Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Multivalent 9-O-Acetylated-sialic acid glycoclusters as potent inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 infection
Multivalent 9-O-Acetylated-sialic acid glycoclusters as potent inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 infection
Cell surface attachment factors, such as glycans, play an important role in viral infection. Here, Petitjean et al. show that SARS-CoV-2 specifically binds to 9-Oacetylated sialic acid and have designed novel inhibitors based on multivalent derivatives.
- Simon J. L. Petitjean
- , Wenzhang Chen
- & David Alsteens
-
Article
| Open Access Reovirus directly engages integrin to recruit clathrin for entry into host cells
Reovirus directly engages integrin to recruit clathrin for entry into host cells
Reovirus endocytosis depends on junctional adhesion molecule A (JAM-A) and β1 integrin binding. Here, Koehler et al. use single-virus force spectroscopy and confocal microscopy to demonstrate a direct interaction between reovirus and β1 integrins via viral capsid protein λ2, which promotes clathrin recruitment to cell-bound reovirus.
- Melanie Koehler
- , Simon J. L. Petitjean
- & David Alsteens
-
Article
| Open Access High-speed atomic force microscopy highlights new molecular mechanism of daptomycin action
High-speed atomic force microscopy highlights new molecular mechanism of daptomycin action
High-speed atomic force imaging allows for the visualisation of molecular‐level activity in real-time. Here, the authors use HS-AFM to image the activity of an antimicrobial peptide on a membrane and are able to detect previously unknown molecular mechanisms behind its action.
- Francesca Zuttion
- , Adai Colom
- & Ignacio Casuso
-
Article
| Open Access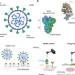 Molecular interaction and inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 binding to the ACE2 receptor
Molecular interaction and inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 binding to the ACE2 receptor
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein binds host ACE2 for virus entry. Here, the authors determine kinetic and thermodynamic properties of this interaction using atomic force microscopy, develop peptides that inhibit binding and suggest existence of additional attachment factors.
- Jinsung Yang
- , Simon J. L. Petitjean
- & David Alsteens
-
Article
| Open Access High force catch bond mechanism of bacterial adhesion in the human gut
High force catch bond mechanism of bacterial adhesion in the human gut
Understanding bacterial adhesion is important in a number of different areas of study. Here using a range of simulations and experimental methods, the authors, report on the molecular mechanism behind the binding of bacteria to cellulose fibers at high shear force in the human gut.
- Zhaowei Liu
- , Haipei Liu
- & Michael A. Nash
-
Article
| Open Access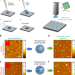 Microfluidic deposition for resolving single-molecule protein architecture and heterogeneity
Microfluidic deposition for resolving single-molecule protein architecture and heterogeneity
Manual sample deposition on a substrate can introduce artifacts in quantitative AFM measurements. Here the authors present a microfluidic spray device for reliable deposition of subpicoliter droplets which dry out in milliseconds after landing on the surface, thereby avoiding protein self-assembly.
- Francesco Simone Ruggeri
- , Jerome Charmet
- & Tuomas P. J. Knowles
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid transport of deformation-tuned nanoparticles across biological hydrogels and cellular barriers
Rapid transport of deformation-tuned nanoparticles across biological hydrogels and cellular barriers
Penetration of the mucus and tumor interstitial matrix is an important consideration for drug delivery devices. Here, the authors report on a study into the optimization of rigidity for the transport of nanoparticles through biological hydrogels using core-shell polymer-lipid nanoparticles.
- Miaorong Yu
- , Lu Xu
- & Huajian Gao
-
Article
| Open Access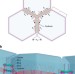 Apical surface supracellular mechanical properties in polarized epithelium using noninvasive acoustic force spectroscopy
Apical surface supracellular mechanical properties in polarized epithelium using noninvasive acoustic force spectroscopy
Determination of apical tension, fluidity, and intercellular adhesive forces in an epithelial monolayer are currently disruptive. Here the authors present a method using acoustic force microscopy to measure changes in these parameters upon tight junction structural alterations in a MDCK monolayer.
- Alexander X. Cartagena-Rivera
- , Christina M. Van Itallie
- & Richard S. Chadwick

 In mitosis integrins reduce adhesion to extracellular matrix and strengthen adhesion to adjacent cells
In mitosis integrins reduce adhesion to extracellular matrix and strengthen adhesion to adjacent cells