Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access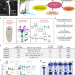 An evolutionarily-conserved Wnt3/β-catenin/Sp5 feedback loop restricts head organizer activity in Hydra
An evolutionarily-conserved Wnt3/β-catenin/Sp5 feedback loop restricts head organizer activity in Hydra
Hydra regenerate various body parts on amputation by activation of the appropriate organiser, but how head formation is controlled is unclear. Here, the authors identify the transcription factor Sp5 as restricting head formation, by being activated by beta-catenin and then acting as a repressor of Wnt3.
- Matthias C. Vogg
- , Leonardo Beccari
- & Brigitte Galliot
-
Article
| Open Access Differential damage and repair of DNA-adducts induced by anti-cancer drug cisplatin across mouse organs
Differential damage and repair of DNA-adducts induced by anti-cancer drug cisplatin across mouse organs
Cisplatin, a platinum chemotherapeutic agent, is widely used to treat several cancers. Here Yimit et al. revert to genome-wide approaches to map and analyze cisplatin damage formation and excision repair with single nucleotide resolution across different mice organs following platinum treatment.
- Askar Yimit
- , Ogun Adebali
- & Yuchao Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access LUBAC controls chromosome alignment by targeting CENP-E to attached kinetochores
LUBAC controls chromosome alignment by targeting CENP-E to attached kinetochores
During cell division, faithful chromosome segregation requires proper chromosome congression and dynamic maintenance of the aligned chromosomes. Here, the authors find that LUBAC promotes dynamic chromosome congression and alignment by targeting kinetochore motor CENP-E to the KMN network.
- Min Wu
- , Yan Chang
- & Huiyan Li
-
Article
| Open Access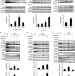 Tip60- and sirtuin 2-regulated MARCKS acetylation and phosphorylation are required for diabetic embryopathy
Tip60- and sirtuin 2-regulated MARCKS acetylation and phosphorylation are required for diabetic embryopathy
Neural tube defects can arise from high glucose levels caused by maternal diabetes, and MARCKS is required for neural tube closure. Here, Yang et al. show that acetylation and phosphorylation of MARCKS in hyperglycemic conditions causes mitochondrial and ER stress, leading to neural tube defects.
- Penghua Yang
- , Cheng Xu
- & Peixin Yang
-
Article
| Open Access WDR76 is a RAS binding protein that functions as a tumor suppressor via RAS degradation
WDR76 is a RAS binding protein that functions as a tumor suppressor via RAS degradation
Overexpression of RAS proteins is frequently observed in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Here, the authors identify an HRAS binding protein, the E3 ubiquitin ligase WDR76, which promotes HRAS degradation, thus functioning as a tumour suppressor in liver cancer
- Woo-Jeong Jeong
- , Jong-Chan Park
- & Kang-Yell Choi
-
Article
| Open Access A conserved dimer interface connects ERH and YTH family proteins to promote gene silencing
A conserved dimer interface connects ERH and YTH family proteins to promote gene silencing
In fission yeast, Erh1, ortholog of human ERH, interacts with the YTH family RNA binding protein Mmi1 to form the Erh1-Mmi1 complex (EMC), which has been implicated in gene silencing. Here, the authors present the cocrystal structure of Erh1 homodimers interacting with Mmi1 and further characterise the role of EMC in facultative heterochromatin assembly and gene silencing.
- Guodong Xie
- , Tommy V. Vo
- & Shiv I. S. Grewal
-
Article
| Open Access The CHD6 chromatin remodeler is an oxidative DNA damage response factor
The CHD6 chromatin remodeler is an oxidative DNA damage response factor
Oxidative DNA damage is associated with nucleosome respacing and transcriptional changes requiring chromatin remodeling enzymes. Here, the authors reveal that the CHD6 remodeler is a DNA damage response factor that relocates to damaged sites and promotes cell survival following oxidative damage.
- Shaun Moore
- , N. Daniel Berger
- & Aaron A. Goodarzi
-
Article
| Open Access Intergenerational inheritance of high fat diet-induced cardiac lipotoxicity in Drosophila
Intergenerational inheritance of high fat diet-induced cardiac lipotoxicity in Drosophila
Animal studies have shown that the nutritional status of parents can predispose the offspring to obesity and obesity-related diseases. Here the authors show that cardiac dysfunction induced by a high-fat diet persists for two generations in Drosophila, and that targeted expression of ATGL/bmm in the offspring, as well as inhibition of H3K27 trimethylation, is cardioprotective.
- Maria Clara Guida
- , Ryan Tyge Birse
- & Rolf Bodmer
-
Article
| Open Access Anti-CRISPR-mediated control of gene editing and synthetic circuits in eukaryotic cells
Anti-CRISPR-mediated control of gene editing and synthetic circuits in eukaryotic cells
Anti-CRISPR proteins derived from phage can abrogate CRISPR activity. The authors repurpose these molecules for demonstrating genomic write-protection and pre-programmed gene expression circuits.
- Muneaki Nakamura
- , Prashanth Srinivasan
- & Lei S. Qi
-
Article
| Open Access Pentatricopeptide repeat poly(A) binding protein KPAF4 stabilizes mitochondrial mRNAs in Trypanosoma brucei
Pentatricopeptide repeat poly(A) binding protein KPAF4 stabilizes mitochondrial mRNAs in Trypanosoma brucei
Polyadenylation stabilizes edited mitochondrial mRNAs in Trypanosoma brucei, but the involved poly(A) binding protein is unknown. Here, Mesitov et al. show that a pentatricopeptide repeat factor KPAF4 binds to A-tail and prevents exonucleolytic degradation as well as translation of incompletely edited mRNAs.
- Mikhail V. Mesitov
- , Tian Yu
- & Inna Aphasizheva
-
Article
| Open Access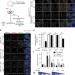 Phosphorylation of CENP-A on serine 7 does not control centromere function
Phosphorylation of CENP-A on serine 7 does not control centromere function
Phosphorylation of CENP-A on serine 7 has been proposed to control centromere assembly and function. Here, the authors use gene targeting at both endogenous CENP-A alleles and gene replacement in human cells to demonstrate that CENP-A that cannot be phosphorylated at serine 7 maintains correct CENP-C recruitment, faithful chromosome segregation and long-term cell viability.
- Viviana Barra
- , Glennis A. Logsdon
- & Daniele Fachinetti
-
Article
| Open Access The splicing factor RBM25 controls MYC activity in acute myeloid leukemia
The splicing factor RBM25 controls MYC activity in acute myeloid leukemia
Splicing factors are often mutated in hematological malignancies. Here, the authors perform an in vivo shRNA screen in a CEBPA mutant AML mouse model and identify that RBM25 controls the splicing of pre-mRNAs encoding BCL-X and BIN1 to exert its tumour suppressor activities in AML.
- Ying Ge
- , Mikkel Bruhn Schuster
- & Bo Torben Porse
-
Article
| Open Access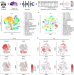 Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of mouse neocortical development
Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of mouse neocortical development
The authors perform single-cell RNA-seq of the mouse neocortex at an embryonic time point and at birth, and identify new and known cell types, and cell relatedness within and across age. These data serve as a resource to understand brain development and the cellular origins of brain diseases.
- Lipin Loo
- , Jeremy M. Simon
- & Mark J. Zylka
-
Article
| Open Access A tRNA half modulates translation as stress response in Trypanosoma brucei
A tRNA half modulates translation as stress response in Trypanosoma brucei
Trypanosoma brucei mainly relies on translational regulation to adjust gene expression, but details are unclear. Here the authors show that, under stress conditions, tRNAThr half level increases, associates with ribosomes and polysomes, and stimulates protein synthesis by facilitating mRNA loading.
- Roger Fricker
- , Rebecca Brogli
- & Norbert Polacek
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell microRNA-mRNA co-sequencing reveals non-genetic heterogeneity and mechanisms of microRNA regulation
Single-cell microRNA-mRNA co-sequencing reveals non-genetic heterogeneity and mechanisms of microRNA regulation
Single-cell RNA sequencing allows characterizing cell-to-cell heterogeneity at transcriptome scale. Here, the authors present an approach that enables microRNA and mRNA sequencing in the same single cell, providing insights into the origins of non-genetic cellular variability and mechanisms of miRNA regulation.
- Nayi Wang
- , Ji Zheng
- & Jun Lu
-
Article
| Open Access A tumor-specific endogenous repetitive element is induced by herpesviruses
A tumor-specific endogenous repetitive element is induced by herpesviruses
The human genome includes a large amount of repetitive sequence, such as human satellite II (HSATII), but their function remains largely unknown. Here, Nogalski et al. show that herpesvirus infection induces HSATII RNA expression, which in turn affects virus replication and cell motility.
- Maciej T. Nogalski
- , Alexander Solovyov
- & Benjamin D. Greenbaum
-
Article
| Open Access Histone H3 binding to the PHD1 domain of histone demethylase KDM5A enables active site remodeling
Histone H3 binding to the PHD1 domain of histone demethylase KDM5A enables active site remodeling
The demethylase activity of KDM5A is allosterically enhanced by binding of histone H3 to its PHD1 reader domain, through an unknown mechanism. Here the authors show that the PHD1 domain drives ligand-induced allosteric stimulation by stabilizing the binding of substrate to the catalytic domain.
- James E. Longbotham
- , Cynthia M. Chio
- & Danica Galonić Fujimori
-
Article
| Open Access The non-canonical SMC protein SmcHD1 antagonises TAD formation and compartmentalisation on the inactive X chromosome
The non-canonical SMC protein SmcHD1 antagonises TAD formation and compartmentalisation on the inactive X chromosome
The inactive X chromosome (Xi) has an atypical structure, with global loss of TADs, A/B compartments and formation of mega-domains. Here the authors show that the non-canonical SMC family protein, SmcHD1, important for developmental gene silencing on Xi, antagonises TAD formation and compartmentalization on the Xi in a transcription independent way.
- Michal R. Gdula
- , Tatyana B. Nesterova
- & Neil Brockdorff
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into trans-histone regulation of H3K4 methylation by unique histone H4 binding of MLL3/4
Structural insights into trans-histone regulation of H3K4 methylation by unique histone H4 binding of MLL3/4
MLL3 and MLL4 are members of the SET1/MLL family of histone H3K4 methyltransferases, which are responsible for monomethylating histone H3K4 on enhancers. Here the authors show that an extended PHD domain (ePHD6) in MLL3 and MLL4 specifically recognizes an H4H18-containing fragment of histone H4, and that modifications of residues surrounding H4H18 modulate H4 binding to MLL3/4.
- Yanli Liu
- , Su Qin
- & Jinrong Min
-
Article
| Open Access A region-resolved mucosa proteome of the human stomach
A region-resolved mucosa proteome of the human stomach
The human stomach is divided into seven anatomically distinct regions but their protein composition is largely unknown. Here, the authors present a region-resolved map of the healthy human stomach mucosa as well as mucosa proteomes of tumor and tumor nearby tissue from gastric cancer patients.
- Xiaotian Ni
- , Zhaoli Tan
- & Jun Qin
-
Article
| Open Access Single cell RNA analysis identifies cellular heterogeneity and adaptive responses of the lung at birth
Single cell RNA analysis identifies cellular heterogeneity and adaptive responses of the lung at birth
The respiratory system is transformed in terms of functional change at birth to adapt to breathing air. Here, the authors examine the molecular changes behind the first breath in the mouse by Drop-seq based RNA sequencing, identifying activation of the unfolded protein response as a perinatal adaptation of the lung.
- Minzhe Guo
- , Yina Du
- & Yan Xu
-
Article
| Open Access A chemical biology toolbox to study protein methyltransferases and epigenetic signaling
A chemical biology toolbox to study protein methyltransferases and epigenetic signaling
Protein methyltransferases (PMTs) are epigenetic regulatory enzymes with significant therapeutic relevance. Here the authors describe a collection of chemical inhibitors and antagonists to modulate most of the key methylation marks on histones H3 and H4, and use the collection to study of the role of PMTs in mouse and human T cell differentiation.
- Sebastian Scheer
- , Suzanne Ackloo
- & Cheryl H. Arrowsmith
-
Article
| Open Access Structure of transcribing RNA polymerase II-nucleosome complex
Structure of transcribing RNA polymerase II-nucleosome complex
Eukaryotic transcription requires passage of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) through chromatin, which is impaired by nucleosomes. Here the authors report the cryo-EM structure of transcribing Pol II engaged with a downstream nucleosome core particle at an overall resolution of 4.4 Å, providing insights into the mechanism of chromatin transcription.
- Lucas Farnung
- , Seychelle M. Vos
- & Patrick Cramer
-
Article
| Open Access CRISPR/Cas9-mediated glycolate oxidase disruption is an efficacious and safe treatment for primary hyperoxaluria type I
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated glycolate oxidase disruption is an efficacious and safe treatment for primary hyperoxaluria type I
Substrate reduction therapies (SRT) are a promising therapeutic approach for monogenic inherited metabolic diseases. Here the authors evaluate the therapeutic potential of an in vivo CRISPR/Cas9-mediated SRT to treat primary hyperoxaluria type I and demonstrate its safety and efficacy.
- Nerea Zabaleta
- , Miren Barberia
- & Juan R. Rodriguez-Madoz
-
Article
| Open Access The H/ACA complex disrupts triplex in hTR precursor to permit processing by RRP6 and PARN
The H/ACA complex disrupts triplex in hTR precursor to permit processing by RRP6 and PARN
Telomerase RNA (hTR) is transcribed as a 3′-extended precursor. Here the authors examine the processing of hTR precursors of various lengths and show that processing occurs in distinct steps involving different nucleases PARN and RRP6.
- Chi-Kang Tseng
- , Hui-Fang Wang
- & Peter Baumann
-
Article
| Open Access A quasi-integral controller for adaptation of genetic modules to variable ribosome demand
A quasi-integral controller for adaptation of genetic modules to variable ribosome demand
Competition for shared cellular resources often renders genetic circuits poorly predictable. Here the authors design a biomolecular quasi-integral controller that allows gene expression to adapt to variable demand in translation resources.
- Hsin-Ho Huang
- , Yili Qian
- & Domitilla Del Vecchio
-
Article
| Open Access Human genome-wide measurement of drug-responsive regulatory activity
Human genome-wide measurement of drug-responsive regulatory activity
Quantification of genomic responses to environmental stimuli by current genome-scale assays is limited to indirect measurements or requires knowledge of the transcription factors involved. Here, the authors use genome-wide high-throughput reporter assays to agnostically map enhancer activity in response to glucocorticoid treatment across the human genome.
- Graham D. Johnson
- , Alejandro Barrera
- & Timothy E. Reddy
-
Article
| Open Access Optimized libraries for CRISPR-Cas9 genetic screens with multiple modalities
Optimized libraries for CRISPR-Cas9 genetic screens with multiple modalities
Genome-wide libraries for CRISPR knockout, interference, and activation have allowed the systemic interrogation of gene function. Here, the authors evaluate the Brunello CRISPRko library and introduce Dolcetto and Calabrese for CRISPRi and CRISPRa, respectively.
- Kendall R. Sanson
- , Ruth E. Hanna
- & John G. Doench
-
Article
| Open Access Distinct adaptive mechanisms drive recovery from aneuploidy caused by loss of the Ulp2 SUMO protease
Distinct adaptive mechanisms drive recovery from aneuploidy caused by loss of the Ulp2 SUMO protease
Transient aneuploidy enables cells to survive sudden environmental changes before longterm cellular adaptations are established. Here, the authors show that yeast cells respond to the acute loss of Ulp2 SUMO protease by rapid induction of aneuploidy, and reveal predictable long-term adaptation mechanisms that restore euploidy.
- Hong-Yeoul Ryu
- , Francesc López-Giráldez
- & Mark Hochstrasser
-
Article
| Open Access Breaking the speed limit with multimode fast scanning of DNA by Endonuclease V
Breaking the speed limit with multimode fast scanning of DNA by Endonuclease V
How DNA repair proteins locate their target sites on DNA is still a matter of debate. Here the authors characterize by single-molecule fluorescence imaging the modes of scanning adopted by bacterial endonuclease V as it moves along linear DNA tracks.
- Arash Ahmadi
- , Ida Rosnes
- & Alexander D. Rowe
-
Article
| Open Access RNA helicases mediate structural transitions and compositional changes in pre-ribosomal complexes
RNA helicases mediate structural transitions and compositional changes in pre-ribosomal complexes
Pre-ribosomes undergo numerous structural rearrangements during their assembly. Here the authors identify the binding sites of three essential RNA helicases on pre-ribosomal particles, enabling them to provide insights into the structural and compositional changes that occur during biogenesis of the large ribosomal subunit.
- Lukas Brüning
- , Philipp Hackert
- & Markus T. Bohnsack
-
Article
| Open Access SCL/TAL1 cooperates with Polycomb RYBP-PRC1 to suppress alternative lineages in blood-fated cells
SCL/TAL1 cooperates with Polycomb RYBP-PRC1 to suppress alternative lineages in blood-fated cells
Mechanisms that operate during embryonic development to restrict cell fate are currently under investigation. Here the authors characterise the role of SCL/TAL1 at the onset of blood specification in embryonic development using mouse EB differentiation culture as a model system.
- Hedia Chagraoui
- , Maiken S. Kristiansen
- & Catherine Porcher
-
Article
| Open Access The ASCIZ-DYNLL1 axis promotes 53BP1-dependent non-homologous end joining and PARP inhibitor sensitivity
The ASCIZ-DYNLL1 axis promotes 53BP1-dependent non-homologous end joining and PARP inhibitor sensitivity
53BP1 is a key player in non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). Here the authors reveal an important role for the multifunctional homodimeric protein hub dynein light chain 1 (DYNLL1) in increasing the efficacy of 53BP1-mediated repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) by NHEJ.
- Jordan R. Becker
- , Raquel Cuella-Martin
- & J. Ross Chapman
-
Article
| Open Access Microbiome characterization by high-throughput transfer RNA sequencing and modification analysis
Microbiome characterization by high-throughput transfer RNA sequencing and modification analysis
The authors present a molecular approach and a software suite for high-throughput sequencing and characterization of microbial tRNA transcripts, which provide unique physiological insights into complex environmental microbes.
- Michael H. Schwartz
- , Haipeng Wang
- & A. Murat Eren
-
Article
| Open Access Kinase-dead ATR differs from ATR loss by limiting the dynamic exchange of ATR and RPA
Kinase-dead ATR differs from ATR loss by limiting the dynamic exchange of ATR and RPA
ATR kinase is a key regulator of chromosome integrity. Here the authors by analysing the phenotype of a mouse model expressing a kinase-dead ATR, reveal the effect of ATR inhibition compared to ATR loss and its consequences for meiosis, DNA replication, checkpoint activation and genome instability .
- Demis Menolfi
- , Wenxia Jiang
- & Shan Zha
-
Article
| Open Access Myopathy associated BAG3 mutations lead to protein aggregation by stalling Hsp70 networks
Myopathy associated BAG3 mutations lead to protein aggregation by stalling Hsp70 networks
BAG3 is a Hsp70 co-chaperone that is highly expressed in muscles. Here the authors show that several myofibrillar myopathy causing BAG3 mutations are not impaired in Hsp70 binding, but rather impair the ADP-ATP exchange step of the Hsp70 cycle, causing the aggregation of BAG3, Hsp70 and Hsp70 clients and leading to a collapse of protein homeostasis.
- Melanie Meister-Broekema
- , Rebecca Freilich
- & Harm H. Kampinga
-
Article
| Open Access Routes of Zika virus dissemination in the testis and epididymis of immunodeficient mice
Routes of Zika virus dissemination in the testis and epididymis of immunodeficient mice
The mechanisms of ZIKV persistence in the male reproductive tract (MRT) are poorly understood. Here, Tsetsarkin et al. applied microRNA-targeting approach to trace routes of ZIKV dissemination in the testis and epididymis and to generate immunogenic live-attenuated ZIKV vaccine candidate, restricted for MRT infection.
- Konstantin A. Tsetsarkin
- , Olga A. Maximova
- & Alexander G. Pletnev
-
Article
| Open Access Local and global chromatin interactions are altered by large genomic deletions associated with human brain development
Local and global chromatin interactions are altered by large genomic deletions associated with human brain development
Copy number variants in the human genome (CNVs) are associated with neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia and autism. Here the authors investigate how the large deletion CNV on chromosome 22q11.2 alters chromatin organization.
- Xianglong Zhang
- , Ying Zhang
- & Alexander E. Urban
-
Article
| Open Access miR-122 removal in the liver activates imprinted microRNAs and enables more effective microRNA-mediated gene repression
miR-122 removal in the liver activates imprinted microRNAs and enables more effective microRNA-mediated gene repression
miR-122 is a highly expressed microRNA in the liver. Here the authors analyse the mouse liver microRNA landscape following depletion of miR-122 and the impact that this has on its target mRNAs.
- Paul N. Valdmanis
- , Hak Kyun Kim
- & Mark A. Kay
-
Article
| Open Access Transcriptomic meta-signatures identified in Anopheles gambiae populations reveal previously undetected insecticide resistance mechanisms
Transcriptomic meta-signatures identified in Anopheles gambiae populations reveal previously undetected insecticide resistance mechanisms
Increasing insecticide resistance of mosquitoes represents a public health threat, and underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. Here, Ingham et al. identify putative insecticide resistance genes in Anopheles gambiae populations across Africa and develop a web-based application that maps their expression.
- V. A. Ingham
- , S. Wagstaff
- & H. Ranson
-
Article
| Open Access Binding of HMGN proteins to cell specific enhancers stabilizes cell identity
Binding of HMGN proteins to cell specific enhancers stabilizes cell identity
HMGN1 and HMGN2 are ubiquitous nucleosome binding proteins. Here the authors provide evidence that HMGN proteins preferentially localize to chromatin regulatory sites to modulate the plasticity of the epigenetic landscape, proposing that HGMNs stabilize, rather than determine, cell identity.
- Bing He
- , Tao Deng
- & Michael Bustin
-
Article
| Open Access Non-invasive monitoring of alternative splicing outcomes to identify candidate therapies for myotonic dystrophy type 1
Non-invasive monitoring of alternative splicing outcomes to identify candidate therapies for myotonic dystrophy type 1
Myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) is associated with aberrant transcript splicing. Here, the authors develop a transgenic mouse model expressing a bi-chromatic reporter system that allows non-invasive monitoring of splicing of a transcript altered in DM1 in vivo, and show that it allows for evaluation of the therapeutic response to treatment with antisense oligonucleotides.
- Ningyan Hu
- , Layal Antoury
- & Thurman M. Wheeler
-
Article
| Open Access NLRP3 lacking the leucine-rich repeat domain can be fully activated via the canonical inflammasome pathway
NLRP3 lacking the leucine-rich repeat domain can be fully activated via the canonical inflammasome pathway
Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome is associated with various diseases but its activation mechanism is not fully understood. Here, the authors determine the impact of different NLRP3 domains on sensing NLRP3 triggers, inflammasome assembly and regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
- Iva Hafner-Bratkovič
- , Petra Sušjan
- & Roman Jerala
-
Article
| Open Access Temporal control of gene expression by the pioneer factor Zelda through transient interactions in hubs
Temporal control of gene expression by the pioneer factor Zelda through transient interactions in hubs
Zelda is a pioneer factor that regulates transcription in Drosophila embryos. Here, the authors use quantitative live imaging and mathematical modeling to measure the effect of Zelda on transcriptional dynamics and memory, observing temporal control of gene expression by Zelda through transient interactions in hubs.
- Jeremy Dufourt
- , Antonio Trullo
- & Mounia Lagha
-
Article
| Open Access Chromatin interactions and expression quantitative trait loci reveal genetic drivers of multimorbidities
Chromatin interactions and expression quantitative trait loci reveal genetic drivers of multimorbidities
Multimorbidities of common diseases often have shared underlying predisposing factors. Here Fadason et al. study the pleiotropy of SNPs and their effects on target genes by integrating chromatin interaction and expression quantitative trait loci data to identify target genes shared between phenotypes.
- Tayaza Fadason
- , William Schierding
- & Justin M. O’Sullivan
-
Review Article
| Open Access DNA interference and beyond: structure and functions of prokaryotic Argonaute proteins
DNA interference and beyond: structure and functions of prokaryotic Argonaute proteins
In this review, Aravin and colleagues examine bacterial and archaeal Argonaute proteins, discuss their diverse architectures and their possible roles in host defense, proposing additional functions for Argonaute proteins in prokaryotic cells.
- Lidiya Lisitskaya
- , Alexei A. Aravin
- & Andrey Kulbachinskiy
-
Article
| Open Access Honey bee Royalactin unlocks conserved pluripotency pathway in mammals
Honey bee Royalactin unlocks conserved pluripotency pathway in mammals
Royal jelly is the queen-maker for the honey bee that also has effects on longevity, fertility, and regeneration in mammals. Here the authors provide evidence that its major protein component Royalactin, and the mammalian structural analog Regina, maintain pluripotency in mouse ESCs by activating a ground-state pluripotency-like gene network.
- Derrick C. Wan
- , Stefanie L. Morgan
- & Kevin C. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Epigenetically reprogrammed methylation landscape drives the DNA self-assembly and serves as a universal cancer biomarker
Epigenetically reprogrammed methylation landscape drives the DNA self-assembly and serves as a universal cancer biomarker
DNA methylation is an epigenetic modification that control genetic programs. Here, the authors found that the methylation landscape influences the physicochemical properties of DNA and that it can serve as a universal cancer biomarker, and developed a one-step assay for the detection of cancer DNA.
- Abu Ali Ibn Sina
- , Laura G. Carrascosa
- & Matt Trau
-
Article
| Open Access MacroH2A1 chromatin specification requires its docking domain and acetylation of H2B lysine 20
MacroH2A1 chromatin specification requires its docking domain and acetylation of H2B lysine 20
The histone variant macroH2A1 localizes to two functionally distinct chromatin subtypes marked by either H3K27me3 or H2B acetylations. Here the authors identify the features of macroH2A1 required for its recruitment to H2B-acetylated chromatin and identify H2BK20 acetylation as a critical requirement for this recruitment.
- Penelope D. Ruiz
- & Matthew J. Gamble
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Cell division
- Chromatin
- Chromosomes
- CRISPR-Cas systems
- DNA damage and repair
- DNA metabolism
- DNA recombination
- DNA replication
- Epigenetics
- Non-coding RNAs
- Nuclear organization
- Post-translational modifications
- Protein folding
- Proteolysis
- Proteomics
- Riboswitches
- Ribozymes
- RNA metabolism
- RNAi
- Single-molecule biophysics
- Transcription
- Transcriptomics
- Translation
- Transposition

 Gut bacterial tyrosine decarboxylases restrict levels of levodopa in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease
Gut bacterial tyrosine decarboxylases restrict levels of levodopa in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease