus-like particles derived from bacteriophage P22 using an encapsulated redox system.
- Ekaterina Selivanovitch
- , Benjamin LaFrance
- & Trevor Douglas
-
Article
| Open Access Programmably tiling rigidified DNA brick on gold nanoparticle as multi-functional shell for cancer-targeted delivery of siRNAs
Programmably tiling rigidified DNA brick on gold nanoparticle as multi-functional shell for cancer-targeted delivery of siRNAs
Small interfering RNA (siRNA) is used to regulate gene expression for therapeutic purposes, but the design of stable and efficient siRNA delivery systems is challenging. Here, the authors develop a siRNA-encapsulated and aptamer-incorporated core/shell nanoparticle for controlled siRNA delivery, with high stability, tumor-specific targeting and long circulation time.
- Chang Xue
- , Shuyao Hu
- & Zai-Sheng Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Microfluidic platform accelerates tissue processing into single cells for molecular analysis and primary culture models
Microfluidic platform accelerates tissue processing into single cells for molecular analysis and primary culture models
Existing methods for tissue dissociation are inefficient and lead to variable outcomes and biases. Here, the authors present a microfluidic platform that combines digestion, disaggregation and filtration of tissue to allow single cell analysis and RNA sequencing.
- Jeremy A. Lombardo
- , Marzieh Aliaghaei
- & Jered B. Haun
-
Article
| Open Access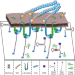 Super-resolved visualization of single DNA-based tension sensors in cell adhesion
Super-resolved visualization of single DNA-based tension sensors in cell adhesion
Relatively little is known about cell-matrix interactions and the intracellular transduction of an initial ligand-receptor binding event on the single-molecule level. Here authors combine ligand-decorated DNA tension sensors with DNA-PAINT super-resolution microscopy to study the mechanical engagement of single integrin receptors and the downstream influence on actin bundling.
- Thomas Schlichthaerle
- , Caroline Lindner
- & Ralf Jungmann
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative imaging of intracellular nanoparticle exposure enables prediction of nanotherapeutic efficacy
Quantitative imaging of intracellular nanoparticle exposure enables prediction of nanotherapeutic efficacy
Quantification of intratumoral nanoparticles internalisation in vivo is crucial but challenging. Here, the authors develop a binary ratiometric nanoreporter that can quantify internalisation and predict nanotherapeutic responses based on intracellular nanoparticle exposure.
- Qingqing Yin
- , Anni Pan
- & Yiguang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access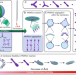 Generating biomembrane-like local curvature in polymersomes via dynamic polymer insertion
Generating biomembrane-like local curvature in polymersomes via dynamic polymer insertion
Investigating biomembrane curvature formation is important for studying intracellular processes, but the instability of liposome models mimicking these membranes restricts exploration of membrane processes. Here, the authors demonstrate control over the curvature formation in polymersome membranes by insertion of PNIPAm as stimuli responsive polymer.
- Jiawei Sun
- , Sjoerd J. Rijpkema
- & Daniela A. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access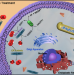 2D vanadium carbide MXenzyme to alleviate ROS-mediated inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases
2D vanadium carbide MXenzyme to alleviate ROS-mediated inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases
Materials with enzymatic-like activities are of interest for a wide range of applications. Here, the authors report on 2D vanadium carbide MXene nanozymes capable of mimicking multiple enzymes and demonstrate application to treat reactive oxygen species-mediated inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Wei Feng
- , Xiuguo Han
- & Yuehua Li
-
Article
| Open Access Stabilization of supramolecular membrane protein–lipid bilayer assemblies through immobilization in a crystalline exoskeleton
Stabilization of supramolecular membrane protein–lipid bilayer assemblies through immobilization in a crystalline exoskeleton
Stabilizing lipid nanoparticles and lipidprotein assemblies is challenging owing to lipid dynamics and protein instability. Here, the authors report on the reversible encapsulation of liposomes and proteoliposomes in a metalorganic framework permitting months-long room temp storage.
- Fabian C. Herbert
- , Sameera S. Abeyrathna
- & Jeremiah J. Gassensmith
-
Article
| Open Access Reovirus directly engages integrin to recruit clathrin for entry into host cells
Reovirus directly engages integrin to recruit clathrin for entry into host cells
Reovirus endocytosis depends on junctional adhesion molecule A (JAM-A) and β1 integrin binding. Here, Koehler et al. use single-virus force spectroscopy and confocal microscopy to demonstrate a direct interaction between reovirus and β1 integrins via viral capsid protein λ2, which promotes clathrin recruitment to cell-bound reovirus.
- Melanie Koehler
- , Simon J. L. Petitjean
- & David Alsteens
-
Article
| Open Access Bioengineered bacteria-derived outer membrane vesicles as a versatile antigen display platform for tumor vaccination via Plug-and-Display technology
Bioengineered bacteria-derived outer membrane vesicles as a versatile antigen display platform for tumor vaccination via Plug-and-Display technology
Outer membrane vesicles (OMVs), non-replicative particles secreted by Gram-negative bacteria, are known for their immunostimulatory and adjuvant properties. Here, by employing a Plug-and-Display technology, the authors engineer OMVs to display tumor antigens on the surface, a platform that promotes anti-tumor immune responses in preclinical cancer models.
- Keman Cheng
- , Ruifang Zhao
- & Guangjun Nie
-
Article
| Open Access Intratumoral immunotherapy using platelet-cloaked nanoparticles enhances antitumor immunity in solid tumors
Intratumoral immunotherapy using platelet-cloaked nanoparticles enhances antitumor immunity in solid tumors
The immunostimulatory properties of TLR7/8 agonists, such as resiquimod, have been exploited for cancer immunotherapy. Here, the authors design platelet membrane-cloaked nanoparticles for selective intratumoral delivery of resiquimod, resulting in potent anti-tumor immune response in a range of preclinical solid tumors.
- Baharak Bahmani
- , Hua Gong
- & Jie Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access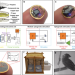 Wireless battery free fully implantable multimodal recording and neuromodulation tools for songbirds
Wireless battery free fully implantable multimodal recording and neuromodulation tools for songbirds
Studies requiring neural modulation in species that fly are difficult because of the need for wired connections to record experimental data. Here, Ausra et al. present a wireless and battery free device that achieves this in songbirds, model organisms used to study vocal learning and maintenance.
- Jokubas Ausra
- , Stephanie J. Munger
- & Philipp Gutruf
-
Article
| Open Access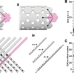 Robust nucleation control via crisscross polymerization of highly coordinated DNA slats
Robust nucleation control via crisscross polymerization of highly coordinated DNA slats
For programmable DNA self-assembly, it is desirable to suppress spontaneous nucleation to enable all-or-nothing assembly of nanostructures far larger than a single DNA origami. Here the authors introduce crisscross polymerization of elongated slat monomers that engage beyond nearest neighbors, providing strictly seed-initiated nucleation of crisscross ribbons with distinct widths and twists.
- Dionis Minev
- , Christopher M. Wintersinger
- & William M. Shih
-
Article
| Open Access Photonic resonator interferometric scattering microscopy
Photonic resonator interferometric scattering microscopy
Here, the authors present photonic resonator interferometric scattering microscopy, which utilises a dielectric photonic crystal as the sample substrate. The resonant near-field enhancement leads to improved signal to noise ratio without increasing illumination intensity.
- Nantao Li
- , Taylor D. Canady
- & Brian T. Cunningham
-
Article
| Open Access A digital single-molecule nanopillar SERS platform for predicting and monitoring immune toxicities in immunotherapy
A digital single-molecule nanopillar SERS platform for predicting and monitoring immune toxicities in immunotherapy
There is a clinical need to monitor immune-related toxicities of immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Here, the authors develop a digital SERS platform for multiplexed single cytokine counting to track immune-toxicities and demonstrate the ability to use pre-screening to identify patients at higher risk.
- Junrong Li
- , Alain Wuethrich
- & Matt Trau

 Multi-targeted 1H/19F MRI unmasks specific danger patterns for emerging cardiovascular disorders
Multi-targeted 1H/19F MRI unmasks specific danger patterns for emerging cardiovascular disorders