Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Near-infrared II plasmonic porous cubic nanoshells for in vivo noninvasive SERS visualization of sub-millimeter microtumors
Near-infrared II plasmonic porous cubic nanoshells for in vivo noninvasive SERS visualization of sub-millimeter microtumors
In vivo surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) imaging allows non-invasive visualization of tumours for biomedical applications. Here, the authors report porous cubic AuAg alloy nanoshells exhibiting plasmonic properties and porosity-dependant SERS in the second window of the near-infrared for in vivo tumour detection.
- Linhu Li
- , Renting Jiang
- & Ming Li
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable and scalable fabrication of block copolymer-based 3D polymorphic artificial cell membrane array
Tunable and scalable fabrication of block copolymer-based 3D polymorphic artificial cell membrane array
In this manuscript, an electric-field-assisted self-assembly technique that can allow controllable and scalable fabrication of 3-dimensional block copolymer (BCP)-based artificial cell membranes (3DBCPMs) immobilized on predefined locations is presented.
Topographically and chemically structured microwell array templates facilitate uniform patterning of BCPs and serve as reactors for the effective growth of 3DBCPMs, which diverse shapes, sizes and stability can be tuned by modulating the BCP concentration and the amplitude/frequency of the electric field.
The potential of 3DBCPMs for a variety of biological applications is highlighted by performance of in vitro protein-membrane assays and mimicking of human intestinal organs.
- Dong-Hyun Kang
- , Won Bae Han
- & Tae Song Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled self-assembly of plant proteins into high-performance multifunctional nanostructured films
Controlled self-assembly of plant proteins into high-performance multifunctional nanostructured films
Green use of plant derived proteins in functional materials has been limited by inefficient methods to control micro and nanoscale structure. Here, the authors use nanoscale assembly of water-insoluble plant proteins to make meter scale films with comparable properties to conventional plastics.
- Ayaka Kamada
- , Marc Rodriguez-Garcia
- & Tuomas P. J. Knowles
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasensitive antibody-aptamer plasmonic biosensor for malaria biomarker detection in whole blood
Ultrasensitive antibody-aptamer plasmonic biosensor for malaria biomarker detection in whole blood
Reliable plasmonic biosensors with high throughput and ease of use are highly sought after. Here, the authors report a plasmon-enhanced fluorescence antibody-aptamer biosensor based on a gold nanoparticle array, and demonstrate its use for effective specific detection of a malaria marker, at femtomolar level, in whole blood.
- Antonio Minopoli
- , Bartolomeo Della Ventura
- & Raffaele Velotta
-
Article
| Open Access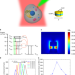 Over 1000-fold enhancement of upconversion luminescence using water-dispersible metal-insulator-metal nanostructures
Over 1000-fold enhancement of upconversion luminescence using water-dispersible metal-insulator-metal nanostructures
Upconversion nanoparticles are already used in bio-imaging but still suffer from low luminescence. Here, metal-insulator-metal nanostructures with 1-2 orders magnitude enhancement in upconversion are introduced enabling bioimaging at reduced particle or excitation power densities, respectively.
- Ananda Das
- , Chenchen Mao
- & Wounjhang Park
-
Article
| Open Access Cell shape information is transduced through tension-independent mechanisms
Cell shape information is transduced through tension-independent mechanisms
It is not known whether the shape of a cell can regulate cellular phenotype independently. Here, the authors show that culturing kidney podocytes or smooth muscle cells on 3-D biomimetic surfaces results in phenotypic changes and that cell shape is sensed by integrin β3 in a tension-independent manner.
- Amit Ron
- , Evren U. Azeloglu
- & Ravi Iyengar
-
Article
| Open Access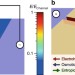 Enhanced nanochannel translocation and localization of genomic DNA molecules using three-dimensional nanofunnels
Enhanced nanochannel translocation and localization of genomic DNA molecules using three-dimensional nanofunnels
Forcing a DNA molecule into a nanoscale channel requires overcoming the free energy barrier associated with confinement. Here, the authors show that DNA injected through a funnel-shaped entrance more efficiently enters the nanochannel, thanks to facilitating forces generated by the nanofunnel geometry.
- Jinsheng Zhou
- , Yanqian Wang
- & J. Michael Ramsey
-
Article
| Open Access Wafer-scale integration of sacrificial nanofluidic chips for detecting and manipulating single DNA molecules
Wafer-scale integration of sacrificial nanofluidic chips for detecting and manipulating single DNA molecules
The wide use of microfluidics for biological analysis demands scalable preparation methods, yet in practice it is very challenging. Here, Wanget al. show a wafer-scale fabrication of nanofluidic chips with single-digit nanometre dimension, which is compatible with standard semiconductor processing.
- Chao Wang
- , Sung-Wook Nam
- & Qinghuang Lin
-
Article
| Open Access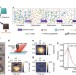 Nanoscale probing of electron-regulated structural transitions in silk proteins by near-field IR imaging and nano-spectroscopy
Nanoscale probing of electron-regulated structural transitions in silk proteins by near-field IR imaging and nano-spectroscopy
Silk protein fibres are exceptionally strong, owing to their high β-sheet nanocrystal content. Here, the authors use an electron beam to guide silk β-sheet crystals through structural transitions, and visualize the changes by infrared near-field optics, achieving close to molecular-level resolution.
- Nan Qin
- , Shaoqing Zhang
- & Tiger H. Tao
-
Article
| Open Access Mass production of two-dimensional oxides by rapid heating of hydrous chlorides
Mass production of two-dimensional oxides by rapid heating of hydrous chlorides
Oxide nanosheets are of interest for a range of applications. Here the authors demonstrate a simple route combining gas evolution and exfoliation of hydrated chloride precursors for making large quantities of oxide nanosheets of various compositions.
- Chunsong Zhao
- , Haitian Zhang
- & Hui Wu
-
Article
| Open Access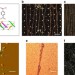 Automated circuit fabrication and direct characterization of carbon nanotube vibrations
Automated circuit fabrication and direct characterization of carbon nanotube vibrations
Integrating carbon nanotubes into electronic devices requires quick and non-invasive imaging of the nanostructures for precision positioning. Here, the authors use the base of the nanotubes to nucleate the growth of optically visible organic nanocrystals, which thus enables simple microscopy.
- G. Zeevi
- , M. Shlafman
- & Y. E. Yaish
-
Article
| Open Access Wafer-scale fabrication and growth dynamics of suspended graphene nanoribbon arrays
Wafer-scale fabrication and growth dynamics of suspended graphene nanoribbon arrays
Shaping atomically thin materials in suspended structures may provide a viable platform for nanoscale mechanical oscillators. Here, the authors demonstrate wafer-scale, high-yield synthesis of suspended graphene nanoribbon arrays using a bottom-up approach and shed light into their growth dynamics.
- Hiroo Suzuki
- , Toshiro Kaneko
- & Toshiaki Kato
-
Article
| Open Access Robust and stretchable indium gallium zinc oxide-based electronic textiles formed by cilia-assisted transfer printing
Robust and stretchable indium gallium zinc oxide-based electronic textiles formed by cilia-assisted transfer printing
The fabrication of smart textiles is currently relying on the printing of ultrathin electronics on fabric, which is subject to the poor adhesion between electronics and textile. Here, Yoon et al. propose the use of cilia-like structure to improve adhesion in addition to release mechanical stress.
- Jongwon Yoon
- , Yunkyung Jeong
- & Heung Cho Ko
-
Article
| Open Access Geometrical assembly of ultrastable protein templates for nanomaterials
Geometrical assembly of ultrastable protein templates for nanomaterials
Protein nanotechnology for the fabrication of protein-based nanoscale devices is gaining momentum but assembling well-defined three-dimensional shapes is still challenging. Here, the authors use an existing prefoldin assembled system to design a template for the construction of geometrically constrained structures.
- Dominic J. Glover
- , Lars Giger
- & Douglas S. Clark
-
Article
| Open Access Viscoelastic lithography for fabricating self-organizing soft micro-honeycomb structures with ultra-high aspect ratios
Viscoelastic lithography for fabricating self-organizing soft micro-honeycomb structures with ultra-high aspect ratios
Tissue engineering applications call for controllable micro-structural units as a platform, but their fabrication remains challenging. Here, Jeong et al. show a method that enables soft materials to self-organize into highly packed micro-honeycomb structures with aspect ratios up to 500, and tunable shapes.
- Gi Seok Jeong
- , Da Yoon No
- & Sang-Hoon Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Highly efficient and ultra-broadband graphene oxide ultrathin lenses with three-dimensional subwavelength focusing
Highly efficient and ultra-broadband graphene oxide ultrathin lenses with three-dimensional subwavelength focusing
Lenses made from metamaterials often suffer from narrow operational bandwidth and complex design. Here, Zheng et al.demonstrate an ultrathin graphene oxide lens with farfield three-dimensional subwavelength focusing from the visible to near infrared and an absolute focusing efficiency greater than 32%.
- Xiaorui Zheng
- , Baohua Jia
- & Min Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Piezotransistive transduction of femtoscale displacement for photoacoustic spectroscopy
Piezotransistive transduction of femtoscale displacement for photoacoustic spectroscopy
Microelectromechanical systems—micrometre-sized devices with movable parts—make highly sensitive transducers. Here, the authors fabricate an integrated gallium nitride microcantilever and heterojunction field effect transistor that uses piezoelectric effects to measure displacement at the femtoscale level.
- Abdul Talukdar
- , M. Faheem Khan
- & Goutam Koley
-
Article |
 Three-dimensional patterning of solid microstructures through laser reduction of colloidal graphene oxide in liquid-crystalline dispersions
Three-dimensional patterning of solid microstructures through laser reduction of colloidal graphene oxide in liquid-crystalline dispersions
Existing lithographic methods for the micropatterning of reduced graphene oxide (rGO) are limited by mask production. Here, the authors fabricate fully 3D rGO microstructures in an aqueous nematic liquid crystal of two-dimensional GO flakes via a scalable, mask-free pulsed near-infrared laser approach.
- Bohdan Senyuk
- , Natnael Behabtu
- & Ivan I. Smalyukh
-
Article
| Open Access Fabrication of three-dimensionally interconnected nanoparticle superlattices and their lithium-ion storage properties
Fabrication of three-dimensionally interconnected nanoparticle superlattices and their lithium-ion storage properties
Three-dimensional nanoparticle superlattices are interesting, but their fabrication is generally limited to materials attainable as monodisperse colloidal nanoparticles. Here, the authors fabricate interconnected superlattices via self-assembly without the presynthesis of the constituent nanoparticles.
- Yucong Jiao
- , Dandan Han
- & Angang Dong
-
Article |
 Self-assembled hydrogels utilizing polymer–nanoparticle interactions
Self-assembled hydrogels utilizing polymer–nanoparticle interactions
Mouldable hydrogels find a variety of applications in the biomedical industry. Here, Appel et al. show a method to fabricate hydrogels through a self-assembly process based on the interaction between biopolymers and functional nanoparticles for multistage drug delivery in vivo.
- Eric A. Appel
- , Mark W. Tibbitt
- & Robert Langer
-
Article |
 Cracking-assisted photolithography for mixed-scale patterning and nanofluidic applications
Cracking-assisted photolithography for mixed-scale patterning and nanofluidic applications
Cracks in material are not always unwanted; sometimes, they can be manipulated to produce micro and nanoscale patterns. Here, Kim et al. report a cracking-assisted nanofabrication technique based on conventional photolithography process, which allows accurate control over the geometry of the nanopatterns in arbitrary shape.
- Minseok Kim
- , Dogyeong Ha
- & Taesung Kim
-
Article |
 Coherent spin control of a nanocavity-enhanced qubit in diamond
Coherent spin control of a nanocavity-enhanced qubit in diamond
Nitrogen-vacancy centres in diamond have established themselves as excellent candidates for solid-state quantum memories due to their optical addressability and long coherence times. Here, the authors report on a diamond-nanocavity system with improved spin-photon interface performances.
- Luozhou Li
- , Tim Schröder
- & Dirk Englund
-
Article |
 Laser-targeted photofabrication of gold nanoparticles inside cells
Laser-targeted photofabrication of gold nanoparticles inside cells
Photonic methods can be greatly improved by metal nanoparticles, but biological targets such as cells prevent spatial control of particles, excluding key regions of interest. Here, the authors show laser light can control nanoparticle growth locations in the cell, and probe intracellular molecules.
- Nicholas I. Smith
- , Kentaro Mochizuki
- & Yutaro Kumagai
-
Article |
 Nanomotor lithography
Nanomotor lithography
Miniaturization of devices and machines requires advanced lithographic techniques, whilst the high cost and complexity are the bottlenecks. Li et al.now show an approach for direct, arbitrary nano-patterning using self-propelled nanomotors acting as mobile nanomasks and near-field lenses.
- Jinxing Li
- , Wei Gao
- & Joseph Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Mesoscale assembly of chemically modified graphene into complex cellular networks
Mesoscale assembly of chemically modified graphene into complex cellular networks
Graphene’s properties are well known, but turning this atomically thin material into three-dimensional devices remains a challenge. Here, the authors report an assembly process for chemically modified graphene into three-dimensional cellular networks, with control over the physical properties of the resulting materials.
- Suelen Barg
- , Felipe Macul Perez
- & Eduardo Saiz
-
Article |
 Self-assembly of free-standing RNA membranes
Self-assembly of free-standing RNA membranes
Nucleic acids possess a number of properties that can be beneficial for the fabrication of nanomaterials. Here, the authors present an enzymatically synthesised RNA membrane, and show how its physical properties can be controlled by changes to base-pairing.
- Daehoon Han
- , Yongkuk Park
- & Jong Bum Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Fabrication of enzyme-degradable and size-controlled protein nanowires using single particle nano-fabrication technique
Fabrication of enzyme-degradable and size-controlled protein nanowires using single particle nano-fabrication technique
High-energy particles can be used for precise fabrication of nanostructures by inducing cross-linking between structures. Here the authors use a single particle fabrication technique to assemble protein nanowires, giving structures with high aspect ratios retaining biological functions.
- Masaaki Omichi
- , Atsushi Asano
- & Shu Seki
-
Article |
 Catalytic subsurface etching of nanoscale channels in graphite
Catalytic subsurface etching of nanoscale channels in graphite
Metallic particles are known to etch the surface layers of graphite by catalytic hydrogenation. Here, the authors report the sub-surface etching of graphite by Ni nanoparticles, revealing the formation of networks of tunnels, which are observed microscopically and could be modified for various applications.
- Maya Lukas
- , Velimir Meded
- & Ralph Krupke
-
Article
| Open Access Mediatorless high-power glucose biofuel cells based on compressed carbon nanotube-enzyme electrodes
Mediatorless high-power glucose biofuel cells based on compressed carbon nanotube-enzyme electrodes
Glucose biofuel cells can be used to produce clean energy from renewable sources, but their use is limited by poor stability and low power output. In this study, bioelectrodes are fabricated using carbon nanotubes and the resulting biofuel cells have improved stability and power.
- Abdelkader Zebda
- , Chantal Gondran
- & Serge Cosnier
-
Article |
 Piezoelectric-nanowire-enabled power source for driving wireless microelectronics
Piezoelectric-nanowire-enabled power source for driving wireless microelectronics
Energy harvesting through mechanical actions of nanosized components could be useful for powering mobile electronics. Here, the authors grow lead zirconate nanowire arrays at comparatively low temperature and use them to power a macroscopic laser diode.
- Sheng Xu
- , Benjamin J. Hansen
- & Zhong Lin Wang

 Direct in situ photolithography of perovskite quantum dots based on photocatalysis of lead bromide complexes
Direct in situ photolithography of perovskite quantum dots based on photocatalysis of lead bromide complexes