Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access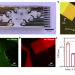 A hybrid transistor with transcriptionally controlled computation and plasticity
A hybrid transistor with transcriptionally controlled computation and plasticity
Interfacing living systems with electronics for biosensing and biocomputing applications is challenging. Here, Gao et al. present hybrid transistors with electroactive bacteria capable of extracellular electron transfer, enabling transduction of biological computations to electrical readouts.
- Yang Gao
- , Yuchen Zhou
- & Benjamin K. Keitz
-
Article
| Open Access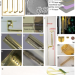 Flexible, scalable, high channel count stereo-electrode for recording in the human brain
Flexible, scalable, high channel count stereo-electrode for recording in the human brain
Electrodes available for deep brain recording and stimulation have a number of limitations. Here the authors describe a thin-film depth electrode that may offer improved spatial and temporal resolution for recording brain activity.
- Keundong Lee
- , Angelique C. Paulk
- & Shadi. A. Dayeh
-
Article
| Open Access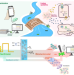 Redox-enabled electronic interrogation and feedback control of hierarchical and networked biological systems
Redox-enabled electronic interrogation and feedback control of hierarchical and networked biological systems
With redox-linked synthetic biology and electrobiofabrication, electronic information can be transmitted in a bidirectional manner between biology and electronics. Here the authors design an electrogenetic platform that allows real time electronic control of biological functions from proteins and gene circuits to cell consortia.
- Sally Wang
- , Chen-Yu Chen
- & William E. Bentley
-
Article
| Open Access The ultra-thin, minimally invasive surface electrode array NeuroWeb for probing neural activity
The ultra-thin, minimally invasive surface electrode array NeuroWeb for probing neural activity
Minimal invasiveness and robust signal detection are required in neural probes. Here, the authors develop NeuroWeb, an ultra-thin, minimally invasive surface electrode array. In vivo electrophysiological and optogenetic experiments show single-unit activity of neurons with high signal-to-noise ratio.
- Jung Min Lee
- , Young-Woo Pyo
- & Hong-Gyu Park
-
Article
| Open Access Visualizing single-molecule conformational transition and binding dynamics of intrinsically disordered proteins
Visualizing single-molecule conformational transition and binding dynamics of intrinsically disordered proteins
Intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) are highly dynamic and play pivotal roles in cellular processes but can be difficult to study. Here, the authors develop a single-molecule nanocircuit for the real-time monitoring of c-Myc conformational transitions and their interaction with ligands.
- Wenzhe Liu
- , Limin Chen
- & Xuefeng Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Improved pharmacodynamics of epidermal growth factor via microneedles-based self-powered transcutaneous electrical stimulation
Improved pharmacodynamics of epidermal growth factor via microneedles-based self-powered transcutaneous electrical stimulation
The use of epidermal growth factor for wound healing is limited by transdermal permeability, reduction, and receptor desensitization. Here the authors develop a microneedle-based self-powered transcutaneous electrical stimulation system to overcome these challenges.
- Yuan Yang
- , Ruizeng Luo
- & Zhong Lin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable CRISPR-Cas9 microneedle patch for long-term capture and real-time monitoring of universal cell-free DNA
Programmable CRISPR-Cas9 microneedle patch for long-term capture and real-time monitoring of universal cell-free DNA
Real-time sensing of biomarkers via the use of wearable devices is a major aim of personalised medicine. Here, authors demonstrate an on-line wearable microneedle patch for real-time capture and monitoring of universal cell-free DNA.
- Bin Yang
- , Jilie Kong
- & Xueen Fang
-
Article
| Open Access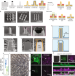 Nanocrown electrodes for parallel and robust intracellular recording of cardiomyocytes
Nanocrown electrodes for parallel and robust intracellular recording of cardiomyocytes
Nanoelectrodes for measuring intracellular action potentials suffer from issues with success rate, signal strength and fabrication. Here, the authors report on a scalable technique which creates robust nanocrown electrodes with high success rates by electroporation and demonstrate the advance towards preclinical drug evaluation.
- Zeinab Jahed
- , Yang Yang
- & Bianxiao Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Self-activating anti-infection implant
Self-activating anti-infection implant
Bone implants with antibacterial and osteogenic properties are important for clinical applications, but creating both properties simultaneously remains challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate a self-activating implant using a hydroxyapatite and molybdenum disulfide coating which accelerates bone regeneration and at the same time prevents bacterial infection.
- Jieni Fu
- , Weidong Zhu
- & Shuilin Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Self-rechargeable cardiac pacemaker system with triboelectric nanogenerators
Self-rechargeable cardiac pacemaker system with triboelectric nanogenerators
Self-powered implantable devices have the potential to extend device operation, though current energy harvesters are both insufficient and inconvenient. Here the authors report on a commercial coin battery-sized high-performance inertia-driven triboelectric nanogenerator based on body motion and gravity that can be used to charge a lithium-ion battery and integrated into a cardiac pacemaker.
- Hanjun Ryu
- , Hyun-moon Park
- & Sang-Woo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Ionic contrast across a lipid membrane for Debye length extension: towards an ultimate bioelectronic transducer
Ionic contrast across a lipid membrane for Debye length extension: towards an ultimate bioelectronic transducer
The design of bioelectronic devices that enables accurate detection of biomolecules in ionic solutions at physiologically-relevant concentrations remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a ion-impermeable supported lipid bilayer-assisted field-effect transistor platform for biomolecule detection.
- Donggeun Lee
- , Woo Hyuk Jung
- & Chulki Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Designing zero-dimensional dimer-type all-inorganic perovskites for ultra-fast switching memory
Designing zero-dimensional dimer-type all-inorganic perovskites for ultra-fast switching memory
Halide perovskite has been applied for resistive switching memory devices, but there are challenges remained to achieve practical application. By using high-throughput screening based on first-principles calculations, the authors discover that lead-free dimer-Cs3Sb2I9 meets the requirements, which exhibits switching speed of 20 ns.
- Youngjun Park
- , Seong Hun Kim
- & Jang-Sik Lee
-
Article
| Open Access A highly conductive fibre network enables centimetre-scale electron transport in multicellular cable bacteria
A highly conductive fibre network enables centimetre-scale electron transport in multicellular cable bacteria
Cable bacteria’ form long multicellular filaments that can transfer electrical currents over centimetre-long distances. Here, Meysman et al. show that the electrical currents run along highly conductive fibres embedded in the cell envelope, and charge transfer is electronic rather than ionic.
- Filip J. R. Meysman
- , Rob Cornelissen
- & Jean V. Manca
-
Article
| Open Access A bioinspired optoelectronically engineered artificial neurorobotics device with sensorimotor functionalities
A bioinspired optoelectronically engineered artificial neurorobotics device with sensorimotor functionalities
The internet of things technologies relies on the development of sensorimotor systems. Here, Karbalaei Akbari and Zhuiykov show a bioinspired sensorimotor system based on an integration of an artificial optical synapse and a liquid metal actuator, which mimics the expansion and contraction of biological muscles.
- Mohammad Karbalaei Akbari
- & Serge Zhuiykov
-
Article
| Open Access A photoelectrochemical platform for the capture and release of rare single cells
A photoelectrochemical platform for the capture and release of rare single cells
Many cell capture systems exist but the characterisation and controlled release of single cells is a challenge. Here, the authors report on the development of a duel trigger release system using a combination of photo and electro triggers to allow for light based analysis without unwanted release.
- Stephen G. Parker
- , Ying Yang
- & J. Justin Gooding
-
Article
| Open Access Cellular interfaces with hydrogen-bonded organic semiconductor hierarchical nanocrystals
Cellular interfaces with hydrogen-bonded organic semiconductor hierarchical nanocrystals
Nanomaterials that form a bioelectronic interface with cells are fascinating tools for controlling cellular behavior. Here, the authors photostimulate single cells with spiky assemblies of semiconducting quinacridone nanocrystals, whose nanoscale needles maximize electronic contact with the cells.
- Mykhailo Sytnyk
- , Marie Jakešová
- & Eric Daniel Głowacki
-
Article
| Open Access Electrostatic melting in a single-molecule field-effect transistor with applications in genomic identification
Electrostatic melting in a single-molecule field-effect transistor with applications in genomic identification
DNA hybridization of two single-strands to form a double-stranded helix is widely used for genomic identification applications. Here, Vernicket al. record duplex formation of 20-mer oligonucleotide using a single-molecule field-effect transistor, where DNA kinetics is affected by electrostatic bias.
- Sefi Vernick
- , Scott M. Trocchia
- & Kenneth L. Shepard
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time encoding and compression of neuronal spikes by metal-oxide memristors
Real-time encoding and compression of neuronal spikes by metal-oxide memristors
The need for intelligent compression of big data, for example in neuroscience, has sparked interest in neuromorphic data processing. Here, Gupta et al.use memristors as event integrators to encode and compress neuronal spiking activity recorded by multi-electrode arrays.
- Isha Gupta
- , Alexantrou Serb
- & Themistoklis Prodromakis
-
Article
| Open Access Bio-recognitive photonics of a DNA-guided organic semiconductor
Bio-recognitive photonics of a DNA-guided organic semiconductor
BioLEDs is an emerging group of light-emitting diodes that use duplex-strand DNA to enhance luminescence intensity. Here, Back et al.show that only the specific binding between a pair of single-strand DNA can trigger the enhancement, which potentially makes BioLEDs an easy platform for DNA recognition.
- Seung Hyuk Back
- , Jin Hyuk Park
- & Dong June Ahn
-
Article
| Open Access Scaling up nanoscale water-driven energy conversion into evaporation-driven engines and generators
Scaling up nanoscale water-driven energy conversion into evaporation-driven engines and generators
Harvesting energy from evaporation is constrained by the limited transport kinetics of materials and the slowly changing humidity of the environment. Chen et al. follow hierarchical design strategies to overcome these problems and create engines that start and run when placed at air-water interfaces.
- Xi Chen
- , Davis Goodnight
- & Ozgur Sahin
-
Article
| Open Access Demonstration of asymmetric electron conduction in pseudosymmetrical photosynthetic reaction centre proteins in an electrical circuit
Demonstration of asymmetric electron conduction in pseudosymmetrical photosynthetic reaction centre proteins in an electrical circuit
Photosynthetic reaction centres have been proposed for applications in bioelectronics. Here, the authors examine electron transport through the reaction centre from R. sphaeroidesusing conductive AFM, observing asymmetric conductance along only one cofactor wire under an applied bias.
- Muhammad Kamran
- , Vincent M. Friebe
- & Michael R. Jones
-
Article |
 A strain-absorbing design for tissue–machine interfaces using a tunable adhesive gel
A strain-absorbing design for tissue–machine interfaces using a tunable adhesive gel
Biocompatibility is a limiting factor in the use of electronic sensors in physiological applications. Here, the authors present a flexible and conductive polymer gel as an adhesive interface material for electronic biosensors, also demonstrating in vivoheart attachment and monitoring.
- Sungwon Lee
- , Yusuke Inoue
- & Takao Someya
-
Article |
 Stretchable silicon nanoribbon electronics for skin prosthesis
Stretchable silicon nanoribbon electronics for skin prosthesis
An integrated electronic platform with site-specific sensitivity is highly needed for medical applications. Here, Kim et al.report a stretchable prosthetic skin composed of ultrathin single crystalline silicon nanoribbon array, which can sense strain, pressure and temperature spontaneously.
- Jaemin Kim
- , Mincheol Lee
- & Dae-Hyeong Kim

 Black phosphorus boosts wet-tissue adhesion of composite patches by enhancing water absorption and mechanical properties
Black phosphorus boosts wet-tissue adhesion of composite patches by enhancing water absorption and mechanical properties