Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access The M-phase regulatory phosphatase PP2A-B55δ opposes protein kinase A on Arpp19 to initiate meiotic division
The M-phase regulatory phosphatase PP2A-B55δ opposes protein kinase A on Arpp19 to initiate meiotic division
Mechanisms triggering meiotic divisions of oocytes remain unclear. Here, the authors report that meiosis resumption relies on the timely phosphorylation of Arpp19 protein at two distinct sites, which depends on two kinases (PKA and Gwl) and a single phosphatase (PP2A-B55δ).
- Tom Lemonnier
- , Enrico Maria Daldello
- & Aude Dupré
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo biomolecular imaging of zebrafish embryos using confocal Raman spectroscopy
In vivo biomolecular imaging of zebrafish embryos using confocal Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopic imaging (RSI) can provide information on the chemical composition of a sample, but application to living organisms has lacked sufficient spatial resolution and signal strength. Here the authors apply confocal RSI to whole-mount zebrafish embryos to distinguish different infectious bacteria and to living zebrafish embryos to monitor the wound healing process.
- Håkon Høgset
- , Conor C. Horgan
- & Molly M. Stevens
-
Article
| Open Access An original infection model identifies host lipoprotein import as a route for blood-brain barrier crossing
An original infection model identifies host lipoprotein import as a route for blood-brain barrier crossing
Bacterial and fungal pathogens that cross the blood-brain-barrier (BBB) can cause severe disease. Here, Benmimoun et al. develop a model to study BBB crossing in the developing Drosophila brain and discover Group B Streptococcus factors important for BBB crossing and virulence, one of which, a lipoprotein, they confirm in mice.
- Billel Benmimoun
- , Florentia Papastefanaki
- & Pauline Spéder
-
Article
| Open Access Vav2 catalysis-dependent pathways contribute to skeletal muscle growth and metabolic homeostasis
Vav2 catalysis-dependent pathways contribute to skeletal muscle growth and metabolic homeostasis
Skeletal muscle plays a key role in regulating systemic glucose and metabolic homeostasis. Here, the authors show that the catalytic activity of Vav2, an activator of Rho GTPases, modulates those processes by favoring the responsiveness of this tissue to insulin and related factors.
- Sonia Rodríguez-Fdez
- , L. Francisco Lorenzo-Martín
- & Xosé R. Bustelo
-
Article
| Open Access Transcriptional activity and strain-specific history of mouse pseudogenes
Transcriptional activity and strain-specific history of mouse pseudogenes
Pseudogenes are key markers of genome remodelling processes. Here the authors present genome-wide annotation of the pseudogenes in the mouse reference genome and 18 inbred mouse strains, update human pseudogene annotations, and characterise the transcription and evolution of mouse pseudogenes.
- Cristina Sisu
- , Paul Muir
- & Mark Gerstein
-
Article
| Open Access A HaloTag-TEV genetic cassette for mechanical phenotyping of proteins from tissues
A HaloTag-TEV genetic cassette for mechanical phenotyping of proteins from tissues
Testing mechanical forces on native molecules in natural environments remains a challenge. Here the authors engineer titin to carry a HaloTag-TEV insertion to allow analysis of dynamics under force in muscle fibers.
- Jaime Andrés Rivas-Pardo
- , Yong Li
- & Jorge Alegre-Cebollada
-
Article
| Open Access Cep55 promotes cytokinesis of neural progenitors but is dispensable for most mammalian cell divisions
Cep55 promotes cytokinesis of neural progenitors but is dispensable for most mammalian cell divisions
In mammalian cell lines, Cep55 protein recruits the endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT) and promotes the completion of cell division. Here, the authors show that Cep55-knockout mice are viable and primary fibroblasts cultured in vitro divide in a Cep55 and ESCRT-independent way.
- Antonio Tedeschi
- , Jorge Almagro
- & Mark Petronczki
-
Article
| Open Access Adverse caregiving in infancy blunts neural processing of the mother
Adverse caregiving in infancy blunts neural processing of the mother
The roots of psychopathology take shape during adverse parent-infant interactions, shown through infant attachment quality. Using rodents, the authors show that blunted infant cortical processing of the mother determines attachment quality through a stress hormone-dependent mechanism.
- Maya Opendak
- , Emma Theisen
- & Regina M. Sullivan
-
Article
| Open Access Tissue mechanics drives regeneration of a mucociliated epidermis on the surface of Xenopus embryonic aggregates
Tissue mechanics drives regeneration of a mucociliated epidermis on the surface of Xenopus embryonic aggregates
The role of tissue mechanics in the regeneration of mucociliated epithelium in Xenopus is unclear. Here, the authors show that Xenopus ectoderm aggregates undergo epithelial-like phenotypic transition prior to differentiation of mucus-secreting goblet cells to enable regeneration.
- Hye Young Kim
- , Timothy R. Jackson
- & Lance A. Davidson
-
Article
| Open Access Image quality guided smart rotation improves coverage in microscopy
Image quality guided smart rotation improves coverage in microscopy
Multi-view SPIM imaging can improve coverage of large samples such as whole embryos, but the procedure increases phototoxicity and involves manual steps that can introduce inconsistencies. Here the authors develop a smart rotation workflow that performs on-the-fly image analysis and identifies optimal set of views to maximize sample coverage.
- Jiaye He
- & Jan Huisken
-
Article
| Open Access Zika virus enhances monocyte adhesion and transmigration favoring viral dissemination to neural cells
Zika virus enhances monocyte adhesion and transmigration favoring viral dissemination to neural cells
Zika virus (ZIKV) can infect the central nervous system, but it is not clear how it reaches the brain. Here, Ayala-Nunez et al. show in ex vivo and in vivo models that ZIKV can hitch a ride in monocytes in a Trojan Horse manner to cross the endothelium and disseminate the virus.
- Nilda Vanesa Ayala-Nunez
- , Gautier Follain
- & Raphael Gaudin
-
Article
| Open Access Inhibition of amyloid beta toxicity in zebrafish with a chaperone-gold nanoparticle dual strategy
Inhibition of amyloid beta toxicity in zebrafish with a chaperone-gold nanoparticle dual strategy
Treating Alzheimer’s disease, one of the most common neurodegenerative diseases, is of wide interest. Here, the authors report on the development of casein coated gold nanoparticles which were able to cross the blood brain barrier and protect against amyloid beta toxicity in a zebrafish model.
- Ibrahim Javed
- , Guotao Peng
- & Sijie Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Repeated semen exposure decreases cervicovaginal SIVmac251 infection in rhesus macaques
Repeated semen exposure decreases cervicovaginal SIVmac251 infection in rhesus macaques
High frequency semen exposure has been associated with activation of anti-HIV mechanisms in HIV negative sex workers. Here, Abdulhaqq et al. show that repeated vaginal exposure to semen reduces vaginal infection by SIV in non-human primates, and is associated with lower CCR5 expression in CD4 T-cells and a local type-I interferon response.
- Shaheed A. Abdulhaqq
- , Melween Martinez
- & Luis J. Montaner
-
Article
| Open Access The autism- and schizophrenia-associated protein CYFIP1 regulates bilateral brain connectivity and behaviour
The autism- and schizophrenia-associated protein CYFIP1 regulates bilateral brain connectivity and behaviour
In humans, copy-number variants of the CYFIP1 gene have been associated with autism spectrum disorders and schizophrenia. Here, the authors characterize Cyfip1-heterozygous mice, revealing that they display deficits in brain white matter structure and functional connectivity along with abnormal behaviours.
- Nuria Domínguez-Iturza
- , Adrian C. Lo
- & Claudia Bagni
-
Article
| Open Access Cyfip1 haploinsufficient rats show white matter changes, myelin thinning, abnormal oligodendrocytes and behavioural inflexibility
Cyfip1 haploinsufficient rats show white matter changes, myelin thinning, abnormal oligodendrocytes and behavioural inflexibility
People with a genetic deletion of the 15q11.2 locus are at increased risk for psychiatric disorders and white matter disturbances, but the gene(s) responsible are unclear. Here, the authors show that low dosage of CYFIP1, present in the human 15q11.2 region, alters white matter structure and cognition in rats.
- Ana I. Silva
- , Josephine E. Haddon
- & Lawrence S. Wilkinson
-
Article
| Open Access The development of synaptic transmission is time-locked to early social behaviors in rats
The development of synaptic transmission is time-locked to early social behaviors in rats
The development of functional synapses is a key milestone in neurodevelopment. Here, the authors show how serotonin signalling coordinates development of glutamatergic and GABAergic currents and triggers the emergence of integrative behavior (huddling) in rat pups.
- Shovan Naskar
- , Roberto Narducci
- & Laura Cancedda
-
Article
| Open Access Etv6 activates vegfa expression through positive and negative transcriptional regulatory networks in Xenopus embryos
Etv6 activates vegfa expression through positive and negative transcriptional regulatory networks in Xenopus embryos
How vegfa expression is transcriptionally regulated in vivo is unclear. Here, the authors demonstrate that the ETS transcription factor Etv6 acts as a repressor and an activator of two direct regulators of vegfa expression (foxo3 and klf4, respectively) to control blood formation in Xenopus.
- Lei Li
- , Rossella Rispoli
- & Catherine Porcher
-
Article
| Open Access Znhit1 controls intestinal stem cell maintenance by regulating H2A.Z incorporation
Znhit1 controls intestinal stem cell maintenance by regulating H2A.Z incorporation
Lgr5+ stem cells in intestinal crypts are critical for gut epithelium homeostasis. Here, the authors show that Znht1 critically regulates intestinal homeostasis by promoting interaction between histone variant H2A.Z and its chaperone YL1 to incorporate H2A.Z into genes involved in intestinal stem cell fate.
- Bing Zhao
- , Ying Chen
- & Xinhua Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Stem cell proliferation is induced by apoptotic bodies from dying cells during epithelial tissue maintenance
Stem cell proliferation is induced by apoptotic bodies from dying cells during epithelial tissue maintenance
Damaged epithelial tissues are known to compensate for cell death through compensatory cell divisions to maintain epithelial integrity. Here, the authors show in living epithelia that dying cells stimulate adjacent stem cells to divide through caspase-dependent production of Wnt8a-containing apoptotic bodies.
- Courtney K. Brock
- , Stephen T. Wallin
- & George T. Eisenhoffer
-
Article
| Open Access tmem33 is essential for VEGF-mediated endothelial calcium oscillations and angiogenesis
tmem33 is essential for VEGF-mediated endothelial calcium oscillations and angiogenesis
Calcium signalling downstream of VEGF is essential for VEGF-induced angiogenesis. Here Savage et al. show that Transmembrane Protein 33 (TMEM33) is required for angiogenesis and the endothelial calcium response to VEGF, revealing a function for TMEM33 in multicellular organisms.
- Aaron M. Savage
- , Sathishkumar Kurusamy
- & Robert N. Wilkinson
-
Article
| Open Access Differentiation of primate primordial germ cell-like cells following transplantation into the adult gonadal niche
Differentiation of primate primordial germ cell-like cells following transplantation into the adult gonadal niche
Human embryonic stem cells can be differentiated in vitro into primordial germ cell-like cells (PGCLCs) that resemble early primordial germ cells (PGCs). Here the authors transplant PGCLCs generated from rhesus macaque iPSCs into mouse and rhesus macaque seminiferous tubules, which matures these into late PGCs and spermatogonia-like cells.
- Enrique Sosa
- , Di Chen
- & Amander T. Clark
-
Article
| Open Access Heart enhancers with deeply conserved regulatory activity are established early in zebrafish development
Heart enhancers with deeply conserved regulatory activity are established early in zebrafish development
During early embryogenesis, critical cardiac specification events occur. Here the authors isolate cardiac progenitor cells from early zebrafish embryos and characterize accessible chromatin regions specific to this cell population, finding that many of these regions overlap with conserved non-coding elements that are ortholgous to accessible chromatin regions in human.
- Xuefei Yuan
- , Mengyi Song
- & Michael D. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Wnt/β-catenin signaling regulates VE-cadherin-mediated anastomosis of brain capillaries by counteracting S1pr1 signaling
Wnt/β-catenin signaling regulates VE-cadherin-mediated anastomosis of brain capillaries by counteracting S1pr1 signaling
Wnt signaling is known to regulate the formation of the blood-brain barrier. Here Hübner et al. dissect the underlying mechanisms using high resolution live imaging in zebrafish, and find that Wnt regulates anastomosis of angiogenic sprouts in the brain by counteracting sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor signaling.
- Kathleen Hübner
- , Pauline Cabochette
- & Wiebke Herzog
-
Article
| Open Access Systems glycomics of adult zebrafish identifies organ-specific sialylation and glycosylation patterns
Systems glycomics of adult zebrafish identifies organ-specific sialylation and glycosylation patterns
Zebrafish is a popular system for studying the molecular basis of glycan-related human diseases. Here, the authors present glycomic profiles of eight zebrafish organs and establish the organ-specific expression patterns of related biosynthetic enzymes.
- Nao Yamakawa
- , Jorick Vanbeselaere
- & Yann Guerardel
-
Article
| Open Access Iridophores as a source of robustness in zebrafish stripes and variability in Danio patterns
Iridophores as a source of robustness in zebrafish stripes and variability in Danio patterns
Iridophores interact with other cells to give zebrafish their stripes, but what drives their form shifts is unknown. Here, modelling allows the authors to identify robust cues that may specify iridophore form and to find changes to these cues that likely account for altered patterns on related fish.
- Alexandria Volkening
- & Björn Sandstede
-
Article
| Open Access Lipoprotein lipase regulates hematopoietic stem progenitor cell maintenance through DHA supply
Lipoprotein lipase regulates hematopoietic stem progenitor cell maintenance through DHA supply
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) hydrolyzes triglycerides to supply free fatty acids (FFAs) to muscle for energy and adipocytes for storage. Here, the authors demonstrate that Lpl and its product, the FFA docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are required for haematopoietic stem progenitor cell expansion during zebrafish embryogenesis.
- Chao Liu
- , Tianxu Han
- & Yury I. Miller
-
Article
| Open Access Zebrafish and medaka offer insights into the neurobehavioral correlates of vertebrate magnetoreception
Zebrafish and medaka offer insights into the neurobehavioral correlates of vertebrate magnetoreception
Advances in animal magnetoreception have been limited by a lack of tractable vertebrate laboratory models. Here, the authors demonstrate light-independent magnetoreception in mature zebrafish and medaka, as well as magnetosensitive locomotion in juvenile medaka associated with neuronal activation in the lateral hindbrain.
- Ahne Myklatun
- , Antonella Lauri
- & Gil G. Westmeyer
-
Article
| Open Access Tbx5a lineage tracing shows cardiomyocyte plasticity during zebrafish heart regeneration
Tbx5a lineage tracing shows cardiomyocyte plasticity during zebrafish heart regeneration
It is not clear if it is the embryonic origin or anatomical location of cardiomyocytes that restrict their contribution to zebrafish heart regeneration. Here, the authors show a plasticity of embryonic precursors following tbx5a fate mapping and that trabecular cardiomyocytes help to rebuild the cortical myocardium.
- Héctor Sánchez-Iranzo
- , María Galardi-Castilla
- & Nadia Mercader
-
Article
| Open Access Small molecule screen in embryonic zebrafish using modular variations to target segmentation
Small molecule screen in embryonic zebrafish using modular variations to target segmentation
Chemical screens can identify small molecules that affect biological development, with potential therapeutic value. Here, the authors use a modular approach in a screen in zebrafish embryos, varying concentration, genotype and timing to target segmentation disorders, birth defects that affect the spinal column.
- Sandra Richter
- , Ulrike Schulze
- & Andrew C. Oates
-
Article
| Open Access Different developmental histories of beta-cells generate functional and proliferative heterogeneity during islet growth
Different developmental histories of beta-cells generate functional and proliferative heterogeneity during islet growth
Βeta-cells have recently been shown to be heterogeneous with regard to morphology and function. Here, the authors show that β-cells in zebrafish switch from proliferative to functional states with increasing time since β-cell birth, leading to functional and proliferative heterogeneity.
- Sumeet Pal Singh
- , Sharan Janjuha
- & Nikolay Ninov
-
Article
| Open Access interleukin-11 induces and maintains progenitors of different cell lineages during Xenopus tadpole tail regeneration
interleukin-11 induces and maintains progenitors of different cell lineages during Xenopus tadpole tail regeneration
Xenopus laevis tadpoles have maintained their ability to regenerate various organs. Here, the authors show that interleukin-11 is necessary for organ regeneration, by inducing and maintaining undifferentiated progenitors across cell lineages during Xenopus tail regeneration.
- Hiroshi Tsujioka
- , Takekazu Kunieda
- & Takeo Kubo
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable base editing of zebrafish genome using a modified CRISPR-Cas9 system
Programmable base editing of zebrafish genome using a modified CRISPR-Cas9 system
The use of base editing enables precise genetic modifications in model animals. Here the authors show high efficient single-base editing in zebrafish using modified Cas9 and its VQR variant with an altered PAM specificity.
- Yihan Zhang
- , Wei Qin
- & Shuo Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Prevalence of sexual dimorphism in mammalian phenotypic traits
Prevalence of sexual dimorphism in mammalian phenotypic traits
Systemic dissection of sexually dimorphic phenotypes in mice is lacking. Here, Karp and the International Mouse Phenotype Consortium show that approximately 10% of qualitative traits and 56% of quantitative traits in mice as measured in laboratory setting are sexually dimorphic.
- Natasha A. Karp
- , Jeremy Mason
- & Jacqueline K. White
-
Article
| Open Access Caloric restriction improves health and survival of rhesus monkeys
Caloric restriction improves health and survival of rhesus monkeys
Caloric restriction (CR) delays ageing of model organisms, but whether it works in nonhuman primates has been controversial. Here, the authors pool and reanalyse data from two long-running CR primate studies, concluding that moderate CR indeed improves health and survival of rhesus monkeys.
- Julie A. Mattison
- , Ricki J. Colman
- & Rozalyn M. Anderson
-
Article
| Open Access Prophylactic orthosteric inhibition of leukocyte integrin CD11b/CD18 prevents long-term fibrotic kidney failure in cynomolgus monkeys
Prophylactic orthosteric inhibition of leukocyte integrin CD11b/CD18 prevents long-term fibrotic kidney failure in cynomolgus monkeys
Acute kidney injury can progress to chronic kidney disease. Here Dehnadiet al. develop a post-ischaemic chronic kidney disease model in cynomolgus monkeys and show that prophylactic inhibition of CD11b/CD18 leukocyte receptor via a monoclonal antibody inhibits progression of kidney disease and fibrosis.
- Abbas Dehnadi
- , A. Benedict Cosimi
- & M. Amin Arnaout
-
Article
| Open Access Novel gene function revealed by mouse mutagenesis screens for models of age-related disease
Novel gene function revealed by mouse mutagenesis screens for models of age-related disease
Random mutagenesis can uncover novel genes involved in phenotypic traits. Here the authors perform a large-scale phenotypic screen on over 100 mouse strains generated by ENU mutagenesis to identify mice with age-related diseases, which they attribute to specific mutations revealed by whole-genome sequencing.
- Paul K. Potter
- , Michael R. Bowl
- & Steve D. M. Brown
-
Article
| Open Access β-Catenin C-terminal signals suppress p53 and are essential for artery formation
β-Catenin C-terminal signals suppress p53 and are essential for artery formation
How p53 is restrained in arterial maturation during embryonic development is unclear. Here, the authors show that β-catenin C-terminal interactions inhibit CREB binding protein-mediated acetylation and activation of p53 in smooth muscle cells, and that this function is essential for artery formation.
- Dario F. Riascos-Bernal
- , Prameladevi Chinnasamy
- & Nicholas E. S. Sibinga
-
Article
| Open Access A mouse model for a partially inactive obesity-associated human MC3R variant
A mouse model for a partially inactive obesity-associated human MC3R variant
The melanocortin receptor, MC3R, regulates organismal energy homeostasis. Here, Lee et al. create knock-in mice with the a mutated version of the human MC3R receptor found in obese children, and show these mice have more fat and smaller bone, yet are by and large metabolically healthy.
- Bonggi Lee
- , Jashin Koo
- & Jack A. Yanovski
-
Article
| Open Access Mouse strains to study cold-inducible beige progenitors and beige adipocyte formation and function
Mouse strains to study cold-inducible beige progenitors and beige adipocyte formation and function
Beige adipocytes are formed in response to cold and thought to contribute to organismal energy homeostasis. Here, the authors study a range of conditional and inducible RFP-expressing Cre mouse strains and find that SMA-based lines are the most useful for mapping beige adipocyte progenitor cells.
- Daniel C. Berry
- , Yuwei Jiang
- & Jonathan M. Graff
-
Article
| Open Access Amygdala lesions in rhesus macaques decrease attention to threat
Amygdala lesions in rhesus macaques decrease attention to threat
The amygdala in the medial temporal lobe of the human and non-human primate brain is known to process salient social stimuli and to mediate threat discrimination. Here, Dal Monte et al.show that rhesus monkeys with amygdala lesions have deficits in detecting threat signals and directing attention to the eye region of a conspecific's face.
- Olga Dal Monte
- , Vincent D. Costa
- & Bruno B. Averbeck
-
Article
| Open Access Spinal corollary discharge modulates motion sensing during vertebrate locomotion
Spinal corollary discharge modulates motion sensing during vertebrate locomotion
Corollary discharges inform the central nervous system about impending motor activity. Here, Chagnaud et al. show that, in Xenopustadpoles, shared efferent neural pathways to the inner ear and lateral line adjust the sensitivity of sensory afferents during locomotor activity.
- Boris P. Chagnaud
- , Roberto Banchi
- & Hans Straka
-
Article
| Open Access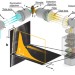 Hyperspectral light sheet microscopy
Hyperspectral light sheet microscopy
Multicolour information is required to study the complex interplay of biological tissues. Here, Jahr et al.acquire spectral information at high resolution for each pixel in a hyperspectral light sheet microscope, while maintaining its perpendicular illumination and low phototoxicity.
- Wiebke Jahr
- , Benjamin Schmid
- & Jan Huisken
-
Article
| Open Access Chamber identity programs drive early functional partitioning of the heart
Chamber identity programs drive early functional partitioning of the heart
The heart forms from combining the first with the second heart field, which in mammals creates left and right ventricle. Here transgenic zebrafish and physiology studies reveal that transcription factors controlling septation in mammals already in teleosts guide muscle coupling by controlling the relative contribution of the two fields to the heart.
- Christian Mosimann
- , Daniela Panáková
- & Leonard I. Zon
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and gating of the nuclear pore complex
Structure and gating of the nuclear pore complex
Nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) are large macromolecular assemblies that mediate the exchange of molecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm. Here the authors present a ∼20 Å cryo-EM structure of the X. laevisNPC in different states of transport to propose a model for the architecture of the NPC’s molecular gate within its central channel.
- Matthias Eibauer
- , Mauro Pellanda
- & Ohad Medalia
-
Article
| Open Access Effective heritable gene knockdown in zebrafish using synthetic microRNAs
Effective heritable gene knockdown in zebrafish using synthetic microRNAs
Zebrafish is a model system for which for no reliable heritable gene silencing method is available. Here the authors provide a system for heritable miRNA-mediated knockdown and demonstrate tunable silencing of the smn1gene that recapitulate different forms of spinal muscular atrophy.
- Jean Giacomotto
- , Silke Rinkwitz
- & Thomas S. Becker
-
Article
| Open Access Pigment cell movement is not required for generation of Turing patterns in zebrafish skin
Pigment cell movement is not required for generation of Turing patterns in zebrafish skin
Pigment pattern formation in zebrafish depends on the interactions between the pigment cells. Here the authors present a mathematical model based on mutual interaction of pigment cells in the absence of cell motion, revising the current model of the pattern formation that relies on reaction–diffusion Turing patterns.
- D. Bullara
- & Y. De Decker
-
Article |
 Efficient genome engineering by targeted homologous recombination in mouse embryos using transcription activator-like effector nucleases
Efficient genome engineering by targeted homologous recombination in mouse embryos using transcription activator-like effector nucleases
Genetically engineered mice are an important aspect of human disease research. Here, the authors use artificial transcription activator-like effector-nucleases to generate a mouse line with a conditionally targeted allele and suggest that this method can be easily adapted to any gene in the mouse genome.
- Daniel Sommer
- , Annika E. Peters
- & Marc Beyer
-
Article |
 A mouse model of adult-onset anaemia due to erythropoietin deficiency
A mouse model of adult-onset anaemia due to erythropoietin deficiency
Kidney diseases often cause anaemia due to damage of renal erythropoietin-producing cells. Yamazaki et al. identify a new population of erythropoietin-producing cells in the renal cortex and outer medulla by establishing a mouse model for adult-onset erythropoietin-deficient anaemia.
- Shun Yamazaki
- , Tomokazu Souma
- & Masayuki Yamamoto
-
Article
| Open Access A chronic model of arthritis supported by a strain-specific periarticular lymph node in BALB/c mice
A chronic model of arthritis supported by a strain-specific periarticular lymph node in BALB/c mice
Mouse models of arthritis generally do not result in both chronic disease and autoantibody production—two key features of the human disease. Here the authors obtain both features by combining two common protocols, and find that disease severity is associated with the presence of a previously unidentified lymph node.
- Uta Baddack
- , Sven Hartmann
- & Gerd Müller

 Spatio-temporal mRNA tracking in the early zebrafish embryo
Spatio-temporal mRNA tracking in the early zebrafish embryo